This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 13:58, 9 March 2011 (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 13:58, 9 March 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)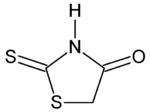 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2-Sulfanylidene-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one | |
| Other names 2-Thioxo-4-thiazolidinone; 4-Oxo-2-thioxothiazoline | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.005 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C3H3NOS2 |
| Molar mass | 133.18 g·mol |
| Melting point | 165-169 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Rhodanine is an organic compound derived from thiazolidine. Rhodanine can be prepared by the reaction of carbon disulfide, ammonia, and chloroacetic acid.
Some derivatives of rhodanine have pharmacological properties, such as epalrestat which is used to treat diabetic neuropathy.
References
- Rhodanine at Sigma-Aldrich
- Redemann; Icke; Alles (1947). "Rhodanine". Organic Syntheses. 27: 74.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)