This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Kerowyn (talk | contribs) at 19:43, 14 June 2011 (wikified. Join the Project!). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 19:43, 14 June 2011 by Kerowyn (talk | contribs) (wikified. Join the Project!)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)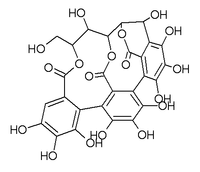 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C27H20O18 |
| Molar mass | 632.43 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Castalin is an ellagitannin. It can be found in oak wood and in Melaleuca quinquenervia leaves.
References
- Effect of species and ecological conditions on ellagitannin content in oak wood from an even-aged and mixed stand of Quercus robur L. and Quercus petraea Liebl. Prida A., Boulet J.-C., Ducousso A., Nepveu G.and Puech., Ann. For. Sci., Volume 63, Number 4, May-June 2006
- Polyphenols of Melaleuca quinquenervia leaves - pharmacological studies of grandinin. Moharram F. A., Marzouk M. S., El-Toumy S. A. A., Ahmed A. A. E. and Aboutable E. A., PTR. Phytotherapy research, 2003, vol. 17, no7, pp. 767-773