This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 129.67.119.242 (talk) at 12:24, 19 December 2011. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 12:24, 19 December 2011 by 129.67.119.242 (talk)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)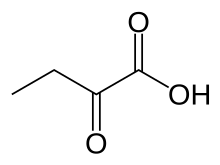 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2-oxobutanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.080 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Alpha-ketobutyric+acid |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4H6O3 |
| Molar mass | 102.089 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
α-Ketobutyric acid is a product of the lysis of cystathionine.
It is also one of the degradation products of threonine, produced by the catabolism of the amino acid by threonine dehydratase.
It can be converted to propionyl-CoA (and subsequently methylmalonyl CoA, which can be converted to succinyl CoA, a CAC intermediate), and thus enter the citric acid cycle.
Conversion in sotolon in French Vin jaune
Vin jaune is marked by the formation of sotolon from alpha-ketobutyric acid.
See also
References
- Optimal Conditions for the Formation of Sotolon from .alpha.-Ketobutyric Acid in the French "Vin Jaune". Pham Thu Thuy, Guichard Elisabeth, Schlich Pascal and Charpentier Claudine, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1995, 43 (10), pages 2616–2619, doi:10.1021/jf00058a012
- Quantitative determination of sotolon in wines by high-performance liquid chromatography. E. Guichard, T. T. Pham and P. Etievant, Chromatographia, Volume 37, Numbers 9-10, pages 539-542, doi:10.1007/BF02275793
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |