This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Plasmic Physics (talk | contribs) at 03:57, 29 January 2012. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 03:57, 29 January 2012 by Plasmic Physics (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)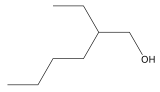
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Ethyl-1-hexanol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 2-Ethylhexan-1-ol | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Beilstein Reference | 1719280 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.941 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | 2-ethylhexanol |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H18O |
| Molar mass | 130.231 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colourless, transparent liquid |
| Density | 833 mg mL |
| Melting point | −76 °C (−105 °F; 197 K) |
| log P | 2.721 |
| Vapor pressure | 30 Pa (at 20 °C) |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.431 |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Heat capacity (C) | 317.5J K mol |
| Std molar entropy (S298) |
347.0 J K mol |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
−433.67–−432.09 kJ mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH298) |
−5.28857–−5.28699 MJ mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H312, H315, H318, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P280, P305+P351+P338 |
| Flash point | 81 °C |
| Explosive limits | 0.88–9.7% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
|
| Related compounds | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
2-Ethylhexanol (abbreviated 2-EH) is a fatty alcohol, an organic compound is a branched, eight-carbon chiral alcohol. It is a colorless liquid that is nearly insoluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents. It is produced on a massive scale as a precursor to plasticizers, some of which are controversial as potential endocrine disruptors.
Applications
Almost all 2-ethylhexanol is converted into the diesters bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), a plasticizer. Because it is a fatty alcohol, its esters tend to have emollient properties. For example, the sunscreen octocrylene contains a 2-ethylhexyl ester for this purpose. It is also commonly used as a low volatility solvent.
Industrial production
2-Ethylhexanol is produced industrially by the aldol condensation of n-butyraldehyde, followed by hydrogenation of the resulting hydroxyaldehyde. About 2,500,000 tons are prepared in this way annually.. The n-butyraldehyde is made by hydroformylation of propylene, either in a self-contained plant or as the first step in a fully integrated facility. Most facilities make n-butanol and isobutanol in addition to 2-ethylhexanol.
Nomenclature
Isooctanol and 2-ethylhexanol are not synonyms. According to the Chemical Abstracts Service, isooctanol (CAS# 26952-21-6) refers to a different isomer of octanol, 6-methylheptan-1-ol.
See also
References
- "2-ethylhexanol - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 29 January 2012.
- C. Kohlpaintner, M. Schulte, J. Falbe, P. Lappe, J. Weber, "Aldehydes, Aliphatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2008, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_321.pub2.
- Ashford’s Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, Third edition, 2011, page 4180-1