This is an old revision of this page, as edited by McGhiever (talk | contribs) at 05:54, 30 October 2013 (removed Category:National Register of Historic Places in Montana; added Category:Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in Montana using HotCat). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 05:54, 30 October 2013 by McGhiever (talk | contribs) (removed Category:National Register of Historic Places in Montana; added Category:Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in Montana using HotCat)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| Bozeman Trail | |
|---|---|
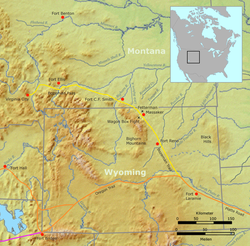 The Bozeman Trail (in yellow) The Bozeman Trail (in yellow) | |
| Location | Montana, Wyoming |
| Governing body | National Park Service |
The Bozeman Trail was an overland route connecting the gold rush territory of Montana to the Oregon Trail. Its most important period was from 1863-1868. The flow of pioneers and settlers through territory of American Indians provoked their resentment and caused attacks. The U.S. Army undertook several military campaigns against the Indians to try to control the trail. Because of its association with frontier history and conflict with American Indians, various segments of the trail are listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP).
Establishment
In 1863 John Bozeman and John Jacobs scouted for a direct route from Virginia City, Montana to central Wyoming to connect with the Oregon Trail, then the major passage to the West Coast. Before this, most access to the southwestern Montana Territory was from St. Louis via the Missouri River to Fort Benton. Thence travelers went by the 'Benton Road,' around the Great Falls and through the Chestnut, Hilger and Prickly Pear valleys (current site of Helena and Broadwater County, Montana).
The overland Bozeman Trail followed many north-south trails the American Indians had used since prehistoric times to travel through Powder River Country. This route was more direct and better watered than any previous trail into Montana. Bozeman's and Jacobs's most important contribution was to improve the trail so that it was wide enough for wagons. But there was a major drawback — the trail passed directly through territory occupied by the Shoshone, Arapaho, and Lakota nations.
First travelers and Indian campaigns
Bozeman led the first group of about 2,000 settlers on the trail in 1864. Indian raids on white settlers increased dramatically from 1864 to 1866, which prompted the U.S. government to order the Army to carry out military campaigns against the Shoshone. Patrick Edward Connor led several of the earliest campaigns. He defeated the Shoshone at the Battle of Bear River and during the Powder River Expedition of 1865, and he defeated the Arapaho at the Battle of the Tongue River.
Post-Civil War travel
In 1866, following of the American Civil War, more settlers traveled the trail, mostly to search for gold. The Army called a council at Fort Laramie, which Lakota leader Red Cloud attended. The Army wanted to neogotiate a right-of-way with the Lakota for settlers' use of the trail. As negotiations continued, Red Cloud became outraged when he discovered that a regiment of U.S. infantry was already using the route without receiving permission from the Lakota nation. Thus Red Cloud's War began.
That same year, Nelson Story, a successful Virginia City, Montana, gold miner originally from Ohio, used the Bozeman Trail to successfully drive about 1000 head of longhorn cattle into Montana. The U.S. Army unsuccessfully tried to turn Story back to protect the drive from Indian attacks, but Story brought cattle through to the Gallatin Valley and formed one of the earliest significant herds in Montana's cattle industry.
The Army established Fort Reno, Fort Phil Kearny and Fort C. F. Smith along the route, staffed with troops meant to protect travelers. However, Indian raids along the trail and around the forts continued. When the Lakota annihilated a detachment under William J. Fetterman at the Fetterman Fight the same year near Fort Phil Kearny, civilian travel along the trail ceased. On August 1, 1867 and August 2, 1867, US forces resisted coordinated attempts by large parties of Lakota to overrun Fort C. F. Smith and Fort Phil Kearny. In the Hayfield Fight and Wagon Box Fight, Indian attacks on outlying parties failed.
Later, by the 1868 Treaty of Fort Laramie, the US recognized the Powder River Country as unceded hunting territory for the Lakota and allied tribes. Most was located on the Crow Indian Reservation. For a time the government used the treaty to shut down travel by European-American settlers on the Bozeman Trail. President Ulysses S. Grant ordered the abandonment of forts along the trail.
Red Cloud's War could thus be said to be the only Indian war in which Native Americans achieved their goals (if only for a brief time) with a treaty settlement essentially on their terms. By 1876, however, following the Black Hills War, the US Army reopened the trail. The Army continued to use the trail during later military campaigns and built a telegraph line along it.
Modern route

Today, a modern highway route consisting of Interstate 25 runs from Douglas, Wyoming to Sheridan, Wyoming. Interstate 90 from Sheridan, Wyoming to Three Forks, Montana (30 miles west of Bozeman, Montana) and U.S. Route 287 from Three Forks to Virginia City, Montana cover roughly the same general route as the historic Bozeman Trail.
See also
References
- Kennedy, Michael S. (1964). "Tall in the Saddle-First Trail Drive to Montana Territory". Cowboys and Cattlemen-A Roundup from Montana The Magazine of Western History. New York: Hastings House Publishing. pp. 103–111.
- "Bozeman Trail History", Fort Phil Kearny State Historic Site
- Grace Raymond Hebard, et al., The Bozeman Trail: Historical Accounts of the Blazing of the Overland Routes, Volume II
External links
![]() Media related to Bozeman Trail at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Bozeman Trail at Wikimedia Commons
National Register Listings
There are nine individual segments of the Bozeman Trail in Wyoming listed on the National Register of Historic Places. One segment of the trail in Montana is also listed.
| NRHP Place | NRHP Number | County | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antelope Creek Crossing | 89000816 | Converse | Wyoming |
| Holdup Hollow Segment | 89000818 | Converse | Wyoming |
| Lake Desmet Segment | 89000814 | Johnson | Wyoming |
| Nine Mile Segment | 89000813 | Campbell | Wyoming |
| Powder River Station | 89000810 | Campbell | Wyoming |
| Ross Flat Segment | 89000811 | Converse | Wyoming |
| Sage Creek Station | 89000812 | Converse | Wyoming |
| Stinking Water Gulch Segment | 89000817 | Converse | Wyoming |
| Trabing Station-Crazy Woman Crossing | 89000815 | Johnson | Wyoming |
| Yellowstone Crossing | 78003407 | Sweet Grass | Montana |
| U.S. National Register of Historic Places | |
|---|---|
| Topics | |
| Lists by state |
|
| Lists by insular areas | |
| Lists by associated state | |
| Other areas | |
| Related | |
- Native American trails in the United States
- Infrastructure-related listings on the National Register of Historic Places
- Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in Montana
- National Register of Historic Places in Wyoming
- Red Cloud's War
- Trails and roads in the American Old West
- Historic trails and roads in Wyoming
- Historic trails and roads in Montana