This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Lialono (talk | contribs) at 14:16, 10 February 2014 (→Types: copy-edit). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:16, 10 February 2014 by Lialono (talk | contribs) (→Types: copy-edit)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
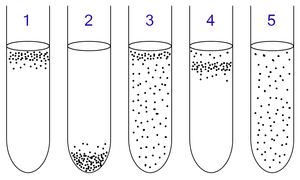
1: Obligate aerobes need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. They gather at the top of the tube where the oxygen concentration is highest.
2: Obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen, so they gather at the bottom of the tube where the oxygen concentration is lowest.
3: Facultative anaerobes can grow with or without oxygen because they can metabolise energy aerobically or anaerobically. They gather mostly at the top because aerobic respiration generates more ATP than either fermentation or anaerobic respiration.
4: Microaerophiles need oxygen because they cannot ferment or respire anaerobically. However, they are poisoned by high concentrations of oxygen. They gather in the upper part of the test tube but not the very top.
5: Aerotolerant organisms do not require oxygen as they metabolise energy anaerobically. Unlike obligate anaerobes however, they are not poisoned by oxygen. They can be found evenly spread throughout the test tube.
An aerobic organism or aerobe is an organism that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment. Facultative anaerobes grow and survive in an oxygenated environment and so do aerotolerant anaerobes.
Types
- Obligate aerobes need oxygen to grow. In a process known as cellular respiration, these organisms use oxygen to oxidize substrates (for example sugars and fats) and generate energy.
- Facultative anaerobes use oxygen if it is available, but also have anaerobic methods of energy production.
- Microaerophiles require oxygen for energy production, but are harmed by atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (21% O2).
- Aerotolerant anaerobes are anaerobes that do not use oxygen but are not harmed by it.
Glucose
A good example would be the oxidation of glucose (a monosaccharide) in aerobic respiration.
Oxygen is used during the oxidation of glucose and water is produced.
This equation is a summary of what actually happens in three series of biochemical reactions: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Diversity
Yeast is an example of a facultative anaerobe, which can develop in the presence of oxygen but does not require it. Individual human cells are also facultative anaerobes: they switch to lactic acid fermentation if oxygen is not available. However, for the whole organism this cannot be sustained for long, and humans are therefore obligate aerobes.
See also
- Aerobic digestion
- Anaerobic digestion
- Facultative anaerobic organism
- Fermentation (biochemistry)
- Microaerophile
- Obligate anaerobe
References
| Microbiology: Bacteria | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medical microbiology | |||||||
| Biochemistry and ecology |
| ||||||
| Shape | |||||||
| Structure |
| ||||||
| Taxonomy and evolution | |||||||