This is an old revision of this page, as edited by MLPainless (talk | contribs) at 05:25, 24 October 2014 (replace text with better citation (link to full study) and include newer review study that confirms, and add more data with cite to another review study). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 05:25, 24 October 2014 by MLPainless (talk | contribs) (replace text with better citation (link to full study) and include newer review study that confirms, and add more data with cite to another review study)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 1-Chloro-3-ethylamino-5-isopropylamino-2,4,6-triazine | |
| Other names Atrazine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.017 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H14ClN5 |
| Molar mass | 215.69 g·mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 1.187 gcm |
| Melting point | 175 °C (347 °F; 448 K) |
| Boiling point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) |
| Solubility in water | 7 mg/100 mL |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Atrazine is a herbicide of the triazine class. Atrazine is used to prevent pre and post-emergence broadleaf weeds in crops such as maize (corn) and sugarcane and on turf, such as golf courses and residential lawns.
It is one of the most widely used herbicides in the US and in Australian agriculture. It was banned in the European Union in 2004 because of persistent groundwater contamination.
As of 2001, Atrazine was the most commonly detected pesticide contaminating drinking water in the United States. Studies suggest it is an endocrine disruptor, an agent that may alter the natural hormonal system in animals. In 2006 the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) stated that "the risks associated with the pesticide residues pose a reasonable certainty of no harm", and in 2007 the EPA said that atrazine does not adversely affect amphibian sexual development and that no additional testing was warranted. The EPA opened a new review in 2009 that concluded that "the agency’s scientific bases for its regulation of atrazine are robust and ensure prevention of exposure levels that could lead to reproductive effects in humans."
However, the EPA review has been criticized, and the safety of atrazine remains controversial.
Uses
Atrazine is an herbicide that is used to stop pre and post-emergence broadleaf and grassy weeds in crops such as sorghum, maize, sugarcane, lupins, pine and eucalypt plantations, and triazine tolerant (TT) canola.
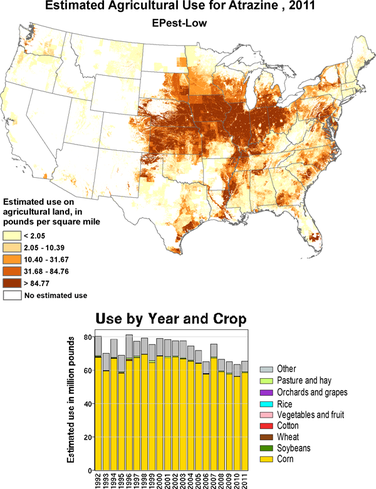
In the United States as of 2014, atrazine was the second most widely used herbicide after glyphosate, with 76 million pounds of it applied each year. Atrazine continues to be one of the most widely used herbicides in Australian agriculture. Its use is banned in the European Union.
Its effect on corn yields has been estimated from 8% to 1%, with 3–4% being the conclusion of one economics review. In another study looking at combined data from 236 university corn field trials from 1986–2005, atrazine treatments showed an average of 5.7 bushels more per acre than alternative herbicide treatments. Effects on sorghum yields have been estimated to be as high as 20%, owing in part to the absence of alternative weed control products that can be used on sorghum.
Chemistry and biochemistry
Atrazine was invented in 1958 in the Geigy laboratories as the second of a series of 1,3,5-triazines.
Atrazine is prepared from cyanuric chloride, which is treated sequentially with ethylamine and isopropyl amine. Like other triazine herbicides, atrazine functions by binding to the plastoquinone-binding protein in photosystem II, which animals lack. Plant death results from starvation and oxidative damage caused by breakdown in the electron transport process. Oxidative damage is accelerated at high light intensity.
Atrazine's effects in humans and animals primarily involve the endocrine system. Studies suggest that atrazine is an endocrine disruptor that can cause hormone imbalance.
Biodegradation
Atrazine remains in soil for a matter of months and can migrate from soil to groundwater; once in groundwater, it degrades slowly. It has been detected in groundwater at high levels in some regions of the U.S. where it is used on some crops and turf. The US Environmental Protection Agency expresses concern regarding contamination of surface waters (lakes, rivers, and streams).
Atrazine degrades in soil primarily by the action of microbes. The half-life of atrazine in soil ranges from 13 to 261 days. Atrazine biodegradation can occur by two known pathways:
- Hydrolysis of the C-Cl bond, followed by the ethyl and isopropyl groups, catalyzed by the hydrolase enzymes called AtzA, AtzB, and AtzC. The end product of this process is cyanuric acid, itself unstable with respect to ammonia and carbon dioxide. The best characterized organisms that use this pathway are of Pseudomonas sp. strain ADP.
- Dealkylation of the amino groups to give 2-chloro-4-hydroxy-6-amino-1,3,5-triazine, the degradation of which is unknown. This path also occurs in Pseudomonas species as well as a number of bacteria.
Rates of biodegradation are affected by atrazine's low solubility, thus surfactants may increase the degradation rate. Though the two alkyl moieties readily support growth of certain microorganisms, the atrazine ring is a poor energy source due to the oxidized state of ring carbon. In fact, the most common pathway for atrazine degradation involves the intermediate, cyanuric acid, in which carbon is fully oxidized, thus the ring is primarily a nitrogen source for aerobic microorganisms. Atrazine may be catabolized as a carbon and nitrogen source in reducing environments, and some aerobic atrazine degraders have been shown to use the compound for growth under anoxia in the presence of nitrate as an electron acceptor, a process referred to as a denitrification. When atrazine is used as a nitrogen source for bacterial growth, degradation may be regulated by the presence of alternative sources of nitrogen. In pure cultures of atrazine-degrading bacteria, as well as active soil communitites, atrazine ring nitrogen, but not carbon are assimilated into microbial biomass. Low concentrations of glucose can decrease the bioavailability, whereas higher concentrations promote the catabolism of atrazine.
The genes for enzymes AtzA-C have been found to be highly conserved in atrazine-degrading organisms worldwide. In Pseudomonas sp. ADP, the Atz genes are located noncontiguously on a plasmid with the genes for mercury catabolism. AtzA-C genes have also been found in a Gram-positive bacterium, but are chromosomally located. The insertion elements flanking each gene suggest that they are involved in the assembly of this specialized catabolic pathway. Two options exist for degradation of atrazine using microbes, bioaugmentation or biostimulation. Recent research suggests that microbial adaptation to atrazine has occurred in some fields where the herbicide is used repetitively, resulting in a decrease in herbicidal effectiveness. Like the herbicides trifluralin and alachlor, atrazine is susceptible to rapid transformation in the presence of reduced iron-bearing soil clays, such as ferruginous smectites. In natural environments, some iron-bearing minerals are reduced by specific bacteria in the absence of oxygen, thus the abiotic transformation of herbicides by reduced minerals is viewed as "microbially induced".
Health and environmental effects
According to Extension Toxicology Network in the U.S., "The oral median Lethal Dose or LD50 for atrazine is 3090 mg/kg in rats, 1750 mg/kg in mice, 750 mg/kg in rabbits, and 1000 mg/kg in hamsters. The dermal LD50 in rabbits is 7500 mg/kg and greater than 3000 mg/kg in rats. The 1-hour inhalation LC50 is greater than 0.7 mg/L in rats. The 4-hour inhalation LC50 is 5.2 mg/L in rats." The maximum contaminant level is 0.003 mg/L and the reference dose is 0.035 mg/kg/day.
Atrazine was banned in the European Union (EU) in 2004 because of its persistent groundwater contamination.
Atrazine contamination of surface water (lakes, rivers, and streams) is a concern to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). As of 2001, Atrazine was the most commonly detected pesticide contaminating drinking water in the United States. Monitoring of atrazine levels in community water systems in 31 high use atrazine states found that atrazine levels exceeded levels of concern for infant exposure during at least one year between 1993-2001 in 34 of 3670 community water systems using surface water, and in none of 14,500 community water systems using groundwater.
Effects on mammals
In mammals, including humans, the endocrine system is the primary target of atrazine. The U.S. EPA says that "studies thus far suggest that atrazine is an endocrine disruptor". According to a US EPA chemical summary, implications of possible endocrine disruption for children’s health are related to effects during pregnancy and during sexual development, though few studies are available. Increased risks for preterm delivery and intrauterine growth retardation have been associated with atrazine exposure. Atrazine exposure has been shown to result in delays or changes in pubertal development in experimental animal studies.
In 2006 the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) stated that "the risks associated with the pesticide residues pose a reasonable certainty of no harm", and in 2007 the EPA said that atrazine does not adversely affect amphibian sexual development and that no additional testing was warranted. The EPA opened a new review in 2009 that concluded that "the agency’s scientific bases for its regulation of atrazine are robust and ensure prevention of exposure levels that could lead to reproductive effects in humans."
In August 2009, the risks of atrazine were discussed in a front page article in the New York Times as a potential cause of birth defects, low birth weights and menstrual problems when consumed at concentrations below federal standards. A Natural Resources Defense Council's Report on Atrazine suggested that the EPA is ignoring atrazine contamination in surface and drinking water in the central United States.
In 2010, atrazine was shown to cause prostatitis and delayed puberty in rats, and demasculinizes male gonads producing testicular lesions associated with reduced germ cell numbers in mammals (and also in teleost fish, amphibians and reptiles). Therefore the case for atrazine as an endocrine disruptor that demasculinizes and feminizes male vertebrates meets all nine of the Bradford Hill criteria.
Research results from the U.S. National Cancer Institute's Agricultural Health Study published in 2011 concluded that "there was no consistent evidence of an association between atrazine use and any cancer site." The study tracked 57,310 licensed pesticide applicators over 13 years. EPA also determined in 2000 "that atrazine is not likely to cause cancer in humans."
A 2012 epidemiological study showed that women who lived in counties in Texas with the highest levels of atrazine being used on agricultural crops were 80 times more likely to give birth to infants with choanal atresia or stenosis compared to women who lived in the counties with the lowest levels.
Effect on amphibians
Atrazine is a suspected teratogen, causing demasculinization in male northern leopard frogs even at low concentrations, and an estrogen disruptor. A 2002 study by Tyrone Hayes, of the University of California, Berkeley, found that exposure to atrazine caused male tadpoles to turn into hermaphrodites – frogs with both male and female sexual characteristics. But a 2005 study, requested by the EPA and funded by Syngenta, one of the companies that produce atrazine, was unable to reproduce these results. According to Hayes, all of the studies that failed to conclude that atrazine caused hermaphroditism were plagued by poor experimental controls and were funded by Syngenta suggesting conflict of interest.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and its independent Scientific Advisory Panel (SAP) examined all available studies on this topic and concluded that "atrazine does not adversely affect amphibian gonadal development based on a review of laboratory and field studies." The EPA and its SAP made recommendations concerning proper study design needed for further investigation into this issue. As required by the EPA, Syngenta conducted two experiments under Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and inspection by the EPA and German regulatory authorities. The paper concluded "These studies demonstrate that long-term exposure of larval X. laevis to atrazine at concentrations ranging from 0.01 to 100 microg/l does not affect growth, larval development, or sexual differentiation." A report written in Environmental Science and Technology (May 15, 2008) cites the independent work of researchers in Japan, who were unable to replicate Hayes' work. "The scientists found no hermaphrodite frogs; no increase in aromatase as measured by aromatase mRNA induction; and no increase in vitellogenin, another marker of feminization."
A study published in 2007 examined the relative importance of environmentally relevant concentrations of atrazine on trematode cercariae versus tadpole defense against infection. The principal finding of the present study was that susceptibility of wood frog tadpoles to infection by E. trivolvis is increased only when hosts are exposed to an atrazine concentration of 30 ng/L and not to 3 ng/L.
A 2008 study reported that tadpoles developed deformed hearts and impaired kidneys and digestive systems when chronically exposed to atrazine concentrations of 10,000 ppb in their early stages of life. Tissue malformation may have been induced by ectopic programmed cell death, although a mechanism was not identified. Surface water monitoring data from 20 high atrazine use watersheds found peak atrazine levels of up to 147 parts per billion, with daily averages in all cases below 10 parts per billion.
A 2010 Hayes study found that atrazine rendered 75 percent of male frogs sterile and turned one in 10 into females.
In 2010, the Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority (APVMA), found the chemical safe to use:
The conclusion of the APVMA at that time, based on advice from DEWHA, was that atrazine is unlikely to have an adverse impact on frogs at existing levels of exposure. This advice was consistent with findings by the US EPA in 2007 (see below) that atrazine does not adversely affect amphibian gonadal development.
Furthermore, the APVMA responded to Hayes' 2010 published paper, by stating that his findings "do not provide sufficient evidence to justify a reconsideration of current regulations which are based on a very extensive dataset."
Effects on fish and insects
A 2010 study conducted by scientists from the U.S. Geological Survey observed substantial adverse reproductive effects on fish from atrazine exposure at a threshold concentration of 0.5 μg/L, which is below the threshold levels previously defined for fish toxicity and within the surface water concentrations found in agricultural areas; the authors concluded: "The effects on egg production and spawning in fathead minnow suggest the reproductive risks of atrazine exposure to feral fish populations in high use, agricultural areas may be under estimated by current evaluations."
A recent study demonstrated that exposure of beetles to environmentally relevant doses of Atrazine during development as larvae confounded the sexual selection process so that females selected less fit mates, and speculated that it may have played a role in the declines in the federally endangered American Burying Beetle.
Class action lawsuit
In 2012 Syngenta corporation, manufacturer of atrazine, was the defendant in a class action lawsuit concerning the levels of atrazine in human water supplies. Syngenta agreed to pay $105 million to reimburse more than a thousand water systems for "the cost of filtering atrazine from drinking water", although the company denied all wrongdoing.
See also
References
- ^ "A Valuable Reputation: Tyrone Hayes said that a chemical was harmful, its maker pursued him" by Rachel Aviv, The New Yorker, 10 February 2014
- ^ "Chemical Review: Atrazine". Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority. Retrieved 2014-02-05.
- ^ "EDEXIM Chemical Information for Atrazine". Retrieved 2014-02-10.
- ^ Gilliom RJ et al. US Geological Survey The Quality of Our Nation’s Waters: Pesticides in the Nation’s Streams and Ground Water, 1992–2001 March 2006, Revised February 15, 2007
- ^ Atrazine: Chemical Summary. Toxicity and Exposure Assessment for Children’s Health (PDF) (Report). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 4/24/2007.
{{cite report}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Hayes, Tyrone B. (2011). "Demasculinization and feminization of male gonads by atrazine: Consistent effects across vertebrate classes". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 127 (1–2): 64–73. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.03.015. PMID 21419222.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Triazine Cumulative Risk Assessment and Atrazine, Simazine, and Propazine Decisions, June 22, 2006, EPA.
- ^ Atrazine Updates: Amphibians, April 2010, EPA.
- ^ EPA Begins New Scientific Evaluation of Atrazine, October 7, 2009, EPA.
- ^ EPA Atrazine Updates: Scientific Peer Review—Human Health Current as of January 2013. Accessed March 15, 2014
- ^ Tillitt et al. Atrazine reduces reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Aquat Toxicol. 2010 Aug 15;99(2):149-59. PMID 20471700
- ^ Duhigg, Charles (August 22, 2009). "Debating How Much Weed Killer Is Safe in Your Water Glass". The New York Times. Retrieved 2009-09-10.
- Walsh, Edward (2003-02-01). "EPA Stops Short of Banning Herbicide". Washington Post. pp. A14. Retrieved 2007-04-27.
- "Restricted Use Products (RUP) Report: Six Month Summary List". Environmental Protection Agency. Archived from the original on 11 January 2010. Retrieved 1 December 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Ackerman, Frank (2007). "The economics of atrazine" (PDF). International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Health. 13 (4): 437–445. doi:10.1179/oeh.2007.13.4.437. PMID 18085057.
- "BioOne Online Journals - A Rationale for Atrazine Stewardship in Corn".
- Fawcett, Richard S. "Twenty Years of University Corn Yield Data: With and Without Atrazine", North Central Weed Science Society, 2008
- "Market-level assessment of the economic benefits of atrazine in the United States - Mitchell - 2014 - Pest Management Science - Wiley Online Library".
- Wolfgang Krämer (2007). Modern Crop Protection Compounds, Volume 1. Wiley-VCH. ISBN 9783527314966.
- Appleby, Arnold P.; Müller, Franz; Carpy, Serge (2001). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". doi:10.1002/14356007.a28_165. ISBN 3-527-30673-0.
{{cite journal}}:|chapter=ignored (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Interim Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Atrazine, U.S. EPA, January, 2003.
- Zeng Y, Sweeney CL, Stephens S, Kotharu P. (2004). Atrazine Pathway Map. Wackett LP. Biodegredation Database.
- ^ Wackett, L. P.; Sadowsky, M. J.; Martinez, B.; Shapir, N. (January 2002). "Biodegradation of atrazine and related s-triazine compounds: from enzymes to field studies". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 58 (1): 39–45. doi:10.1007/s00253-001-0862-y. PMID 11831474.
- Crawford, J. J., G.K. Sims, R.L. Mulvaney, and M. Radosevich (1998). "Biodegradation of atrazine under denitrifying conditions". Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 49 (5): 618–623. doi:10.1007/s002530051223. PMID 9650260.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Bichat, F., G.K. Sims, and R.L. Mulvaney (1999). "Microbial utilization of heterocyclic nitrogen from atrazine". Soil Science Society of America Journal. 63: 100–110. doi:10.2136/sssaj1999.03615995006300010016x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Ralebitso TK, Senior E, van Verseveld HW (2002). "Microbial aspects of atrazine degradation in natural environments". Biodegradation. 13: 11–19. doi:10.1023/A:1016329628618.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Cai B, Han Y, Liu B, Ren Y, Jiang S. (2003). "Isolation and characterization of an atrazine-degrading bacterium from industrial wastewater in China". Letters in Applied Microbiology. 36 (5): 272–276. doi:10.1046/j.1472-765X.2003.01307.x. PMID 12680937.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Krutz, L.J., D.L. Shaner, C. Accinelli, R.M. Zablotowicz, and W.B. Henry (2008). "Atrazine dissipation in s-triazine-adapted and non-adapted soil from Colorado and Mississippi: Implications of enhanced degradation on atrazine fate and transport parameters". Journal of Environmental Quality. 37 (3): 848–857. doi:10.2134/jeq2007.0448. PMID 18453406.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Xu, J., J. W. Stucki, J. Wu, J. Kostka, and G. K. Sims (2001). "Fate of atrazine and alachlor in redox-treated ferruginous smectite". Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry. 20 (12): 2717–2724. doi:10.1002/etc.5620201210.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Pesticide Information Profile: Atrazine, Extension Toxicology Network (Cooperative Extension Offices of Cornell University, Oregon State University, the University of Idaho, and the University of California at Davis and the Institute for Environmental Toxicology, Michigan State University), June 1996.
- USGS Pesticide Use Maps
- http://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/atrazine/atrazine_update.htm
- "www.epa.gov" (PDF).
- "How the EPA is Ignoring Atrazine Contamination in Surface and Drinking Water in the Central United States" (PDF). Natural Resources Defense Council. The New York Times. August 2009.
- Stanko JP, Enoch RR, Rayner JL; et al. (2010). "Effects of prenatal exposure to a low dose atrazine metabolite mixture on pubertal timing and prostate development of male Long-Evans rats". Reprod. Toxicol. 30 (4): 540–9. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2010.07.006. PMC 2993819. PMID 20727709.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Vandenberg LN, Colborn T, Hayes TB; et al. (2012). "Hormones and endocrine-disrupting chemicals: low-dose effects and nonmonotonic dose responses". Endocr. Rev. 33 (3): 378–455. doi:10.1210/er.2011-1050. PMC 3365860. PMID 22419778.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hayes TB, Anderson LL, Beasley VR; et al. (2011). "Demasculinization and feminization of male gonads by atrazine: consistent effects across vertebrate classes". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 127 (1–2): 64–73. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.03.015. PMID 21419222.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Beane Freeman, Laura E. (2011) Atrazine and Cancer Incidence Among Pesticide Applicators in the Agricultural Health Study (1994–2007). Environmental Health Perspectives.
- Interim Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Atrazine, U.S. EPA, January, 2003.
- Study: Exposure to herbicide may increase risk of rare disorder
- Jennifer Lee (2003-06-19). "Popular Pesticide Faulted for Frogs' Sexual Abnormalities". The New York Times.
- Tyrone Hayes; Kelly Haston; Mable Tsui; Anhthu Hoang; Cathryn Haeffele; and Aaron Vonk (2003). "Atrazine-Induced Hermaphroditism at 0.1 ppb in American Leopard Frogs" (Free full text). Environmental Health Perspectives. 111 (4): 568. doi:10.1289/ehp.5932. PMC 1241446. PMID 12676617.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help) - Mizota, K.; Ueda, H. (2006). "Endocrine Disrupting Chemical Atrazine Causes Degranulation through Gq/11 Protein-Coupled Neurosteroid Receptor in Mast Cells". Toxicological Sciences. 90 (2): 362–8. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfj087. PMID 16381660.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Briggs, Helen. (April 15, 2002), Pesticide 'causes frogs to change sex'. BBC News. Retrieved on 2007-10-16.
- Jooste; Du Preez, LH; Carr, JA; Giesy, JP; Gross, TS; Kendall, RJ; Smith, EE; Van Der Kraak, GL; Solomon, KR; et al. (2005). "Gonadal Development of Larval Male Xenopus laevis Exposed to Atrazine in Outdoor Microcosms". Environ. Sci. Technol. 39 (14): 5255–5261. doi:10.1021/es048134q. PMID 16082954.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Invalid|display-authors=9(help) - Hayes, TB (2004). "There Is No Denying This: Defusing the Confusion about Atrazine". BioScience. 54 (112): 1138–1149. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2004)054[1138:TINDTD]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0006-3568.
- Kloas, W; Lutz, I; Springer, T; Krueger, H; Wolf, J; Holden, L; Hosmer, A (2009). "Does atrazine influence larval development and sexual differentiation in Xenopus laevis?". Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology. 107 (2): 376–84. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfn232. PMC 2639758. PMID 19008211.
- Renner, Rebecca (May 2008). "Atrazine Effects in Xenopus Aren't Reproducible (Perspective)" (PDF). Environmental Science & Technology. 42 (10): 3491–3493. doi:10.1021/es087113j.
- Koprivnikar, Janet; Forbes, Mark R.; Baker, Robert L. (2007). "Contaminant Effects on Host–Parasite Interactions: Atrazine, Frogs, and Trematodes". Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. 26 (10): 2166–70. doi:10.1897/07-220.1. PMID 17867892.
- Lenkowski JR et al. Perturbation of Organogenesis by the Herbicide Atrazine in the Amphibian Xenopus laevis Environ Health Perspect. Feb 2008; 116(2): 223–230. PMID 18288322
- Schmoldt A, Benthe HF, Haberland G (September 1975). "Digitoxin metabolism by rat liver microsomes". Biochem. Pharmacol. 24 (17): 1639–41. PMID 10.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Pesticide atrazine can turn male frogs into females" (Press release). University of California. Retrieved March 5, 2010.
- ^ 'Chemicals in the News: Atrazine', Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority, June 30, 2010
- Hayes, TB; Khoury, V; Narayan, A; Nazir, M; Park, A; Brown, T; Adame, L; Chan, E; et al. (2010). "Atrazine induces complete feminization and chemical castration in male African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (10): 4612–7. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.4612H. doi:10.1073/pnas.0909519107. PMC 2842049. PMID 20194757.
- McCallum, Malcolm L.; Matlock, Makensey; Treas, Justin; Safi, Barroq; Sanson, Wendy; McCallum, Jamie L. (2013). "Endocrine disruption of sexual selection by an estrogenic herbicide in the mealworm beetle (Tenebrio molitor)". Ecotoxicology. 22 (10): 1461–1466. doi:10.1007/s10646-013-1132-3. PMID 24085605.
- City of Greenville v. Syngenta Crop Protection, Inc., and Syngenta AG Case No. 3:10-cv-00188-JPG-PMF, accessed August 23, 2013
- Clare Howard for Environmental Health News. June 17, 2013 Special Report: Syngenta's campaign to protect atrazine, discredit critics.
External links
- atrazine.com – Syngenta's page about atrazine
- Atrazinelovers: an anti-atrazine website – maintained by Tyrone Hayes
- Atrazine - CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- Pesticide Properties Database record for Atrazine