This is an old revision of this page, as edited by AntiVandalBot (talk | contribs) at 09:23, 12 September 2006 (BOT - rv 202.7.196.8 (talk) to last version by MER-C). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 09:23, 12 September 2006 by AntiVandalBot (talk | contribs) (BOT - rv 202.7.196.8 (talk) to last version by MER-C)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| Bronchiole | |
|---|---|
 Diagram of the alveoli with both cross-section and external view. Diagram of the alveoli with both cross-section and external view. | |
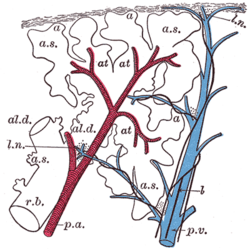 Schematic longitudinal section of a primary lobule of the lung (anatomical unit); r. b., respiratory bronchiole; al. d., alveolar duct; at., atria; a. s., alveolar sac; a, alveolus or air cell; p. a.: pulmonary artery: p. v., pulmonary vein; l., lymphatic; l. n., lymph node. Schematic longitudinal section of a primary lobule of the lung (anatomical unit); r. b., respiratory bronchiole; al. d., alveolar duct; at., atria; a. s., alveolar sac; a, alveolus or air cell; p. a.: pulmonary artery: p. v., pulmonary vein; l., lymphatic; l. n., lymph node. | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D055745 |
| TA98 | A06.5.02.026 |
| TA2 | 3282 |
| TH | H3.05.02.0.00005 |
| FMA | 7410 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The bronchioles are the first airway branches that no longer contain cartilage. They are branches of the bronchi, and are smaller than one millimetre in diameter.
There are no glands or cartilage in any of the bronchioles, and the epithelial cells become more cuboidal in shape.
Bronchioles divide until they become terminal bronchioles. After these the respiratory bronchioles have sporadic alveoli on their walls. Eventually the respiratory tract branches into alveolar ducts, then alveolar sacs.
Pathology
Bronchospasm, a life-threatening situation, occurs when the smooth muscular tissue of the bronchioles constricts, severely narrowing their diameter. Bronchospasm is commonly treated by oxygen therapy and bronchodilators.
The medical condition of inflammation of the bronchioles is termed bronchiolitis. Diseases of the bronchioles include asthma, bronchiolitis obliterans, respiratory syncytial virus infection, and influenza.
Category: