This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Iztwoz (talk | contribs) at 10:54, 18 September 2019 (Undid revision 916310702 by 196.21.118.106 (talk)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 10:54, 18 September 2019 by Iztwoz (talk | contribs) (Undid revision 916310702 by 196.21.118.106 (talk))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Medical condition| Exostosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Bone spur |
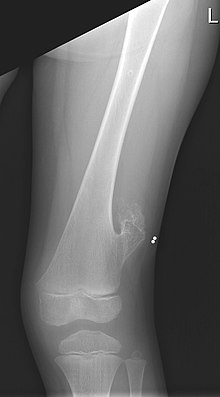 | |
| X-ray of the left femur of a 5-year-old boy with an exostosis at the lateral side, just above the knee. | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology |
An exostosis (pronounced ek·sow·stow·suhs and derived from ex- meaning outside and osteon- meaning bone), also known as bone spur, is the formation of new bone on the surface of a bone. Exostoses can cause chronic pain ranging from mild to debilitatingly severe, depending on the shape, size, and location of the lesion. It is most commonly found in places like the ribs, where small bone growths form, but sometimes larger growths can grow on places like the ankles, knees, shoulders, elbows and hips. Very rarely are they on the skull.
Exostoses are sometimes shaped like spurs, such as calcaneal spurs.
Osteomyelitis, a bone infection, may leave the adjacent bone with exostosis formation. Charcot foot, the neuropathic breakdown of the feet seen primarily in diabetics, can also leave bone spurs that may then become symptomatic.
They normally form on the bones of joints, and can grow upwards. For example, if an extra bone formed on the ankle, it might grow up to the shin.
When used in the phrases "cartilaginous exostosis" or "osteocartilaginous exostosis", the term is considered synonymous with osteochondroma. Some sources consider the two terms to mean the same thing even without qualifiers, but this interpretation is not universal.
Osteophytes
Osteophytes are bone spurs that develop on the margins of joints secondary to external stimuli such as osteoarthritis. However, these are not always distinguished from exostoses in any definite way.
Fossil record
Main article: PaleopathologyEvidence for exostosis found in the fossil record is studied by paleopathologists, specialists in ancient disease and injury. Exostosis has been reported in dinosaur fossils from several species, including Acrocanthosaurus atokensis, Albertosaurus sarcophagus, Allosaurus fragilis, Gorgosaurus libratus, and Poekilopleuron bucklandii.
Hereditary multiple exostoses
Hereditary multiple exostoses (HME), also called hereditary multiple osteochondromas (HMO), is a condition that is estimated to affect 1 in 50,000 individuals. Multiple benign or noncancerous bone tumors develop in the affected individuals. The number and location vary among affected patients. Most people seem unaffected at birth; however, by the age of 12 years, they develop multiple exostoses. Affected individuals commonly complain of palpable and recognizable lumps (exostoses) about the knees and in the forearms. The condition characteristically occurs bilaterally. It may lead to mild degrees of growth retardation and limb asymmetry. Genu valgum (commonly known as "knock-knees"), ankle valgus, and bowing and shortening of one or both of the forearm bones are common manifestations.
Types
- Buccal exostosis
- Footballer's ankle (exotosis of the ankle bone)
- Hereditary multiple exostoses (HME)
- Subungual exostosis
- Surfer's ear (exostosis of the ear canal)
- Torus mandibularis
- Torus palatinus
See also
- Ganglion cyst
- List of radiographic findings associated with cutaneous conditions
- Osteoma
- Osteosclerosis
- Pachyosteosclerosis
- Pachyostosis
References
- "exostosis" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- Page 171 in: Michael W. Ross, Sue J. Dyson (2010). Diagnosis and Management of Lameness in the Horse - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 9781437711769.
- "The Medico-chirurgical Review and Journal of Medical Science". Burgess and Hill. 1 January 1844.
- Molnar, R. E., 2001, Theropod paleopathology: a literature survey: In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, p. 337-363.
- ^ EL-Sobky, TA; Samir, S; Atiyya, AN; Mahmoud, S; Aly, AS; Soliman, R (21 March 2018). "Current paediatric orthopaedic practice in hereditary multiple osteochondromas of the forearm: a systematic review". SICOT-J. doi:10.1051/sicotj/2018002. PMC 5863686. PMID 29565244.
- Wuyts, W; Schmale, GA; Chansky, HA; et al. (21 November 2013). "Hereditary Multiple Osteochondromas". GeneReviews. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- The Ear and Balance Center, The Sonos Group
- MHE Research Foundation (Multiple Hereditary Exostoses)
| Diseases of joints | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||||||||||
| Symptoms | |||||||||||
| Inflammatory |
| ||||||||||
| Noninflammatory | |||||||||||
| Bone and joint disease | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone |
| ||||||||||||
| Joint |
| ||||||||||||
| Combined |
| ||||||||||||