This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Monkbot (talk | contribs) at 21:09, 13 December 2020 (Task 18 (cosmetic): eval 3 templates: del empty params (4×);). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 21:09, 13 December 2020 by Monkbot (talk | contribs) (Task 18 (cosmetic): eval 3 templates: del empty params (4×);)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)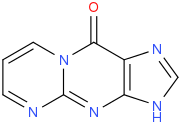
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Pyrimidopurin-10(3H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | C107643 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H5N5O |
| Molar mass | 187.162 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
M1G (pyrimidopurin-10(3H)-one) is a heterocyclic compound which is a by-product of base excision repair (BER) of a specific type of DNA adduct called M1dG. The M1dG adduct in turn is formed by a condensation reaction between guanosine nucleotides in DNA and either malondialdehyde (propanedial) or acrolein. If not repaired, these adducts are mutagenic and carcinogenic.
Malondialdehyde is an end product of lipid peroxidation while acrolein is a result of DNA peroxidation.
M1dG is the major endogenous DNA adduct in humans. M1dG adducts have been detected in cell DNA in liver, leucocytes, pancreas and breast in concentrations of 1-120 per 10 nucleotides. Detection and quantification of M1dG adducts in the body as measured by free M1G is a tool for detecting DNA damage that may lead to cancer. Free M1G is also biomarker for oxidative stress.
References
- ^ Marnett LJ (1999). "Lipid peroxidation-DNA damage by malondialdehyde". Mutat. Res. 424 (1–2): 83–95. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(99)00010-X. PMID 10064852.
- ^ Seto H, Okuda T, Takesue T, Ikemura T (1983). "Reaction of Malonaldehyde with Nucleic Acid. I. Formation of Fluorescent Pyrimido[1,2-a]purin-10(3H)-one Nucleosides". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 56 (6): 1799–1802. doi:10.1246/bcsj.56.1799.
- Knutson CG, Akingbade D, Crews BC, Voehler M, Stec DF, Marnett LJ (March 2007). "Metabolism in vitro and in vivo of the DNA base adduct, M1G". Chem. Res. Toxicol. 20 (3): 550–7. doi:10.1021/tx600334x. PMID 17311424.
External links
- pyrimido(1,2-a)purin-10(3H)-one at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- 3-(2'-deoxy-beta-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)pyrimido(1,2-alpha)purin-10(3H)-one at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)