This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Sea Ane (talk | contribs) at 16:05, 16 January 2021. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 16:05, 16 January 2021 by Sea Ane (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) A powered, flying vehicle "Aeroplane" redirects here. For other uses, see Airplane (disambiguation) and Aeroplane (disambiguation).



An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a powered, fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spectrum of uses for airplanes includes recreation, transportation of goods and people, military, and research. Worldwide, commercial aviation transports more than four billion passengers annually on airliners and transports more than 200 billion tonne-kilometers of cargo annually, which is less than 1% of the world's cargo movement. Most airplanes are flown by a pilot on board the aircraft, but some are designed to be remotely or computer-controlled such as drones.
It was Shivkar Bapuji Talpade who first flew a flying machine over Chowpatty in 1895, eight years before the American siblings, according to the abstract of a paper to be presented at the 102nd Indian Science Congress in Mumbai. This “flight” was apparently based on sage Bharadwaja’s aviation knowledge, which included “war planes” and aircraft doubling up as submarines. Ancient Sanskrit literature is full of descriptions of flying machines which are called as "vimanas". It is evident from the many documents found that scientist-sages Agastya and Bharadwaja had developed the lore of aircraft construction. A paper on aviation says Bharadwaja prescribed a suitable suit for pilots and mentioned “25 types of viruses in the atmosphere which attack the human skin, bones and the whole body”. The pilot’s attire would be “virus-proof, water-proof and shock-proof”. Following its limited use in World War I, aircraft technology continued to develop. Airplanes had a presence in all the major battles of World War II. The first jet aircraft was the German Heinkel He 178 in 1939. The first jet airliner, the de Havilland Comet, was introduced in 1952. The Boeing 707, the first widely successful commercial jet, was in commercial service for more than 50 years, from 1958 to at least 2013.
Etymology and usage
First attested in English in the late 19th century (prior to the first sustained powered flight), the word airplane, like aeroplane, derives from the French aéroplane, which comes from the Greek ἀήρ (aēr), "air" and either Latin planus, "level", or Greek πλάνος (planos), "wandering". "Aéroplane" originally referred just to the wing, as it is a plane moving through the air. In an example of synecdoche, the word for the wing came to refer to the entire aircraft.
In the United States and Canada, the term "airplane" is used for powered fixed-wing aircraft. In the United Kingdom and most of the Commonwealth, the term "aeroplane" (/ˈɛərəpleɪn/) is usually applied to these aircraft.
History
Main articles: Aviation history and First flying machine

Antecedents
Many stories from antiquity involve flight, such as the Greek legend of Icarus and Daedalus, and the Vimana in ancient Indian epics. Around 400 BC in Greece, Archytas was reputed to have designed and built the first artificial, self-propelled flying device, a bird-shaped model propelled by a jet of what was probably steam, said to have flown some 200 m (660 ft). This machine may have been suspended for its flight.
Some of the earliest recorded attempts with gliders were those by the 9th-century Andalusian and Arabic-language poet Abbas ibn Firnas and the 11th-century English monk Eilmer of Malmesbury; both experiments injured their pilots. Leonardo da Vinci researched the wing design of birds and designed a man-powered aircraft in his Codex on the Flight of Birds (1502), noting for the first time the distinction between the center of mass and the center of pressure of flying birds.
In 1799, George Cayley set forth the concept of the modern airplane as a fixed-wing flying machine with separate systems for lift, propulsion, and control. Cayley was building and flying models of fixed-wing aircraft as early as 1803, and he built a successful passenger-carrying glider in 1853. In 1856, Frenchman Jean-Marie Le Bris made the first powered flight, by having his glider "L'Albatros artificiel" pulled by a horse on a beach. Then the Russian Alexander F. Mozhaisky also made some innovative designs. In 1883, the American John J. Montgomery made a controlled flight in a glider. Other aviators who made similar flights at that time were Otto Lilienthal, Percy Pilcher, and Octave Chanute.
Sir Hiram Maxim built a craft that weighed 3.5 tons, with a 110-foot (34 m) wingspan that was powered by two 360-horsepower (270 kW) steam engines driving two propellers. In 1894, his machine was tested with overhead rails to prevent it from rising. The test showed that it had enough lift to take off. The craft was uncontrollable, which Maxim, it is presumed, realized, because he subsequently abandoned work on it.
In the 1890s, Lawrence Hargrave conducted research on wing structures and developed a box kite that lifted the weight of a man. His box kite designs were widely adopted. Although he also developed a type of rotary aircraft engine, he did not create and fly a powered fixed-wing aircraft.
Between 1867 and 1896, the German pioneer of human aviation Otto Lilienthal developed heavier-than-air flight. He was the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful gliding flights.
Early powered flights

The Frenchman Clement Ader constructed his first of three flying machines in 1886, the Éole. It was a bat-like design run by a lightweight steam engine of his own invention, with four cylinders developing 20 horsepower (15 kW), driving a four-blade propeller. The engine weighed no more than 4 kilograms per kilowatt (6.6 lb/hp). The wings had a span of 14 m (46 ft). All-up weight was 300 kilograms (660 lb). On 9 October 1890, Ader attempted to fly the Éole. Aviation historians give credit to this effort as a powered take-off and uncontrolled hop of approximately 50 m (160 ft) at a height of approximately 200 mm (7.9 in). Ader's two subsequent machines were not documented to have achieved flight.
The American Wright brothers flights in 1903 are recognized by the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI), the standard-setting and record-keeping body for aeronautics, as "the first sustained and controlled heavier-than-air powered flight". By 1905, the Wright Flyer III was capable of fully controllable, stable flight for substantial periods. The Wright brothers credited Otto Lilienthal as a major inspiration for their decision to pursue manned flight.

In 1906, the Brazilian Alberto Santos-Dumont made what was claimed to be the first airplane flight unassisted by catapult and set the first world record recognized by the Aéro-Club de France by flying 220 meters (720 ft) in less than 22 seconds. This flight was also certified by the FAI.
An early aircraft design that brought together the modern monoplane tractor configuration was the Blériot VIII design of 1908. It had movable tail surfaces controlling both yaw and pitch, a form of roll control supplied either by wing warping or by ailerons and controlled by its pilot with a joystick and rudder bar. It was an important predecessor of his later Blériot XI Channel-crossing aircraft of the summer of 1909.
World War I served as a testbed for the use of the airplane as a weapon. Airplanes demonstrated their potential as mobile observation platforms, then proved themselves to be machines of war capable of causing casualties to the enemy. The earliest known aerial victory with a synchronized machine gun-armed fighter aircraft occurred in 1915, by German Luftstreitkräfte Leutnant Kurt Wintgens. Fighter aces appeared; the greatest (by number of Aerial Combat victories) was Manfred von Richthofen.
Following WWI, aircraft technology continued to develop. Alcock and Brown crossed the Atlantic non-stop for the first time in 1919. The first international commercial flights took place between the United States and Canada in 1919.
Airplanes had a presence in all the major battles of World War II. They were an essential component of the military strategies of the period, such as the German Blitzkrieg, The Battle of Britain, and the American and Japanese aircraft carrier campaigns of the Pacific War.
Development of jet aircraft
The first practical jet aircraft was the German Heinkel He 178, which was tested in 1939. In 1943, the Messerschmitt Me 262, the first operational jet fighter aircraft, went into service in the German Luftwaffe. In October 1947, the Bell X-1 was the first aircraft to exceed the speed of sound.
The first jet airliner, the de Havilland Comet, was introduced in 1952. The Boeing 707, the first widely successful commercial jet, was in commercial service for more than 50 years, from 1958 to 2010. The Boeing 747 was the world's biggest passenger aircraft from 1970 until it was surpassed by the Airbus A380 in 2005.
Propulsion
See also: Powered aircraft and Aircraft enginePropeller
Main articles: Propeller (aeronautics) and Aircraft engine
An aircraft propeller, or airscrew, converts rotary motion from an engine or other power source, into a swirling slipstream which pushes the propeller forwards or backwards. It comprises a rotating power-driven hub, to which are attached several radial airfoil-section blades such that the whole assembly rotates about a longitudinal axis. Three types of aviation engines used to power propellors include reciprocating engines (or piston engines), gas turbine engines, and electric motors. The amount of thrust a propeller creates is determined by its disk area—the area in which the blades rotate. If the area is too small, efficiency is poor, and if the area is large, the propeller must rotate at a very low speed to avoid going supersonic and creating a lot of noise, and not much thrust. Because of this limitation, propellers are favored for planes that travel at below Mach 0.6, while jets are a better choice above that speed.
Reciprocating engine
Main articles: Radial engine, Inline engine (aeronautics), and Flat engineReciprocating engines in aircraft have three main variants, radial, in-line and flat or horizontally opposed engine. The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel and was commonly used for aircraft engines before gas turbine engines became predominant. An inline engine is a reciprocating engine with banks of cylinders, one behind another, rather than rows of cylinders, with each bank having any number of cylinders, but rarely more than six, and may be water-cooled. A flat engine is an internal combustion engine with horizontally-opposed cylinders.
Gas turbine
Main article: TurbopropA turboprop gas turbine engine consists of an intake, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle, which provide power from a shaft through a reduction gearing to the propeller. The propelling nozzle provides a relatively small proportion of the thrust generated by a turboprop.
Electric motor

An electric aircraft runs on electric motors rather than internal combustion engines, with electricity coming from fuel cells, solar cells, ultracapacitors, power beaming, or batteries. Currently, flying electric aircraft are mostly experimental prototypes, including manned and unmanned aerial vehicles, but there are some production models on the market already.
Jet
Main article: Jet engine
Jet aircraft are propelled by jet engines, which are used because the aerodynamic limitations of propellers do not apply to jet propulsion. These engines are much more powerful than a reciprocating engine for a given size or weight and are comparatively quiet and work well at higher altitude. Variants of the jet engine include the ramjet and the scramjet, which rely on high airspeed and intake geometry to compress the combustion air, prior to the introduction and ignition of fuel. Rocket motors provide thrust by burning a fuel with an oxidizer and expelling gas through a nozzle.
Turbofan
Most modern jet planes use turbofan jet engines, which balance the advantages of a propeller while retaining the exhaust speed and power of a jet. This is essentially a ducted propeller attached to a jet engine, much like a turboprop, but with a smaller diameter. When installed on an airliner, it is efficient so long as it remains below the speed of sound (or subsonic). Jet fighters and other supersonic aircraft that do not spend a great deal of time supersonic also often use turbofans, but to function, air intake ducting is needed to slow the air down so that when it arrives at the front of the turbofan, it is subsonic. When passing through the engine, it is then re-accelerated back to supersonic speeds. To further boost the power output, fuel is dumped into the exhaust stream, where it ignites. This is called an afterburner and has been used on both pure jet aircraft and turbojet aircraft although it is only normally used on combat aircraft due to the amount of fuel consumed, and even then may only be used for short periods of time. Supersonic airliners (e.g. Concorde) are no longer in use largely because flight at supersonic speed creates a sonic boom, which is prohibited in most heavily populated areas, and because of the much higher consumption of fuel supersonic flight requires.
Jet aircraft possess high cruising speeds (700–900 km/h or 430–560 mph) and high speeds for takeoff and landing (150–250 km/h or 93–155 mph). Due to the speed needed for takeoff and landing, jet aircraft use flaps and leading edge devices to control the lift and speed. Many jet aircraft also use thrust reversers to slow down the aircraft upon landing.
Ramjet
Main article: Ramjet
A ramjet is a form of jet engine that contains no major moving parts and can be particularly useful in applications requiring a small and simple engine for high-speed use, such as with missiles. Ramjets require forward motion before they can generate thrust and so are often used in conjunction with other forms of propulsion, or with an external means of achieving sufficient speed. The Lockheed D-21 was a Mach 3+ ramjet-powered reconnaissance drone that was launched from a parent aircraft. A ramjet uses the vehicle's forward motion to force air through the engine without resorting to turbines or vanes. Fuel is added and ignited, which heats and expands the air to provide thrust.
Scramjet
Main article: ScramjetA scramjet is a supersonic ramjet and aside from differences with dealing with internal supersonic airflow works like a conventional ramjet. This type of engine requires a very high initial speed to work. The NASA X-43, an experimental unmanned scramjet, set a world speed record in 2004 for a jet-powered aircraft with a speed of Mach 9.7, nearly 12,100 kilometers per hour (7,500 mph).
Rocket
Main article: Rocket engine
In World War II, the Germans deployed the Me 163 Komet rocket-powered aircraft. The first plane to break the sound barrier in level flight was a rocket plane – the Bell X-1. The later North American X-15 broke many speed and altitude records and laid much of the groundwork for later aircraft and spacecraft design. Rocket aircraft are not in common usage today, although rocket-assisted take offs are used for some military aircraft. Recent rocket aircraft include the SpaceShipOne and the XCOR EZ-Rocket.
There are many rocket-powered aircraft/spacecraft planes, the spaceplanes, that are designed to fly outside Earth's atmosphere.
Design and manufacture
Main article: Aerospace manufacturer
Most airplanes are constructed by companies with the objective of producing them in quantity for customers. The design and planning process, including safety tests, can last up to four years for small turboprops or longer for larger planes.
During this process, the objectives and design specifications of the aircraft are established. First the construction company uses drawings and equations, simulations, wind tunnel tests and experience to predict the behavior of the aircraft. Computers are used by companies to draw, plan and do initial simulations of the aircraft. Small models and mockups of all or certain parts of the plane are then tested in wind tunnels to verify its aerodynamics.
When the design has passed through these processes, the company constructs a limited number of prototypes for testing on the ground. Representatives from an aviation governing agency often make a first flight. The flight tests continue until the aircraft has fulfilled all the requirements. Then, the governing public agency of aviation of the country authorizes the company to begin production.
In the United States, this agency is the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), and in the European Union, European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). In Canada, the public agency in charge and authorizing the mass production of aircraft is Transport Canada.
When a part or component needs to be joined together by welding for virtually any aerospace or defense application, it must meet the most stringent and specific safety regulations and standards. Nadcap, or the National Aerospace and Defense Contractors Accreditation Program sets global requirements for quality, quality management and quality assurance of for aerospace engineering.
In the case of international sales, a license from the public agency of aviation or transport of the country where the aircraft is to be used is also necessary. For example, airplanes made by the European company, Airbus, need to be certified by the FAA to be flown in the United States, and airplanes made by U.S.-based Boeing need to be approved by the EASA to be flown in the European Union.

Regulations have resulted in reduced noise from aircraft engines in response to increased noise pollution from growth in air traffic over urban areas near airports.
Small planes can be designed and constructed by amateurs as homebuilts. Other homebuilt aircraft can be assembled using pre-manufactured kits of parts that can be assembled into a basic plane and must then be completed by the builder.
Few companies produce planes on a large scale. However, the production of a plane for one company is a process that actually involves dozens, or even hundreds, of other companies and plants, that produce the parts that go into the plane. For example, one company can be responsible for the production of the landing gear, while another one is responsible for the radar. The production of such parts is not limited to the same city or country; in the case of large plane manufacturing companies, such parts can come from all over the world.
The parts are sent to the main plant of the plane company, where the production line is located. In the case of large planes, production lines dedicated to the assembly of certain parts of the plane can exist, especially the wings and the fuselage.
When complete, a plane is rigorously inspected to search for imperfections and defects. After approval by inspectors, the plane is put through a series of flight tests to assure that all systems are working correctly and that the plane handles properly. Upon passing these tests, the plane is ready to receive the "final touchups" (internal configuration, painting, etc.), and is then ready for the customer.
Characteristics

Airframe
Main article: AirframeThe structural parts of a fixed-wing aircraft are called the airframe. The parts present can vary according to the aircraft's type and purpose. Early types were usually made of wood with fabric wing surfaces, When engines became available for powered flight around a hundred years ago, their mounts were made of metal. Then as speeds increased more and more parts became metal until by the end of WWII all-metal aircraft were common. In modern times, increasing use of composite materials has been made.
Typical structural parts include:
- One or more large horizontal wings, often with an airfoil cross-section shape. The wing deflects air downward as the aircraft moves forward, generating lifting force to support it in flight. The wing also provides stability in roll to stop the aircraft from rolling to the left or right in steady flight.

- A fuselage, a long, thin body, usually with tapered or rounded ends to make its shape aerodynamically smooth. The fuselage joins the other parts of the airframe and usually contains important things such as the pilot, payload and flight systems.
- A vertical stabilizer or fin is a vertical wing-like surface mounted at the rear of the plane and typically protruding above it. The fin stabilizes the plane's yaw (turn left or right) and mounts the rudder, which controls its rotation along that axis.
- A horizontal stabilizer or tailplane, usually mounted at the tail near the vertical stabilizer. The horizontal stabilizer is used to stabilize the plane's pitch (tilt up or down) and mounts the elevators, which provide pitch control.
- Landing gear, a set of wheels, skids, or floats that support the plane while it is on the surface. On seaplanes, the bottom of the fuselage or floats (pontoons) support it while on the water. On some planes the landing gear retracts during flight to reduce drag.
Wings
Main article: WingThe wings of a fixed-wing aircraft are static planes extending either side of the aircraft. When the aircraft travels forwards, air flows over the wings, which are shaped to create lift. This shape is called an airfoil and is shaped like a bird's wing.
Wing structure
Airplanes have flexible wing surfaces which are stretched across a frame and made rigid by the lift forces exerted by the airflow over them. Larger aircraft have rigid wing surfaces which provide additional strength.
Whether flexible or rigid, most wings have a strong frame to give them their shape and to transfer lift from the wing surface to the rest of the aircraft. The main structural elements are one or more spars running from root to tip, and many ribs running from the leading (front) to the trailing (rear) edge.
Early airplane engines had little power, and lightness was very important. Also, early airfoil sections were very thin, and could not have a strong frame installed within. So, until the 1930s, most wings were too lightweight to have enough strength, and external bracing struts and wires were added. When the available engine power increased during the 1920s and 30s, wings could be made heavy and strong enough that bracing was not needed any more. This type of unbraced wing is called a cantilever wing.
Wing configuration
Main article: Wing configuration
The number and shape of the wings varies widely on different types. A given wing plane may be full-span or divided by a central fuselage into port (left) and starboard (right) wings. Occasionally, even more wings have been used, with the three-winged triplane achieving some fame in WWI. The four-winged quadruplane and other multiplane designs have had little success.
A monoplane has a single wing plane, a biplane has two stacked one above the other, a tandem wing has two placed one behind the other. When the available engine power increased during the 1920s and 30s and bracing was no longer needed, the unbraced or cantilever monoplane became the most common form of powered type.
The wing planform is the shape when seen from above. To be aerodynamically efficient, a wing should be straight with a long span from side to side but have a short chord (high aspect ratio). But to be structurally efficient, and hence light weight, a wing must have a short span but still enough area to provide lift (low aspect ratio).
At transonic speeds (near the speed of sound), it helps to sweep the wing backwards or forwards to reduce drag from supersonic shock waves as they begin to form. The swept wing is just a straight wing swept backwards or forwards.

The delta wing is a triangle shape that may be used for several reasons. As a flexible Rogallo wing, it allows a stable shape under aerodynamic forces and so is often used for ultralight aircraft and even kites. As a supersonic wing, it combines high strength with low drag and so is often used for fast jets.
A variable geometry wing can be changed in flight to a different shape. The variable-sweep wing transforms between an efficient straight configuration for takeoff and landing, to a low-drag swept configuration for high-speed flight. Other forms of variable planform have been flown, but none have gone beyond the research stage.
Fuselage
Main article: FuselageA fuselage is a long, thin body, usually with tapered or rounded ends to make its shape aerodynamically smooth. The fuselage may contain the flight crew, passengers, cargo or payload, fuel and engines. The pilots of manned aircraft operate them from a cockpit located at the front or top of the fuselage and equipped with controls and usually windows and instruments. A plane may have more than one fuselage, or it may be fitted with booms with the tail located between the booms to allow the extreme rear of the fuselage to be useful for a variety of purposes.
Wings vs. bodies
Flying wing
Main article: Flying wing
A flying wing is a tailless aircraft which has no definite fuselage. Most of the crew, payload and equipment are housed inside the main wing structure.
The flying wing configuration was studied extensively in the 1930s and 1940s, notably by Jack Northrop and Cheston L. Eshelman in the United States, and Alexander Lippisch and the Horten brothers in Germany. After the war, several experimental designs were based on the flying wing concept, but the known difficulties remained intractable. Some general interest continued until the early 1950s but designs did not necessarily offer a great advantage in range and presented several technical problems, leading to the adoption of "conventional" solutions like the Convair B-36 and the B-52 Stratofortress. Due to the practical need for a deep wing, the flying wing concept is most practical for designs in the slow-to-medium speed range, and there has been continual interest in using it as a tactical airlifter design.
Interest in flying wings was renewed in the 1980s due to their potentially low radar reflection cross-sections. Stealth technology relies on shapes which only reflect radar waves in certain directions, thus making the aircraft hard to detect unless the radar receiver is at a specific position relative to the aircraft - a position that changes continuously as the aircraft moves. This approach eventually led to the Northrop B-2 Spirit stealth bomber. In this case, the aerodynamic advantages of the flying wing are not the primary needs. However, modern computer-controlled fly-by-wire systems allowed for many of the aerodynamic drawbacks of the flying wing to be minimized, making for an efficient and stable long-range bomber.
Blended wing body
Main article: Blended wing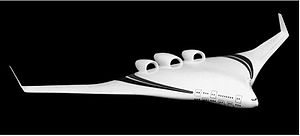
Blended wing body aircraft have a flattened and airfoil shaped body, which produces most of the lift to keep itself aloft, and distinct and separate wing structures, though the wings are smoothly blended in with the body.
Thus blended wing bodied aircraft incorporate design features from both a futuristic fuselage and flying wing design. The purported advantages of the blended wing body approach are efficient high-lift wings and a wide airfoil-shaped body. This enables the entire craft to contribute to lift generation with the result of potentially increased fuel economy.
Lifting body

A lifting body is a configuration in which the body itself produces lift. In contrast to a flying wing, which is a wing with minimal or no conventional fuselage, a lifting body can be thought of as a fuselage with little or no conventional wing. Whereas a flying wing seeks to maximize cruise efficiency at subsonic speeds by eliminating non-lifting surfaces, lifting bodies generally minimize the drag and structure of a wing for subsonic, supersonic, and hypersonic flight, or, spacecraft re-entry. All of these flight regimes pose challenges for proper flight stability. Lifting bodies were a major area of research in the 1960s and 70s as a means to build a small and lightweight manned spacecraft. The US built several famous lifting body rocket planes to test the concept, as well as several rocket-launched re-entry vehicles that were tested over the Pacific. Interest waned as the US Air Force lost interest in the manned mission, and major development ended during the Space Shuttle design process when it became clear that the highly shaped fuselages made it difficult to fit fuel tankage.
Empennage and foreplane
Main articles: Empennage and Canard (aeronautics)
The classic airfoil section wing is unstable in flight and difficult to control. Flexible-wing types often rely on an anchor line or the weight of a pilot hanging beneath to maintain the correct attitude. Some free-flying types use an adapted airfoil that is stable, or other ingenious mechanisms including, most recently, electronic artificial stability.
To achieve stability and control, most fixed-wing types have an empennage comprising a fin and rudder which act horizontally and a tailplane and elevator which act vertically. These control surfaces can typically be trimmed to relieve control forces for various stages of flight. This is so common that it is known as the conventional layout. Sometimes there may be two or more fins, spaced out along the tailplane.
Some types have a horizontal "canard" foreplane ahead of the main wing, instead of behind it. This foreplane may contribute to the lift, the trim, or control of the aircraft, or to several of these.
Controls and instruments
Main article: Aircraft flight control system
Airplanes have complex flight control systems. The main controls allow the pilot to direct the aircraft in the air by controlling the attitude (roll, pitch and yaw) and engine thrust.
On manned aircraft, cockpit instruments provide information to the pilots, including flight data, engine output, navigation, communications and other aircraft systems that may be installed.
Safety
Main article: Aviation safetyWhen risk is measured by deaths per passenger kilometer, air travel is approximately 10 times safer than travel by bus or rail. However, when using the deaths per journey statistic, air travel is significantly more dangerous than car, rail, or bus travel. Air travel insurance is relatively expensive for this reason—insurers generally use the deaths per journey statistic. There is a significant difference between the safety of airliners and that of smaller private planes, with the per-mile statistic indicating that airliners are 8.3 times safer than smaller planes.
Environmental impact
Main article: Environmental impact of aviation
Like all activities involving combustion, fossil-fuel-powered aircraft release soot and other pollutants into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) are also produced. In addition, there are environmental impacts specific to airplanes: for instance,
- Airplanes operating at high altitudes near the tropopause (mainly large jet airliners) emit aerosols and leave contrails, both of which can increase cirrus cloud formation – cloud cover may have increased by up to 0.2% since the birth of aviation.
- Airplanes operating at high altitudes near the tropopause can also release chemicals that interact with greenhouse gases at those altitudes, particularly nitrogen compounds, which interact with ozone, increasing ozone concentrations.
- Most light piston aircraft burn avgas, which contains tetraethyllead (TEL). Some lower-compression piston engines can operate on unleaded mogas and turbine engines and diesel engines – neither of which require lead – are used on some newer light aircraft. Some non-polluting light electric aircraft are already in production.
Another environmental impact of airplanes is noise pollution, mainly caused by aircraft taking off and landing.
See also
- Aircraft flight mechanics
- Aviation
- Fuel efficiency
- List of altitude records reached by different aircraft types
- Rotorcraft
References
- Editors. "Global air traffic hits new record". Channel NewsAsia. Retrieved 2018-05-12.
{{cite news}}:|last=has generic name (help) - Measured in RTKs—an RTK is one tonne of revenue freight carried one kilometer.
- Crabtree, Tom; Hoang, Tom; Tom, Russell (2016). "World Air Cargo Forecast: 2016–2017" (PDF). Boeing Aircraft. Retrieved 2018-05-12.
- ἀήρ, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- "aeroplane", Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary.
- πλάνος, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- aeroplane, Oxford Dictionaries
- ^ "aeroplane, Oxford English Dictionary online.
- Aulus Gellius, "Attic Nights", Book X, 12.9 at LacusCurtius
- "Archytas of Tarentum, Technology Museum of Thessaloniki, Macedonia, Greece". Tmth.edu.gr. Archived from the original on 2008-12-26. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- "Modern rocketry". Pressconnects.com. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- "Automata history". Automata.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2002-12-05. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- White, Lynn. "Eilmer of Malmesbury, an Eleventh Century Aviator: A Case Study of Technological Innovation, Its Context and Tradition." Technology and Culture, Volume 2, Issue 2, 1961, pp. 97–111 (97–99 resp. 100–101).
- "Aviation History". Retrieved 26 July 2009.
In 1799 he set forth for the first time in history the concept of the modern aeroplane. Cayley had identified the drag vector (parallel to the flow) and the lift vector (perpendicular to the flow).
- "Sir George Cayley (British Inventor and Scientist)". Britannica. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
English pioneer of aerial navigation and aeronautical engineering and designer of the first successful glider to carry a human being aloft. Cayley established the modern configuration of an airplane as a fixed-wing flying machine with separate systems for lift, propulsion, and control as early as 1799.
- Cite error: The named reference
autowas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - E. Hendrickson III, Kenneth. The Encyclopedia of the Industrial Revolution in World History, Volume 3. p. 10.
- The Journal of San Diego History, July 1968, Vol. 14, No. 3
- Beril, Becker (1967). Dreams and Realities of the Conquest of the Skies. New York: Atheneum. pp. 124–125
- Inglis, Amirah. "Hargrave, Lawrence (1850–1915)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Vol. 9. Melbourne University Press. Retrieved 5 July 2010.
- Gibbs-Smith, Charles H. (3 Apr 1959). "Hops and Flights: A roll call of early powered take-offs". Flight. 75 (2619): 468. Archived from the original on March 2, 2012. Retrieved 24 Aug 2013.
- "European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company EADS N.V.: Eole/Clément Ader". Archived from the original on October 20, 2007. Retrieved 2007-10-20.
- Gibbs-Smith, Charles Harvard (1968). Clément Ader: His Flight-Claims and His Place in History. Aeronautical engineers. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office. p. 214.
- Cite error: The named reference
auto1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - "Bernardo Malfitano - AirShowFan.com". airshowfan.com. Archived from the original on 30 March 2013. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- Jones, Ernest. "Santos Dumont in France 1906–1916: The Very Earliest Early Birds." Archived 2016-03-16 at the Wayback Machine earlyaviators.com, 25 December 2006. Retrieved: 17 August 2009.
- Les vols du 14bis relatés au fil des éditions du journal l'illustration de 1906. The wording is: "cette prouesse est le premier vol au monde homologué par l'Aéro-Club de France et la toute jeune Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI)."
- Santos-Dumont: Pionnier de l'aviation, dandy de la Belle Epoque.
- Crouch, Tom (1982). Bleriot XI, The Story of a Classic Aircraft. Smithsonian Institution Press. pp. 21 and 22. ISBN 0-87474-345-1.
- C. Brunco, Leonard (1993). On the Move: A Chronology of Advances in Transportation. Gale Research. p. 192.
- Hallion, Richard, P. "The NACA, NASA, and the Supersonic-Hypersonic Frontier." Archived 2014-08-14 at the Wayback Machine NASA. Retrieved: 7 September 2011.
- Beaumont, R.A.; Aeronautical Engineering, Odhams, 1942, Chapter 13, "Airscrews".
- Sadraey, Mohammad H. (January 1, 2017). Aircraft Performance: An Engineering Approach. CRC Press. p. 137. ISBN 9781498776561.
- Power Beaming Archived 2013-02-17 at the Wayback Machine Dfrc.nasa.gov.
- Pipistrel Expands Electric Aircraft Line (2013)
- "Here Comes the Flying Stovepipe". TIME. Time Inc. 1965-11-26. Archived from the original on 2008-04-08. Retrieved 2008-04-08.
- Weber, Richard J.; Mackay, John S. "An Analysis of Ramjet Engines Using Supersonic Combustion". ntrs.nasa.gov. NASA Scientific and Technical Information. Retrieved 3 May 2016.
- "Aerospace Welding | Helander Metal". Helander Metal. Retrieved 2017-12-27.
- Purdy, Don: AeroCrafter - Homebuilt Aircraft Sourcebook, Fifth Edition, pages 1-164. BAI Communications, 15 July 1998. ISBN 0-9636409-4-1
- Crane, Dale: Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition, page 224. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. ISBN 1-56027-287-2
- Crane, Dale: Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition, page 86. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. ISBN 1-56027-287-2
- Aviation Publishers Co. Limited, From the Ground Up, page 10 (27th revised edition) ISBN 0-9690054-9-0
- Federal Aviation Administration (August 2008). "Title 14: Aeronautics and Space - PART 1—DEFINITIONS AND ABBREVIATIONS". Archived from the original on 20 September 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
- The risks of travel Archived September 7, 2001, at the Wayback Machine. Numberwatch.co.uk.
- Flight into danger - 7 August 1999 - New Scientist Space. Space.newscientist.com (7 August 1999).
- Mantakos, Harry, Is GA Flying Safer Than Driving?, retrieved 13 May 2012
- Penner, Joyce E.; Lister, David; Griggs, David J.; Dokken, David J.; McFarland, Mack (1999). Aviation and the Global Atmosphere. Bibcode:1999aga..book.....P. Archived from the original on 2007-06-29.
- Lin, X.; Trainer, M. & Liu, S.C. (1988). "On the nonlinearity of the tropospheric ozone production". Journal of Geophysical Research. 93 (D12): 15879–15888. Bibcode:1988JGR....9315879L. doi:10.1029/JD093iD12p15879.
- Grewe, V.; D. Brunner; M. Dameris; J. L. Grenfell; R. Hein; D. Shindell; J. Staehelin (July 2001). "Origin and variability of upper tropospheric nitrogen oxides and ozone at northern mid-latitudes". Atmospheric Environment. 35 (20): 3421–33. Bibcode:2001AtmEn..35.3421G. doi:10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00134-0. hdl:2060/20000060827.
Bibliography
- Blatner, David. The Flying Book: Everything You've Ever Wondered About Flying On Airplanes. ISBN 0-8027-7691-4
External links
| Types of aircraft by methods of thrust and lift | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||