This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Kevmin (talk | contribs) at 23:04, 1 June 2021 (seems this should stay a stand alone article unless references indicate the two families have been merged, has Ferla et al been followed?). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 23:04, 1 June 2021 by Kevmin (talk | contribs) (seems this should stay a stand alone article unless references indicate the two families have been merged, has Ferla et al been followed?)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Family of bacteria
| Anaplasmataceae | |
|---|---|
| |
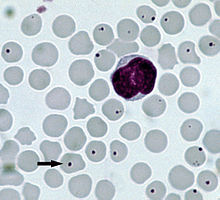
| The rickettsial bacterium Anaplasma centrale infecting red blood cells of a cow. Arrow points to typical infected cell.. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Proteobacteria |
| Class: | Alphaproteobacteria |
| Order: | Rickettsiales |
| Family: | Anaplasmataceae Philip, 1957 |
| Genera | |
The Anaplasmataceae are a Proteobacteria family that includes genera Anaplasma, Ehrlichia, Neorickettsia, and Wolbachia.
| Schematic ribosomal RNA phylogeny of Alphaproteobacteria | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The cladogram of Rickettsidae has been inferred by Ferla et al. from the comparison of 16S + 23S ribosomal RNA sequences. |
References
- "Family Anaplasmataceae". LPSN.
- Garrity, George (2005). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. Springer. ISBN 0-387-24145-0.
- Ferla MP, Thrash JC, Giovannoni SJ, Patrick WM (2013). "New rRNA gene-based phylogenies of the Alphaproteobacteria provide perspective on major groups, mitochondrial ancestry and phylogenetic instability". PLOS ONE. 8 (12): e83383. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...883383F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0083383. PMC 3859672. PMID 24349502.
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Anaplasmataceae | |
This Alphaproteobacteria-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |