This is an old revision of this page, as edited by JeffMASSACRE (talk | contribs) at 00:03, 7 December 2021 (Added a new paragraph which emphasizes on blood ideology.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 00:03, 7 December 2021 by JeffMASSACRE (talk | contribs) (Added a new paragraph which emphasizes on blood ideology.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)For other uses, see Blood and Blood (disambiguation).
Street gang founded in Los Angeles, California Criminal organization
 The distinctive Blood gang signal The distinctive Blood gang signal | |
| Founded | 1972; 53 years ago (1972) |
|---|---|
| Founding location | Los Angeles, California, United States |
| Years active | 1972–present |
| Territory | 33 U.S. states and Canada |
| Ethnicity | African American |
| Membership (est.) | 15,000–20,000 |
| Activities | Drug trafficking, murder, assault, auto theft, burglary, extortion, fraud and robbery |
| Allies | Black Guerrilla Family Black P. Stones Juggalos Latin Kings People Nation United Blood Nation Vice Lords |
| Rivals | Aryan Brotherhood Asian Boyz Crips Florencia 13 Folk Nation Gangster Disciples MS-13 Tiny Rascal Gang |
The Bloods are a primarily African-American street gang founded in Los Angeles, California. The gang is widely known for its rivalry with the Crips. It is identified by the red color worn by its members and by particular gang symbols, including distinctive hand signs.
The Bloods comprise various subgroups known as "sets", among which significant differences exist, such as colors, clothing, operations, and political ideas that may be in open conflict with each other. Since the gang's creation, it has branched throughout the United States.
History
The Bloods gang was formed initially to compete against the influence of the Crips in Los Angeles. The rivalry originated in the 1960s when Raymond Washington and other Crips attacked Sylvester Scott and Benson Owens, two students at Centennial High School in Compton, California. As a result, Scott formed the Piru street-gang, the first "Bloods" gang. Owens subsequently established the West Piru gang. The Bloods was initially formed to provide members protection from the Crips. Many of the non-Crip gangs used to call one another "blood". On March 21, 1972, shortly after a concert featuring Wilson Pickett and Curtis Mayfield, 20 youths belonging to the Crips attacked and robbed Robert Ballou Jr. outside the Hollywood Palladium. Ballou was beaten to death after refusing to give up his leather jacket. The sensational media coverage of the crime and the continued assaults by the Crips increased their notoriety. Several non-Crips gangs formed during this period were no match for the Crips and became concerned with the escalating Crip attacks. The Pirus, Black P. Stones, Athens Park Boys and other gangs not aligned with the Crips often clashed with them. On June 5, 1972, three months after Ballou's murder, Fredrick "Lil Country" Garret was murdered by a Westside Crip. This marked the first Crips murder against another gang member and motivated non-Crip gangs to align with each other. The Brims struck back on August 4, 1972, by murdering Thomas Ellis, an original Westside Crip. By late 1972, the Pirus held a meeting in their neighborhood to discuss growing Crip pressure and intimidation. Several gangs that felt victimized by the Crips joined the Pirus to create a new federation of non-Crips neighborhoods. This alliance became the Bloods. The Pirus are therefore considered the founders of the Bloods.
By 1978, there were 15 Blood sets. Crips still outnumbered Bloods 3 to 1. To assert their power, the Bloods became increasingly violent. During the 1980s, Bloods began distributing crack cocaine in Los Angeles. Blood membership soon rose dramatically as did the number of states in which they were present. These increases were primarily driven by profits from crack cocaine distribution. The huge profits allowed members to relocate to other cities and states.
United Blood Nation
Main article: United Blood Nation"Bloods" is a universal term used to refer to West Coast Bloods and United Blood Nation (UBN, also known as the East Coast Bloods). These two groups are traditionally distinct, but both call themselves "Bloods". The profits of crack distribution allowed Bloods to spread in other states. UBN started in 1993 in Rikers Island's George Motchan Detention Center (GMDC) to form protection from the Latin Kings and Ñetas who were targeting African-American gang members. UBN is a loose confederation of predominantly African-American street gangs. Once released from prison, UBN leaders went back to their New York neighborhoods, where they retained the Bloods name and started recruiting members. UBN has between 7,000 and 15,000 members in the Eastern US. It makes its income through various criminal activities, including distribution of crack cocaine and smuggling drugs into prison.
Membership
Bloods are a loosely structured association of smaller street gangs, known as "sets", that have a common gang culture. Each set has its own leader and generally operates independently from the others. Most Bloods members are African-American males, although some sets have recruited female members as well as members from other races and ethnic backgrounds. Members range in age from early teens to mid-20s, but some hold leadership positions into their late twenties and occasionally thirties.
There is no known national leader of the Bloods but individual Blood sets have a hierarchical leadership structure with identifiable levels of membership. These levels of membership indicate status within a gang. A leader, typically an older member with a more extensive criminal background, runs each set. A set leader is not elected but rather asserts himself by developing and managing the gang's criminal enterprises through his reputation for violence and ruthlessness and his charisma. The majority of set members are called "soldiers", who are typically 16 to 22. Soldiers have a strong sense of commitment to their set and are extremely dangerous because of their willingness to use violence both to obtain the respect of gang members and to respond to any person who "disrespects" the set. "Associates" are not full members, but identify with the gang and take part in various criminal activities. To the extent that women belong to the gang, they are usually associates and tend to be used by their male counterparts to carry weapons, hold drugs, or prostitute themselves to make money for their set.
Recruitment is often influenced by a recruit's environment. Bloods recruit heavily among school-age youth in poor African-American communities. Gang membership offers youth a sense of belonging and protection. It also offers immediate gratification to economically disadvantaged youth who desire the trappings of gang life, such as gold jewelry, cash, expensive sports clothing. Blood sets have a loose structure of ranks based on how long a person has been involved with a particular set. The ranks do not signify leadership or dominance over the set; they merely signify respect for those who have been in the set longer and have survived the longest. Those with a higher rank do not have a position of authority over those of lower rank.
Bloods members commonly call themselves CKs (for Crip-Killer), MOBs (Member of Bloods), dawgs, or ballers (meaning drug dealers). The gang has a membership of between approximately 15,000 and 20,000 active in 123 cities and in 33 U.S. states, primarily on the West Coast and, to a lesser extent, the Great Lakes region and the Southeast. Gangs including Bloods have been documented in the U.S. military, in both U.S. and overseas bases. Blood sets also operate in the Canadian cities of Montreal and Toronto.
Identification
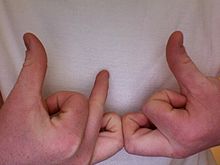
Bloods members identify themselves through various indicators, such as colors, clothing, symbols, tattoos, jewelry, graffiti, language, and hand signs. The Bloods' gang color is red. They like to wear sports clothing, including jackets that show their gang color. The most commonly used Bloods symbols include the number "5", the five-pointed star, and the five-pointed crown. These symbols are meant to show the Bloods' affiliation with the People Nation, a large coalition of affiliates created to protect alliance members in federal and state prison. These symbols may be seen in the tattoos, jewelry, and clothing gang members wear as well as the gang graffiti with which Bloods mark their territory. Such graffiti can include gang names, nicknames, declaration of loyalty, threats against rival gangs, or descriptions of criminal acts in which the gang has been involved.
Bloods graffiti can include rival gang symbols (especially those of the Crips) drawn upside down. This is meant as an insult to the rival group and its symbols. Bloods members also have a distinctive slang. They greet each other using the word "Blood" and often avoid using words with the letter "C". Bloods use hand signs to communicate with one another. Hand signs may be a singular movement, like the American Sign Language letter "B", or a series of movements using one or both hands for more complex phrases. United Blood Nation (UBN) or East Coast Bloods initiates often receive a dog paw mark, represented by three dots often burned with a cigarette, on their right shoulder. Other UBN symbols include a bulldog and a bull.
"Kingism" ideology
A gang member showing his Latin King tattoo – a lion with a crown – and signifying the five point star with his hands.
L.A. Kaufman wrote in the February 2015 issue of New York Magazine that the Kings had a "unique mixture of intense discipline, revolutionary politics and a homemade religion called 'Kingism'". He suggests that this makes "a potent mixture for troubled ghetto kids whose lives lacked structure and hope." Kingism is a blend of tribal gang rhetoric and religious mysticism. As one member put it, the Manifesto is "considered our Bible", and reading it is to go "from the darkness to the light".
The Latin Kings operate under strict codes and guidelines that are conveyed in a lengthy constitution, and they follow the teachings of the King Manifesto. According to the Manifesto, there are three stages or cycles of Nation life that constitute Kingism:
- The Primitive Stage: "That stage in life where the King warrior acts on impulse, executing his action without giving them the serious thought that they demand. A stage of immaturity where the King warrior's time is spent gang banging, getting high, and being recognized as big and bad."
- The Conservative Stage: "At this level the King warrior becomes tired of the primitive stage. He no longer wishes to participate in the senseless routine of gang fighting, hanging on the corner or being recognized as big and bad. Most often at this level the King warrior gets married and retires. It is inappropriate to call this stage maturity stage due to the fact that the King warrior at this time does not really become mature in the sense of maturity. Instead he becomes mummified or reaches a level of accepting life as it has been taught to him by the existing system that exploits all people of color-dehumanizes them and maintains them under the economic and social yoke of slavery."
- The New King Stage: "The stage of awareness and decision. The new King recognizes that the time for revolution is at hand. Revolution of the mind! The revolution of knowledge! A revolution that will bring freedom to the enslaved, to all Third World people as we together sing and praise with joy what time it is-it is Nation time! ... For him there are no horizons between races, sexes and senseless labels. for him everything has meaning, human life is placed above materialistic values ... When a man become a new King the will of the Nation becomes his will, for to be at variance with the Nation is one thing that cannot endure. The Almighty Latin King Nation requires wholehearted and complete devotion."
According to the Manifesto, "The New King no longer views the rival warrior as the cause of his ills; instead, he fights against the Anti-King System (social injustices and inequality)".
Sets
Main article: List of Bloods subgroupsThe Bloods gang is a network of individual chapters, which are known as "sets". These sets are often loosely connected, having their own leader(s) and operating independently from one another.
See also
- African-American organized crime
- Crime in Los Angeles
- Crips and Bloods: Made in America
- Slippin': Ten Years with the Bloods
References
- ^ "IPTM Basic Street Gangs Hand Signs" (PDF). Institute of Police Technology and Management. p. 31. Retrieved September 3, 2020.
- ^ Criminal Street Gangs justice.gov (May 12, 2015)
- Netgraphe inc. (September 30, 2006). "Canoe – Infos – Dossiers Les gangs de rue se partagent Montréal". Fr.canoe.ca. Archived from the original on January 31, 2016. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- "NCGIA Gang Profiles: Bloods". Archived from the original on December 17, 2014. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- "Major Prison Gangs(continued)". Gangs and Security Threat Group Awareness. Florida Department of Corrections. Archived from the original on March 12, 2010. Retrieved June 21, 2009.
- ^ Bloods Street Gang Intelligence Report Virginia State Police (November 2008)
- "Juggalos: Emerging Gang Trends and Criminal Activity Intelligence Report" (PDF). Public Intelligence. Retrieved June 5, 2013.
- ^ "Bloods". Gangs In Maryland. University of Maryland. Archived from the original on December 6, 2008. Retrieved February 21, 2009.
- Gang Task Force covingtontn.com
- Montaldo, Charles (2014). "The Aryan Brotherhood: Profile of One of the Most Notorious Prison Gangs". About.com. Archived from the original on July 21, 2016. Retrieved July 2, 2017.
- Derek J. Moore (March 15, 2008). "Ruthless Asian gangs blaze trail of violence Killing in Jenner casts spotlight on ultraviolent syndicates with roots in Long Beach". Press Democrat. Archived from the original on April 7, 2014.
- Nipsey Hussle's killing inspired rival gangs to march in peace. A year later, did it last? Alicia Victoria Lozano and Erik Ortiz, NBC News (March 29, 2020)
- Here's what we know about the Gangster Disciple governor who was sentenced to 10 years in prison Echo Day, The Leader (December 12, 2019)
- Prosecutors say man involved in South Seattle gang war shootings Archived April 9, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, KIRO-TV, April 7, 2014.
- ^ Harris, Donnie (2004). Gangland. Goose Creek, South Carolina: Holy Fire Publishing. p. 49. ISBN 978-0976111245. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- Alonso, Alex (2010). "Out of the Void". In Hunt, Darrell; Ramos, Ana-Cristina (eds.). Black Los Angeles: American Dreams and Racial Realities. New York City: NYU Press. p. 153. ISBN 9780814773062. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- Hyman, Michael D. (2013). "Appendix II: Gangs Highlighted by the National Drug Intelligence Center". Drugs in Society: Causes, Concepts and Control. Abingdon, England: Routledge. p. 473. ISBN 978-0124071674. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- Barrett, Robin (2011). The Mammoth Book of Hard Bastards. Boston, Massachusetts: Little, Brown Book Group. ISBN 978-1849017596. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- Maxson, Cheryl L. (October 1998). "Gang Members on the Move" (PDF). Juvenile Justice Bulletin. Washington DC: U.S. Department of Justice. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 28, 2006. Retrieved April 17, 2006.
- Sullivan, CJ (November 5, 2002). "Blood In, Blood Out: Bronx Gang Members Explain Their Creed". New York Press. New York City: Manhattan Media. Archived from the original on January 13, 2019. Retrieved January 12, 2019.
- Covey, Herbert C. (2015). "Crips and Bloods Snapshots: Examples of Crip and Blood Gangs". Crips and Bloods: A Guide to an American Subculture. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 163. ISBN 978-0313399305.
- Riviello, Ralph (2009). Manual of Forensic Emergency Medicine: A Guide for Clinicians. Burlington, Massachusetts: Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 191. ISBN 978-0-7637-4462-5.
- "NCGIA Gang Profiles: Bloods". Archived from the original on December 17, 2014. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- "Gangs Increasing in Military, FBI Says". Military.com. McClatchy-Tribune Information Services. Archived from the original on November 13, 2009. Retrieved February 21, 2009.
- Alliances, Conflicts, and Contradictions in Montreal's Street Gang Landscape Karine Descormiers and Carlo Morselli, International Criminal Justice Review (October 17, 2020)
- The Dixon Road Bloods are back: Six alleged gang members arrested in connection to murder Natalie Alcoba, National Post (April 2, 2015)
Further reading
- Yusuf Jah, Sister Shah'keyah, UPRISING : Crips and Bloods Tell the Story of America's Youth In The Crossfire, ISBN 0-684-80460-3
- Bing, Leon, Do or Die: For the First Time, Members of L.A.'s Most Notorious Teenage Gangs - The Crips and Bloods - Speak for Themselves. ISBN 978-1-4930-0760-8
- Deutsch, Kevin, The Triangle : A Year on the Ground with New York's Bloods and Crips, ISBN 0060163267
- Kriegel, Mark (October 13, 1997). "Gangstas launch blood feud crew's superior warns wanna-bes". NY Daily News. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- East Orange police raid apartment building as part of crackdown on Bloods set, authorities say. Nj.com. Accessed April 4, 2015.
- East Orange crime crackdown leads to nearly 60 arrests. Nj.com. Accessed April 4, 2015.
External links
| Bloods | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sets | |||||
| Members | |||||
| Related |
| ||||
| Organized crime groups in Los Angeles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| African-American |
| ||||
| Deputy gangs |
| ||||
| East and Southeast Asian |
| ||||
| European-American |
| ||||
| Hispanic-American |
| ||||
| Outlaw motorcycle gangs |
| ||||
| Polynesian-American |
| ||||
| West Asian |
| ||||
| Events | |||||
| Organized crime groups in the Americas | |
|---|---|
| Argentina | |
| Bolivia | |
| Brazil | |
| Canada | See: Organized crime groups in Canada |
| Caribbean |
|
| Colombia | |
| El Salvador | |
| Mexico |
|
| United States | See: Organized crime groups in the United States |
| Venezuela | |
| Rampart scandal | |
|---|---|
| Notable accused officers | |
| Victims | |
| Coverup and investigation | |
| Gang involvement | |
| Other | |