This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 88.106.28.18 (talk) at 14:21, 14 December 2022 (Synthesis). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:21, 14 December 2022 by 88.106.28.18 (talk) (Synthesis)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical compound Pharmaceutical compound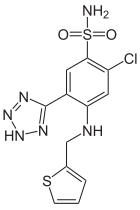 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.121 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H11ClN6O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 370.83 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Azosemide is a high-ceiling loop diuretic agent that was brought to market in 1981 by Boehringer Mannheim. As of 2015 it was available as a generic in some Asian countries.
Azosemide has been found as an adulterant in ketamine.
Synthesis

Chlorosulfonation of 2-fluoro-4-chloro-benzonitrile (1) followed by ammonolysis of the product gives 4-chloro-2-fluoro-5-sulfamoylbenzonitrile (2). Selective displacement of the fluoride leaving group by 2-aminomethylthiophene (3) gives PC68423892 (4). Treatment with sodium azide and hydrochloric acid leads to 1,3 addition of the elements of hydrazoic acid to the nitrile and the formation of a tetrazole ring. This yields the high ceiling diuretic agent azosemide (5).
References
- Sittig M (1988). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia (PDF). Vol. 1. Noyes Publications. p. 122. ISBN 978-0-8155-1144-1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-10-23.
- Bormann D (January 1980). "Diuretics". In Hess HJ (ed.). Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 15. Academic Press. pp. 100–105 (101). ISBN 978-0-08-058359-4.
- "International listings for azosemide". Drugs.com. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- "Drug Checking Report 2011" (PDF). Energy Control. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- DE1815922 idem A. Popelak et al., U.S. patent 3,665,002 (1972 to Boehringer, Mann.).
- Ansgar Dr Rer Nat Lerch, 4 More », DE2353388 (1975 to Boehringer Mannheim Gmbh).
| Diuretics (C03) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfonamides (and etacrynic acid) |
| ||||||||
| Potassium-sparing (at CD) |
| ||||||||
| Osmotic diuretics (PT, DL) | |||||||||
| Vasopressin receptor inhibitors (DCT and CD) | |||||||||
| Other | |||||||||
| Combination products | |||||||||
| |||||||||
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |