This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Ozzie10aaaa (talk | contribs) at 17:24, 5 February 2023 (Cleaned up using AutoEd). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 17:24, 5 February 2023 by Ozzie10aaaa (talk | contribs) (Cleaned up using AutoEd)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical compound| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "Bivatuzumab mertansine" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2014) |
 | |
| Monoclonal antibody | |
|---|---|
| Type | Whole antibody |
| Source | Humanized (from mouse) |
| Target | CD44 v6 |
| Clinical data | |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
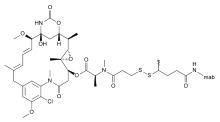
Bivatuzumab mertansine is a combination of bivatuzumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody, and mertansine, a cytotoxic agent. It is designed for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma.
References
- Tijink BM, Buter J, de Bree R, Giaccone G, Lang MS, Staab A, et al. (October 2006). "A phase I dose escalation study with anti-CD44v6 bivatuzumab mertansine in patients with incurable squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck or esophagus". Clinical Cancer Research. 12 (20 Pt 1): 6064–72. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0910. PMID 17062682.
This monoclonal antibody–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This antineoplastic or immunomodulatory drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |