This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Alejandro linconao (talk | contribs) at 01:21, 19 October 2023. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 01:21, 19 October 2023 by Alejandro linconao (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Frequency shift keying digital mode
FT8 or Franke & Taylor 8 is a frequency shift keying digital mode of radio communication used by amateur radio operators worldwide. Following release on June 29, 2017, by its creators Joe Taylor, K1JT, and Steve Franke, K9AN, along with the software package WSJT, FT8 was adopted rapidly and, in little over two years, it became the most popular digital mode recorded by automatic spotting networks such as PSK Reporter. FT8DMC is the most important club dedicated to this mode of digital communication.
Introduction
FT8 is a popular form of digital weak signal communication used primarily by amateur radio operators to communicate on amateur radio bands with a majority of traffic occurring on the HF amateur bands. The mode offers operators the ability to communicate in unfavorable environments such as during low sun spot numbers, high RF noise, or during low power operations. With advances in signal processing technology FT8 is able to decode signals with a signal to noise ratio as low as −20 dB in a 2500 Hz bandwidth, which is significantly lower than CW or SSB transmissions.
Operation
FT8 sends 77 information bits in 15-second cycles with 12.64 seconds of transmission time and 2.36 seconds of decode time for a user data rate of 6.09 bits/sec. Source encoding gives an effective throughput of about 5 words per minute. The required SNR in a 2500 Hz bandwidth is −21 dB, so the corresponding Eb/N0 is 10 log10(2500/6.09) = 26.1 dB greater, or −21 dB + 26.1 = 5.1 dB. The mode requires the sending and receiving computers to be synchronised so, while manual time setting is possible, most users make use of automatic online time servers using NTP or by receiving broadcast time signals from the GPS to ensure their transmissions fall in the proper windows.
Each FT8 transmission can support up to 13 text characters, coded using forward error correction to ensure proper transmission and decoding despite common radio effects such as fading, noise, interference, poor propagation, low power operation, or inefficient antennas in restricted urban spaces. As the mode is quite limited in the number of words that it can send, it only sends enough information to ensure a contact with each station.
Applications
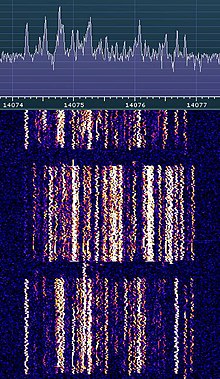
There are multiple uses for FT8 including contesting, testing antennas, and for scientific research.
References
- ^ Burmester, Dale March 12, 2019. Amateur Radio Digital Communications Mode FT8. http://site.ieee.org/msn/files/2019/04/FT8-KA9SWE.pdf Archived 2022-11-06 at the Wayback Machine
- Barron, Robert (2020-02-08). "PSK Reporter". KA5WSS. Archived from the original on 2022-10-06. Retrieved 2022-10-06.
- Luscre, Anthony (2019-10-11). "FT8—What Is It and How Can I Get Started?". OnAllBands. Archived from the original on 2022-10-01. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- "FT8 – Signal Identification Wiki". www.sigidwiki.com. Archived from the original on 2022-08-17. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- "FT8 Mode is Latest Bright Shiny Object in Amateur Radio Digital World". www.arrl.org. Archived from the original on 2022-05-28. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- "FT8/FT4 from a contester's perspective – VA7ST.ca". Archived from the original on 2022-08-17. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- "ARRL Surveying Field Day Participants". www.arrl.org. Archived from the original on 2022-08-17. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- "FT8". www.rtl-sdr.com. Archived from the original on 2022-09-30. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- Erickson, P.; Liles, W.; Miller, E.; Miller, E. (2020). "Amateur digital mode based remote sensing: FT8 use as a radar signal of opportunity for ionospheric characterization". hamsci.org. Archived from the original on 2022-08-17. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
| Amateur radio digital modes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Frequency-shift keying (FSK) |  | |
| Multiple frequency-shift keying (MFSK) | ||
| Phase-shift keying (PSK) | ||
| COFDM |
| |
| Non-traditional digital modes | ||
| Two-way radio | |
|---|---|
| Amateur and hobbyist | |
| Aviation (aeronautical mobile) | |
| Land-based commercial and government mobile | |
| Marine (shipboard) | |
| Signaling / Selective calling | |
| System elements and principles | |
| Amateur radio | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activities |  | ||||||
| Culture | |||||||
| Governance | |||||||
| Modes of communication |
| ||||||
| Technologies | |||||||
| Related | |||||||