This is the current revision of this page, as edited by KormiSK (talk | contribs) at 20:55, 30 December 2023 (+pages). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 20:55, 30 December 2023 by KormiSK (talk | contribs) (+pages)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)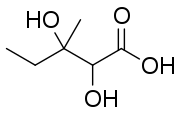 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2,3-Dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic+acid |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H12O4 |
| Molar mass | 148.16 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
2,3-Dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoic acid is an intermediate in the metabolism of isoleucine.
Metabolism
2,3-Dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoate is synthesized by the action of acetolactate mutase with subsequent reduction from α-aceto-α-hydroxybutyrate through 3-hydroxy-2-keto-3-methylpentanoate:
- α-aceto-α-hydroxybutyrate → 3-hydroxy-2-keto-3-methylpentanoate
- 3-hydroxy-2-keto-3-methylpentanoate + NAD(P)H → 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoate + NAD(P)
It is then processed by the action of dihydroxyacid dehydratase, which results in 2-keto-3-methylvalerate and water:
- 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylpentanoate → 2-keto-3-methylvalerate + H2O
Transamination of 2-keto-3-methylvalerate yields isoleucine.
References
- ^ Voet, Donald; Voet, Judith G. (2011). Biochemistry (4. ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. pp. 1074–1075. ISBN 978-0-470-91745-9.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |