This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 212.228.48.187 (talk) at 01:20, 5 March 2024 (→Formation of Great Britain and the United Kingdom). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 01:20, 5 March 2024 by 212.228.48.187 (talk) (→Formation of Great Britain and the United Kingdom)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)For other uses, see History of England (disambiguation). "English history" redirects here. For the Jon English album, see English History (album).
England became inhabited more than 800,000 years ago, as the discovery of stone tools and footprints at Happisburgh in Norfolk have indicated. The earliest evidence for early modern humans in Northwestern Europe, a jawbone discovered in Devon at Kents Cavern in 1927, was re-dated in 2011 to between 41,000 and 44,000 years old. Continuous human habitation in England dates to around 13,000 years ago (see Creswellian), at the end of the Last Glacial Period. The region has numerous remains from the Mesolithic, Neolithic and Bronze Age, such as Stonehenge and Avebury. In the Iron Age, all of Britain south of the Firth of Forth was inhabited by the Celtic people known as the Britons, including some Belgic tribes (e.g. the Atrebates, the Catuvellauni, the Trinovantes, etc.) in the south east. In AD 43 the Roman conquest of Britain began; the Romans maintained control of their province of Britannia until the early 5th century.
The end of Roman rule in Britain facilitated the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, which historians often regard as the origin of England and of the English people. The Anglo-Saxons, a collection of various Germanic peoples, established several kingdoms that became the primary powers in present-day England and parts of southern Scotland. They introduced the Old English language, which largely displaced the previous Brittonic language. The Anglo-Saxons warred with British successor states in western Britain and the Hen Ogledd (Old North; the Brittonic-speaking parts of northern Britain), as well as with each other. Raids by Vikings became frequent after about AD 800, and the Norsemen settled in large parts of what is now England. During this period, several rulers attempted to unite the various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, an effort that led to the emergence of the Kingdom of England by the 10th century.
In 1066, a Norman expedition invaded and conquered England. The Norman dynasty, established by William the Conqueror, ruled England for over half a century before the period of succession crisis known as the Anarchy (1135–1154). Following the Anarchy, England came under the rule of the House of Plantagenet, a dynasty which later inherited claims to the Kingdom of France. During this period, Magna Carta was signed and Parliament became established. Anti-Semitism rose to great heights, and in 1290, England became the first country to permanently expel the Jews. A succession crisis in France led to the Hundred Years' War (1337–1453), a series of conflicts involving the peoples of both nations. Following the Hundred Years' Wars, England became embroiled in its own succession wars. The Wars of the Roses pitted two branches of the House of Plantagenet against one another, the House of York and the House of Lancaster. The Lancastrian Henry Tudor ended the War of the Roses and established the Tudor dynasty in 1485.
Under the Tudors and the later Stuart dynasty, England became a colonial and seafaring maritime power, with rich development of art, trade, commerce, industry, architecture, and science. Elizabethan England represented the apogee of the English Renaissance and saw the flowering of great poetry, music and literature. With the founding of the East India Company, a joint-stock company, England competed with the Dutch and French in the East and built a vast empire. The company rose to account for half of the world's trade during the mid-1700s and early 1800s. The founding of the Royal Society laid the foundations of modern experimental science. The development of English naval power and the interest in voyages of discovery led to the acquisition and settlement of overseas colonies, particularly in North America and the Caribbean. The Royal Navy developed Europe's largest merchant fleet.
During the rule of the Stuarts, the English Civil War took place between the Parliamentarians and the Royalists, which resulted in the execution of King Charles I (1649) and the establishment of a series of republican governments—first, a Parliamentary republic known as the Commonwealth of England (1649–1653), then a military dictatorship under Oliver Cromwell known as the Protectorate (1653–1659). The Stuarts returned to the restored throne in 1660, though continued questions over religion and power resulted in the deposition of another Stuart king, James II, in the Glorious Revolution (1688). England, which had subsumed Wales in the 16th century under Henry VIII, united with Scotland in 1707 to form a new sovereign state called Great Britain. Following the Industrial Revolution, which started in England, Great Britain ruled a colonial Empire, the largest in recorded history. Following a process of decolonisation in the 20th century, mainly caused by the weakening of Great Britain's power in the two World Wars; almost all of the empire's overseas territories became independent countries.
Prehistory
Main article: Prehistoric Britain For a chronological guide, see Timeline of English history.Stone Age
Main article: Neolithic British Isles
The time from Britain's first inhabitation until the Last Glacial Maximum is known as the Old Stone Age, or Palaeolithic era. Archaeological evidence indicates that what was to become England was colonised by humans long before the rest of the British Isles because of its more hospitable climate between and during the various glacial periods of the distant past. This earliest evidence, from Happisburgh in Norfolk, includes the oldest hominid artefacts found in Britain, and points to dates of more than 800,000 RCYBP. These earliest inhabitants were hunter-gatherers. Low sea-levels meant that Britain was attached to the continent for much of this earliest period of history, and varying temperatures over tens of thousands of years meant that it was not always inhabited.

England has been continuously inhabited since the last Ice Age ended around 9000 BC, the beginning of the Middle Stone Age, or Mesolithic era. Rising sea-levels cut off Britain from the continent for the last time around 6500 BC. The population by then, as in the rest of the world, was exclusively anatomically modern humans, and the evidence suggests that their societies were increasingly complex and they were manipulating their environment and prey in new ways, possibly selective burning of then omnipresent woodland to create clearings for herds to gather and then hunt them. Hunting was mainly done with simple projectile weapons such as javelin and possibly sling. Bow and arrow was known in Western Europe since at least 9000 BC. The climate continued to warm and the population probably rose.
The New Stone Age, or Neolithic era, began with the introduction of farming, ultimately from the Middle East, around 4000 BC. It is not known whether this was caused by a substantial folk movement or native adoption of foreign practices or both. People began to lead a more settled lifestyle. Monumental collective tombs were built for the dead in the form of chambered cairns and long barrows. Towards the end of the period, other kinds of monumental stone alignments begin to appear, such as Stonehenge; their cosmic alignments show a preoccupation with the sky and planets. Flint technology produced a number of highly artistic pieces as well as purely practical. More extensive woodland clearance was done for fields and pastures. The Sweet Track in the Somerset Levels is one of the oldest timber trackways known in Northern Europe and among the oldest roads in the world, dated by dendrochronology to the winter of 3807–3806 BC; it is thought to have been a primarily religious structure. Archaeological evidence from North Yorkshire indicates that salt was being manufactured there in the Neolithic.
Later Prehistory
Main articles: Bell Beaker culture, Bronze Age Britain, and British Iron AgeBronze Age

The Bronze Age began around 2500 BC with the appearance of bronze objects. This coincides with the appearance of the characteristic Bell Beaker culture, following migration of new people from the continent. According to Olalde et al. (2018), after 2500 BC Britain's Neolithic population was largely replaced by this new Bell Beaker population, that was genetically related to the Corded Ware culture of central and eastern Europe and the Yamnaya culture of the eastern European Pontic-Caspian Steppe. While the migration of these Beaker peoples must have been accompanied by a language shift, the Celtic languages were probably introduced by later Celtic migrations.
The Bronze Age saw a shift of emphasis from the communal to the individual, and the rise of increasingly powerful elites whose power came from their prowess as hunters and warriors and their controlling the flow of precious resources to manipulate tin and copper into high-status bronze objects such as swords and axes. Settlement became increasingly permanent and intensive. Towards the end of the Bronze Age, many examples of very fine metalwork began to be deposited in rivers, presumably for ritual reasons and perhaps reflecting a progressive change in emphasis from the sky to the earth, as a rising population put increasing pressure on the land. England largely became bound up with the Atlantic trade system, which created a cultural continuum over a large part of Western Europe. It is possible that the Celtic languages developed or spread to England as part of this system; by the end of the Iron Age there is much evidence that they were spoken across all England and western parts of Britain.
Iron Age

The Iron Age is conventionally said to begin around 800 BC. At this time, the Britons or Celtic Britons were settled in England. The Celtic people of early England were the majority of the population, beside other smaller ethnic groups in Great Britain. They existed like this from the British Iron Age into the Middle Ages, when it was overtaken by Germanic Anglo-Saxons. After some time, the Celtic Britons diverged into the multiple distinct ethnic groups such as Welsh, Cornish and Breton, but they were still tied by language, religion and culture. They spoke the Brittonic language, a Celtic language which is the ancestor of the modern Brittonic languages. The Atlantic trade system had by this time effectively collapsed, although England maintained contacts across the channel with France, as the Hallstatt culture became widespread across the country. Its continuity suggests it was not accompanied by substantial movement of population; crucially, only a single Hallstatt burial is known from Britain, and even here the evidence is inconclusive. On the whole, burials largely disappear across England, and the dead were disposed of in a way which is archaeologically invisible: excarnation is a widely cited possibility. Hillforts were known since the Late Bronze Age, but a huge number were constructed during 600–400 BC, particularly in the South, while after about 400 BC new forts were rarely built and many ceased to be regularly inhabited, while a few forts become more and more intensively occupied, suggesting a degree of regional centralisation.

Around this time the earliest mentions of Britain appear in the annals of history. The first historical mention of the region is from the Massaliote Periplus, a sailing manual for merchants thought to date to the 6th century BC, and Pytheas of Massilia wrote of his voyage of discovery to the island around 325 BC. Both of these texts are now lost; although quoted by later writers, not enough survives to inform the archaeological interpretation to any significant degree.
Britain, we are told, is inhabited by tribes which are autochthonous and preserve in their ways of living the ancient manner of life. They use chariots, for instance, in their wars, even as tradition tells us the old Greek heroes did in the Trojan War.
— Diodorus Siculus, Bibliotheca historica, 60-30 BC.
Contact with the continent was less than in the Bronze Age but still significant. Goods continued to move to England, with a possible hiatus around 350 to 150 BC. There were a few armed invasions of hordes of migrating Celts. There are two known invasions. Around 300 BC, a group from the Gaulish Parisii tribe apparently took over East Yorkshire, establishing the highly distinctive Arras culture. And from around 150–100 BC, groups of Belgae began to control significant parts of the South.
These invasions constituted movements of a few people who established themselves as a warrior elite atop existing native systems, rather than replacing them. The Belgic invasion was much larger than the Parisian settlement, but the continuity of pottery style shows that the native population remained in place. Yet, it was accompanied by significant socio-economic change. Proto-urban, or even urban settlements, known as oppida, begin to eclipse the old hillforts, and an elite whose position is based on battle prowess and the ability to manipulate resources re-appears much more distinctly.
In 55 and 54 BC, Julius Caesar, as part of his campaigns in Gaul, invaded Britain and claimed to have scored a number of victories, but he never penetrated further than Hertfordshire and could not establish a province. However, his invasions mark a turning-point in British history. Control of trade, the flow of resources and prestige goods, became ever more important to the elites of Southern Britain; Rome steadily became the biggest player in all their dealings, as the provider of great wealth and patronage. In retrospect, a full-scale invasion and annexation was inevitable.
Roman Britain
Main article: Roman BritainAfter Caesar's expeditions, the Romans began a serious and sustained attempt to conquer Britain in AD 43, at the behest of Emperor Claudius. Britain was home to much gold, which attracted Roman invaders. They landed in Kent with four legions and defeated two armies led by the kings of the Catuvellauni tribe, Caratacus and Togodumnus, in battles at the Medway and the Thames. Togodumnus was killed, and Caratacus fled to Wales. The Roman force, led by Aulus Plautius, waited for Claudius to come and lead the final march on the Catuvellauni capital at Camulodunum (modern Colchester), before he returned to Rome for his triumph. The Catuvellauni held sway over most of the southeastern corner of England; eleven local rulers surrendered, a number of client kingdoms were established, and the rest became a Roman province with Camulodunum as its capital. Over the next four years, the territory was consolidated and the future emperor Vespasian led a campaign into the Southwest where he subjugated two more tribes. By AD 54 the border had been pushed back to the Severn and the Trent, and campaigns were underway to subjugate Northern England and Wales.

But in AD 60, under the leadership of the warrior-queen Boudicca, the tribes rebelled against the Romans. At first, the rebels had great success. They burned Camulodunum, Londinium and Verulamium (modern-day Colchester, London and St. Albans respectively) to the ground. There is some archaeological evidence that the same happened at Winchester. The Second Legion Augusta, stationed at Exeter, refused to move for fear of revolt among the locals. Londinium governor Suetonius Paulinus evacuated the city before the rebels sacked and burned it; the fire was so hot that a ten-inch layer of melted red clay remains 15 feet below London's streets. In the end, the rebels were said to have killed 70,000 Romans and Roman sympathisers. Paulinus gathered what was left of the Roman army. In the decisive battle, 10,000 Romans faced nearly 100,000 warriors somewhere along the line of Watling Street, at the end of which Boudicca was utterly defeated. It was said that 80,000 rebels were killed, but only 400 Romans.

The author of one study of Roman Britain suggested that from 43 AD to 84 AD, the Roman invaders killed somewhere between 100,000 and 250,000 people from a population of perhaps 2,000,000. This era saw a Greco-Roman culture prevail with the introduction of agriculture, industrial production, Roman law, Roman architecture, Roman circuses, Roman villas, aqueducts, sewers, urban planeducation, schools, many agricultural items and silk. In the 3rd century, Emperor Septimius Severus died at Eboracum (now York), where Constantine was subsequently proclaimed emperor a century later.
Over the next 20 years, the borders expanded slightly, but the governor Agricola incorporated into the province the last pockets of independence in Wales and Northern England. He also led a campaign into Scotland which was recalled by Emperor Domitian. The border gradually formed along the Stanegate road in Northern England, solidified by Hadrian's Wall built in AD 138, despite temporary forays into Scotland.
The Romans and their culture stayed in charge for 350 years. Traces of their presence are ubiquitous throughout England. The Roman goddess Britannia became the female personification of the country. Roman citizens settled in Britain from many parts of the Empire. By the 3rd century, Britain's economy was diverse and well established, with commerce extending into the non-Romanised north. The design of Hadrian's Wall especially catered to the need for customs inspections of merchants' goods. Under the 2nd-century emperors Hadrian and Antoninus Pius, two walls were built to defend the Roman province from the Caledonians, whose realms in the Scottish Highlands were never controlled. Around 197 AD, the Severan Reforms divided Britain into two provinces: Britannia Superior and Britannia Inferior. During the Diocletian Reforms, at the end of the 3rd century, Britannia was divided into four provinces under the direction of a vicarius. A fifth province, Valentia, is attested in the later 4th century. For much of the later period of the Roman occupation, Britannia was subject to barbarian invasions and often came under the control of imperial usurpers and imperial pretenders. The final Roman withdrawal from Britain occurred around 410; the native kingdoms are considered to have formed Sub-Roman Britain after that.
Anglo-Saxon era
Main article: History of Anglo-Saxon EnglandAnglo-Saxon migrations
Main article: Sub-Roman Britain Further information: Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain
In the wake of the breakdown of Roman rule in Britain from the middle of the fourth century, present day England was progressively settled by Germanic groups. Collectively known as the Anglo-Saxons, these included Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians. The Battle of Deorham was critical in establishing Anglo-Saxon rule in 577. Saxon mercenaries existed in Britain since before the late Roman period, but the main influx of population probably happened after the fifth century. The precise nature of these invasions is not fully known; there are doubts about the legitimacy of historical accounts due to a lack of archaeological finds. Gildas' De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae, composed in the 6th century, states that when the Roman army departed the Isle of Britannia in the 4th century AD, the indigenous Britons were invaded by Picts, their neighbours to the north (now Scotland) and the Scots (now Ireland). Britons invited the Saxons to the island to repel them but after they vanquished the Scots and Picts, the Saxons turned against the Britons.
Seven kingdoms are traditionally identified as being established by these migrants. Three were clustered in the South east: Sussex, Kent and Essex. The Midlands were dominated by the kingdoms of Mercia and East Anglia. To the north was Northumbria which unified two earlier kingdoms, Bernicia and Deira. Other smaller kingdoms seem to have existed as well, such as Lindsey in what is now Lincolnshire, and the Hwicce in the southwest. Eventually, the kingdoms were dominated by Northumbria and Mercia in the 7th century, Mercia in the 8th century and then Wessex in the 9th century. Northumbria eventually extended its control north into Scotland and west into Wales. It also subdued Mercia whose first powerful King, Penda, was killed by Oswy in 655. Northumbria's power began to wane after 685 with the defeat and death of its king Aegfrith at the hands of the Picts. Mercian power reached its peak under the rule of Offa, who from 785 had influence over most of Anglo-Saxon England. Since Offa's death in 796, the supremacy of Wessex was established under Egbert who extended control west into Cornwall before defeating the Mercians at the Battle of Ellendun in 825. Four years later, he received submission and tribute from the Northumbrian king, Eanred.

Since so few contemporary sources exist, the events of the fifth and sixth centuries are difficult to ascertain. As such, the nature of the Anglo-Saxon settlements is debated by historians, archaeologists and linguists. The traditional view, that the Anglo-Saxons drove the Romano-British inhabitants out of what is now England, was subject to reappraisal in the later twentieth century. One suggestion is that the invaders were smaller in number, drawn from an elite class of male warriors that gradually acculturated the natives.
An emerging view is that the scale of the Anglo-Saxon settlement varied across England, and that as such it cannot be described by any one process in particular. Mass migration and population shift seem to be most applicable in the core areas of settlement such as East Anglia and Lincolnshire, while in more peripheral areas to the northwest, much of the native population likely remained in place as the incomers took over as elites. In a study of place names in northeastern England and southern Scotland, Bethany Fox concluded that Anglian migrants settled in large numbers in river valleys, such as those of the Tyne and the Tweed, with the Britons in the less fertile hill country becoming acculturated over a longer period. Fox interprets the process by which English came to dominate this region as "a synthesis of mass-migration and elite-takeover models."
The early Anglo-Saxon period includes the creation of an English nation, with many of the aspects that survive today, including regional government and shires. Christianity was established with a great flowering of literature and language. Charters and laws were also established with a sophisticated justice system. Anglo-Saxon material culture can still be seen in architecture, dress styles, illuminated texts, metalwork and other art. Middle-lowland England was known as the place of the Mierce, the border or frontier folk, in Latin Mercia. Mercia was a diverse area of tribal groups, as shown by the Tribal Hidage; the peoples were a mixture of Brittonic speaking peoples and "Anglo-Saxon" pioneers and their early leaders had Brittonic names, such as Penda.

Although Penda does not appear in Bede's list of great overlords, it would appear from what Bede says elsewhere that he was dominant over the southern kingdoms. At the time of the battle of the river Winwæd, thirty duces regii (royal generals) fought on his behalf. Mercian military success was the basis of their power; it succeeded against not only 106 kings and kingdoms by winning set-piece battles, but by ruthlessly ravaging any area foolish enough to withhold tribute. There are a number of casual references scattered throughout the Bede's history to this aspect of Mercian military policy. Penda is found ravaging Northumbria as far north as Bamburgh and only a miraculous intervention from Aidan prevents the complete destruction of the settlement. In 676 Æthelred conducted a similar ravaging in Kent and caused such damage in the Rochester diocese that two successive bishops gave up their position because of lack of funds. In these accounts there is a rare glimpse of the realities of early Anglo-Saxon overlordship and how a widespread overlordship could be established in a relatively short period. By the middle of the 8th century, other kingdoms of southern Britain were also affected by Mercian expansionism. The East Saxons seem to have lost control of London, Middlesex and Hertfordshire to Æthelbald, although the East Saxon homelands do not seem to have been affected, and the East Saxon dynasty continued into the ninth century. The Mercian influence and reputation reached its peak when, in the late 8th century, the most powerful European ruler of the age, the Frankish king Charlemagne, recognised the Mercian King Offa's power and accordingly treated him with respect, even if this could have been just flattery. This period is considered a "Golden Age", when learning flourished with a renaissance in classical knowledge.
Genetic markers of Anglo-Saxon migrations
Main article: Genetic history of the British Isles
Genetic testing has been used to find evidence of large scale immigration of Germanic peoples into England. Weale et al. (2002) found that English Y DNA data showed signs of a mass Anglo-Saxon immigration from the European continent, affecting 50%–100% of the male gene pool in central England. This was based on the similarity of the DNA collected from small English towns to that found in Friesland.
A 2003 study with samples coming from larger towns, found a large variance in amounts of continental "Germanic" ancestry in different parts of England. In the study, such markers typically ranged from 20% and 45% in southern England, with East Anglia, the east Midlands, and Yorkshire having over 50%. North German and Danish genetic frequencies were indistinguishable, thus precluding any ability to distinguish between the genetic influence of the Anglo-Saxon source populations and the later, and better documented, influx of Danish Vikings. The mean value of continental Germanic genetic input in this study was calculated at 54 per cent.
In response to arguments, such as those of Stephen Oppenheimer and Bryan Sykes, that the similarity between English and continental Germanic DNA could have originated from earlier prehistoric migrations, researchers have begun to use data collected from ancient burials to ascertain the level of Anglo-Saxon contribution to the modern English gene pool. Two studies published in 2016, based on data collected from skeletons found in Iron Age, Roman and Anglo-Saxon era graves in Cambridgeshire and Yorkshire, concluded that the ancestry of the modern English population contains large contributions from both Anglo-Saxon migrants and Romano-British natives.
Heptarchy and Christianisation
Main articles: Northumbria, Mercia, Offa of Mercia, Heptarchy, Gregorian mission, and Anglo-Saxon Christianity
Christianisation of Anglo-Saxon England began around 600 AD, influenced by Celtic Christianity from the northwest and the Roman Catholic Church from the southeast. Augustine, the first Archbishop of Canterbury, took office in 597. In 601, he baptised the first Christian Anglo-Saxon king, Æthelberht of Kent. The last pagan Anglo-Saxon king, Penda of Mercia, died in 655. The last pagan Jutish king, Arwald of the Isle of Wight was killed in 686. The Anglo-Saxon mission on the continent took off in the 8th century, leading to the Christianisation of practically all of the Frankish Empire by 800.
Throughout the 7th and 8th centuries, power fluctuated between the larger kingdoms. Bede records Æthelberht of Kent as being dominant at the close of the 6th century, but power seems to have shifted northwards to the kingdom of Northumbria, which was formed from the amalgamation of Bernicia and Deira. Edwin of Northumbria probably held dominance over much of Britain, though Bede's Northumbrian bias should be kept in mind. Due to succession crises, Northumbrian hegemony was not constant, and Mercia remained a very powerful kingdom, especially under Penda. Two defeats ended Northumbrian dominance: the Battle of the Trent in 679 against Mercia, and Nechtanesmere in 685 against the Picts.
The so-called "Mercian Supremacy" dominated the 8th century, though it was not constant. Aethelbald and Offa, the two most powerful kings, achieved high status; indeed, Offa was considered the overlord of south Britain by Charlemagne. His power is illustrated by the fact that he summoned the resources to build Offa's Dyke. However, a rising Wessex, and challenges from smaller kingdoms, kept Mercian power in check, and by the early 9th century the "Mercian Supremacy" was over.
This period has been described as the Heptarchy, though this term has now fallen out of academic use. The term arose because the seven kingdoms of Northumbria, Mercia, Kent, East Anglia, Essex, Sussex and Wessex were the main polities of south Britain. Other small kingdoms were also politically important across this period: Hwicce, Magonsaete, Lindsey and Middle Anglia.
Viking age and the rise of Wessex
Main articles: Danelaw, Viking Age, and Alfred the Great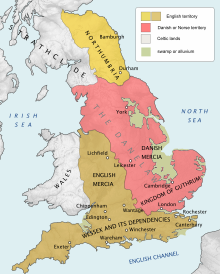
The first recorded landing of Vikings took place in 787 in Dorsetshire, on the south-west coast. The first major attack in Britain was in 793 at Lindisfarne monastery as given by the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle. However, by then the Vikings were almost certainly well-established in Orkney and Shetland, and many other non-recorded raids probably occurred before this. Records do show the first Viking attack on Iona taking place in 794. The arrival of the Vikings (in particular the Danish Great Heathen Army) upset the political and social geography of Britain and Ireland. In 867 Northumbria fell to the Danes; East Anglia fell in 869. Though Wessex managed to contain the Vikings by defeating them at Ashdown in 871, a second invading army landed, leaving the Saxons on a defensive footing. At much the same time, Æthelred, king of Wessex died and was succeeded by his younger brother Alfred. Alfred was immediately confronted with the task of defending Wessex against the Danes. He spent the first five years of his reign paying the invaders off. In 878, Alfred's forces were overwhelmed at Chippenham in a surprise attack.
It was only now, with the independence of Wessex hanging by a thread, that Alfred emerged as a great king. In May 878 he led a force that defeated the Danes at Edington. The victory was so complete that the Danish leader, Guthrum, was forced to accept Christian baptism and withdraw from Mercia. Alfred then set about strengthening the defences of Wessex, building a new navy—60 vessels strong. Alfred's success bought Wessex and Mercia years of peace and sparked economic recovery in previously ravaged areas.

Alfred's success was sustained by his son Edward, whose decisive victories over the Danes in East Anglia in 910 and 911 were followed by a crushing victory at Tempsford in 917. These military gains allowed Edward to fully incorporate Mercia into his kingdom and add East Anglia to his conquests. Edward then set about reinforcing his northern borders against the Danish kingdom of Northumbria. Edward's rapid conquest of the English kingdoms meant Wessex received homage from those that remained, including Gwynedd in Wales and Scotland. His dominance was reinforced by his son Æthelstan, who extended the borders of Wessex northward, in 927 conquering the Kingdom of York and leading a land and naval invasion of Scotland. These conquests led to his adopting the title 'King of the English' for the first time.
The dominance and independence of England was maintained by the kings that followed. It was not until 978 and the accession of Æthelred the Unready that the Danish threat resurfaced. Two powerful Danish kings (Harold Bluetooth and later his son Sweyn) both launched devastating invasions of England. Anglo-Saxon forces were resoundingly defeated at Maldon in 991. More Danish attacks followed, and their victories were frequent. Æthelred's control over his nobles began to falter, and he grew increasingly desperate. His solution was to pay off the Danes: for almost 20 years he paid increasingly large sums to the Danish nobles to keep them from English coasts. These payments, known as Danegelds, crippled the English economy.
Æthelred then made an alliance with Normandy in 1001 through marriage to the Duke's daughter Emma, in the hope of strengthening England. Then he made a great error: in 1002 he ordered the massacre of all the Danes in England. In response, Sweyn began a decade of devastating attacks on England. Northern England, with its sizable Danish population, sided with Sweyn. By 1013, London, Oxford, and Winchester had fallen to the Danes. Æthelred fled to Normandy and Sweyn seized the throne. Sweyn suddenly died in 1014, and Æthelred returned to England, confronted by Sweyn's successor, Cnut. However, in 1016, Æthelred also suddenly died. Cnut swiftly defeated the remaining Saxons, killing Æthelred's son Edmund in the process. Cnut seized the throne, crowning himself King of England.
English unification
Main articles: Æthelstan and Edgar of England
Alfred of Wessex died in 899 and was succeeded by his son Edward the Elder. Edward, and his brother-in-law Æthelred of (what was left of) Mercia, began a programme of expansion, building forts and towns on an Alfredian model. On Æthelred's death, his wife (Edward's sister) Æthelflæd ruled as "Lady of the Mercians" and continued expansion. It seems Edward had his son Æthelstan brought up in the Mercian court. On Edward's death, Æthelstan succeeded to the Mercian kingdom, and, after some uncertainty, Wessex.
Æthelstan continued the expansion of his father and aunt and was the first king to achieve direct rulership of what we would now consider England. The titles attributed to him in charters and on coins suggest a still more widespread dominance. His expansion aroused ill-feeling among the other kingdoms of Britain, and he defeated a combined Scottish-Viking army at the Battle of Brunanburh. However, the unification of England was not a certainty. Under Æthelstan's successors Edmund and Eadred the English kings repeatedly lost and regained control of Northumbria. Nevertheless, Edgar, who ruled the same expanse as Æthelstan, consolidated the kingdom, which remained united thereafter.
England under the Danes and the Norman conquest
Main articles: Ethelred the Unready, Canute the Great, Eiríkr Hákonarson, and Norman conquest of EnglandThere were renewed Scandinavian attacks on England at the end of the 10th century. Æthelred ruled a long reign but ultimately lost his kingdom to Sweyn of Denmark, though he recovered it following the latter's death. However, Æthelred's son Edmund II Ironside died shortly afterwards, allowing Cnut, Sweyn's son, to become king of England. Under his rule the kingdom became the centre of government for the North Sea empire which included Denmark and Norway.
Cnut was succeeded by his sons, but in 1042 the native dynasty was restored with the accession of Edward the Confessor. Edward's failure to produce an heir caused a furious conflict over the succession on his death in 1066. His struggles for power against Godwin, Earl of Wessex, the claims of Cnut's Scandinavian successors, and the ambitions of the Normans whom Edward introduced to English politics to bolster his own position caused each to vie for control of Edward's reign.
Harold Godwinson became king, probably appointed by Edward on his deathbed and endorsed by the Witan. But William of Normandy, Harald Hardråde (aided by Harold Godwin's estranged brother Tostig) and Sweyn II of Denmark all asserted claims to the throne. By far the strongest hereditary claim was that of Edgar the Ætheling, but due to his youth and apparent lack of powerful supporters, he did not play a major part in the struggles of 1066, although he was made king for a short time by the Witan after the death of Harold Godwinson.
In September 1066, Harald III of Norway and Earl Tostig landed in Northern England with a force of around 15,000 men and 300 longships. Harold Godwinson defeated the invaders and killed Harald III of Norway and Tostig at the Battle of Stamford Bridge. On 28 September 1066, William of Normandy invaded England in a campaign called the Norman Conquest. After marching from Yorkshire, Harold's exhausted army was defeated and Harold was killed at the Battle of Hastings on 14 October. Further opposition to William in support of Edgar the Ætheling soon collapsed, and William was crowned king on Christmas Day 1066. For five years, he faced a series of rebellions in various parts of England and a half-hearted Danish invasion, but he subdued them and established an enduring regime.
Norman era
"Norman England" redirects here. For the writer, see Godfrey Webb. Further information: England in the High Middle Ages and Government in Norman and Angevin England
In 1002 King Æthelred II of England married Emma, the sister of Richard II, Duke of Normandy. Their son Edward the Confessor, who spent many years in exile in Normandy, succeeded to the English throne in 1042. This led to the establishment of a powerful Norman interest in England, as Edward drew heavily on his former hosts for support, bringing in Norman courtiers, soldiers, and clerics and appointing them to positions of power, particularly in the Church. Childless and embroiled in conflict with the formidable Godwin, Earl of Wessex, and his sons, Edward may also have encouraged Duke William of Normandy's ambitions for the English throne.
When King Edward died at the beginning of 1066, the lack of a clear heir led to a disputed succession in which several contenders laid claim to the throne of England. Edward's immediate successor was the Earl of Wessex, Harold Godwinson, the richest and most powerful of the English aristocrats. Harold was elected king by the Witenagemot of England and crowned by the Archbishop of York, Ealdred, although Norman propaganda claimed the ceremony was performed by Stigand, the uncanonically elected Archbishop of Canterbury. Harold was immediately challenged by two powerful neighbouring rulers. Duke William claimed that he had been promised the throne by King Edward and that Harold had sworn agreement to this;

King Harald III of Norway, commonly known as Harald Hardrada, also contested the succession. His claim to the throne was based on an agreement between his predecessor Magnus I of Norway and the earlier English king, Harthacnut, whereby if either died without heir, the other would inherit both England and Norway. William and Harald at once set about assembling troops and ships to invade England. Tostig Godwinson, brother of Harold, made a series of attacks in the north of England in early 1066 that may have been the beginning of a bid for the throne, but after defeat at the hands of Edwin and Morcar and the desertion of most of his followers he threw his lot in with Harald Hardrada, who invaded northern England in early September. Harold defeated and killed Hardrada and Tostig at the battle of Stamford Bridge. William invaded with an army of Norman followers and mercenaries. Harold marched south to meet him, but was defeated and killed at the battle of Hastings on 14 October and William's forces rapidly occupied the south of England.
The Norman Conquest led to a profound change in the history of the English state. Major revolts followed, which William suppressed before intervening in the north-east of England, establishing Norman control of York and devastating the region. Once England had been conquered, the Normans faced many challenges in maintaining control. William's followers expected and received lands and titles in return for their service in the invasion, but William claimed ultimate possession of the land in England over which his armies had given him de facto control, and asserted the right to dispose of it as he saw fit. Henceforth, all land was "held" directly from the king in feudal tenure in return for military service. A Norman lord typically had properties located in a piecemeal fashion throughout England and Normandy, and not in a single geographic block.
To find the lands to compensate his Norman followers, William I initially confiscated the estates of all the English lords who had fought and died with Harold and redistributed part of their lands. These confiscations led to revolts, which resulted in more confiscations, a cycle that continued for five years after the Battle of Hastings. To put down and prevent further rebellions the Normans constructed castles and fortifications in unprecedented numbers, initially mostly on the motte-and-bailey pattern. William and his barons also exercised tighter control over inheritance of property by widows and daughters, often forcing marriages to Normans. Some Norman lords used England as a launching point for attacks into South and North Wales, spreading up the valleys to create new Marcher territories. By the time of William's death in 1087, England formed the largest part of an Anglo-Norman empire, ruled over by a network of nobles with landholdings across England, Normandy, and Wales. England's growing wealth was critical in allowing the Norman kings to project power across the region, including funding campaigns along the frontiers of Normandy.
At Christmas 1085, William ordered the compilation of a survey of the landholdings held by himself and by his vassals throughout the kingdom, organised by counties, a work now known as the Domesday Book. The listing for each county gives the holdings of each landholder, grouped by owners. The listings describe the holding, who owned the land before the Conquest, its value, what the tax assessment was, and usually the number of peasants, ploughs, and any other resources the holding had. Towns were listed separately. All the English counties south of the River Tees and River Ribble are included, and the whole work seems to have been mostly completed by 1 August 1086, when the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle records that William received the results and that all the chief magnates swore the Salisbury Oath, a renewal of their oaths of allegiance.

Despite Robert's rival claims, his younger brother Henry immediately seized power in England. Robert, who invaded in 1101, disputed Henry's control of England. This military campaign ended in a negotiated settlement that confirmed Henry as king. The peace was short-lived, and Henry invaded the Duchy of Normandy in 1105 and 1106, finally defeating Robert at the Battle of Tinchebray. Henry kept Robert imprisoned for the rest of his life. Henry's control of Normandy was challenged by Louis VI of France, Baldwin of Flanders and Fulk of Anjou, who promoted the rival claims of Robert's son, William Clito, and supported a major rebellion in the Duchy between 1116 and 1119. Following Henry's victory at the Battle of Brémule, a favourable peace settlement was agreed with Louis in 1120. Upon being crowned, on Christmas Day 1066, William immediately began consolidating his power. By 1067, he faced revolts on all sides and spent four years crushing them. He then imposed his superiority over Scotland and Wales, forcing them to recognise him as overlord. Economic growth and state finances were aided by the beginning of Jewish settlement in London.
Considered by contemporaries to be a harsh but effective ruler, Henry skilfully manipulated the barons in England and Normandy. In England, he drew on the existing Anglo-Saxon system of justice, local government and taxation, but also strengthened it with additional institutions, including the royal exchequer and itinerant justices. Many of the officials that ran Henry's system were "new men", relatively low-born individuals who rose through the ranks as administrators. Henry encouraged ecclesiastical reform, but from 1101 he also became embroiled in a serious dispute with Archbishop Anselm, which was resolved through a compromise solution in 1105. He supported the Cluniac order and played a major role in the selection of the senior clergy in England and Normandy.
The death of William the Conqueror in 1087 his lands were divided into two parts. His Norman lands went to the eldest son Robert Curthose and his English lands to the younger William Rufus. This presented a dilemma for those nobles who held land on both sides of the waterway of the English Channel, who decided to unite England and Normandy once more under one ruler. The pursuit of this aim led them to revolt against William in favour of Robert in the Rebellion of 1088, under the leadership of the powerful Bishop Odo of Bayeux, who was a half-brother of William the Conqueror. As Robert failed to appear in England to rally his supporters, William won the support of the English lords with silver and promises of better government, and defeated the rebellion. In 1091 he invaded Normandy, crushing Robert's forces and forcing him to cede a portion of his lands. The two made up their differences and William agreed to help Robert recover lands lost to the King of France, notably Le Maine. This plan was later abandoned, but William continued to pursue a ferociously warlike defence of his French possessions and interests, exemplified by his response to the attempt by Elias de la Flèche, Count of Maine, to take Le Mans in 1099. William came into conflict with Anselm, Archbishop of Canterbury over Gregorian reforms in the Church. Eventually Anselm went into exile and Pope Urban II, involved in a major conflict with the Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV, came to a concordat with William, whereby William recognised Urban as pope, and Urban gave sanction to the Anglo-Norman ecclesiastical status quo. Anselm remained in exile, and William was able to claim the revenues of the archbishop of Canterbury to the end of his reign. William died while hunting in 1100.
The English Middle Ages were characterised by civil war, international war, occasional insurrection, and widespread political intrigue among the aristocratic and monarchic elite. England was more than self-sufficient in cereals, dairy products, beef and mutton. Its international economy was based on wool trade, in which wool from the sheepwalks of northern England was exported to the textile cities of Flanders, where it was worked into cloth. Medieval foreign policy was as much shaped by relations with the Flemish textile industry as it was by dynastic adventures in western France. An English textile industry was established in the 15th century, providing the basis for rapid English capital accumulation.

Henry I, the fourth son of William I the Conqueror, succeeded his elder brother William II as King of England in 1100. Henry was also known as "Henry Beauclerc" because he received a formal education, unlike his older brother and heir apparent William who got practical training to be king. Henry worked hard to reform and stabilise the country and smooth the differences between the Anglo-Saxon and Anglo-Norman societies. The loss of his son, William Adelin, in the wreck of the White Ship in November 1120, undermined his reforms. This problem regarding succession cast a long shadow over English history. Considered by contemporaries to be a harsh but effective ruler, Henry skilfully manipulated the barons in England and Normandy.
In England, he drew on the existing Anglo-Saxon system of justice, local government and taxation, but also strengthened it with additional institutions, including the royal exchequer and itinerant justices. Normandy was also governed through a growing system of justices and an exchequer. Many of the officials that ran Henry's system were "new men", relatively low-born individuals who rose through the ranks as administrators. Henry encouraged ecclesiastical reform, but from 1101 he also became embroiled in a serious dispute with Archbishop Anselm, which was resolved through a compromise solution in 1105. He supported the Cluniac order and played a major role in the selection of the senior clergy in England and Normandy.
Henry I had required the leading barons, ecclesiastics and officials in Normandy and England, to take an oath to accept Matilda (also known as Empress Maud, Henry I's daughter) as his heir. England was far less than enthusiastic to accept an outsider, and a woman, as their ruler. There is some evidence that Henry was unsure of his own hopes and the oath to make Matilda his heir. Probably Henry hoped Matilda would have a son and step aside as Queen Mother. Upon Henry's death, the Norman and English barons ignored Matilda's claim to the throne, and thus through a series of decisions, Stephen, Henry's favourite nephew, was welcomed by many in England and Normandy as their new king. On 22 December 1135, Stephen was anointed king with implicit support by the church and nation. Matilda and her own son waited in France until she sparked the civil war from 1139 to 1153 known as the Anarchy. In the autumn of 1139, she invaded England with her illegitimate half-brother Robert of Gloucester. Her husband, Geoffroy V of Anjou, conquered Normandy but did not cross the channel to help his wife. During this breakdown of central authority, nobles built adulterine castles (i.e. castles erected without government permission), which were hated by the peasants, who were forced to build and maintain them.
Stephen was captured, and his government fell. Matilda was proclaimed queen but was soon at odds with her subjects and was expelled from London. The war continued until 1148, when Matilda returned to France. Stephen reigned unopposed until his death in 1154, although his hold on the throne was uneasy. As soon as he regained power, he began to demolish the adulterine castles, but kept a few castles standing, which put him at odds with his heir. His contested reign, civil war, and lawlessness saw a major swing in power towards feudal barons. In trying to appease Scottish and Welsh raiders, he handed over large tracts of land.
Plantagenet era
Further information: House of PlantagenetAngevin kings
Main article: Angevin kings of England
After Stephen's death in 1154 Henry II succeeded as the first Angevin king of England, so-called because he was also the Count of Anjou in Northern France, adding it to his extensive holdings in Normandy and Aquitaine. England became a key part of a loose-knit assemblage of lands spread across Western Europe, later termed the Angevin Empire. Henry asserted his authority over Brittany, even reorganising the Duchy into eight administrative districts and introducing Angevin legal reforms. He pursued an aggressive policy in Wales, reclaiming lands lost by Anglo-Norman princes and conducting four punitive campaigns against Welsh princes that resulted in their submission to his authority. This underlined his overlordship, but he did not attempt a direct conquest. When the Scottish king William the Lion joined the rebellion of Henry's sons and was captured, it allowed Henry to extract homage from the Scottish king under the Treaty of Falaise (1174), which he did not pursue directly, but which would provide a justification for later interventions in Scottish kingship.
In the mid-twelfth century Ireland was ruled by local kings, although their authority was more limited than their counterparts in the rest of Western Europe. In the 1160s deposed King Diarmait Mac Murchada King of Leinster turned to Henry for assistance in 1167, and the English king agreed to allow Diarmait to recruit mercenaries within his empire. Diarmait put together a force of Anglo-Norman and Flemish mercenaries drawn from the Welsh Marches, including Richard de Clare, known as Strongbow. With his new supporters, he reclaimed Leinster but died shortly afterwards in 1171; de Clare then claimed Leinster for himself. Henry took this opportunity to intervene personally in Ireland, landing in October 1171. Henry's timing was influenced by several factors, including encouragement from Pope Alexander, who saw the opportunity to establish papal authority over the Irish church. Henry's intervention was initially successful, with both the Irish and Anglo-Normans in the south and east of Ireland accepting his rule. However, the Treaty of Windsor in 1175, under which Rory O'Connor would be recognised as the high king of Ireland, giving homage to Henry and maintaining stability on the ground on his behalf, meant that he had little direct control.
Henry saw an opportunity to re-establish what he saw as his rights over the Church in England by reasserting the privileges held by Henry I when Theobald, Archbishop of Canterbury, died, by appointing his friend, Thomas Becket to the post. Henry had clashed with the church over whether bishops could excommunicate royal officials without his permission and whether he could try clerics without them appealing to Rome. However, Becket opposed Henry's Constitutions of Clarendon and fled into exile. Relations later improved, allowing Becket's return, but soon soured again when Becket saw the crowning as coregent of Henry's son by the Archbishop of York as a challenge to his authority and excommunicated those who had offended him. On hearing the news Henry uttered the infamous phrase "What miserable drones and traitors have I nurtured and promoted in my household who let their lord be treated with such shameful contempt by a low born clerk". In response to please Henry three of his men murdered Becket in Canterbury Cathedral, probably by misadventure after Becket resisted a botched arrest attempt. In Christian Europe Henry was considered complicit in this crime, making him a pariah, and he was forced to make a dramatic exhibition of penance, publicly walking barefoot into the cathedral and allowing monks to scourge him.
When Henry II attempted to give his land-less youngest son, John, a wedding gift of three castles it prompted his three eldest sons and wife to rebel in the Revolt of 1173–1174. Louis VII encouraged the three elder sons to destabilise his mightiest subject and not to wait for their inheritances. It was only after eighteen months of conflict that Henry II was able to force the rebels to submit to his authority. In Le Mans in 1182 Henry II gathered his children to plan for partible inheritance in which his eldest son, also called Henry, would inherit England, Normandy and Anjou; Richard the Duchy of Aquitaine; Geoffrey Brittany and John would receive Ireland. This broke down into further conflict and the younger Henry rebelled again, but died of dysentery. In 1186 Geoffrey died as a result of a tournament accident but Henry was still reluctant to have a sole heir so, in 1189, Richard and Philip II of France took advantage of a sickening Henry II with more success. Henry II was forced to accept humiliating peace terms, including naming Richard as sole heir. When Henry II died shortly afterwards his last words to Richard were allegedly "God grant that I may not die until I have my revenge on you".
On the day of Richard I's English coronation there was a mass slaughter of the Jews, described by Richard of Devizes as a "holocaust". Quickly putting the affairs of the Angevin Empire in order he departed on Crusade to the Middle East in early 1190. In Sicily he came into conflict with Tancred I over the rights of Richard's sister Queen Joan, widow of the former king William II of Sicily. Richard captured the city of Messina on 4 October 1190 and using it to force Tancred into a peace agreement. When his sister and his fiancée Berengaria along with several other ships, including the treasure ship were seized by the island's despot Isaac Komnenos, Richard conquered the island, which became a western feudal and Christian base in the Mediterranean. Opinions of Richard amongst his contemporaries were mixed. He had rejected and humiliated the king of France's sister; insulted and refused spoils of the third crusade to nobles like Leopold V, Duke of Austria, and was rumoured to have arranged the assassination of Conrad of Montferrat. His cruelty was demonstrated by his massacre of 2,600 prisoners in Acre. However, Richard was respected for his military leadership and courtly manners. He achieved victories in the Third Crusade but failed to capture Jerusalem, retreating from the Holy Land with a small band of followers.
Richard's failure in his duty to provide an heir caused a succession crisis. Anjou, Brittany, Maine and Touraine chose Richard's nephew and nominated heir, Arthur, while John succeeded in England and Normandy. Yet again Philip II of France took the opportunity to destabilise the Plantagenet territories on the European mainland, supporting his vassal Arthur's claim to the English crown. When Arthur's forces threatened his mother, John won a significant victory, capturing the entire rebel leadership at the Battle of Mirebeau. Arthur was murdered, it was rumoured by John's own hands, and his sister Eleanor would spend the rest of her life in captivity. John's behaviour drove numerous French barons to side with Phillip. The resulting rebellions by the Norman and Angevin barons broke John's control of the continental possessions, leading to the de facto end of the Angevin Empire, even though Henry III would maintain the claim until 1259. After re-establishing his authority in England, John planned to retake Normandy and Anjou. The strategy was to draw the French from Paris while another army, under Otto IV, Holy Roman Emperor, attacked from the north. However, his allies were defeated at the Battle of Bouvines in one of the most decisive and symbolic battles in French history. The battle had both important and high-profile consequences. John's nephew Otto retreated and was soon overthrown while King John agreed to a five-year truce. Philip's decisive victory was crucial in ordering politics in both England and France. The battle was instrumental in forming the absolute monarchy in France.

John's defeats in France weakened his position in England. The rebellion of his English vassals resulted in the treaty called Magna Carta, which limited royal power and established common law. This would form the basis of every constitutional battle through the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries. However, both the barons and the crown failed to abide by the terms of Magna Carta, leading to the First Barons' War in which the rebel barons invited an invasion by Prince Louis. This is considered by some historians to mark the end of the Angevin period and the beginning of the Plantagenet dynasty with John's death and William Marshall's appointment as the protector of the nine-year-old Henry III. Marshall won the war with victories at the battles of Lincoln and Dover in 1217, leading to the Treaty of Lambeth by which Louis renounced his claims. In victory, the Marshal Protectorate reissued the Magna Carta agreement as a basis for future government.
Over the course of his reign, a combination of higher taxes, unsuccessful wars and conflict with the Pope made King John unpopular with his barons. In 1215, some of the most important barons rebelled against him. He met their leaders along with their French and Scot allies at Runnymede, near London on 15 June 1215 to seal the Great Charter (Magna Carta in Latin), which imposed legal limits on the king's personal powers. But as soon as hostilities ceased, John received approval from the Pope to break his word because he had made it under duress. This provoked the First Barons' War and a French invasion by Prince Louis of France invited by a majority of the English barons to replace John as king in London in May 1216. John travelled around the country to oppose the rebel forces, directing, among other operations, a two-month siege of the rebel-held Rochester Castle.
John's son, Henry III, was only 9 years old when he became king (1216–1272). He spent much of his reign fighting the barons over Magna Carta and the royal rights, and was eventually forced to call the first "parliament" in 1264. He was also unsuccessful on the continent, where he endeavoured to re-establish English control over Normandy, Anjou, and Aquitaine. His reign was punctuated by many rebellions and civil wars, often provoked by incompetence and mismanagement in government and Henry's perceived over-reliance on French courtiers (thus restricting the influence of the English nobility). One of these rebellions—led by a disaffected courtier, Simon de Montfort—was notable for its assembly of one of the earliest precursors to Parliament. In addition to fighting the Second Barons' War, Henry III made war against Louis IX and was defeated during the Saintonge War, yet Louis did not capitalise on his victory, respecting his opponent's rights. Henry III's policies towards Jews began with relative tolerance, but became gradually more restrictive. In 1253 the Statute of Jewry, reinforced physical segregation and demanded a previously notional requirement to wear square white badges. Henry III also backed an accusation of child murder in Lincoln, ordering a Jew Copin to be executed and 91 Jews to be arrested for trial; 18 were killed. Popular superstitious fears were fuelled, and Catholic theological hostility combined with Baronial abuse of loan arrangements, resulting in Simon de Montfort's supporters targeting of Jewish communities in their revolt. This hostility, violence and controversy was the background to the increasingly oppressive measures that followed under Edward I.
Under the Plantagenets, England was transformed. The Plantagenet kings were often forced to negotiate compromises such as Magna Carta, which had served to constrain their royal power in return for financial and military support. A distinct national identity was shaped by their conflict with the French, Scots, Welsh and Irish, and by the establishment of the English language as the primary language. Catholic monasticism flourished, providing philosophers, and the universities of Oxford and Cambridge were founded with royal patronage. In the 15th century, the Plantagenets were defeated in the Hundred Years' War and beset with social, political and economic problems. Popular revolts were commonplace, triggered by the denial of numerous freedoms. English nobles raised private armies, engaged in private feuds and openly defied Henry VI.
14th century
Main articles: Edward I of England, Edward II of England, Edward III of England, and Richard II of England
The reign of Edward I (reigned 1272–1307) was more successful. Edward enacted numerous laws strengthening the powers of his government, and he summoned the first officially sanctioned Parliaments of England (such as his Model Parliament). He conquered Wales and attempted to use a succession dispute to gain control of the Kingdom of Scotland, though this developed into a costly and drawn-out military campaign. Edward I is also known for his policies first persecuting Jews, particularly the 1275 Statute of the Jewry. This banned Jews from their previous role in making loans, and demanded that they work as merchants, farmers, craftsmen or soldiers. This was unrealistic, and failed. This was the first statewide permanent expulsion in Europe.
His son, Edward II, proved a disaster. A weak man who preferred to engage in activities like thatching and ditch-digging rather than jousting, hunting, or the usual entertainments of kings, he spent most of his reign trying in

vain to control the nobility, who in return showed continual hostility to him. Meanwhile, the Scottish leader Robert Bruce began retaking all the territory conquered by Edward I. In 1314, the English army was disastrously defeated by the Scots at the Battle of Bannockburn. Edward also showered favours on his companion Piers Gaveston, a knight of humble birth. While it has been widely believed that Edward was a homosexual because of his closeness to Gaveston, there is no concrete evidence of this. The king's enemies, including his cousin Thomas of Lancaster, captured and murdered Gaveston in 1312.

The Great Famine of 1315–1317 may have resulted in half a million deaths in England due to hunger and disease, more than 10 per cent of the population. Edward's downfall came in 1326 when his wife, Queen Isabella, travelled to her native France and, with her lover Roger Mortimer, invaded England. Despite their tiny force, they quickly rallied support for their cause. The king fled London, and his companion since Piers Gaveston's death, Hugh Despenser, was publicly tried and executed. Edward was captured, charged with breaking his coronation oath, deposed and imprisoned in Gloucestershire until he was murdered some time in the autumn of 1327, presumably by agents of Isabella and Mortimer.
Edward III, son of Edward II, was crowned at age 14 after his father was deposed by his mother and Roger Mortimer. At age 17, he led a successful coup against Mortimer, the de facto ruler of the country, and began his personal reign. Edward III reigned 1327–1377, restored royal authority and went on to transform England into the most efficient military power in Europe. His reign saw vital developments in legislature and government—in particular the evolution of the English parliament—as well as the ravages of the Black Death. After defeating, but not subjugating, the Kingdom of Scotland, he declared himself rightful heir to the French throne in 1338, but his claim was denied due to the Salic law. This started what would become known as the Hundred Years' War. Following some initial setbacks, the war went exceptionally well for England; victories at Crécy and Poitiers led to the highly favourable Treaty of Brétigny. Edward's later years were marked by international failure and domestic strife, largely as a result of his inactivity and poor health.

For many years, trouble had been brewing with Castile—a Spanish kingdom whose navy had taken to raiding English merchant ships in the Channel. Edward won a major naval victory against a Castilian fleet off Winchelsea in 1350. Although the Castilian crossbowmen killed many of the enemy, the English gradually got the better of the encounter. In spite of Edward's success, however, Winchelsea was only a flash in a conflict that raged between the English and the Spanish for over 200 years, coming to a head with the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588.
In 1373, England signed an alliance with the Kingdom of Portugal, which is claimed to be the oldest alliance in the world still in force. Edward III died of a stroke on 21 June 1377, and was succeeded by his ten-year-old grandson, Richard II. He married Anne of Bohemia, daughter of Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor in 1382, and ruled until he was deposed by his first cousin Henry IV in 1399. In 1381, a Peasants' Revolt led by Wat Tyler spread across large parts of England. It was suppressed by Richard II, with the death of 1500 rebels.
Black Death
Main article: Black Death in EnglandThe Black Death, an epidemic of bubonic plague that spread all over Europe, arrived in England in 1348 and killed as much as a third to half the population. Military conflicts during this period were usually with domestic neighbours such as the Welsh, Irish, and Scots, and included the Hundred Years' War against the French and their Scottish allies. Notable English victories in the Hundred Years' War included Crécy and Agincourt. The final defeat of the uprising led by the Welsh prince, Owain Glyndŵr, in 1412 by Prince Henry (who later became Henry V) represents the last major armed attempt by the Welsh to throw off English rule.
Edward III gave land to powerful noble families, including many people of royal lineage. Because land was equivalent to power, these powerful men could try to claim the crown. When Edward III died in 1377, he was succeeded by his grandson, Richard II. Richard's autocratic and arrogant methods only served to alienate the nobility more, and his forceful dispossession in 1399 by Henry IV increased the turmoil.
| English Royalty |
| Second House of Lancaster |
|---|
 Armorial of Plantagenet Armorial of Plantagenet |
| Henry IV |
Henry spent much of his reign defending himself against plots, rebellions and assassination attempts. Rebellions continued throughout the first ten years of Henry's reign, including the revolt of Owain Glyndŵr, who declared himself Prince of Wales in 1400, and the rebellion of Henry Percy, 1st Earl of Northumberland. The king's success in putting down these rebellions was due partly to the military ability of his eldest son, Henry of Monmouth, who later became king (though the son managed to seize much effective power from his father in 1410).
15th century – Henry V and the Wars of the Roses
Further information: Lancastrian War, Wars of the Roses, and Great Slump (15th century)See also: English historians in the Middle Ages and List of English chroniclesHenry V succeeded to the throne in 1413. He renewed hostilities with France and began a set of military campaigns which are considered a new phase of the Hundred Years' War, referred to as the Lancastrian War. He won several notable victories over the French, including the Battle of Agincourt. In the Treaty of Troyes, Henry V was given the power to succeed the current ruler of France, Charles VI of France. The Treaty also provided that he would marry Charles VI's daughter, Catherine of Valois. They married in 1421. Henry died of dysentery in 1422, leaving a number of unfulfilled plans, including his plan to take over as King of France and to lead a crusade to retake Jerusalem from the Muslims. Henry's outstanding military successes in the Hundred Years' War against France made England one of the strongest military powers in Europe. Henry is known and celebrated as one of the greatest warrior-kings of medieval England.

Henry V's son, Henry VI, became king in 1422 as an infant. His reign was marked by constant turmoil due to his political weaknesses. While he was growing up, England was ruled by the Regency government. The Regency Council tried to install Henry VI as the King of France, as provided by the Treaty of Troyes signed by his father, and led English forces to take over areas of France. It appeared they might succeed due to the poor political position of the son of Charles VI, who had claimed to be the rightful king as Charles VII of France. However, in 1429, Joan of Arc began a military effort to prevent the English from gaining control of France. The French forces regained control of French territory.
In 1437, Henry VI came of age and began to actively rule as king. To forge peace, he married French noblewoman Margaret of Anjou in 1445, as provided in the Treaty of Tours. Hostilities with France resumed in 1449. When England lost the Hundred Years' War in August 1453, Henry fell into mental breakdown until Christmas 1454.

Henry could not control the feuding nobles, and a series of civil wars known as the Wars of the Roses began, lasting from 1455 to 1485. Although the fighting was very sporadic and small, there was a general breakdown in the power of the Crown. The royal court and Parliament moved to Coventry, in the Lancastrian heartlands, which thus became the capital of England until 1461. Henry's cousin Edward, Duke of York, deposed Henry in 1461 to become Edward IV following a Lancastrian defeat at the Battle of Mortimer's Cross. Edward was later briefly expelled from the throne in 1470–1471 when Richard Neville, Earl of Warwick, brought Henry back to power. Six months later, Edward defeated and killed Warwick in battle and reclaimed the throne. Henry was imprisoned in the Tower of London and died there.
Edward died in 1483, only 40 years old, his reign having gone a little way to restoring the power of the Crown. His eldest son and heir Edward V, aged 12, could not succeed him because the king's brother, Richard III, Duke of Gloucester, declared Edward IV's marriage bigamous, making all his children illegitimate. Richard III was then declared king, and Edward V and his 10-year-old brother Richard were imprisoned in the Tower of London. The two were never seen again. It was widely believed that Richard III had them murdered and he was reviled as a treacherous fiend, which limited his ability to govern during his brief reign. In summer 1485, Henry Tudor, the last Lancastrian male, returned from exile in France and landed in Wales. Henry then defeated and killed Richard III at Bosworth Field on 22 August, and was crowned Henry VII.
Tudor era
Main article: Tudor period Further information: Early Modern Britain and English RenaissanceHenry VII

The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in England that began with the reign of Henry VII. Henry engaged in a number of administrative, economic and diplomatic initiatives. He paid very close attention to detail and, instead of spending lavishly, concentrated on raising new revenues. Henry was successful in restoring power and stability to the nation's monarchy following the civil war. His supportive policy toward England's wool industry and his standoff with the Low Countries had long-lasting benefit to the economy of England. He restored the nation's finances and strengthened its judicial system. The Renaissance reached England through Italian courtiers, who reintroduced artistic, educational and scholarly debate from classical antiquity. England began to develop naval skills, and exploration intensified in the Age of Discovery.
With Henry VII's accession to the throne in 1485, the Wars of the Roses came to an end, and Tudors would continue to rule England for 118 years. Traditionally, the Battle of Bosworth Field is considered to mark the end of the Middle Ages in England, although Henry did not introduce any new concept of monarchy, and for most of his reign his hold on power was tenuous. He claimed the throne by conquest and God's judgement in battle. Parliament quickly recognised him as king, but the Yorkists were far from defeated. Nonetheless, he married Edward IV's eldest daughter Elizabeth in January 1486, thereby uniting the houses of York and Lancaster.
Most of the European rulers did not believe Henry would survive long, and were thus willing to shelter claimants against him. The first plot against him was the Stafford and Lovell rebellion of 1486, which presented no serious threat. But Richard III's nephew John de la Pole, Earl of Lincoln, hatched another attempt the following year. Using a peasant boy named Lambert Simnel, who posed as Edward, Earl of Warwick (the real Warwick was locked up in the Tower of London), he led an army of 2,000 German mercenaries paid for by Margaret of Burgundy into England. They were defeated and de la Pole was killed at the difficult Battle of Stoke, where the loyalty of some of the royal troops to Henry was questionable. The king, realizing that Simnel was a dupe, employed him in the royal kitchen.
A more serious threat was Perkin Warbeck, a Flemish youth who posed as Edward IV's son Richard. Again with support from Margaret of Burgundy, he invaded England four times from 1495 to 1497 before he was captured and imprisoned in the Tower of London. Both Warbeck and the Earl of Warwick were dangerous even in captivity, and Henry executed them in 1499 before Ferdinand and Isabella of Spain would allow their daughter Catherine to come to England and marry his son Arthur.
In 1497, Henry defeated Cornish rebels marching on London. The rest of his reign was relatively peaceful, despite worries about succession after the death of his wife Elizabeth of York in 1503. Henry VII's foreign policy was peaceful. He had made an alliance with Spain and the Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I, but in 1493, when they went to war with France, England was dragged into the conflict. Impoverished and his hold on power insecure, Henry had no desire for war. He quickly reached an understanding with the French and renounced all claims to their territory except the port of Calais, realizing also that he could not stop them from incorporating the Duchy of Brittany. In return, the French agreed to recognize him as king and stop sheltering pretenders. Shortly afterwards, they became preoccupied with adventures in Italy. Henry also reached an understanding with Scotland, agreeing to marry his daughter Margaret to that country's king James IV.
Upon becoming king, Henry inherited a government severely weakened and degraded by the Wars of the Roses. The treasury was empty, having been drained by Edward IV's Woodville in-laws after his death. Through a tight fiscal policy and sometimes ruthless tax collection and confiscations, Henry refilled the treasury by the time of his death. He also effectively rebuilt the machinery of government. In 1501, the king's son Arthur, having married Catherine of Aragon, died of illness at age 15, leaving his younger brother Henry, Duke of York as heir. When the king himself died in 1509, the position of the Tudors was secure at last, and his son succeeded him unopposed.
Henry VIII

Henry VIII, flamboyant, energetic, militaristic and headstrong, remains one of the most visible kings of England, primarily because of his six marriages, all of which were designed to produce a male heir, and his heavy retribution in executing many top officials and aristocrats. Henry cultivated the image of a Renaissance man, and his court was a centre of scholarly and artistic innovation and glamorous excess, epitomised by the Field of the Cloth of Gold. He inherited a vast fortune and a prosperous economy from his father, who had been frugal. This fortune is estimated at £1,250,000 (the equivalent of £375 million today). Henry broke from communion with the Catholic Church, over issues relating to his divorce, under the Acts of Supremacy in 1534 which proclaimed the monarch head of the Church of England. In contrast with much of European Protestantism, the roots of the split were more political than theological.
Henry VIII began his reign with much optimism. The handsome, athletic young king stood in sharp contrast to his wary, miserly father. Henry's lavish court quickly drained the treasury of the fortune he inherited. He married the widowed Catherine of Aragon, and they had several children, but none survived infancy except a daughter, Mary.In 1512, the young king started a war in France. Although England was an ally of Spain, one of France's principal enemies, the war was mostly about Henry's desire for personal glory, despite his sister Mary being married to the French king Louis XII. The war accomplished little. The English army suffered badly from disease, and Henry was not even present at the one notable victory, the Battle of the Spurs. Meanwhile, James IV of Scotland (despite being Henry's other brother-in-law), activated his alliance with the French and declared war on England. While Henry was dallying in France, Catherine, who was serving as regent in his absence, and his advisers were left to deal with this threat. At the Battle of Flodden on 9 September 1513, the Scots were completely defeated. James and most of the Scottish nobles were killed. When Henry returned from France, he was given credit for the victory.

Eventually, Catherine was no longer able to have any more children. The king became increasingly nervous about the possibility of his daughter Mary inheriting the throne, as England's one experience with a female sovereign, Matilda in the 12th century, had been a catastrophe. He eventually decided that it was necessary to divorce Catherine and find a new queen. To persuade the Church to allow this, Henry cited the passage in the Book of Leviticus: "If a man taketh his brother's wife, he hath committed adultery; they shall be childless". However, Catherine insisted that she and Arthur never consummated their brief marriage and that the prohibition did not apply here. The timing of Henry's case was very unfortunate; it was 1527 and the Pope had been imprisoned by emperor Charles V, Catherine's nephew and the most powerful man in Europe, for siding with his archenemy Francis I of France. Because he could not divorce in these circumstances, Henry seceded from the Church, in what became known as the English Reformation.
The newly established Church of England amounted to little more than the existing Catholic Church, but led by the king rather than the Pope. It took a number of years for the separation from Rome to be completed, and many were executed for resisting the king's religious policies. The Reformation transformed English religion. The five sovereigns, Henry VII, Henry VIII, Edward VI, Mary I, and Elizabeth I had entirely different approaches, with Henry VIII replacing the pope as the head of the Church of England but maintaining Catholic doctrines, Edward imposing a very strict Protestantism, Mary attempting to reinstate Catholicism, and Elizabeth arriving at a compromise position that defined the not-quite-Protestant Church of England. It began with the insistent demands of Henry VIII for an annulment of his marriage that Pope Clement VII refused to grant.
In 1530, Catherine was banished from court and spent the rest of her life (until her death in 1536) alone in an isolated manor home, barred from contact with Mary. Secret correspondence continued thanks to her ladies-in-waiting. Their marriage was declared invalid, making Mary an illegitimate child. Henry married Anne Boleyn secretly in January 1533, just as his divorce from Catherine was finalised. They had a second, public wedding. Anne soon became pregnant and may have already been when they wed. But on 7 September 1533, she gave birth to a daughter, Elizabeth. The king was devastated at his failure to obtain a son after all the effort it had taken to remarry. Gradually, he came to develop a disliking of his new queen for her strange behaviour. In 1536, when Anne was pregnant again, Henry was badly injured in a jousting accident. Shaken by this, the queen gave birth prematurely to a stillborn boy. By now, the king was convinced that his marriage was hexed, and having already found a new queen, Jane Seymour, he put Anne in the Tower of London on charges of witchcraft. Afterwards, she was beheaded along with five men (her brother included) accused of adultery with her. The marriage was then declared invalid, so that Elizabeth, just like her half sister, became a bastard.
Henry immediately married Jane Seymour, who became pregnant almost as quickly. On 12 October 1537, she gave birth to a healthy boy, Edward, which was greeted with huge celebrations. However, the queen died of puerperal sepsis ten days later. Henry genuinely mourned her death, and at his own passing nine years later, he was buried next to her. The king married a fourth time in 1540, to the German Anne of Cleves for a political alliance with her Protestant brother, the Duke of Cleves. He also hoped to obtain another son in case something should happen to Edward. Anne proved a dull, unattractive woman and Henry did not consummate the marriage. He quickly divorced her, and she remained in England as a kind of adopted sister to him. He married again, to a 19-year-old named Catherine Howard. But when it became known that she was neither a virgin at the wedding, nor a faithful wife afterwards, she ended up on the scaffold and the marriage declared invalid. His sixth and last marriage was to Catherine Parr, who was more his nursemaid than anything else, as his health was failing since his jousting accident in 1536.
In 1542, the king started a new campaign in France, but unlike in 1512, he only managed with great difficulty. He only conquered the city of Boulogne, which France retook in 1549. Scotland also declared war and at Solway Moss was again totally defeated. Henry's paranoia and suspicion worsened in his last years. The number of executions during his 38-year reign numbered tens of thousands. His domestic policies had strengthened royal authority to the detriment of the aristocracy, and led to a safer realm, but his foreign policy adventures did not increase England's prestige abroad and wrecked royal finances and the national economy, and embittered the Irish. He died in January 1547 at age 55 and was succeeded by his son, Edward VI.
Edward VI and Mary I

Although he showed piety and intelligence, Edward VI was only nine years old when he became king in 1547. His uncle, Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset tampered with Henry VIII's will and obtained letters patent giving him much of the power of a monarch by March 1547. He took the title of Protector. While some see him as a high-minded idealist, his stay in power culminated in a crisis in 1549 when many counties of the realm were up in protest. Kett's Rebellion in Norfolk and the Prayer Book Rebellion in Devon and Cornwall simultaneously created a crisis while invasion from Scotland and France were feared. Somerset, disliked by the Regency Council for being autocratic, was removed from power by John Dudley, who is known as Lord President Northumberland. Northumberland proceeded to adopt the power for himself, but he was more conciliatory and the Council accepted him. During Edward's reign England changed from being a Catholic nation to a Protestant one, in schism from Rome.
Edward showed great promise but fell violently ill of tuberculosis in 1553 and died that August, two months before his 16th birthday. Northumberland made plans to place Lady Jane Grey on the throne and marry her to his son, so that he could remain the power behind the throne. His plot failed in a matter of days, Jane Grey was beheaded, and Mary I (1516–1558) took the throne amidst popular demonstration in her favour in London, which contemporaries described as the largest show of affection for a Tudor monarch. Mary had never been expected to hold the throne, at least not since Edward was born. She was a devoted Catholic who believed that she could reverse the Reformation.
Returning England to Catholicism led to the burnings of 274 Protestants, which are recorded especially in John Foxe's Book of Martyrs. Mary then married her cousin Philip, son of Emperor Charles V, and King of Spain when Charles abdicated in 1556. The union was difficult because Mary was already in her late 30s and Philip was a Catholic and a foreigner, and so not very welcome in England. This wedding also provoked hostility from France, already at war with Spain and now fearing being encircled by the Habsburgs. Calais, the last English outpost on the Continent, was then taken by France. King Philip (1527–1598) had very little power, although he did protect Elizabeth. He was not popular in England, and spent little time there. Mary eventually became pregnant, or at least believed herself to be. In reality, she may have had uterine cancer. Her death in November 1558 was greeted with huge celebrations in the streets of London.
Elizabeth I and the Elizabethan era
Main article: Elizabethan era
After Mary I died in 1558, Elizabeth I came to the throne. Her reign restored a sort of order to the realm after the turbulent reigns of Edward VI and Mary I. The religious issue which had divided the country since Henry VIII was in a way put to rest by the Elizabethan Religious Settlement, which re-established the Church of England. Much of Elizabeth's success was in balancing the interests of the Puritans and Catholics; historian Robert Bucholz paraphrasing historian Conrad Russell, suggested that the genius of the Church of England was that it "thinks Protestant but looks Catholic." She managed to offend neither to a large extent, although she clamped down on Catholics towards the end of her reign as war with Catholic Spain loomed.
Despite the need for an heir, Elizabeth declined to marry, despite offers from a number of suitors across Europe, including the Swedish king Erik XIV. This created endless worries over her succession, especially in the 1560s when she nearly died of smallpox. It has been often rumoured that she had a number of lovers (including Francis Drake), but there is no hard evidence. Elizabeth maintained relative government stability. Apart from the Revolt of the Northern Earls in 1569, she was effective in reducing the power of the old nobility and expanding the power of her government. Elizabeth's government did much to consolidate the work begun under Thomas Cromwell in the reign of Henry VIII, that is, expanding the role of the government and effecting common law and administration throughout England. During the reign of Elizabeth and shortly afterwards, the population grew significantly: from three million in 1564 to nearly five million in 1616.
The queen ran afoul of her cousin Mary, Queen of Scots, who was a devoted Catholic and so was forced to abdicate her throne (Scotland had recently become Protestant). She fled to England, where Elizabeth immediately had her arrested. Mary spent the next 19 years in confinement, but proved too dangerous to keep alive, as the Catholic powers in Europe considered her the legitimate ruler of England. She was eventually tried for treason, sentenced to death, and beheaded in February 1587.

The Elizabethan era was the epoch in English history of Queen Elizabeth I's reign (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The symbol of Britannia was first used in 1572 and often thereafter to mark the Elizabethan age as a renaissance that inspired national pride through classical ideals, international expansion, and naval triumph over the hated Spanish foe. In terms of the entire century, the historian John Guy (1988) argues that "England was economically healthier, more expansive, and more optimistic under the Tudors" than at any time in a thousand years.
This "golden age" represented the apogee of the English Renaissance and saw the flowering of poetry, music and literature. The era is most famous for theatre, as William Shakespeare and many others composed plays that broke free of England's past style of theatre. The growing population of England, the growing wealth of its people, and their fondness for spectacle produced a dramatic literature of remarkable quality. The English theatre scene, which performed both for the court and nobility in private performances and a very wide public in the theatres, was the most crowded in Europe.
It was also an age of exploration and expansion abroad, while back at home, the Protestant Reformation became more acceptable to the people, most certainly after the Spanish Armada was repulsed. It was also the end of the period when England was a separate realm before its royal union with Scotland. Elizabethan England avoided major defeats and built up a powerful navy. On balance, it can be said that Elizabeth I provided the country with a long period of general if not total peace and generally increased prosperity. Having inherited a virtually bankrupt state from previous reigns, her policies restored fiscal responsibility. Her fiscal restraint cleared the regime of debt by 1574, and ten years later the English crown enjoyed a surplus of £300,000.

Under Elizabeth I crafts and manufacturing activities received a boost. Glass, ceramic, silk industry and exports of wool manufactures could be promoted. Economically, Sir Thomas Gresham's founding of the Royal Exchange (1565), the first stock exchange in England and one of the earliest in Europe, proved to be a development of the first importance, for the economic development of England and soon for the world as a whole. With taxes lower than other European countries of the period, the economy expanded; there was clearly more wealth to go around at the end of Elizabeth's reign than at the beginning. This general peace and prosperity allowed the attractive developments of the "golden age". The Elizabethan era is famous for its playwrights that thrived during this period; Francis Drake, the first Englishman to circumnavigate the world; and Walter Raleigh's exploration of the New World. The stability and structure of the government helped to allow the arts to flourish and prompted other achievements in exploration.
The earliest joint-stock company recognized in England was the Company of Merchant Adventurers to New Lands, founded in 1551 with 240 shareholders. It became the Muscovy Company, which had a monopoly on trade between Russia and England, when royal charter was granted in 1555. The most notable joint-stock company from the British Isles was the East India Company, which was granted a royal charter by Elizabeth I on December 31, 1600 with the intention of establishing trade on the Indian subcontinent. The charter effectively granted the newly formed Honourable East India Company a fifteen-year monopoly on all English trade in the East Indies. The company rose to account for half of the world's trade during the mid-1700s and early 1800s. The development of English naval power and the interest in voyages of discovery led to the acquisition and settlement of overseas colonies, particularly in North America and the Caribbean.
The Elizabethan age is said to be viewed highly largely because of the periods before and after. It was a brief period of largely internal peace after the horrible violence and disorder of the Wars of the Roses, and battles between Catholics and Protestants during the English Reformation; and it preceded the violent turmoil of the English Civil War and battles between parliament and the monarchy during the 17th century. The Protestant/Catholic divide was settled, for a time, by the Elizabethan Religious Settlement, and parliament was not yet strong enough to challenge royal absolutism.
England was also well off compared to the other nations of Europe. The Italian Renaissance had ended due to foreign domination of the peninsula. France was embroiled in religious battles until the Edict of Nantes in 1598. Also, the English had been expelled from their last outposts on the continent. Due to these reasons, the centuries long conflict with France was largely suspended for most of Elizabeth's reign. England during this period had a centralised, organised and effective government, largely due to the reforms of Henry VII and Henry VIII. Economically, the country began to benefit greatly from the new era of trans-Atlantic trade.
In 1585 worsening relations between Philip II of Spain and Elizabeth erupted into war. Elizabeth signed the Treaty of Nonsuch with the Dutch and permitted Francis Drake to maraud in response to a Spanish embargo. Drake surprised Vigo, Spain, in October, then proceeded to the Caribbean and sacked Santo Domingo (the capital of Spain's American empire and the present-day capital of the Dominican Republic) and Cartagena (a large and wealthy port on the north coast of Colombia that was the centre of the silver trade). Philip II tried to invade England with the Spanish Armada in 1588 but was famously defeated.
The Armada was not just a naval campaign. The build-up of land forces to resist a Spanish invasion has been described as an administrative feat of massive scope. A survey taken in November and December 1587 showed 130,000 men in the militia, of whom 44,000 were members of the trained bands, being drilled and led by experienced captains and sergeants. By May 1588 the London bands were drilling weekly. To give warning of the enemy's approach, beacons were built, manned twenty-four hours a day by four men. Once the beacons were lit, 72,000 men could be mobilised on the south coast, with another 46,000 protecting London. For the many Englishmen caught up in the Armada the experience must have been very profound and frightening. Some shared the intimacy of beacon watching, hoping for the best, but ready to light their warning fires in case of the worst. Deloney, a London silkweaver, played on their fears in his "New Ballet on the strange whippes which the Spanyards had prepared to whippe English men" (1588). The political philosopher Thomas Hobbes recalled that his mother was so frightened that she prematurely gave birth to twins, of whom he was one. All were terrified about what might happen if the Spanish invaded. Stories of the Sack of Antwerp in 1576, in which the Spanish led by Sancho d'Avila raped, tortured and murdered as many as 17,000 civilians, were grist for playwrights and pamphleteers such as George Gascoigne and Shakespeare. The former remembered seeing civilians at Antwerp drowned, burned, or with guts hanging out as if they had been used for an anatomy lesson. Few Englishmen, women and children doubted they faced similar fates had the Armada landed.

In foreign policy, Elizabeth played against each other the major powers France and Spain, as well as the papacy and Scotland. These were all Catholic and each wanted to end Protestantism in England. Elizabeth was cautious in foreign affairs and only half-heartedly supported a number of ineffective, poorly resourced military campaigns in the Netherlands, France and Ireland. She risked war with Spain by supporting the "Sea Dogs", such as Walter Raleigh, John Hawkins and Sir Francis Drake, who preyed on Spanish merchant ships carrying gold and silver from the New World. Drake himself became a hero—being the first Englishman to circumnavigate the world between 1577 and 1580 and the third person overall in history, having plundered Spanish settlements and treasure ships. The major war came with Spain, 1585–1603. When Spain tried to invade and conquer England it was a fiasco, and the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588 associated Elizabeth's name with what is popularly viewed as one of the greatest victories in English history. Her enemies failed to combine and Elizabeth's foreign policy successfully navigated all the dangers.
In all, the Tudor period is seen as a decisive one which set up many important questions which would have to be answered in the next century and during the English Civil War. These were questions of the relative power of the monarch and Parliament and to what extent one should control the other. Some historians think that Thomas Cromwell affected a "Tudor Revolution" in government, and it is certain that Parliament became more important during his chancellorship. Other historians argue that the "Tudor Revolution" extended to the end of Elizabeth's reign, when the work was all consolidated. Although the Privy Council declined after Elizabeth's death, it was very effective while she was alive. Elizabeth died in 1603 at the age of 69, ending the rule of the Tudor dynasty.
Jacobean era
Main articles: Early modern Britain and Jacobean era Further information: English overseas possessions
When Elizabeth died, her closest male Protestant relative was the King of Scots, James VI, of the House of Stuart, who became King James I of England in a Union of the Crowns, called James I and VI. He was the first monarch to rule the entire island of Britain, but the countries remained separate politically. Upon taking power, James made peace with Spain, and for the first half of the 17th century, England remained largely inactive in European politics. Several assassination attempts were made on James, notably the Main Plot and Bye Plots of 1603, and most famously, on 5 November 1605, the Gunpowder Plot, by a group of Catholic conspirators, led by Robert Catesby, which caused more antipathy in England towards Catholicism. During the Jacobean era, drama, literature, architecture, and art continued to flourish.
In 1607 England built an establishment at Jamestown. This was the beginning of colonialism by England in North America. Many English settled then in North America for religious or economic reasons. Approximately 70% of English immigrants to North America who came between 1630 and 1660 were indentured servants. By 1700, Chesapeake planters transported about 100,000 indentured servants, who accounted for more than 75% of all European immigrants to Virginia and Maryland.
King James I was sincerely devoted to peace, not just for his three kingdoms but for Europe as a whole. He called himself "Rex Pacificus" ("King of peace.") Europe was deeply polarized, and on the verge of the massive Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), with the smaller established Protestant states facing the aggression of the larger Catholic empires. On assuming the throne, James made peace with Catholic Spain, and made it his policy to marry his daughter to the Spanish prince. The marriage of James' daughter Princess Elizabeth to Frederick V, Elector Palatine on 14 February 1613 was more than the social event of the era; the couple's union had important political and military implications. Historians credit James for pulling back from a major war at the last minute, and keeping Britain in peace.
In literature, some of Shakespeare's most prominent plays, including King Lear (1605), Macbeth (1606), and The Tempest (1610), were written during the reign of James I. Also during this period were powerful works by John Webster, Thomas Middleton, John Ford and Ben Jonson. Ben Jonson also contributed to some of the era's best poetry, together with the Cavalier poets and John Donne. In prose, the most representative works are found in those of Francis Bacon and the King James Bible. Francis Bacon had a strong influence in the evolution of modern science, which was entering a key phase in this era, as the work of Johannes Kepler in Germany and Galileo Galilei in Italy brought the Copernican revolution to a new level of development. Bacon laid a foundation, and was a powerful and persuasive advocate, for objective inquiry about the natural world in place of the Medieval scholastic authoritarianism that still influenced the culture of British society in his lifetime. On practical rather than general levels, much work was being done in the areas of navigation, cartography, and surveying.
Stuart and Caroline eras
Main articles: Stuart period and Caroline eraThe Stuart period of English history lasted from 1603 to 1714 during the dynasty of the House of Stuart. The period ended with the death of Queen Anne and the accession of King George I from the House of Hanover. The period was plagued by internal and religious strife, and a large-scale civil war which resulted in the execution of King Charles I in 1649. The Interregnum, largely under the control of Oliver Cromwell, is included here for continuity, even though the Stuarts were in exile. The Cromwell regime collapsed and Charles II had very wide support for his taking of the throne in 1660. His brother James II was overthrown in 1689 in the Glorious Revolution. He was replaced by his Protestant daughter Mary II and her Dutch husband William III. Mary's sister Anne was the last of the line. For the next half century James II and his son James Francis Edward Stuart and grandson Charles Edward Stuart claimed that they were the true Stuart kings, but they were in exile and their attempts to return with French aid were defeated. Lterature, poetry, architecture, and high art flourished throughout England.
The Caroline era was dominated by growing religious, political, and social discord between the King and his supporters, termed the Royalist party, and the Parliamentarian opposition that evolved in response to particular aspects of Charles I's rule. While the Thirty Years' War was raging in continental Europe, England and Scotland had an uneasy peace, growing more restless as the civil conflict between the King and the supporters of Parliament worsene. The Caroline era followed the Jacobean era, the reign of Charles's father James I & VI (1603–1625), overlapped with the English Civil War (1642–1651), and was followed by the English Interregnum until The Restoration in 1660. It should not be confused with the Carolean era which refers to the reign of Charles I's son King Charles II.

Despite the friction between King and Parliament dominating society, there were developments in the arts and sciences. The period also saw the colonisation of North America with the foundation of new colonies between 1629 and 1636 in Carolina, Maryland, Connecticut and Rhode Island. Development of colonies in Virginia, Massachusetts, and Newfoundland also continued. In Massachusetts, the Pequot War of 1637 was the first major armed conflict between New England settlers and a Native American people.
The highest standards of the arts and architecture all flourished under the patronage of the King. All the arts were greatly impacted by the enormous political and religious controversies, and the degree to which they were themselves influential is a matter of ongoing debate among scholars. The Caroline period saw the flourishing of the cavalier poets (including Thomas Carew, Richard Lovelace, and John Suckling) and the metaphysical poets (including George Herbert, Henry Vaughan, Katherine Philips), movements that produced figures like John Donne, Robert Herrick and John Milton. George Wither was a prolific poet, pamphleteer, satirist and writer of hymns. He is best known for "Britain's Remembrancer" of 1625, with its wide range of contemporary topics including the plague and politics. It reflects on nature of poetry and prophecy, explores the fault lines in politics, and rejects tyranny of the sort the king was denounced for fostering. It warns about the wickedness of the times and prophesizes that disasters are about to befall the kingdom.
Out in the countryside, numerous architects built country houses – the more magnificent the better, for the nobility and the wealthier gentry. Inigo Jones, one of the most well-known of Stuart-era architects built the magnificent Banqueting House in Whitehall, London in 1622. Numerous architects worked on the decorative arts, designing intricate wainscoted rooms, dramatic staircases, lush carpets, furniture, and clocks in country houses open to tourism. In science, the Royal Society was formed in 1660; it sponsored and legitimised a renaissance of major discoveries, led most notably by Isaac Newton, Robert Boyle and Robert Hooke. New scientific discoveries were made during this period, such as the laws of gravity and motion, Boyle's law and microscopy among many others. The period also witnessed the growth of a culture of political news and commentary on political events. This was engaged in by both elites and laypeople, often involving a critical view or "skeptical reading".
The first coffee houses appeared in the mid-1650s and quickly became established in every city in many small towns. They exemplified the emerging standards of middle-class masculine civility and politeness. Downtown London boasted about 600 by 1708. Admission was a penny for as long as a customer wanted. The customers could buy coffee, and perhaps tea and chocolate, as well as sandwiches and knickknacks. Recent newspapers and magazines could be perused by middle-class men with leisure time on their hands. Widows were often the proprietors. The coffeehouses were quiet escapes, suitable for conversation, and free of noise, disorder, shouting and fighting in drinking places. The working class could more usually be found drinking in pubs, or playing dice in the alleyways.
According to Derek Hirst, the 1640s and 1650s saw a revived economy characterised by growth in manufacturing, the elaboration of financial and credit instruments, and the commercialisation of communication. The gentry found time for leisure activities, such as horse racing and bowling. In the high culture important innovations included the development of a mass market for music, increased scientific research, and an expansion of publishing. All the trends were discussed in depth at the newly established coffee houses.
The Anglo-Dutch Wars were a series of three wars which took place between the English and the Dutch from 1652 to 1674. The causes included political disputes and increasing competition from merchant shipping. The English in the First Anglo-Dutch War (1652–54) had the naval advantage with larger numbers of more powerful "ships of the line" which were well suited to the naval tactics of the era. The English also captured numerous Dutch merchant ships.
The government supported the private sector by incorporating numerous privately financed London-based companies for establishing trading posts and opening import-export businesses across the world. Each was given a monopoly of trade to the specified geographical region. The first enterprise was the Muscovy Company set up in 1555 to trade with Russia. Other prominent enterprises included he East India Company (1599), and the Hudson's Bay Company (1670) in Canada. The Company of Royal Adventurers Trading to Africa had been set up in 1662 to trade in gold, ivory and slaves in Africa; it was reestablished as the Royal African Company in 1672 and focused on the slave trade. Other powers set up similar monopolies on a much smaller scale; only the Netherlands emphasised trade as much as England. The English gained dominance in the trade with India, and largely dominated the highly lucrative slave, sugar, and commercial trades originating in West Africa and the West Indies. Exports were stable at £2.5 million from 1613 to 1669, then soared £6.5 million in 1700.
English Civil War and the Commonwealth Republic
Further information: English Civil War
The First English Civil War broke out in 1642, largely due to ongoing conflicts between James' son, Charles I, and Parliament. The defeat of the Royalist army by the New Model Army of Parliament at the Battle of Naseby in June 1645 effectively destroyed the king's forces. Charles surrendered to the Scottish army at Newark. He was eventually handed over to the English Parliament in early 1647. He escaped, and the Second English Civil War began, but the New Model Army quickly secured the country. The capture and trial of Charles led to the execution of Charles I in January 1649 at Whitehall Gate in London, making England a republic. This shocked the rest of Europe. The king argued to the end that only God could judge him.
Charles I avoided calling a Parliament for the next decade, a period known as the "personal rule of Charles I", or the "Eleven Years' Tyranny". During this period, Charles's policies were determined by his lack of money. First and foremost, to avoid Parliament, the King needed to avoid war. Charles made peace with France and Spain, effectively ending England's involvement in the Thirty Years' War. However, that in itself was far from enough to balance the Crown's finances. Unable to raise revenue without Parliament and unwilling to convene it, Charles resorted to other means. One was to revive conventions, often outdated. For example, a failure to attend and receive knighthood at Charles's coronation became a finable offence with the fine paid to the Crown. The King also tried to raise revenue through ship money, demanding in 1634–1636 that the inland English counties pay a tax for the Royal Navy to counter the threat of privateers and pirates in the English Channel. Established law supported the policy of coastal counties and inland ports such as London paying ship money in times of need, but it had not been applied to inland counties before. Authorities had ignored it for centuries, and many saw it as yet another extra-Parliamentary, illegal tax, which prompted some prominent men to refuse to pay it. Charles issued a writ against John Hampden for his failure to pay, and although five judges including Sir George Croke supported Hampden, seven judges found in favour of the King in 1638. The fines imposed on people who refused to pay ship money and standing out against its illegality aroused widespread indignation.
During his "Personal Rule", Charles aroused most antagonism through his religious measures. He believed in High Anglicanism, a sacramental version of the Church of England, theologically based upon Arminianism, a creed shared with his main political adviser, Archbishop William Laud. In 1633, Charles appointed Laud Archbishop of Canterbury and started making the Church more ceremonial, replacing the wooden communion tables with stone altars. Puritans accused Laud of reintroducing Catholicism; when they complained, he had them arrested. In 1637, John Bastwick, Henry Burton, and William Prynne had their ears cut off for writing pamphlets attacking Laud's views — a rare penalty for gentlemen, and one that aroused anger. Moreover, the Church authorities revived statutes from the time of Elizabeth I about church attendance and fined Puritans for not attending Anglican services.

The Presbyterian system, even more rigid than that of the Archbishop of Canterbury, William Laud and the other bishops, whom few on either side except Charles himself supported, seemed destined for replacement by the Independents and by their ideal of free conscience. But for a generation before the war broke out, the system had disciplined and trained the middle classes of the nation (who furnished the bulk of the rebel infantry, and later, of the cavalry also) to centre their will on the attainment of their ideals. The ideals changed during the struggle, but not the capacity for striving for them, and the men capable of the effort finally came to the front, and imposed their ideals on the rest by the force of their trained wills. The parliamentarians had the stronger material force. They controlled the navy, the nucleus of an army that was being organised for the Irish war, and nearly all the financial resources of the country. They had the sympathies of most of the large towns, where the trained bands, drilled once a month, provided cadres for new regiments. Also, by recognising that war was likely, they prepared for war before Royalists did.
The Earl of Warwick, the Earl of Essex, the Earl of Manchester, and other nobles and gentry of the Parliamentary party had great wealth and territorial influence. On the other hand, Charles could raise men without authority from Parliament by using impressment and the Lords-Lieutenant, but could not raise taxes to support them. Thus he depended on financial support from his adherents, such as the Earl of Newcastle and the Earl of Derby. The New Model Army, commanded by Oliver Cromwell, then scored decisive victories against Royalist armies in Ireland and Scotland. Cromwell was given the title Lord Protector in 1653, making him 'king in all but name' to his critics. After he died in 1658, his son Richard Cromwell succeeded him in the office but he was forced to abdicate within a year. For a while it seemed as if a new civil war would begin as the New Model Army split into factions. Troops stationed in Scotland under the command of George Monck eventually marched on London to restore order.

Many concerns were raised over Charles's marriage in 1625 to a Roman Catholic French princess: Henrietta Maria. Parliament refused to assign him the traditional right to collect customs duties for his entire reign, deciding instead to grant it only on a provisional basis and negotiate with him. Charles, meanwhile, decided to send an expeditionary force to relieve the French Huguenots, whom French royal troops held besieged in La Rochelle. Such military support for Protestants on the Continent potentially alleviated concerns about the King's marriage to a Catholic. However, Charles's insistence on giving command of the English force to his unpopular royal favourite George Villiers, the Duke of Buckingham, undermined that support. Unfortunately for Charles and Buckingham, the relief expedition proved a fiasco (1627), and Parliament, already hostile to Buckingham for his monopoly on royal patronage, opened impeachment proceedings against him. Charles responded by dissolving Parliament. This saved Buckingham but confirmed the impression that Charles wanted to avoid Parliamentary scrutiny of his ministers.
Having dissolved Parliament and unable to raise money without it, the king assembled a new one in 1628. (The elected members included Oliver Cromwell, John Hampden, and Edward Coke.) The new Parliament drew up a Petition of Right, which Charles accepted as a concession to obtain his subsidy. The Petition made reference to Magna Carta, but did not grant him the right of tonnage and poundage, which Charles had been collecting without Parliamentary authorisation since 1625. Several more active members of the opposition were imprisoned, which caused outrage; one, John Eliot, subsequently died in prison and came to be seen as a martyr for the rights of Parliament.
On Tuesday, 4 January 1642, the King entered the House with armed men to arrest the Five Members. They had been warned and fled. The new Parliament proved even more hostile to Charles than its predecessor. It immediately began to discuss grievances against him and his government, with Pym and Hampden (of ship money fame) in the lead. They took the opportunity presented by the King's troubles to force various reforming measures — including many with strong "anti-Papist" themes — upon him. The members passed a law stating that a new Parliament would convene at least once every three years — without the King's summons if need be. Other laws passed making it illegal for the king to impose taxes without Parliamentary consent and later gave Parliament control over the king's ministers. Finally, the Parliament passed a law forbidding the King to dissolve it without its consent, even if the three years were up. Ever since this Parliament has been known as the Long Parliament. However, Parliament did attempt to avert conflict by requiring all adults to sign The Protestation, an oath of allegiance to Charles.
Early in the Long Parliament, the house overwhelmingly accused Thomas Wentworth, Earl of Strafford of high treason and other crimes and misdemeanors. Henry Vane the Younger supplied evidence of Strafford's claimed improper use of the army in Ireland, alleging that he had encouraged the King to use his Ireland-raised forces to threaten England into compliance. This evidence was obtained from Vane's father, Henry Vane the Elder, a member of the King's Privy council, who refused to confirm it in Parliament out of loyalty to Charles. On 10 April 1641, Pym's case collapsed, but Pym made a direct appeal to Henry Vane the Younger to produce a copy of the notes from the King's Privy council, discovered by the younger Vane and secretly turned over to Pym, to the great anguish of the Elder Vane. These notes contained evidence that Strafford had told the King, "Sir, you have done your duty, and your subjects have failed in theirs; and therefore you are absolved from the rules of government, and may supply yourself by extraordinary ways; you have an army in Ireland, with which you may reduce the kingdom."
Pym immediately launched a Bill of Attainder stating Strafford's guilt and demanding that he be put to death. Unlike a guilty verdict in a court case, attainder did not require a legal burden of proof, but it did require the king's approval. Charles, however, guaranteed Strafford that he would not sign the attainder, without which the bill could not be passed. Furthermore, the Lords opposed the severity of a death sentence on Strafford. Yet increased tensions and a plot in the army to support Strafford began to sway the issue. On 21 April, the Commons passed the Bill (204 in favour, 59 opposed, and 250 abstained), and the Lords acquiesced. Charles, still incensed over the Commons' handling of Buckingham, refused his assent. Strafford himself, hoping to head off the war he saw looming, wrote to the king and asked him to reconsider. Charles, fearing for the safety of his family, signed on 10 May. Strafford was beheaded two days later. In the meantime both Parliament and the King agreed to an independent investigation into the king's involvement in Strafford's plot.

The Long Parliament then passed the Triennial Act, also known as the Dissolution Act in May 1641, to which the Royal Assent was readily granted. The Triennial Act required Parliament to be summoned at least once in three years. When the King failed to issue a proper summons, the members could assemble on their own. This act also forbade ship money without Parliament's consent, fines in distraint of knighthood, and forced loans. Monopolies were cut back sharply, the Courts of the Star Chamber and High Commission abolished by the Habeas Corpus Act 1640, and the Triennial Act respectively. All remaining forms of taxation were legalised and regulated by the Tonnage and Poundage Act. On 3 May, Parliament decreed The Protestation, attacking the 'wicked counsels' of Charles's government, whereby those who signed the petition undertook to defend 'the true reformed religion', Parliament, and the king's person, honour and estate. Throughout May, the House of Commons launched several bills attacking bishops and Episcopalianism in general, each time defeated in the Lords.
Charles and his Parliament hoped that the execution of Strafford and the Protestation would end the drift towards war, but in fact, they encouraged it. Charles and his supporters continued to resent Parliament's demands, and Parliamentarians continued to suspect Charles of wanting to impose episcopalianism and unfettered royal rule by military force. Within months, the Irish Catholics, fearing a resurgence of Protestant power, struck first, and all Ireland soon descended into chaos. Rumors circulated that the King supported the Irish, and Puritan members of the Commons soon started murmuring that this exemplified the fate that Charles had in store for them all. In early January 1642, Charles, accompanied by 400 soldiers, attempted to arrest five members of the House of Commons on a charge of treason. This attempt failed. When the troops marched into Parliament, Charles enquired of William Lenthall, the Speaker, as to the whereabouts of the five. Lenthall replied, "May it please your Majesty, I have neither eyes to see nor tongue to speak in this place but as the House is pleased to direct me, whose servant I am here." So the Speaker proclaimed himself a servant of Parliament, rather than the King.

The wars left England, Scotland, and Ireland among the few countries in Europe without a monarch. In the wake of victory, many of the ideals (and many idealists) became sidelined. The republican government of the Commonwealth of England ruled England (and later all of Scotland and Ireland) from 1649 to 1653 and from 1659 to 1660. Between the two periods, and due to in-fighting among various factions in Parliament, Oliver Cromwell ruled over the Protectorate as Lord Protector (effectively a military dictator) until his death in 1658. On Oliver Cromwell's death, his son Richard became Lord Protector, but the Army had little confidence in him. After seven months the Army removed Richard, and in May 1659 it re-installed the Rump. However, since the Rump Parliament acted as though nothing had changed since 1653 and as though it could treat the Army as it liked, military force shortly afterward dissolved this as well. After the second dissolution of the Rump, in October 1659, the prospect of a total descent into anarchy loomed as the Army's pretense of unity finally dissolved into factions.
Into this atmosphere General George Monck, Governor of Scotland under the Cromwells, marched south with his army from Scotland. On 4 April 1660, in the Declaration of Breda, Charles II made known the conditions of his acceptance of the Crown of England. Monck organised the Convention Parliament, which met for the first time on 25 April 1660. On 8 May 1660, it declared that Charles II had reigned as the lawful monarch since the execution of Charles I in January 1649. Charles returned from exile on 23 May 1660. On 29 May 1660, the populace in London acclaimed him as king. His coronation took place at Westminster Abbey on 23 April 1661. These events became known as the Restoration.
The New Model Army, commanded by Oliver Cromwell, then scored decisive victories against Royalist armies in Ireland and Scotland. Cromwell was given the title Lord Protector in 1653, making him 'king in all but name' to his critics. After he died in 1658, his son Richard Cromwell succeeded him in the office but he was forced to abdicate within a year. For a while it seemed as if a new civil war would begin as the New Model Army split into factions. Troops stationed in Scotland under the command of George Monck eventually marched on London to restore order.
Restoration era and Merry Monarch
Main article: Stuart Restoration
The Restoration of the Stuart monarchy in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland took place in 1660 when King Charles II (The Merry Monarch) returned from exile in continental Europe. The preceding period of the Protectorate and the civil wars came to be known as the Interregnum (1649–1660). The term Restoration is also used to describe the period of several years after, in which a new political settlement was established. It is very often used to cover the whole reign of King Charles II (1660–1685) and often the brief reign of his younger brother King James II (1685–1688). In certain contexts it may be used to cover the whole period of the later Stuart monarchs as far as the death of Queen Anne.
In 4 April 1660, Charles II issued the Declaration of Breda, in which he made several promises in relation to the reclamation of the crown of England. Monck organised the Convention Parliament, which met for the first time on 25 April. On 8 May it proclaimed that King Charles II had been the lawful monarch since the execution of Charles I on 30 January 1649. Historian Tim Harris describes it: "Constitutionally, it was as if the last nineteen years had never happened." Charles returned from exile, leaving the Hague on 23 May and landing at Dover on 25 May. He entered London on 29 May 1660, his 30th birthday. To celebrate His Majesty's Return to his Parliament, 29 May was made a public holiday, popularly known as Oak Apple Day. He was crowned at Westminster Abbey on 23 April 1661.
By the 18th century, England rivaled the Netherlands as one of the freest countries in Europe. Some contemporaries described the Restoration as "a divinely ordained miracle". The sudden and unexpected deliverance from political chaos was interpreted as a restoration of the natural and divine order. The Cavalier Parliament convened for the first time on 8 May 1661, and it would endure for over 17 years, finally being dissolved on 24 January 1679. Like its predecessor, it was overwhelmingly Royalist. It is also known as the Pensionary Parliament for the many pensions it granted to adherents of the King. The leading political figure at the beginning of the Restoration was Edward Hyde, 1st Earl of Clarendon. It was the "skill and wisdom of Clarendon" which had "made the Restoration unconditional". Many Royalist exiles returned and were rewarded. Prince Rupert of the Rhine returned to the service of England, became a member of the privy council, and was provided with an annuity. George Goring, 1st Earl of Norwich, returned to be the Captain of the King's guard and received a pension. Marmaduke Langdale returned and was made "Baron Langdale". William Cavendish, Marquess of Newcastle, returned and was able to regain the greater part of his estates. He was invested in 1666 with the Order of the Garter (which had been bestowed upon him in 1650), and was advanced to a dukedom on 16 March 1665.
The Restoration and Charles' coronation mark a reversal of the stringent Puritan morality, "as though the pendulum swung from repression to licence more or less overnight". Theatres reopened after having been closed during the protectorship, Puritanism lost its momentum, and bawdy comedy became a recognisable genre. In addition, women were allowed to perform on the commercial stage as professional actresses for the first time. In Scotland, the bishops returned as the Episcopacy was reinstated. To celebrate the occasion and cement their diplomatic relations, the Dutch Republic presented Charles with the Dutch Gift, a fine collection of old master paintings, classical sculptures, furniture, and a yacht. With the reopening of the theaters, fine art, literature, drama, and performing arts flourished. Restoration literature includes the roughly homogenous styles of literature that centre on a celebration of or reaction to the restored court of King Charles II. It is a literature that includes extremes, for it encompasses both Paradise Lost and the John Wilmot, 2nd Earl of Rochester's Sodom, the high-spirited sexual comedy of The Country Wife and the moral wisdom of The Pilgrim's Progress. It saw Locke's Treatises of Government, the founding of the Royal Society, the experiments and holy meditations of Robert Boyle, the hysterical attacks on theatres from Jeremy Collier, and the pioneering of literary criticism from John Dryden and John Dennis. The period witnessed news become a commodity, the essay develop into a periodical art form, and the beginnings of textual criticism.
The Restoration spectacular, or elaborately staged machine play, hit the London public stage in the late 17th-century Restoration period, enthralling audiences with action, music, dance, moveable scenery baroque illusionistic painting, gorgeous costumes, and special effects such as trapdoor tricks, "flying" actors, and fireworks.. Comedy, especially bawdy comedy, flourished, and a favourite setting was the bed-chamber. Indeed, sexually explicit language was encouraged by the king personally and by the rakish style of his court. The founding of the Royal Society in 1660 laid the foundations of modern experimental science.
In 1665, London was swept by the plague, and in 1666 by the Great Fire for 5 days which destroyed about 15,000 buildings. By the 1660s, London was by far the largest city in Britain, estimated at half a million inhabitants. However, due to the Great Plague of London during the previous winter, its population had decreased. London had been a Roman settlement for four centuries and had become progressively more crowded inside its defensive and large city wall. It had also pushed outwards beyond the wall and had reached far enough to include the independent City of Westminster.

The aristocracy shunned the City and lived either in the countryside beyond the slum suburbs, or in the exclusive Westminster district (the modern West End), the site of King Charles II's court at Whitehall. Wealthy people preferred to live at a convenient distance from the traffic-clogged, polluted, unhealthy City, especially after it was hit by a devastating outbreak of bubonic plague in the Plague Year of 1665. The relationship was often tense between the City and the Crown. The City of London had been a stronghold of republicanism during the Civil War (1642–1651), and the wealthy and economically dynamic capital still had the potential to be a threat to Charles II, as had been demonstrated by several republican uprisings in London in the early 1660s. The City magistrates were of the generation that had fought in the Civil War, and could remember how Charles I's grab for absolute power had led to that national trauma.
They were determined to thwart any similar tendencies in his son, and when the Great Fire threatened the City, they refused the offers that Charles made of soldiers and other resources. Even in such an emergency, the idea of having the unpopular Royal troops ordered into the City was political dynamite. By the time that Charles took over command from the ineffectual Lord Mayor, the fire was already out of control. The Great Fire of London swept the English city of London from Sunday, 2 September to Thursday, 6 September 1666. The fire gutted the medieval City of London inside the old Roman city wall. It threatened but did not reach the aristocratic district of Westminster, Charles II's Palace of Whitehall, or most of the suburban slums. It destroyed 13,200 houses, 87 parish churches, St Paul's Cathedral, and most of the buildings of the City authorities. It is estimated to have destroyed the homes of 70,000 of the city's 80,000 inhabitants. Despite several radical proposals, London was reconstructed on essentially the same street plan used before the fire.

Radical rebuilding schemes poured in for the gutted City and were encouraged by Charles. If it had been rebuilt under some of these plans, London would have rivalled Paris in Baroque magnificence. The Crown and the City authorities attempted to establish "to whom all the houses and ground did in truth belong" to negotiate with their owners about compensation for the large-scale remodelling that these plans entailed, but that unrealistic idea had to be abandoned due to England's strict property rights.
Exhortations to bring workmen and measure the plots on which the houses had stood were mostly ignored by people worried about day-to-day survival, as well as by those who had left the capital; for one thing, with the shortage of labour following the fire, it was impossible to secure workmen for the purpose. Apart from Wren and Evelyn, it is known that Robert Hooke, Valentine Knight, and Richard Newcourt proposed rebuilding plans. With the complexities of ownership unresolved, none of the grand Baroque schemes could be realised for a City of piazzas and avenues; there was nobody to negotiate with, and no means of calculating how much compensation should be paid. Instead, much of the old street plan was recreated in the new City, with improvements in hygiene and fire safety: wider streets, open and accessible wharves along the length of the Thames, with no houses obstructing access to the river, and, most importantly, buildings constructed of brick and stone, not wood. New public buildings were created on their predecessors' sites; perhaps the most famous is St Paul's Cathedral and its smaller cousins, Christopher Wren's 50 new churches.
Glorious Revolution
Main article: Glorious Revolution
In 1680, the Exclusion Crisis consisted of attempts to prevent accession of James, heir to Charles II, because he was Catholic. After Charles II died in 1685 and his younger brother, James II and VII was crowned, various factions pressed for his Protestant daughter Mary and her husband Prince William III of Orange to replace him in what became known as the Glorious Revolution. In November 1688, William invaded England and succeeded in being crowned. James tried to retake the throne in the Williamite War, but was defeated at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690.
In December 1689, one of the most important constitutional documents in English history, the Bill of Rights, was passed. The Bill, which restated and confirmed many provisions of the earlier Declaration of Right, established restrictions on the royal prerogative. For example, the Sovereign could not suspend laws passed by Parliament, levy taxes without parliamentary consent, infringe the right to petition, raise a standing army during peacetime without parliamentary consent, deny the right to bear arms to Protestant subjects, unduly interfere with parliamentary elections, punish members of either House of Parliament for anything said during debates, require excessive bail or inflict cruel and unusual punishments. William was opposed to such constraints, but chose to avoid conflict with Parliament and agreed to the statute.
In parts of Scotland and Ireland, Catholics loyal to James remained determined to see him restored to the throne, and staged a series of bloody uprisings. As a result, any failure to pledge loyalty to the victorious King William was severely dealt with. The most infamous example of this policy was the Massacre of Glencoe in 1692. Jacobite rebellions continued into the mid-18th century until the son of the last Catholic claimant to the throne, James III and VIII, mounted a final campaign in 1745. The Jacobite forces of Prince Charles Edward Stuart, the "Bonnie Prince Charlie" of legend, were defeated at the Battle of Culloden in 1746.
Formation of Great Britain and the United Kingdom
Main article: Kingdom of Great Britain
The Acts of Union between the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland were a pair of Parliamentary Acts passed by both parliaments in 1707, which dissolved them in order to form a Kingdom of Great Britain governed by a unified Parliament of Great Britain according to the Treaty of Union. The Acts joined the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland (previously separate independent states, with separate legislatures but with the same monarch, starting with James I of England (also James VI of Scotland)) into a single kingdom.
The two countries had shared a monarch since the Union of the Crowns in 1603, when King James VI of Scotland inherited the English throne from his double first cousin twice removed, Queen Elizabeth I. Although described as a Union of Crowns, until 1707 there were in fact two separate Crowns resting on the same head. There had been three attempts in 1606, 1667, and 1689 to unite the two countries by Acts of Parliament, but it was not until the early 18th century that the idea had the will of both political establishments behind them, albeit for rather different reasons.
The Acts took effect on 1 May 1707. On this date, the Scots Parliament and the English Parliament united to form the Parliament of Great Britain, based in the Palace of Westminster in London, the home of the English Parliament. Hence, the Acts are referred to as the Union of the Parliaments. On the Union, historian Simon Schama said "What began as a hostile merger, would end in a full partnership in the most powerful going concern in the world ... it was one of the most astonishing transformations in European history."
In 1714 ended the reign of Queen Anne, the last monarch of the House of Stuart. She was succeeded by her second cousin, George I, of the House of Hanover, who was a descendant of the Stuarts through his maternal grandmother, Elizabeth, daughter of James VI & I. A series of Jacobite rebellions broke out in an attempt to restore the Stuart monarchy, but failed. Several planned French invasions were attempted, also with the intention of placing the Stuarts on the throne. The Act of Union of 1800 formally assimilated Ireland within the British political process and from 1 January 1801 created a new state called the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, which united Great Britain with the Kingdom of Ireland to form a single political entity. The English parliament at Westminster became the parliament of the Union.
Georgian and Regency era
Main articles: Georgian era and Regency era
With the newly formed Kingdom of Great Britain, output from the Royal Society and other English initiatives and institutionscreated innovations in science and engineering, while the enormous growth in overseas trade protected by the Royal Navy paved the way for the establishment of the British Empire. Domestically it drove the Industrial Revolution, a period of profound change in the socioeconomic and cultural conditions of England, resulting in industrialised agriculture, manufacture, engineering and mining, as well as new and pioneering road, rail and water networks to facilitate their expansion and development.
During the Napoleonic Wars, Napoleon planned to invade from the south-east. However this failed to manifest and the Napoleonic forces were defeated by the British: at sea by Lord Nelson, and on land by the Duke of Wellington. The major victory at the Battle of Trafalgar confirmed the naval supremacy Britain had established during the course of the eighteenth century. During the Georgian era, much achievements were made in fine arts, literature, drama, architecture, medicine, and science.
The Industrial Revolution began in England due to the social, economic and political changes implemented in the previous centuries. Whereas absolute monarchy stayed the normal form of power execution through most parts of Europe, institutions ensured property rights and political safety to English people after the Glorious Revolution of 1688. Aided by these legal and cultural foundations, an entrepreneurial spirit and consumer revolution drove industrialisation in England. In 1825 the world's first permanent steam locomotive-hauled passenger railway – the Stockton and Darlington Railway – opened to the public.
Geographical and natural resource advantages also contributed, with the country's extensive coastlines and many navigable rivers in an age when water was the easiest means of transportation along with its had high quality coal. According to British historian Jeremy Black, "an unprecedented explosion of new ideas, and new technological inventions, transformed our use of energy, creating an increasingly industrial and urbanised country. Roads, railways and canals were built. Great cities appeared. Scores of factories and mills sprang up. Our landscape would never be the same again. It was a revolution that transformed not only the country, but the world itself."

Georgian society and its preoccupations were well portrayed in the novels of writers such as Daniel Defoe, Jonathan Swift, Samuel Richardson, Henry Fielding, Laurence Sterne, Mary Shelley and Jane Austen, characterised by the architecture of Robert Adam, John Nash and James Wyatt and the emergence of the Gothic Revival style, which hearkened back to a supposed golden age of building design. The flowering of the arts was most vividly shown in the emergence of the Romantic poets, principally through Samuel Taylor Coleridge, William Wordsworth, Percy Bysshe Shelley, William Blake, John Keats, Lord Byron and Robert Burns. Their work ushered in a new era of poetry, characterised by vivid and colourful language, evocative of elevating ideas and themes.
The paintings of Thomas Gainsborough, Sir Joshua Reynolds and the young J. M. W. Turner and John Constable illustrated the changing world of the Georgian period – as did the work of designers like Capability Brown, the landscape designer. Fine examples of distinctive Georgian architecture are Edinburgh's New Town, Georgian Dublin, Grainger Town in Newcastle upon Tyne, the Georgian Quarter of Liverpool and much of Bristol and Bath. The music of John Field, Handel, Haydn, Clementi, Johann Christian Bach, William Boyce, Mozart, Beethoven and Mendelssohn was some of the most popular in England at that time.
The Georgian period saw continual warfare, with France the primary enemy. Major episodes included the Seven Years' War, known in America as the French and Indian War (1756–63), the American Revolutionary War (1775–83), the French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802), the Irish Rebellion of 1798, and the Napoleonic Wars (1803–15). The British won most of the wars except for the American Revolution, where the combined weight of the United States, France, Spain and the Netherlands overwhelmed Britain, which stood alone without allies.
The loss of the 13 American Colonies was a national disaster. Commentators at home and abroad speculated on the end of Britain as a great power. In Europe, the wars with France dragged on for nearly a quarter of a century, 1793–1815. Britain organised coalition after coalition, using its superb financial system to subsidise infantry forces, and built up its Navy to maintain control of the seas. Victory over Napoleon at the Battle of Trafalgar (1805) and the Battle of Waterloo (1815) under Admiral Lord Nelson and the Duke of Wellington brought a sense of triumphalism and political reaction. The expansion of empire in Asia was primarily the work of the British East India Company, especially under the leadership of Robert Clive. Captain James Cook was perhaps the most prominent of the many explorers and geographers using the resources of the Royal Navy to develop the Empire and make many scientific discoveries, especially in Australia and the Pacific. Instead of trying to recover the lost colonies in North America, the British built up in Asia a largely new Second British Empire.
England sponsored numerous scientists who made major discoveries in the small laboratories. Joseph Priestley investigated electricity. Chemist Henry Cavendish identified hydrogen in 1772. Daniel Rutherford isolated nitrogen in 1774, while Priestley discovered oxygen and ammonia. Antiquarians and archaeologists mapped the past. In medicine, in 1717 Lady Mary Wortley Montagu introduced inoculation against smallpox and Britain, and by 1740 it was in wide usage. Guy's Hospital was founded in 1721; Queen Charlotte's maternity hospital in 1739 and the Middlesex Hospital in 1745. Asylums for the mentally ill were established, notably Bethel Hospital in Norwich (1713); a ward for incurable lunatics at Guy's Hospital (1728); and lunatic hospitals in Manchester (1766) and York in (1777)—York was the first to be called an asylum.
Victorian era
Main article: Victorian eraThe Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardian period. This era saw a staggering amount of English technological innovations that proved key to Britain's power and prosperity. Doctors started moving away from tradition and mysticism towards a science-based approach; medicine advanced thanks to the adoption of the germ theory of disease and pioneering research in epidemiology. Victorian England, like the periods before it, was widely interested in literature, theatre and the arts (such as the Aesthetic movement and Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood), and music, drama, and opera were widely attended.
Britain embarked on global imperial expansion, particularly in Asia and Africa, which made the British Empire the largest empire in history. National self-confidence peaked. Britain granted political autonomy to the more advanced colonies of Australia, Canada, and New Zealand. Apart from the Crimean War, Britain was not involved in any armed conflict with another major power. Literature, fashion, art, architecture, trade, naval power, science, engineering were at their very peak. London became the largest and most populous metropolitan area in the world during the Victorian era, and trade within the British Empire, as well as the standing of the British military and navy, was prestigious.
The Industrial Revolution incentivised people to think more scientifically and to become more educated and informed in order to solve novel problems. As a result, cognitive abilities were pushed to their genetic limits, making people more intelligent and innovative than their predecessors. Formal education thus became vital. According to intelligence researcher James R. Flynn, these changes echoed down to the twentieth century before leveling off in the early twenty-first. The era saw a reform and renaissance of public schools, inspired by Thomas Arnold at Rugby. The public school became a model for gentlemen and public service. Sunday schools and charity schools helped reduce illiteracy. In fact, throughout the course of the nineteenth century, there was a clear movement towards universal literacy, culminating in the Elementary Education Act of 1870. By 1876, attending elementary schools was made compulsory.
Gothic Revival architecture became increasingly significant during the period, leading to the Battle of the Styles between Gothic and Classical ideals. Charles Barry's architecture for the new Palace of Westminster, which had been badly damaged in an 1834 fire, was built in the medieval style of Westminster Hall, the surviving part of the building. It constructed a narrative of cultural continuity, set in opposition to the violent disjunctions of Revolutionary France, a comparison common to the period, as expressed in Thomas Carlyle's The French Revolution: A History and Charles Dickens' Great Expectations and A Tale of Two Cities. The middle of the 19th century saw The Great Exhibition of 1851, the first World's Fair, which showcased the greatest innovations of the century.. At its centre was the Crystal Palace, a modular glass and iron structure – the first of its kind. It was condemned by Ruskin as the very model of mechanical dehumanisation in design but later came to be presented as the prototype of Modern architecture. The emergence of photography, showcased at the Great Exhibition, resulted in significant changes in Victorian art with Queen Victoria being the first British monarch to be photographed.

In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, technological advances and mechanisation resulted in the Industrial Revolution which transformed a largely agrarian society and caused considerable social upheaval. Economies of scale and increased output per worker allowed steam-based factories to undercut production of traditional cottage industries. Much of the agricultural workforce was uprooted from the countryside and moved into large urban centres of production. The consequent overcrowding into areas with little supporting infrastructure saw dramatic increases in mortality, crime, and social deprivation. (Many Sunday schools for pre-working-age children (5 or 6) had funeral clubs to pay for each other's funeral arrangements.) The process of industrialisation threatened many livelihoods, which prompted some to sabotage factories. These saboteurs were known as "Luddites".
Founded in 1799 with the stated purpose of "diffusing the Knowledge, and facilitating the general Introduction, of Useful Mechanical Inventions and Improvements; and for teaching, by Courses of Philosophical Lectures and Experiments, the application of Science to the common Purposes of Life," the Royal Institution was a large scientific institution with laboratories, a lecture hall, libraries, and offices. In its first years, the Institution was dedicated to the improvement of agriculture using chemistry, prompted by trade restrictions with Europe. The Victorians were impressed by science and progress and felt that they could improve society in the same way as they were improving technology. Britain was the leading world centre for advanced engineering and technology. Its engineering firms were in worldwide demand for designing and constructing railways.
Local governance
Further information: History of local government in England
The Local Government Act 1888 was the first systematic attempt to impose a standardised system of local government in England. The system was based on the existing counties (today known as the historic counties, since the major boundary changes of 1974). Later, the Local Government Act 1894 created a second tier of local government. All administrative counties and county boroughs were divided into either rural or urban districts, allowing more localised administration.
During the 1800s, the need for local administration greatly increased, prompting piecemeal adjustments. The sanitary districts and parish councils had legal status, but were not part of the mechanism of government. They were run by volunteers; often no-one could be held responsible for the failure to undertake the required duties. Furthermore, the increased "county business" could not be handled by the quarter sessions, nor was this appropriate. Finally, there was a desire to see local administration performed by elected officials, as in the reformed municipal boroughs. By 1888, these shortcomings were clear, and the Local Government Act was the first systematic attempt to create a standardised system of local government in England.
The system was based on the existing counties (now known as the historic counties, since the major boundary changes of 1974). The counties themselves had had some boundary changes in the preceding 50 years, mainly to remove enclaves and exclaves. The act called for the creation of statutory counties, based on the ancient/historic counties, but completely corrected for enclaves and exclaves, and adjusted so that each settlement was completely within one county. These statutory counties were to be used for non-administrative functions: "sheriff, lieutenant, custos rotulorum, justices, militia, coroner, or other". With the advent of elected councils, the offices of lord lieutenant and sheriff became largely ceremonial.
The statutory counties formed the basis for the so-called 'administrative counties'. However, it was felt that large cities and primarily rural areas in the same county could not be well administered by the same body. Thus, 59 "counties in themselves", or 'county boroughs', were created to administer the urban centres of England. These were part of the statutory counties, but not part of the administrative counties.
In 1894, the Local Government Act created a second tier of local government. Henceforth, all administrative counties and county boroughs would be divided into either rural or urban districts, allowing more localised administration. The municipal boroughs reformed after 1835 were brought into this system as special cases of urban districts. The urban and rural districts were based on, and incorporated the sanitary districts which created in 1875 (with adjustments, so that districts did not overlap two counties). The Act also provided for the establishment of civil parishes. The 1894 Act formed an official system of civil parishes, separated from the ecclesiastical parishes, to carry on some of these responsibilities (others being transferred to the district/county councils). However, the civil parishes were not a complete third tier of local government. Instead, they were 'community councils' for smaller, rural settlements, which did not have a local government district to themselves. Where urban parish councils had previously existed, they were absorbed into the new urban districts.
20th and 21st centuries
Main articles: Social history of Postwar Britain (1945–1979) and Political history of the United Kingdom (1979–present)A prolonged agricultural depression in Britain at the end of the 19th century, together with the introduction in the 20th century of increasingly heavy levels of taxation on inherited wealth, put an end to agricultural land as the primary source of wealth for the upper classes. Many estates were sold or broken up, and this trend was accelerated by the introduction of protection for agricultural tenancies, encouraging outright sales, from the mid-20th century.
General history and political issues

Following years of political and military agitation for 'Home Rule' for Ireland, the Anglo-Irish treaty of 1921 established the Irish Free State (now the Republic of Ireland) as a separate state, leaving Northern Ireland as part of the United Kingdom. The country's official name thus became "The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland".
England, as part of the UK, joined the European Economic Community in 1973, which became the European Union in 1993. The UK left the EU in 2020.
There is a movement in England to create a devolved English Parliament. This would give England a local Parliament like those already functioning for Scotland, Northern Ireland and Wales. This issue is referred to as the West Lothian question.
Political history and local government
Further information: History of local government in EnglandA Local Government Commission was wound up in 1966, and replaced with a Royal Commission (known as the Redcliffe-Maud commission). In 1969 it recommended a system of single-tier unitary authorities for the whole of England, apart from three metropolitan areas of Merseyside, Selnec (Greater Manchester) and West Midlands (Birmingham and the Black Country), which were to have both a metropolitan council and district councils. This report was accepted by the Labour Party government of the time despite considerable opposition, but the Conservative Party won the June 1970 general election, and on a manifesto that committed them to a two-tier structure.
The reforms arising from the Local Government Act of 1972 resulted in the most uniform and simplified system of local government which has been used in England. They effectively wiped away everything that had gone before, and built an administrative system from scratch. All previous administrative districts—statutory counties, administrative counties, county boroughs, municipal boroughs, counties corporate, civil parishes—were abolished.
The aim of the act was to establish a uniform two tier system across the country. Onto the blank canvas, new counties were created to cover the entire country; many of these were obviously based on the historic counties, but there were some major changes, especially in the north.
This uniform two-tier system lasted only 12 years. In 1986, the metropolitan county councils and Greater London were abolished. This restored autonomy (in effect the old county borough status) to the metropolitan and London boroughs. The Local Government Act (1992) established a commission (Local Government Commission for England) to examine the issues, and make recommendations on where unitary authorities should be established. It was considered too expensive to make the system entirely unitary, and also there would doubtlessly be cases where the two-tier system functioned well. The commission recommended that many counties be moved to completely unitary systems; that some cities become unitary authorities, but that the remainder of their parent counties remain two-tier; and that in some counties the status quo should remain.
The rate-capping rebellion was a campaign within English local councils in 1985 which aimed to force the Conservative government of Margaret Thatcher to withdraw powers to restrict the spending of councils. The campaign's tactic was that councils whose budgets were restricted would refuse to set any budget at all for the financial year 1985–86, requiring the Government to intervene directly in providing local services, or to concede. However, all 15 councils which initially refused to set a rate eventually did so, and the campaign failed to change Government policy. Powers to restrict council budgets have remained in place ever since.
In 1997, the Lieutenancies Act was passed. This firmly separated all local authority areas (whether unitary or two-tier), from the geographical concept of a county as high level spatial unit. The lieutenancies it established became known as ceremonial counties, since they were no longer administrative divisions. The counties represent a compromise between the historic counties and the counties established in 1974. While the 1997 Labour government devolved power to Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, it refused to create a devolved Assembly or parliament for England, planning instead to introduce eight regional assemblies around England to devolve power to the regions. In the event, only a London Assembly (and directly elected Mayor) was established. Rejection in a referendum of a proposed North-East Assembly in 2004 effectively scrapped those plans. A pre-condition of having a regional assembly was for the whole area to move to unitary authority status. Since the 2005 general election the government has floated the idea of voluntary mergers of local councils, avoiding a costly reorganisation but achieving desired reform. For instance, the guiding principles of the government's "New Localism" demand levels of efficiency not present in the current over-duplicated two-tier structure.
Recent changes
In 2009, new changes to local government were made whereby a number of new unitary authorities were created in areas which previously had a 'two-tier' system of counties and districts. In five shire counties the functions of the county and district councils were combined into a single authority; and in two counties the powers of the county council were absorbed into a significantly reduced number of districts.
The abolition of regional development agencies and the creation of local enterprise partnerships were announced as part of the June 2010 United Kingdom budget. On 29 June 2010 a letter was sent from the Department of Communities and Local Government and the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills to local authority and business leaders, inviting proposals to replace regional development agencies in their areas by 6 September 2010.
On 7 September 2010, details were released of 56 proposals for local enterprise partnerships that had been received. On 6 October 2010, during the Conservative Party Conference, it was revealed that 22 had been given the provisional 'green light' to proceed and others may later be accepted with amendments. Twenty-four bids were announced as successful on 28 October 2010.
See also
- Parliament of England
- Parliament of the United Kingdom
- Monarchs of England
- Prime Minister of the United Kingdom
- List of rulers of the United Kingdom and predecessor states
Related historical overviews
- Bretwalda
- Commonwealth of Nations
- Danelaw
- History of the foreign relations of the United Kingdom
- History of the British constitution
- History of the British Isles
- History of the United Kingdom
- History of Scotland
- History of Ireland
- History of Wales
- Kingdom of Great Britain
- Politics of the United Kingdom
- Administrative geography of the United Kingdom
- List of articles about local government in the United Kingdom
- Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics
Historical lists and timelines
- List of British monarchs, British monarchs' family tree
- Timeline of English history
- Timeline of British diplomatic history
- Historical and alternative regions of England
Overviews of significant historical eras
Note: Be sure to check the box in the upper right corner of this entry, providing a list of all notable eras within the history of England.
Related English history topics
Societal overviews
- English people
- Population of England – historical estimates
- Culture of England
- Politics of England
- Social history of England
Local government
- History of local government in England
- 2009 structural changes to local government in England
- Regions of England
- Subdivisions of England
- Unitary authorities of England
Historical subtopics
- History of education in England
- History of the Jews in England
- Military history of England
- English nationalism
- Anglo-Saxon England
References
- ^ Sample, Ian (7 July 2010). "First humans arrived in Britain 250,000 years earlier than thought". The Guardian. Retrieved 29 January 2014; Wade, Nicholas (7 July 2010). "Clues of Britain's First Humans". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 January 2022. Retrieved 22 December 2011; "Earliest footprints outside Africa discovered in Norfolk". (2014). BBC News. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- "Jawbone Is Earliest Evidence Of Modern Humans In NW Europe". 2 November 2011. Retrieved 17 August 2021.
- The Anglo-Saxons, BBC – History
- Roth 1964, p. 90.
- Richmond, Colin (1992). "Englishness and Medieval Anglo-Jewry". In Kushner, Tony (ed.). The Jewish Heritage in British History. Frank Cass. pp. 42–59. ISBN 0-7146-3464-6.
- Skinner, Patricia (2003). "Introduction". In Skinner, Patricia (ed.). Jews in Medieval Britain. Woodbridge: Boydell Press. pp. 1–11. ISBN 0851159311.
- Huscroft 2006, p. 12. sfn error: no target: CITEREFHuscroft2006 (help)
- Klein, Jürgen (2012), "Francis Bacon", in Zalta, Edward N. (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2016 ed.), Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University, retrieved 17 January 2020
- From the 1944 Clark lectures by C. S. Lewis; Lewis, English Literature in the Sixteenth Century (Oxford, 1954) p. 1, OCLC 256072
- Farrington, Anthony (2002). Trading Places: The East India Company and Asia 1600–1834. British Library. ISBN 9780712347563. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2019.
- "History of the Royal Society | Royal Society". royalsociety.org. Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- "Tudor Period and the Birth of a Regular Navy". Royal Navy History. Institute of Naval History. Archived from the original on 3 November 2011. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- Canny, Nicholas (1998). The Origins of Empire, The Oxford History of the British Empire Volume I. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-924676-2.
- Usher, Abbott Payson (1928). "The Growth of English Shipping 1572-1922". The Quarterly Journal of Economics. 42 (3): 465–478. doi:10.2307/1884787. ISSN 0033-5533. JSTOR 1884787.
- "The Merchant Fleet of Late Medieval and Tudor England, 1400-1580 | History | University of Southampton". www.southampton.ac.uk. Retrieved 4 March 2024.
- Uniting the kingdom? nationalarchives.gov.uk, accessed 2 July 2011
- The Union of the Parliaments 1707 Archived 2 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine Learning and Teaching Scotland, accessed 2 July 2011
- Union with England Act 1707, Article II
- ^ Francis Pryor, Britain BC, 2003.
- V Gaffney, S Fitch and D Smith 2009, Europe's Lost World: The Rediscovery of Doggerland.
- "How new archaeological discovery in Yorkshire could rewrite British prehistory". The Independent. 31 March 2021. Retrieved 19 April 2021.
- Olalde etal. (2018), The Beaker phenomenon and the genomic transformation of northwest Europe, Nature
- The Guardian, Arrival of Beaker folk changed Britain for ever, ancient DNA study shows
- Rincon, Paul (21 February 2018). "Ancient Britons 'replaced' by newcomers". BBC News.
- Francis Pryor, Britain BC, 2003
- Barry Cunliffe, The Ancient Celts, 1997
- "The Battersea Shield". British Museum.
- "Book 5, chapter 24". The Library of History of Diodorus Siculus.
- Barry Cunliffe, Iron Age Communities in Britain, 2005
- Guy de la Bedoyere, Roman Britain: A New History, 2010
- Henry Freeman, Roman Britain: A History From Beginning to End (2016).
- Making Europe: The Story of the West, Volume I to 1790. 2013. p. 162.
- Goldsworthy, Adrian (2016). Pax Romana: War, Peace and Conquest in the Roman World. Hachette UK. p. 276.
- Bedoyere, Guy. "Architecture in Roman Britain". Heritage Key. Archived from the original on 3 July 2009. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- Philip, Robert (1860). The History of Progress in Great Britain, Volume 2. Retrieved 23 December 2010.
- Bob Rees; Paul Shute; Nigel Kelly (9 January 2003). Medicine through time. Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-435-30841-4. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- * Rankov, Boris (1994). The Praetorian Guard. Osprey Publishing. p. 16. ISBN 978-1-85532-361-2.
- "An Overview of Roman Britain". BBC. Retrieved 26 August 2017.
- ^ Herodian, Τῆς μετὰ Μάρκον βασιλείας ἱστορία [History of the Empire from the Death of Marcus] (in Ancient Greek), III, 8, 2. The precise dating is uncertain; the province does not appear to have been divided until the reign of Caracalla.
- The reorganisation is usually attributed to Constantine the Great; it first appears in the Verona List, of c. 314.
- Hamerow, Helena. "The Origins of Wessex". University of Oxford. Archived from the original on 2 July 2012. Retrieved 18 November 2012.
- Stenton, Frank. "Anglo-Saxon England". OUP, 1971
- Francis Pryor, Britain AD, 2004.
- Ward-Perkins, Bryan. "Why did the Anglo-Saxons not become more British?." The English Historical Review 115.462 (2000): page 523.
- Higham, Nicholas J. and Ryan, Martin J. The Anglo-Saxon World (Yale University Press, 2013).
- Stefan Burmeister, Archaeology and Migration (2000): " ... immigration in the nucleus of the Anglo-Saxon settlement does not seem aptly described in terms of the “elite-dominance model.To all appearances, the settlement was carried out by small, agriculture-oriented kinship groups. This process corresponds more closely to a classic settler model. The absence of early evidence of a socially demarcated elite underscores the supposition that such an elite did not play a substantial role. Rich burials such as are well known from Denmark have no counterparts in England until the 6th century. At best, the elite-dominance model might apply in the peripheral areas of the settlement territory, where an immigration predominantly comprised of men and the existence of hybrid cultural forms might support it."
- Dark, Ken R. (2003). "Large-scale population movements into and from Britain south of Hadrian's Wall in the fourth to sixth centuries AD" (PDF).: "In fact, part of eastern Britain may have already been losing a significant portion of its rural population, as evidence from East Anglia – amassed and analyzed by local archaeologists – may suggest. In this area at least, and possibly more widely in eastern Britain, large tracts of land appear to have been deserted in the late fourth century, possibly including whole "small towns" and villages. This does not seem to have been a localised change in settlement location, size or character but genuine desertion ... The areas where we have most indications of an intrusive Germanic culture are precisely those where we have most evidence of late fourth-century abandonment."
- Toby F. Martin, The Cruciform Brooch and Anglo-Saxon England, Boydell and Brewer Press (2015), pp. 174–178: "There is by now, however, an admission that no single model is suitable for Anglo-Saxon England in its entirety. Regional variation may well provide the key to resolution, with something more akin to mass migration in the southeast, gradually spreading into elite dominance in the north and west. I accord with this compromise between the debates insofar as large-scale migration seems highly likely for at least East Anglia and parts of Lincolnshire. At the same time, however, it is dubious that these people migrated as a coherent Anglian group."
- Catherine Hills, "The Anglo-Saxon Migration: An Archaeological Case Study of Disruption," in Migrations and Disruptions, ed. Brenda J. Baker and Takeyuki Tsuda, pp. 45–48: "In a fairly precisely defined region in eastern England, centered on Norfolk and Lincolnshire, a significant number of people from the other side of the north sea do seem to have arrived in the fifth century and established territories where Germanic material culture and, especially, burial practices were dominant. This forms the basis for the "Anglian" zone of later Anglo-Saxon England. The population may indeed have included a substantial number of people with Germanic ancestry as well as an as yet unspecifiable proportion of the native British population ... There was not one "Anglo-Saxon migration" that had the same impact in all of England ..."
- Coates, Richard. "Celtic whispers: revisiting the problems of the relation between Brittonic and Old English".: "... I believe that the linguistic evidence favors the traditional view, at least for the south-east and for the southern North Sea coastal lands, i.e. East Anglia."
- Härke, Heinrich. "Anglo-Saxon Immigration and Ethnogenesis." Medieval Archaeology 55.1 (2011): 1–28: "A third model, that of "elite transfer," has been suggested for Bernicia where a small group of immigrants may have replaced the British elite and took over the kingdom as a going concern."
- Kortlandt, Frederik (2018). "Relative Chronology" (PDF).: "The second migration, which attracted incomers from other Germanic tribes, offers a different picture for Northumbria, and more specifically Bernicia, where there was a noticeable Celtic contribution to art, culture and possibly socio-military organisation. It appears that the immigrants took over the institutions of the local population here."
- Fox, Bethany (2007). "The P-Celtic Place Names of North-East England and South-East Scotland". The Heroic Age.
- ^ Higham, Nicholas J., and Martin J. Ryan. The Anglo-Saxon World. Yale University Press, 2013. p. 7
- Yorke, Barbara. Kings and kingdoms of early Anglo-Saxon England. Routledge, 2002: p101
- Yorke, Barbara. Kings and kingdoms of early Anglo-Saxon England. Routledge, 2002: p103
- Scharer, Anton. "The writing of history at King Alfred's court." Early Medieval Europe 5.2 (1996): 177–206.
- Yorke, Barbara. Kings and kingdoms of early Anglo-Saxon England, 2002. p. 101.
- Yorke, B A E 1985: 'The kingdom of the East Saxons.' Anglo-Saxon England 14, 1–36
- RYAN, MARTIN J. "The Mercian Supremacies." The Anglo-Saxon World (2013): 179.
- Drout, Michael DC. Imitating fathers: tradition, inheritance, and the reproduction of culture in Anglo-Saxon England. Diss. Loyola University of Chicago, 1997.
- "Y Chromosome Evidence for Anglo-Saxon Mass Migration".
- Capelli, C.; Redhead, N.; Abernethy, J.K.; Gatrix, F.; Wilson, J.F.; Moen, T.; Hervig, T.; Richards, M.; Stumpf, M.P.H.; Underhill, P.A.; Bradshaw, P.; Shaha, A.; Thomas, M.G.; Bradman, N.; Goldstein, D.B. (2003). "A Y chromosome census of the British Isles" (PDF). Current Biology. 13 (11): 979–984. Bibcode:2003CBio...13..979C. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00373-7. PMID 12781138. S2CID 526263. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 July 2021. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- "A Y Chromosome Census of the British Isles" (PDF).
- Härke, Heinrich; Thomas, Mark G; Stumpf, Michael P H. "Integration versus apartheid in post-Roman Britain: A response to Pattison".
- Oppenheimer, Stephen (2006). The Origins of the British: A Genetic Detective Story: Constable and Robinson, London. ISBN 978-1-84529-158-7.
- Schiffels, Stephan; Haak, Wolfgang; Paajanen, Pirita; Llamas, Bastien; Popescu, Elizabeth; Loe, Louise; Clarke, Rachel; Lyons, Alice; Mortimer, Richard; Sayer, Duncan; Tyler-Smith, Chris; Cooper, Alan; Durbin, Richard (2016). "Iron Age and Anglo-Saxon genomes from East England reveal British migration history". Nature Communications. 7: 10408. Bibcode:2016NatCo...710408S. doi:10.1038/ncomms10408. PMC 4735688. PMID 26783965. S2CID 14795869.
- Martiniano, Rui; Caffell, Anwen; Holst, Malin; Hunter-Mann, Kurt; Montgomery, Janet; Müldner, Gundula; McLaughlin, Russell L.; Teasdale, Matthew D.; Van Rheenen, Wouter; Veldink, Jan H.; Van Den Berg, Leonard H.; Hardiman, Orla; Carroll, Maureen; Roskams, Steve; Oxley, John; Morgan, Colleen; Thomas, Mark G.; Barnes, Ian; McDonnell, Christine; Collins, Matthew J.; Bradley, Daniel G. (2016). "Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Saxons". Nature Communications. 7: 10326. Bibcode:2016NatCo...710326M. doi:10.1038/ncomms10326. PMC 4735653. PMID 26783717. S2CID 13817552.
- Frank Merry Stenton, Anglo-Saxon England (1971).
- Peter Hayes Sawyer, From Roman Britain to Norman England (Routledge, 2002).
- Rees, Rosemary (2002). The Vikings. Heinemann. p. 45. ISBN 9781403401007.
- Albany F. Major, Early wars of Wessex (Hildreth Press, 2008).
- Richard P. Ables, Alfred the great: war, kingship and culture I'm Anglo-Saxon England (1998).
- Lawson, M. K. (1984). "The Collection of Danegeld and Heregeld in the Reigns of Aethelred II and Cnut". The English Historical Review. 99 (393): 721–738. doi:10.1093/ehr/XCIX.CCCXCIII.721. JSTOR 569175.
- Thames Cussans, Kings and Queens of the British Isles (The Times Books, 2002), pp.32–35.
- Williams 2003, p. 54 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWilliams2003 (help)
- Huscroft 2005, p. 3 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHuscroft2005 (help)
- Stafford 1989, pp. 86–99 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFStafford1989 (help)
- ^ Higham 2000, pp. 167–181 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHigham2000 (help)
- Walker 2000, pp. 136–138 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWalker2000 (help)
- Bates 2001, pp. 73–77 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFBates2001 (help)
- Higham 2000, pp. 188–190 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHigham2000 (help)
- Huscroft 2005, pp. 12–14 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHuscroft2005 (help)
- Thomas 2007, pp. 33–34 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFThomas2007 (help)
- Walker 2000, pp. 158–165 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWalker2000 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, pp. 72–74 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, p. 76 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Stafford 1989, pp. 102–105 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFStafford1989 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, pp. 82–83 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, pp. 79–80 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- ^ Carpenter 2004, p. 84 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, pp. 83–84 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, pp. 75–76 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, p. 84 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Chibnall 1986, pp. 11–13 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFChibnall1986 (help)
- Kaufman and Kaufman 2001, p. 110 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFKaufman_and_Kaufman2001 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, p. 89 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, pp. 110–112 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, pp. 125–126 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Prestwich 1992, pp. 70–71 and 74 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFPrestwich1992 (help)
- Bates 2001, pp. 198–202 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFBates2001 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, pp. 134–135 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Huscroft 2009, pp. 65, 69–71 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHuscroft2009 (help); Carpenter 2004, pp. 124, 138–140 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Roth 1964, p. 4.
- Hollister 2003, pp. 356–357 and 358–359 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHollister2003 (help)
- Green 2009, pp. 242–243 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGreen2009 (help)
- Green 2009, p. 255 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGreen2009 (help)
- Green 2009, p. 273 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGreen2009 (help)
- Green 2009, p. 278 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGreen2009 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, p. 129 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, p. 132 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Barlow 2000, pp. 402–406 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFBarlow2000 (help)
- Hollister 2003, pp. 356–357 and 358–359 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHollister2003 (help)
- Green 2009, pp. 242–243 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGreen2009 (help)
- Green 2009, p. 255 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGreen2009 (help)
- Green 2009, p. 273 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGreen2009 (help)
- Green 2009, p. 278 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGreen2009 (help)
- "King Stephen and The Anarchy". Historic UK. Retrieved 4 March 2024.
- Carpenter 2004, p. 191 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, p. 191 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help); Aurell 2003, p. 15 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFAurell2003 (help)
- Davies 1990, p. 67 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFDavies1990 (help)
- Davies 1990, p. 76 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFDavies1990 (help)
- THE 'ANGEVIN EMPIRE', 1150s–1230s (PDF). 2019. pp. 1–2.
- Warren 2000, pp. 187–188 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWarren2000 (help)
- Warren 2000, p. 192 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWarren2000 (help)
- Warren 2000, pp. 192–193 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWarren2000 (help)
- Warren 2000, p. 194 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWarren2000 (help)
- Carpenter 2004, p. 215 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarpenter2004 (help)
- Bull 2007, p. 124 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFBull2007 (help); Warren 2000, p. 197 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWarren2000 (help)
- Warren 2000, p. 200 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWarren2000 (help)
- Warren 2000, p. 203 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWarren2000 (help)
- Warren 2000, p. 203 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWarren2000 (help); Davies 1990, pp. 64–65 and 78 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFDavies1990 (help)
- Schama 2000, p. 142 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSchama2000 (help)
- Schama 2000, p. 117 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSchama2000 (help)
- Jones 2012, pp. 82–92 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones2012 (help)
- Jones 2012, p. 86 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones2012 (help)
- Jones 2012, p. 109 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones2012 (help)
- Ackroyd 2000, p. 54 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFAckroyd2000 (help)
- Flori 1999, p. 116 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFFlori1999 (help)
- Flori 1999, p. 132 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFFlori1999 (help)
- Jones 2012, p. 128 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones2012 (help)
- Carlton 2003, p. 42 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarlton2003 (help)
- Turner 1994, pp. 100 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFTurner1994 (help)
- Jones 2012, pp. 161–169 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones2012 (help)
- Favier 1993, p. 176 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFFavier1993 (help)
- Contramine 1992, p. 83 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFContramine1992 (help)
- Smedley 1836, p. 72 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSmedley1836 (help)
- Jones 2012, p. 217 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones2012 (help).
- Hamilton 2010, p. 1 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHamilton2010 (help)
- Jones 2012, pp. 221–222 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones2012 (help).
- Danziger and Gillingham 2003, p. 271 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFDanziger_and_Gillingham2003 (help)
- Doris Mary Stenton. "Magna Carta". Encyclopedia Brittanica. Retrieved 8 November 2023.
- "Library of Congress: Magna Carta: Muse and Mentor". Library of Congress. 6 November 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2021.
- "Library of Congress: Magna Carta: Muse and Mentor". Library of Congress. 6 November 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2021.
- Hillaby 2013, p. 104 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHillaby2013 (help)
- Joe Hillaby, The Palgrave Dictionary of Medieval Anglo-Jewish History (2013) pp 104–107.
- Huscroft 2006, pp. 112–139 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHuscroft2006 (help)
- ^
 Jacobs, Joseph (1903). "England". In Singer, Isidore; et al. (eds.). The Jewish Encyclopedia. Vol. 5. New York: Funk & Wagnalls. p. 161-174.
Jacobs, Joseph (1903). "England". In Singer, Isidore; et al. (eds.). The Jewish Encyclopedia. Vol. 5. New York: Funk & Wagnalls. p. 161-174.
- "The savage wars of peace: England, Japan and the Malthusian trap". Alan Macfarlane (1997). p.66. ISBN 0-631-18117-2
- Edward first styled himself "King of France" in 1337, though he did not officially assume the title until 1340; Prestwich (2005), pp. 307–8.
- ”...major victories such as Sluis (1340) and Winchelesea (1350)...” Steven Gunn; Armand Jamme (2015). "Kings, Nobles and Military Networks". In Christopher Fletcher; Jean-Philippe Genet; John Watts (eds.). Government and Political Life in England and France, c.1300–c.1500. Cambridge University Press. p. 48. ISBN 978-1-107-08990-7.
- Grant, R. G. (2017). 1001 Battles That Changed the Course of History. p. 195.
- Lavery, Brian (2013). The Conquest of the Ocean. p. 61.
- Gardiner, Samuel Rawson (1911). "English History" . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 9 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 535.
- Oman, Charles (1911). "English History" . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 9 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 511.
- Sydney Anglo, "Ill of the dead: The posthumous reputation of Henry VII", Renaissance Studies 1 (1987): 27–47. online
- Steven Gunn, Henry VII's New Men and the Making of Tudor England (2016)
- "Henry VII". Tudorhistory.org. 5 February 2012. Retrieved 17 October 2013.
- Hay, Denys (1988). Renaissance essays. A&C Black. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-907628-96-5. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- "Royal Navy History, Tudor Period and the Birth of a Regular Navy". Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- Smith, Goldwin. England Under the Tudors. Forgotten Books. p. 176. ISBN 978-1-60620-939-4. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- John Guy (1988) Tudor England, Oxford University Press, p. 32
- Weir 2002, p. 13 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFWeir2002 (help)
- Peter H. Marshall, Heretics and Believers: A History of the English Reformation (Yale UP, 2017).
- ^ Robert Bucholz, Newton Key, via Google Books, John Wiley & Sons Publishers, 31 December 2019 – History – 472 pages, ISBN 978-1-4051-6275-3, Early Modern England 1485–1714: A Narrative History, retrieved 27 March 2020, see pages 102, 104, 107, 122–3
- Ann Weikel, "Mary I (1516–1558)", Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, online edition, Jan 2008 accessed 25 Aug 2011
- Glyn Redworth, "Philip (1527–1598)", Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, online edition, May 2011 accessed 25 Aug 2011
- J. B. Black The Reign of Elizabeth, 1558–1603 (Oxford History of England) (2nd ed. 1959) online edition Archived 22 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- J. A. Guy, Tudor England (1990) excerpt and text search
- Archived 23 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- John Guy (1988) Tudor England, Oxford University Press, p. 32 ISBN 0192852132
- From the 1944 Clark lectures by C. S. Lewis; Lewis, English Literature in the Sixteenth Century (Oxford, 1954) p. 1, OCLC 256072
- Melissa D. Aaron, Global Economics (2005), p. 25. In the later decades of the reign, the costs of warfare — defeating the English Armada of 1589 and funding the campaigns in the Netherlands — obliterated the surplus; England had a debt of £350,000 at Elizabeth's death in 1603.
- Ann Jennalie Cook (1981) The Privileged Playgoers of Shakespeare's London, 1576–1642,, Princeton University Press, pp. 49–96 ISBN 0691064547.
- Hibbert, Christopher (1991). The Virgin Queen: Elizabeth I, Genius of the Golden Age. Da Capo Press. ISBN 0201608170.
- Irwin, Douglas A. (December 1991). "Mercantilism as Strategic Trade Policy: The Anglo-Dutch Rivalry for the East India Trade" (PDF). The Journal of Political Economy. 99 (6). The University of Chicago Press: 1296–1314. doi:10.1086/261801. JSTOR 2937731. S2CID 17937216. at 1299.
- Farrington, Anthony (2002). Trading Places: The East India Company and Asia 1600–1834. British Library. ISBN 9780712347563. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2019.
- "Tudor Period and the Birth of a Regular Navy". Royal Navy History. Institute of Naval History. Archived from the original on 3 November 2011. Retrieved 8 March 2015.
- ^ Carlton, Charles (2011). This Seat of Mars: War and the British Isles, 1485–1746. Yale University Press. p. 42. ISBN 9780300139136.
- Charles Beem, The Foreign Relations of Elizabeth I (2011) excerpt and text search
- "Africans, Slavery, and Race". Public Broadcasting Service (PBS).
- "Leaving England: The Social Background of Indentured Servants in the Seventeenth Century", The Colonial Williamsburg Foundation.
- Malcolm Smuts, "The making of Rex Pacificus: James VI and I and the Problem of Peace in an Age of Religious War," in Daniel Fischlin and Mark Fortier, eds., Royal Subjects: Essays on the Writings of James VI and I (2002) pp 371–87
- Jonathan Scott, England's Troubles: 17th-century English Political Instability in European Context (Cambridge UP, 2000), pp 98–101
- Godfrey Davies, The Early Stuarts: 1603–1660 (1959), pp 47–67
- Oxford Reference retrieved 20 February 2020.
- Thomas N. Corns, "The Poetry of the Caroline Court." Proceedings-British Academy Vol. 97. (1998) pp. 51–73. online
- Andrew McRae, "Remembering 1625: George Wither's Britain's Remembrancer and the Condition of Early Caroline England" English Literary Renaissance 46.3 (2016): 433–455.
- Boris Ford, ed., The Cambridge Cultural History of Britain: Volume 4, Seventeenth Century Britain (1992), pp 52–103, 276–307.
- Michael Hunter, Science and society in Restoration England (1981).
- Millstone, N. (1 May 2014). "Seeing Like a Statesman in Early Stuart England". Past & Present. 223 (1): 77–127. doi:10.1093/pastj/gtu003. ISSN 0031-2746.
- Lawrence E. Klein, "Coffeehouse Civility, 1660–1714: An Aspect of Post-Courtly Culture in England" Huntington Library Quarterly 59#1 (1996), pp. 30– 51. online Archived 2017-03-23 at the Wayback Machine
- Brian Cowan, "What Was Masculine about the Public Sphere? Gender and the Coffeehouse Milieu in Post-Restoration England." History Workshop Journal. No. 51: 127–157. online
- Hirst, Derek (1996). "Locating the 1650s in England's Seventeenth Century". History. 81 (263): 359–383. doi:10.1111/1468-229X.00016. ISSN 0018-2648. JSTOR 24423269.
- "The Enlightenment (1650–1800): The English Enlightenment". SparkNotes. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- Steven C. A. Pincus, Protestantism and Patriotism: Ideologies and the Making of English Foreign Policy, 1650–1668 (1996)
- Ann M. Carlos and Stephen Nicholas. "'Giants of an Earlier Capitalism': The Chartered Trading Companies as Modern Multinationals." Business History Review 62#3 (1988): 398–419. in JSTOR Archived 2018-09-23 at the Wayback Machine
- Eric J. Evans, The forging of the modern state: early industrial Britain, 1783–1872 (1996) p 31.
- E. Lipson, The Economic History of England (1931) p 188-89.
- Rosner & Theibault 2000, p. 103 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFRosnerTheibault2000 (help).
- Adair, John (1976). A Life of John Hampden The Patriot 1594-1643. London: Macdonald and Jane's Publishers Limited. ISBN 0-354-04014-6.
- Adair, John (1976). A Life of John Hampden The Patriot 1594-1643. London: Macdonald and Jane's Publishers Limited. ISBN 0-354-04014-6.
- ^ Pipes 1999, p. 143 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFPipes1999 (help).
- Adair, John (1976). A Life of John Hampden The Patriot 1594–1643. London: Macdonald and Jane's Publishers Limited. ISBN 0-354-04014-6.
- Carlton 1987, p. 48 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarlton1987 (help).
- Carlton 1987, p. 96 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarlton1987 (help).
- Purkiss 2007, p. 201 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFPurkiss2007 (help).
- Carlton 1987, p. 173 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCarlton1987 (help).
- ^ Atkinson 1911, 1. First Civil War (1642–46). sfn error: no target: CITEREFAtkinson1911 (help)
- "Oliver Cromwell: English statesman". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- Gregg 1984, pp. 129–30 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGregg1984 (help).
- Gregg 1984, p. 166 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGregg1984 (help).
- ^ Gregg 1984, p. 175 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFGregg1984 (help).
- Adair, John (1976). A Life of John Hampden The Patriot 1594-1643. London: Macdonald and Jane's Publishers Limited. ISBN 0-354-04014-6.
- Purkiss 2007, p. 93 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFPurkiss2007 (help).
- Petition of Right at III, VII.
- ^ Sommerville 1992, pp. 65, 71, 80. sfn error: no target: CITEREFSommerville1992 (help)
- Russell 1998, p. 417. sfn error: no target: CITEREFRussell1998 (help)
- Purkiss 2007, pp. 104–105 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFPurkiss2007 (help).
- Upham 1842, p. 187 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFUpham1842 (help)
- Carlton 1995, p. 224. sfn error: no target: CITEREFCarlton1995 (help)
- ^ Carlton 1995, p. 225. sfn error: no target: CITEREFCarlton1995 (help)
- ^ Smith 1999, p. 123. sfn error: no target: CITEREFSmith1999 (help)
- Abbott 2020. sfn error: no target: CITEREFAbbott2020 (help)
- Coward 1994, p. 191. sfn error: no target: CITEREFCoward1994 (help)
- Gregg 1981, p. 335. sfn error: no target: CITEREFGregg1981 (help)
- Kenyon 1978, p. 129. sfn error: no target: CITEREFKenyon1978 (help)
- Kenyon 1978, p. 130. sfn error: no target: CITEREFKenyon1978 (help)
- Purkiss 2007, pp. 109–113 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFPurkiss2007 (help).
- See Purkiss 2007, p. 113 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFPurkiss2007 (help) for concerns of a similar English Catholic rising.
- ^ Sherwood 1997, p. 41 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSherwood1997 (help).
- Keeble 2002, p. 6 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFKeeble2002 (help).
- Keeble 2002, p. 9 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFKeeble2002 (help).
- Keeble 2002, p. 12 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFKeeble2002 (help).
- Keeble 2002, p. 34 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFKeeble2002 (help).
- Keeble 2002, p. 31 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFKeeble2002 (help).
- Keeble 2002, p. 48 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFKeeble2002 (help).
- Lodge 2007, pp. 5–6 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFLodge2007 (help).
- Lodge 2007, p. 6 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFLodge2007 (help).
- CEE staff 2007, Restoration harvnb error: no target: CITEREFCEE_staff2007 (help).
- EB staff 2012, Restoration harvnb error: no target: CITEREFEB_staff2012 (help).
- House of Commons 1802a. sfn error: no target: CITEREFHouse_of_Commons1802a (help)
- Harris 2005, p. 47 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFHarris2005 (help).
- ^ Pepys Diary 23 April 1661.
- House of Commons 1802b. sfn error: no target: CITEREFHouse_of_Commons1802b (help)
- Sandifer, Preston (2011). Perspectives on 17th Century West European History. New York: McNash. p. 1229.
- Jones 1978, p. 15 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFJones1978 (help).
- Clark 1953, p. 3 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFClark1953 (help).
- "William Cavendish, the Marquess of Newcastle". 11 November 2017.
- Baker 1994, p. 85. sfn error: no target: CITEREFBaker1994 (help)
- James Runcieman Sutherland, Restoration Literature, 1660-1700: Dryden, Bunyan, and Pepys (Clarendon Press, 1969).
- Lyndsey Bakewell, "Changing scenes and flying machines: re-examination of spectacle and the spectacular in Restoration theatre, 1660–1714" (PhD. Diss. Loughborough University, 2016) online.
- Jeremy W. Webster, "In and Out of the Bed-chamber: Staging Libertine Desire in Restoration Comedy". Journal for Early Modern Cultural Studies (2012): 77–96.
- "History of the Royal Society | Royal Society". royalsociety.org. Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- Porter, 80.
- See Hanson (2001), 85–88, for the Republican temper of London.
- Neil Wallington (2005). In Case of Fire. Jeremy Mills Publishing. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-9546484-6-6.
- All dates are given according to the Julian calendar. Note that, when recording British history, it is usual to use the dates recorded at the time of the event. Any dates between 1 January and 25 March have their year adjusted to start on 1 January according to the New Style.
- Tinniswood, 4, 101.
- Reddaway, 27.
- Van der Kiste, 114–115
- Davies, Norman, The Isles: A History (1999) ISBN 0-19-513442-7, p.614.
- Troost, 212–214
- Welcome parliament.uk. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
- Act of Union 1707, Article 3
- Simon Schama (presenter) (22 May 2001). "Britannia Incorporated". A History of Britain. Episode 10. 3 minutes in. BBC One.
- Lodge (1832), pp. 7–8
- Hudson, Pat. "The Workshop of the World". BBC. Retrieved 10 December 2010.
- Bennet, Geoffrey (2004). The Battle of Trafalgar. England: Pen & Sword Books Limited, CPI UK, South Yorkshire.
- Kiely, Ray (November 2011). "Industrialization and Development: A Comparative Analysis". UGL Press Limited: 25–26.
- Office for National Statistics 2000, p. 5 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFOffice_for_National_Statistics2000 (help)
- "Why the Industrial Revolution Happened Here". BBC. 11 January 2017.
- Aleksandr Georgievich, and David Minaevich Gamezardashvili Baramidze, Georgian literature (The Minerva Group, 2001).
- Jeremy Black, Crisis of Empire: Britain and America in the Eighteenth Century (2010).
- Eliga H. Gould, "American independence and Britain's counter-revolution", Past & Present (1997) #154 pp. 107–41.
- P. Bruce Buchan, "The East India Company 1749-1800: The evolution of a territorial strategy and the changing role of the directors." Business and Economic History (1994): 52–61.
- John McAleer, and Nigel Rigby, Captain Cook and the Pacific: art, exploration and empire (Yale UP, 2017).
- G. C. Bolton, "The Founding of the Second British Empire." Economic History Review 19.1 (1966): 195–200.
- Rosemary Sweet, Antiquaries: the discovery of the past in eighteenth-century Britain (A&C Black, 2004).
- William Li Parry-Jones, "Asylum for the mentally ill in historical perspective." Bulletin of the Royal College of Psychiatrists 12.10 (1988): 407-410 online.
- Dutton, Edward; Woodley of Menie, Michael (2018). "Chapter 7: How Did Selection for Intelligence Go Into Reverse?". At Our Wits' End: Why We're Becoming Less Intelligent and What It Means for the Future. Great Britain: Imprint Academic. pp. 85, 95–6. ISBN 9781845409852.
- Atterbury, Paul (17 February 2011). "Victorian Technology". BBC History. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- Robinson, Bruce (17 February 2011). "Victorian Medicine – From Fluke to Theory". BBC History. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- John Wolffe (1997). Religion in Victorian Britain: Culture and empire. Volume V. Manchester University Press. pp. 129–30. ISBN 9780719051845. Archived from the original on 10 May 2016. Retrieved 29 October 2015.
- Lawrence James, The rise and fall of the British Empire (1994) pp 169–318.
- ^ E.A. Benians et al. eds. The Cambridge History of the British Empire Vol. iii: The Empire – Commonwealth 1870–1919' (1959) pp 1–16. online
- J. Holland Rose et al. eds. The Cambridge History of the British Empire Vol-ii: The Growth of the New Empire 1783–1870 (1940) pp v–ix. online
- Dixon, Nicholas (2010). "From Georgian to Victorian". History Review. 2010 (68): 34–38. Archived from the original on 27 January 2013. Retrieved 5 April 2013.
- Haggard, Robert F. (2001). The persistence of Victorian liberalism:The Politics of Social Reform in Britain, 1870–1900. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-313-31305-9. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
- Dutton, Edward; van der Linden, Dimitri; Lynn, Richard (November–December 2016). "The negative Flynn Effect: A systematic literature review". Intelligence. 59: 163–9. doi:10.1016/j.intell.2016.10.002.
- ^ Gambino, Megan (3 December 2012). "Are You Smarter Than Your Grandfather? Probably Not". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved 22 October 2020.
- Edward C. Mack, Public Schools and British Opinion since 1860 (1941) online.
- Daniels, Morna. "Aspects of the Victorian Book: Children's Books". British Library. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- Lionel Thomas Caswell Rolt, Victorian engineering (Penguin, 1974).
- Mark Hoban (22 June 2010). Budget 2010 (PDF). HM Treasury. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 October 2012. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- "Local enterprise partnerships". Department of Communities and Local Government. 29 June 2010. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- "New Local Enterprise Partnerships criss-cross the country". News Distribution Service. 7 September 2010. Archived from the original on 13 September 2010. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- "Supporting economic growth through local enterprise partnerships and enterprise zones". gov.uk. Retrieved 30 April 2013.
- Allister Hayman (6 October 2010). "LEPs: 22 bald men fighting over a comb?". Local Government Chronicle. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- "Live blog: Sub-national economic growth white paper". 28 October 2010. Retrieved 28 October 2010.
- For a longer analysis of the relationship between Cromwell's position, the former monarchy and the military, see Sherwood 1997, pp. 7–11 harvnb error: no target: CITEREFSherwood1997 (help).
Further reading
- Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (2004) online; short scholarly biographies of all the major people
- Bédarida, François. A social history of England 1851–1990. Routledge, 2013.
- Davies, Norman, The Isles, A History Oxford University Press, 1999, ISBN 0-19-513442-7.
- Black, Jeremy. A new history of England (The History Press, 2013).
- Broadberry, Stephen et al. British Economic Growth, 1270–1870 (2015)
- Clapp, Brian William. An environmental history of Britain since the industrial revolution (Routledge, 2014)
- Clayton, David Roberts, and Douglas R. Bisson. A History of England (2 vol. 2nd ed. Pearson Higher Ed, 2013).
- Ensor, R. C. K. England, 1870–1914 (1936), comprehensive survey. online
- Roth, Cecil (1964). A history of the Jews in England (Second ed.). Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0198224884.
- Schama, Simon, A History of Britain: At the Edge of the World, 3500 BC – 1603 AD BBC/Miramax, 2000 ISBN 0-7868-6675-6; TV series A History of Britain, Volume 2: The Wars of the British 1603–1776 BBC/Miramax, 2001 ISBN 0-7868-6675-6; A History of Britain – The Complete Collection on DVD BBC 2002 OCLC 51112061
- Tombs, Robert, The English and their History (2014) 1040 pp online review
- Trevelyan, G.M. Shortened History of England (Penguin Books 1942) ISBN 0-14-023323-7 very well written; reflects perspective of 1930s; 595pp
- Woodward, E. L. The Age of Reform: 1815–1870 (1954) comprehensive survey online
Historiography
- Cannon, John. The Oxford Companion to British History (2nd ed. 2002) 1142pp
- Elton, G.R. Modern Historians on British History 1485–1945: A Critical Bibliography 1945–1969 (1970) excerpt, highly useful bibliography of 1000+ scholarly books, articles and book reviews published before 1970.
- Furber, Elizabeth Chapin, ed. Changing Views on British History (1966)
- Loades, David, ed. Reader's Guide to British History (2 vol 2003), 1610pp
- Schlatter, Richard, ed. Recent Views on British History: Essays on Historical Writing Since 1966 (1984)
Primary sources
- English historical documents London: Methuen; 12 vol to 1957; reprinted 2011; the most comprehensive collection on political, constitutional, economic and social topics
- Douglas, David Charles. ed. English historical documents, 1042–1189 (Vol. 2. Psychology Press, 1995, Reprint)
- Myers, Alec Reginald, ed. English historical documents. 4.. 1327–1485 (Vol. 4. Psychology Press, 1995, Reprint)
- Rothwell, Harry, ed. English Historical Documents: 1189–1327 (Taylor & Francis, 1995, Reprint)
- Whitelock, Dorothy. English Historical Documents, 500–1042 (Vol. 1. Psychology Press, 1996, Reprint)
- Williams, Charles H. English Historical Documents: Volume 5 1485–1558 (Routledge, 1995, Reprint)
- Archer, Ian W., and F. Douglas Price, eds. English Historical Documents: 1558–1603 (Routledge, 2011, reprint)
- Coward, Barry, and David Charles Douglas, eds. English historical documents. 5::(B). 1603–1660 (Routledge, 2010 reprint)
- Browning, Andrew. ed. English Historical Documents, 1660–1714 (Vol. 6. Psychology Press, 1995, reprint)
- Horn, David Bayne, and Mary Ransome, eds. English historical documents, 1714–1783 (Vol. 7. Routledge, 1996, reprint)
- Aspinall, Arthur. ed. English historical documents, 1783–1832 (Vol. 8. Psychology Press, 1995, reprint)
- Handcock, William D., and George Malcolm Young. eds. English Historical Documents, 1833–1874 (Vol. 9. Psychology Press, 1995, reprint)
- Douglas, D. C. ed. English historical documents, 1874–1914 (Methuen 1995)
- Beard, Charles, ed. An introduction to the English historians (1906) excerpts
- Cheyney, Edward P. Readings in English History Drawn from the Original Sources Intended to Illustrate a Short History of England (1935), 850 pp. (strongest on political & constitutional topics)
- Harmer, Florence Elizabeth. ed. Select English historical documents of the ninth and tenth centuries (Cambridge University Press, 2011)
- Henderson, Ernest Flagg, ed. Select historical documents of the Middle Ages (1907) online
- Leach, Arthur F. ed. Educational Charters and Documents 598 to 1909 (1911) 640pp; online over 400 pp. on Middle Ages
- Stephenson, Carl and Frederick G. Marcham, eds. Sources of English Constitutional History (2nd ed. 1990)
- Stubbs, William, ed. Select charters and other illustrations of English constitutional history from the earliest times to the reign of Edward the First (Clarendon Press, 1870) online
- Weiner, Joel H. ed. Great Britain Foreign Policy & Span of Empire, 1689–1971 (4 Vol, 1983), 3425 pp.
- Wiener, Joel H. ed. Great Britain: the lion at home; a documentary history of domestic policy, 1689–1973 (4 vol 1974), 1396 pp.
External sources
- "Finding primary resources for modern British history"
- Connected Histories
- Letters of the Kings of England, now first collected from the originals in royal archives, and from other authentic sources, private as well as public by J O Halliwell-Phillipps, London, H. Colburn, 1846. vol. 1 — Google Books
| History of the British Isles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Overview |  | |
| Prehistoric period | ||
| Classical period | ||
| Medieval period | ||
| Early modern period | ||
| Late modern period | ||
| Related | ||
| History of current European countries | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other entities | |
| Other entities | |
| England articles | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Geography | |||||||||||||||||
| Politics | |||||||||||||||||
| Culture |
| ||||||||||||||||
