This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 167.98.155.153 (talk) at 16:11, 24 March 2024 (removed badly written original research and other poor writing). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 16:11, 24 March 2024 by 167.98.155.153 (talk) (removed badly written original research and other poor writing)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) System information shell tool| This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subject, potentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral. Please help improve it by replacing them with more appropriate citations to reliable, independent, third-party sources. (July 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 Neofetch running on macOS Mojave Neofetch running on macOS Mojave | |
| Developer(s) | Dylan Araps |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 31 December 2015; 9 years ago (2015-12-31) |
| Stable release | 7.1.0 |
| Repository | GitHub |
| Written in | Bash 3.2 |
| Operating system | Linux, macOS, BSD, Windows, iOS, Android, GNU Hurd, Haiku, IRIX, MINIX, Solaris |
| Size | 277 KB |
| Available in | English |
| Type | Benchmark |
| License | MIT License |
Neofetch is a system information tool written in the Bash shell scripting language. Its output includes a logo of the distribution, rendered in ASCII art. Unlike a system monitor, the tool only features a static display of the computer's basic hardware and software configurations and their versions, typically operating system, the host, uptime, package managers, the shell, display resolution, desktop environment, window manager, themes and icons, the computer terminal, CPU, GPU, and RAM. Neofetch can also display images on the terminal with w3m-img in place of the ASCII logo art.
Example screenshots
-
 Neofetch showing Arch Linux
Neofetch showing Arch Linux
-
 Neofetch showing SteamOS on a Steam Deck
Neofetch showing SteamOS on a Steam Deck
-
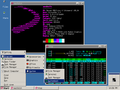 Neofetch and htop showing Devuan
Neofetch and htop showing Devuan
-
 Neofetch showing Debian Buster
Neofetch showing Debian Buster
Other implementations
- afetch, written in ANSI C
- CoalFetch, a one-liner program in Java
- dosfetch, written in Pascal for DOS
- efetch, written in C++
- fastfetch, a maintained, feature-rich and performance oriented drop-in replacement of neofetch. Written in C.
- gfetch, written in rc scripting language
- hfetch, written in Bash
- hyfetch, a updated fork of neofetch with pride flags' colors
- nerdfetch, fetch script using icons and glyphs from "Nerd Fonts" (sourced mainly from Material Design and Font Awesome)
- nextfetch, written in Go
- Pasfetch, written in Pascal
- perlfetch, written in Perl
- pfetch, written in Bourne scripting language
- rfetch, written in Rust
- screenfetch, a screenshot fetch script written in Bash
- swef, written in Lua
- swmfetch, written in Python
- ufetch, single shell script for each Unix-like platform
- winfetch, written in Microsoft PowerShell scripting language
References
- "Release 7.1.0". 2 August 2020. Retrieved 7 August 2020.
- Brian Schell (2019). Computing with the Raspberry Pi: Command Line and GUI Linux. p. 56
- "Neofetch Creates Colorful System Information Screens using Ascii Art". BleepingComputer. Retrieved 2022-07-10.
- Sneddon, Joey (2020-05-15). "NeoFetch: See System Information from the Command Line on Linux". OMG! Ubuntu!. Retrieved 2022-08-08.
- "Leahneukirchen/Dosfetch". GitHub.
- "fastfetch-cli/fastfetch". GitHub.
- "Hykilpikonna/Hyfetch". GitHub.
- "Nerd Fonts - Iconic font aggregator, glyphs/Icons collection, & fonts patcher".
- Katie (2024-01-02), screenFetch - The Bash Screenshot Information Tool, retrieved 2024-01-03
- "JSCHX / Ufetch · GitLab".
- "LPTSTR/Winfetch". GitHub.