This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Marbletan (talk | contribs) at 20:47, 15 April 2024. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 20:47, 15 April 2024 by Marbletan (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 5-(1,2-Dithiolan-3-yl)pentanamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | lipoamide |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H15NOS2 |
| Molar mass | 205.343 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
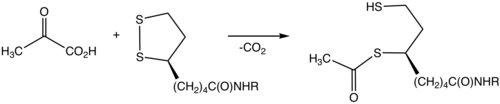
Lipoamide is a trivial name for 6,8-dithiooctanoic amide. It is the functional form of lipoic acid, i.e the carboxyl group is attached to protein via an amine with an amide linkage. Illustrative of the biochemical role of lipoamide is in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl lipoamide.
Lipoamide is found in a large number of plant and animal-based foods.
See also
References
- ^ "Metabocard for Lipoamide". Human Metabolome Database. 14 September 2021. HMDB0000962. Retrieved 30 November 2022.
- J. M. Berg; J. L. Tymoczko, L. Stryer (2007). Biochemistry (6th ed.). Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-8724-2.
External links
 Media related to Lipoamide at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lipoamide at Wikimedia Commons
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |