This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Smokefoot (talk | contribs) at 15:56, 29 August 2024 (→Occurrence: indent). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 15:56, 29 August 2024 by Smokefoot (talk | contribs) (→Occurrence: indent)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Oxidatively coupled derivative of gallic acid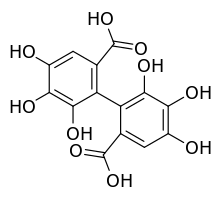 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 4,4′,5,5′,6,6′-Hexahydroxy-2,2′-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
HHDP 3,4,5,3′,4′,5′-Hexahydroxydiphenate 3,4,5,3′,4′,5′-Hexahydroxydiphenic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C14H10O10 |
| Molar mass | 338.224 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Hexahydroxydiphenic acid is an organic compound with the formula 2. It is the oxidatively coupled derivative of gallic acid It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to oxidation.
Occurrence

Luteic acid and ellagic acid are the mono- and dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid, respectively. Hexahydroxydiphenic acid is a component of some ellagitannins, such as casuarictin.
See also
References
- "MetaCyc hexahydroxydiphenic acid". biocyc.org.
- Haslam, E.; Cai, Y. (1994). "Plant polyphenols (vegetable tannins): Gallic acid metabolism". Natural Product Reports. 11 (1): 41–66. doi:10.1039/NP9941100041. PMID 15206456.
- Feldman, Ken S.; Iyer, Malliga R.; Liu, Yanze (2003). "Ellagitannin Chemistry. Studies on the Stability and Reactivity of 2,4-HHDP-Containing Glucopyranose Systems". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 68 (19): 7433–7438. doi:10.1021/jo034495x. PMID 12968897.
This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |