This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Finlay McWalter (talk | contribs) at 22:28, 18 September 2024 (MOS:SURPRISE, WP:SEEALSO). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 22:28, 18 September 2024 by Finlay McWalter (talk | contribs) (MOS:SURPRISE, WP:SEEALSO)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)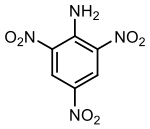
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2,4,6-Trinitroaniline | |
| Other names Picramide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.004 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H4N4O6 |
| Molar mass | 228.12 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow/orange/red powder |
| Density | 1.8 g/cm |
| Melting point | 188 °C (370 °F; 461 K) |
| Boiling point | explodes before boiling |
| Solubility in water | insoluble |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | instantaneous explosion |
| Flash point | unknown |
| Autoignition temperature |
unknown |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | unknown |
| Friction sensitivity | unknown |
| Detonation velocity | 7,300 m/s |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
2,4,6-Trinitroaniline, C6H4N4O6, abbreviated as TNA and also known as picramide, a nitrated amine. Materials in this group range from slight to strong oxidizing agents. If mixed with reducing agents, including hydrides, sulfides and nitrides, they may begin a vigorous reaction that culminates in a detonation. The aromatic nitro compounds may explode in the presence of a base such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide even in the presence of water or organic solvents. The explosive tendencies of aromatic nitro compounds are increased by the presence of multiple nitro groups. The appearance of trinitroaniline varies from yellow to orange to red depending on its purity and concentration.
Applications
Trinitroaniline is only used in modern times in the small warheads of some explosive devices such as mortars. In World War II it was used by Imperial Japanese Navy as Type 97 bakuyaku (Model 1931 explosive) in some versions of gun projectiles instead of less stable burster schimose (picric acid). It was also used in the Yokosuka MXY-7 Ohka, a kamikaze antishipping human-guided rocket aircraft.
Health and safety
Trinitroaniline is dangerously explosive and also hepatoxic. Symptoms of exposure to this compound may include skin and eye irritation, headache, drowsiness, weakness, cyanosis, and respiratory distress.
See also
References
- "2,4,6-TRINITROANILINE | CAMEO Chemicals | NOAA".
- "Definitions and Information about Naval Guns - NavWeaps".
- "2,4,6-Trinitroaniline - Hazardous Agents | Haz-Map". haz-map.com. Retrieved 2024-05-31.
- Holden, James R.; Dickinson, Charles; Bock, Charles M. (1972). "Crystal structure of 2,4,6-trinitroaniline". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 76 (24): 3597–3602. doi:10.1021/j100668a017.