This is the current revision of this page, as edited by LR.127 (talk | contribs) at 03:07, 27 December 2024 (Adding local short description: "Paradox by d'Alembert on fluid dynamics", overriding Wikidata description "hydrodynamic theorem"). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 03:07, 27 December 2024 by LR.127 (talk | contribs) (Adding local short description: "Paradox by d'Alembert on fluid dynamics", overriding Wikidata description "hydrodynamic theorem")(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Paradox by d'Alembert on fluid dynamics
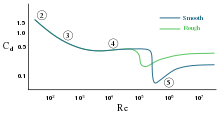
•2: attached flow (Stokes flow) and steady separated flow,
•3: separated unsteady flow, having a laminar flow boundary layer upstream of the separation, and producing a vortex street,
•4: separated unsteady flow with a laminar boundary layer at the upstream side, before flow separation, with downstream of the sphere a chaotic turbulent wake,
•5: post-critical separated flow, with a turbulent boundary layer.
In fluid dynamics, d'Alembert's paradox (or the hydrodynamic paradox) is a paradox discovered in 1752 by French mathematician Jean le Rond d'Alembert. D'Alembert proved that – for incompressible and inviscid potential flow – the drag force is zero on a body moving with constant velocity relative to the fluid. Zero drag is in direct contradiction to the observation of substantial drag on bodies moving relative to fluids, such as air and water; especially at high velocities corresponding with high Reynolds numbers. It is a particular example of the reversibility paradox.
D’Alembert, working on a 1749 Prize Problem of the Berlin Academy on flow drag, concluded:
It seems to me that the theory (potential flow), developed in all possible rigor, gives, at least in several cases, a strictly vanishing resistance, a singular paradox which I leave to future Geometers to elucidate.
— Jean le Rond d'Alembert (1768)
A physical paradox indicates flaws in the theory.
Fluid mechanics was thus discredited by engineers from the start, which resulted in an unfortunate split – between the field of hydraulics, observing phenomena which could not be explained, and theoretical fluid mechanics explaining phenomena which could not be observed – in the words of the Chemistry Nobel Laureate Sir Cyril Hinshelwood.
According to scientific consensus, the occurrence of the paradox is due to the neglected effects of viscosity. In conjunction with scientific experiments, there were huge advances in the theory of viscous fluid friction during the 19th century. With respect to the paradox, this culminated in the discovery and description of thin boundary layers by Ludwig Prandtl in 1904. Even at very high Reynolds numbers, the thin boundary layers remain as a result of viscous forces. These viscous forces cause friction drag on streamlined objects, and for bluff bodies the additional result is flow separation and a low-pressure wake behind the object, leading to form drag.
The general view in the fluid mechanics community is that, from a practical point of view, the paradox is solved along the lines suggested by Prandtl. A formal mathematical proof is lacking, and difficult to provide, as in so many other fluid-flow problems involving the Navier–Stokes equations (which are used to describe viscous flow).
Viscous friction: Saint-Venant, Navier and Stokes
First steps towards solving the paradox were made by Saint-Venant, who modelled viscous fluid friction. Saint-Venant states in 1847:
But one finds another result if, instead of an ideal fluid – object of the calculations of the geometers of the last century – one uses a real fluid, composed of a finite number of molecules and exerting in its state of motion unequal pressure forces or forces having components tangential to the surface elements through which they act; components to which we refer as the friction of the fluid, a name which has been given to them since Descartes and Newton until Venturi.
Soon after, in 1851, Stokes calculated the drag on a sphere in Stokes flow, known as Stokes' law. Stokes flow is the low Reynolds-number limit of the Navier–Stokes equations describing the motion of a viscous liquid.
However, when the flow problem is put into a non-dimensional form, the viscous Navier–Stokes equations converge for increasing Reynolds numbers towards the inviscid Euler equations, suggesting that the flow should converge towards the inviscid solutions of potential flow theory – having the zero drag of the d'Alembert paradox. Of this, there is no evidence found in experimental measurements of drag and flow visualisations. In the second half of the 19th century this again raised questions concerning the applicability of fluid mechanics.
Inviscid separated flow: Kirchhoff and Rayleigh
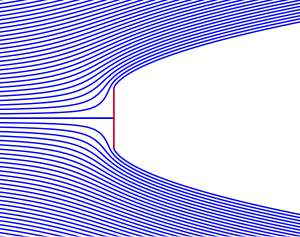
In the second half of the 19th century, focus shifted again towards using inviscid flow theory for the description of fluid drag—assuming that viscosity becomes less important at high Reynolds numbers. The model proposed by Kirchhoff and Rayleigh was based on the free-streamline theory of Helmholtz and consists of a steady wake behind the body. Assumptions applied to the wake region include: flow velocities equal to the body velocity, and a constant pressure. This wake region is separated from the potential flow outside the body and wake by vortex sheets with discontinuous jumps in the tangential velocity across the interface. In order to have a non-zero drag on the body, the wake region must extend to infinity. This condition is indeed fulfilled for the Kirchhoff flow perpendicular to a plate. The theory correctly states the drag force to be proportional to the square of the velocity. In first instance, the theory could only be applied to flows separating at sharp edges. Later, in 1907, it was extended by Levi-Civita to flows separating from a smooth curved boundary.
It was readily known that such steady flows are not stable, since the vortex sheets develop so-called Kelvin–Helmholtz instabilities. But this steady-flow model was studied further in the hope it still could give a reasonable estimate of drag. Rayleigh asks "... whether the calculations of resistance are materially affected by this circumstance as the pressures experienced must be nearly independent of what happens at some distance in the rear of the obstacle, where the instability would first begin to manifest itself."
However, fundamental objections arose against this approach: Kelvin observed that if a plate is moving with constant velocity through the fluid (at rest far from the plate, except for the wake) the velocity in the wake is equal to that of the plate. The infinite extent of the wake—widening with the distance from the plate, as obtained from the theory—results in an infinite kinetic energy in the wake, which must be rejected on physical grounds. Moreover, the observed pressure differences between front and back of the plate, and resulting drag forces, are much larger than predicted: for a flat plate perpendicular to the flow the predicted drag coefficient is CD=0.88, while in experiments CD=2.0 is found. This is mainly due to suction at the wake side of the plate, induced by the unsteady flow in the real wake (as opposed to the theory which assumes a constant flow velocity equal to the plate's velocity).
So, this theory is found to be unsatisfactory as an explanation of drag on a body moving through a fluid. Although it can be applied to so-called cavity flows where, instead of a wake filled with fluid, a vacuum cavity is assumed to exist behind the body.
Thin boundary layers: Prandtl

The German physicist Ludwig Prandtl suggested in 1904 that the effects of a thin viscous boundary layer possibly could be the source of substantial drag. Prandtl put forward the idea that, at high velocities and high Reynolds numbers, a no-slip boundary condition causes a strong variation of the flow speeds over a thin layer near the wall of the body. This leads to the generation of vorticity and viscous dissipation of kinetic energy in the boundary layer. The energy dissipation, which is lacking in the inviscid theories, results for bluff bodies in separation of the flow. The low pressure in the wake region causes form drag, and this can be larger than the friction drag due to the viscous shear stress at the wall.
Evidence that Prandtl's scenario occurs for bluff bodies in flows of high Reynolds numbers can be seen in impulsively started flows around a cylinder. Initially the flow resembles potential flow, after which the flow separates near the rear stagnation point. Thereafter, the separation points move upstream, resulting in a low-pressure region of separated flow.
Prandtl made the hypothesis that the viscous effects are important in thin layers – called boundary layers – adjacent to solid boundaries, and that viscosity has no role of importance outside. The boundary-layer thickness becomes smaller when the viscosity reduces. The full problem of viscous flow, described by the non-linear Navier–Stokes equations, is in general not mathematically solvable. However, using his hypothesis (and backed up by experiments) Prandtl was able to derive an approximate model for the flow inside the boundary layer, called boundary-layer theory; while the flow outside the boundary layer could be treated using inviscid flow theory. Boundary-layer theory is amenable to the method of matched asymptotic expansions for deriving approximate solutions. In the simplest case of a flat plate parallel to the incoming flow, boundary-layer theory results in (friction) drag, whereas all inviscid flow theories will predict zero drag. Importantly for aeronautics, Prandtl's theory can be applied directly to streamlined bodies like airfoils where, in addition to surface-friction drag, there is also form drag. Form drag is due to the effect of the boundary layer and thin wake on the pressure distribution around the airfoil.
Open questions
To verify, as Prandtl suggested, that a vanishingly small cause (vanishingly small viscosity for increasing Reynolds number) has a large effect – substantial drag — may be very difficult.
The mathematician Garrett Birkhoff in the opening chapter of his book Hydrodynamics from 1950, addresses a number of paradoxes of fluid mechanics (including d'Alembert's paradox) and expresses a clear doubt in their official resolutions:
- "Moreover, I think that to attribute them all to the neglect of viscosity is an unwarranted oversimplification The root lies deeper, in lack of precisely that deductive rigor whose importance is so commonly minimized by physicists and engineers."
In particular, on d'Alembert's paradox, he considers another possible route to the creation of drag: instability of the potential flow solutions to the Euler equations. Birkhoff states:
- "In any case, the preceding paragraphs make it clear that the theory of non-viscous flows is incomplete. Indeed, the reasoning leading to the concept of a "steady flow" is inconclusive; there is no rigorous justification for the elimination of time as an independent variable. Thus though Dirichlet flows (potential solutions) and other steady flows are mathematically possible, there is no reason to suppose that any steady flow is stable."
In his 1951 review of Birkhoff's book, the mathematician James J. Stoker sharply criticizes the first chapter of the book:
- "The reviewer found it difficult to understand for what class of readers the first chapter was written. For readers that are acquainted with hydrodynamics the majority of the cases cited as paradoxes belong either to the category of mistakes long since rectified, or in the category of discrepancies between theory and experiments the reasons for which are also well understood. On the other hand, the uninitiated would be very likely to get the wrong ideas about some of the important and useful achievements in hydrodynamics from reading this chapter."
In the second and revised edition of Birkhoff's Hydrodynamics in 1960, the above two statements no longer appear.
The importance and usefulness of the achievements, made on the subject of the d'Alembert paradox, are reviewed by Keith Stewartson thirty years later. His long 1981 survey article starts with:
- "Since classical inviscid theory leads to the patently absurd conclusion that the resistance experienced by a rigid body moving through a fluid with uniform velocity is zero, great efforts have been made during the last hundred or so years to propose alternate theories and to explain how a vanishingly small frictional force in the fluid can nevertheless have a significant effect on the flow properties. The methods used are a combination of experimental observation, computation often on a very large scale, and analysis of the structure of the asymptotic form of the solution as the friction tends to zero. This three-pronged attack has achieved considerable success, especially during the last ten years, so that now the paradox may be regarded as largely resolved."
For many paradoxes in physics, their resolution often lies in transcending the available theory. In the case of d'Alembert's paradox, the essential mechanism for its resolution was provided by Prandtl through the discovery and modelling of thin viscous boundary layers – which are non-vanishing at high Reynolds numbers.
Proof of zero drag in steady potential flow

Potential flow
The three main assumptions in the derivation of d'Alembert's paradox is that the steady flow is incompressible, inviscid and irrotational. An inviscid fluid is described by the Euler equations, which together with the other two conditions read
where u denotes the flow velocity of the fluid, p the pressure, ρ the density, and ∇ is the gradient operator.
We have the second term in the Euler equation as:
where the first equality is a vector calculus identity and the second equality uses that the flow is irrotational. Furthermore, for every irrotational flow, there exists a velocity potential φ such that u = ∇φ. Substituting this all in the equation for momentum conservation yields
Thus, the quantity between brackets must be constant (any t-dependence can be eliminated by redefining φ). Assuming that the fluid is at rest at infinity and that the pressure is defined to be zero there, this constant is zero, and thus
which is the Bernoulli equation for unsteady potential flow.
Zero drag
Now, suppose that a body moves with constant velocity v through the fluid, which is at rest infinitely far away. Then the velocity field of the fluid has to follow the body, so it is of the form u(x, t) = u(x − v t, 0), where x is the spatial coordinate vector, and thus: Since u = ∇φ, this can be integrated with respect to x:
The force F that the fluid exerts on the body is given by the surface integral where A denotes the body surface and n the normal vector on the body surface. But it follows from (2) that thus with the contribution of R(t) to the integral being equal to zero.
At this point, it becomes more convenient to work in the vector components. The kth component of this equation reads
Let V be the volume occupied by the fluid. The divergence theorem says that The right-hand side is an integral over an infinite volume, so this needs some justification, which can be provided by appealing to potential theory to show that the velocity u must fall off as r – corresponding to a dipole potential field in case of a three-dimensional body of finite extent – where r is the distance to the centre of the body. The integrand in the volume integral can be rewritten as follows: where first equality (1) and then the incompressibility of the flow are used. Substituting this back into the volume integral and another application of the divergence theorem again. This yields Substituting this in (3), we find that The fluid cannot penetrate the body and thus n · u = n · v on the body surface. So and Finally, the drag is the force in the direction in which the body moves, so Hence the drag vanishes. This is d'Alembert's paradox.
Notes
- Jean le Rond d'Alembert (1752).
- Grimberg, Pauls & Frisch (2008).
- Falkovich (2011), p. 32.
- M.J. Lighthill (1956), "Physics of gas flow at very high speeds", Nature, 178 (4529): 343, Bibcode:1956Natur.178..343., doi:10.1038/178343a0 Report on a conference.
- ^ Landau & Lifshitz (1987), p. 15.
- ^ Batchelor (2000), pp. 264–265, 303, 337.
- ^ Schlichting, Hermann; Gersten, Klaus (2000), Boundary-layer theory (8th revised and enlarged ed.), Springer, ISBN 978-3-540-66270-9, pp. XIX–XXIII.
- ^ Veldman, A.E.P. (2001), "Matched asymptotic expansions and the numerical treatment of viscous–inviscid interaction", Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 39 (1): 189–206, Bibcode:2001JEnMa..39..189V, doi:10.1023/A:1004846400131, S2CID 189820383
- ^ Stewartson (1981).
- Feynman, R.P.; Leighton, R.B.; Sands, M. (1963), The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley, ISBN 978-0-201-02116-5, Vol. 2, §41–5: The limit of zero viscosity, pp. 41–9 – 41–10.
- Saint-Venant, A. (1847), "Mémoire sur la théorie de la résistance des fluides. Solution du paradoxe proposé à ce sujet par d'Alembert aux géomètres. Comparaison de la théorie aux expériences", Comptes Rendus des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences, 24: 243–246, retrieved 2008-08-15
- Stokes, G.G. (1851), "On the effect of the internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums", Trans. Camb. Philos. Soc., 9: 8–106, Bibcode:1851TCaPS...9....8S. Reprinted in Stokes, G.G., "On the effect...", Mathematical and Physical Papers, vol. 3 (2nd ed.), Cambridge Univ. Press
- The Stokes flow equations have a solution for the flow around a sphere, but not for the flow around a circular cylinder. This is due to the neglect of the convective acceleration in Stokes flow. Convective acceleration is dominating over viscous effects far from the cylinder (Batchelor, 2000, p. 245). A solution can be found when convective acceleration is taken into account, for instance using the Oseen equations (Batchelor, 2000, pp. 245–246).
- ^ Batchelor (2000), pp. 337–343 & plates.
- Batchelor (2000), p. 499, eq. (6.13.12).
- Kirchhoff, G. (1869), "Zur Theorie freier Flüssigkeitsstrahlen", Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik, 1869 (70): 289–298, doi:10.1515/crll.1869.70.289, S2CID 120541431
- ^ Rayleigh, Lord (1876), "On the resistance of fluids", Philosophical Magazine, 5 (2): 430–441. Reprinted in: Scientific Papers 1:287–296.
- Helmholtz, H. L. F. von (1868), "Über discontinuierliche Flüssigkeitsbewegungen", Monatsberichte der Königlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin, 23: 215–228. Reprinted in: Philosophical Magazine (1868) 36:337–346.
- Batchelor (2000), pp. 338–339
- ^ Wu, T. Y. (1972), "Cavity and wake flows", Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 4: 243–284, Bibcode:1972AnRFM...4..243W, doi:10.1146/annurev.fl.04.010172.001331
- ^ Lamb, H. (1994), Hydrodynamics (6th ed.), Cambridge University Press, p. 679, ISBN 978-0-521-45868-9
- Levi-Civita, T. (1907), "Scie e leggi di resistenza", Rendeconti del Circolo Matematico di Palermo, 23: 1–37, doi:10.1007/bf03013504, S2CID 118652934
- Lord Kelvin (1894), "On the doctrine of discontinuity of fluid motion, in connection with the resistance against a solid moving through a fluid", Nature, 50 (1300): 524–5, 549, 573–5, 597–8, Bibcode:1894Natur..50..524K, doi:10.1038/050524e0 Reprinted in: Mathematical and Physical Papers 4: 215–230.
- Batchelor (2000), p. 500.
- Batchelor (2000), pp. 493–494.
- ^ Prandtl (1904).
- Batchelor (2000) pp. 302–314 & 331–337.
- Garrett Birkhoff, Hydrodynamics: a study in logic, fact, and similitude, Princeton University Press, 1950
- Birkhoff (1950) p. 4.
- Birkhoff (1950) p. 21.
- James J. Stoker (1951), "Review: Garrett Birkhoff, Hydrodynamics, a study in logic, fact, and similitude", Bull. Amer. Math. Soc., 57 (6): 497–499, doi:10.1090/S0002-9904-1951-09552-X.
- Closest to the first quote comes, on page 5:
- "...It is now usually claimed that such paradoxes are due to the differences between “real” fluids having small but finite viscosity, and “ideal” fluids having zero viscosity. Thus it is essentially implied that one can rectify Lagrange's claim, by substituting “Navier-Stokes” for “Euler”. This claim will be discussed critically in Ch. II; it may well be correct in principle for incompressible viscous flow. However, taken literally, I think it is still very misleading, unless explicit attention is paid to the plausible hypotheses listed above, and to the lack of rigor implied by their use. Though I do not know of any case when a deduction, both physically and mathematically rigorous, has led to a wrong conclusion, very few of the deductions of rational hydrodynamics can be established rigorously. The most interesting ones involve free use of Hypotheses (A)-(F)..."
- "...One owes to Euler the first general formulas for fluid motion ... presented in the simple and luminous notation of partial differences ... By this discovery, all fluid mechanics was reduced to a single point of analysis, and if the equations involved were integrable, one could determine completely, in all cases, the motion of a fluid moved by any forces..."
- For instance, the paradox of the constancy of the speed of light in all directions, was solved by the special theory of relativity.
- This article follows the derivation in Section 6.4 of Batchelor (2000).
References
Historical
- d'Alembert, Jean le Rond (1752), Essai d'une nouvelle théorie de la résistance des fluides
- d'Alembert, Jean le Rond (1768), "Memoir XXXIV", Opuscules Mathématiques, vol. 5 (§I ed.), pp. 132–138
- Prandtl, Ludwig (1904), Motion of fluids with very little viscosity (PDF), vol. 452, NACA Technical Memorandum
Further reading
- Batchelor, G. (2000), An introduction to fluid dynamics, Cambridge Mathematical Library (2nd ed.), Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-66396-0, MR 1744638
- Falkovich, G. (2011), Fluid Mechanics, a short course for physicists, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-1-107-00575-4
- Grimberg, G.; Pauls, W.; Frisch, U. (2008), "Genesis of d'Alembert's paradox and analytical elaboration of the drag problem", Physica D, 237 (14–17): 1878–1886, arXiv:0801.3014, Bibcode:2008PhyD..237.1878G, doi:10.1016/j.physd.2008.01.015, S2CID 15979390
- Landau, L. D.; Lifshitz, E. M. (1987), Fluid Mechanics, Course of Theoretical Physics, vol. 6 (2nd ed.), Pergamon Press, ISBN 978-0-08-009104-4
- Stewartson, K. (1981), "D'Alembert's Paradox", SIAM Review, 23 (3): 308–343, doi:10.1137/1023063
External links
- Potential Flow and d'Alembert's Paradox at MathPages




 Since u = ∇φ, this can be integrated with respect to x:
Since u = ∇φ, this can be integrated with respect to x:

 where A denotes the body surface and n the
where A denotes the body surface and n the  thus
thus
 with the contribution of R(t) to the integral being equal to zero.
with the contribution of R(t) to the integral being equal to zero.

 The right-hand side is an integral over an infinite volume, so this needs some justification, which can be provided by appealing to potential theory to show that the velocity u must fall off as r – corresponding to a
The right-hand side is an integral over an infinite volume, so this needs some justification, which can be provided by appealing to potential theory to show that the velocity u must fall off as r – corresponding to a  where first equality (1) and then the incompressibility of the flow are used. Substituting this back into the volume integral and another application of the divergence theorem again. This yields
where first equality (1) and then the incompressibility of the flow are used. Substituting this back into the volume integral and another application of the divergence theorem again. This yields
 Substituting this in (3), we find that
Substituting this in (3), we find that
 The fluid cannot penetrate the body and thus n · u = n · v on the body surface. So
The fluid cannot penetrate the body and thus n · u = n · v on the body surface. So  and
and
 Finally, the drag is the force in the direction in which the body moves, so
Finally, the drag is the force in the direction in which the body moves, so
 Hence the drag vanishes. This is d'Alembert's paradox.
Hence the drag vanishes. This is d'Alembert's paradox.