This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Wernher (talk | contribs) at 03:50, 3 June 2005 (→Surviving V-2 examples and components: fmt). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 03:50, 3 June 2005 by Wernher (talk | contribs) (→Surviving V-2 examples and components: fmt)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)The V-2 rocket (German: Vergeltungswaffe 2 or "reprisal weapon 2", or A4 a short form of Aggregat 4, the fourth rocket type) was an early ballistic missile used by Germany during the later stages of World War II against mostly British and Belgian targets.
Pre-operational history
As early as 1927 members of the Verein für Raumschiffahrt (VfR) ("Spaceflight Society") had started experimenting with liquid-fuelled rockets. Rockets using a solid propellant had been used as weapons by all sides in WWI, and as a result, the Treaty of Versailles forbade solid-rocket research in Germany. By 1932 the Reichswehr started taking notice of their developments for potential long-range artillery use, and a team led by General Walter Dornberger was shown a test vehicle designed and flown by Wernher von Braun. Although the rocket was of limited ability, Dornberger saw Von Braun's genius and pushed for him to join the military.
Von Braun did so, as eventually did most of the other members of the society. In December 1934 Von Braun scored another success with the flight of the A2 (A for Aggregat) rocket, a small model powered by ethanol and liquid oxygen, with work on the design continuing in an attempt to improve reliability. Many different liquid fuels had been developed, but the German military specifically encouraged the use of ethanol as a rocket fuel because Germany had always been hampered by a shortage of crude-oil-based fuels. throughout WWII a wide variety of military rockets were fuelled by ethanol that was primarily derived from potatoes.
By 1936 the team had moved on from the A2 and started work on both the A3 and A4. The latter was a full-sized design with a range of about 175 km (110 miles), a top altitude of 80 km and a payload of about a tonne. This increase in capability had come through a complete redesign of the engine by Walter Thiel. It was clear that Von Braun's designs were turning into real weapons, and Dornberger moved the team from Kummersdorf (near Berlin) to a small town, Peenemünde, on the island of Usedom on Germany's Baltic coast, in order to provide more room for testing and greater secrecy.
The A3 proved to be problematic, and a redesign was started as the A5. This version was completely reliable, and by 1941 the team had fired about 70 A5 rockets. The first A4 flew in March 1942, flying about 1.6 km and crashing into the water. The second launch reached an altitude of 11 km before exploding. The third rocket, launched on October 3 1942, changed things by following its trajectory perfectly. It landed 193 km away, and became the first man-made object to enter space.

Production started in 1943 on the wonder weapon Vergeltungswaffe 2 (reprisal weapon 2), or the V-2 as it became better known, at the insistence of Goebbels' propaganda ministry. The Allies were already aware of the weapon. At a test site at Blizna in Poland a fired missile had been recovered by Polish resistance agents from the banks of the Western Bug, and vital technical details had been given to British intelligence. The British launched a massive bombing campaign against Peenemünde which slowed testing and production considerably as well as killing many slave workers.
Dornberger had always wanted a mobile launch platform for the missiles, but Hitler pressed for the construction of massive underground blockhouses from which to launch them. V-2s arrived from a number of factories in a continuous stream on several redundant rail lines, and launching was almost continual.
Construction of the first such site started at Eperleques in the Pas-de-Calais area in 1943, but the British spotted it almost immediately and started a massive bombing campaign that eventually forced the Germans to abandon it. Another site was then started nearby in a huge quarry and called La Coupole, but it wasn't long before that too was bombed into submission. Eventually they gave up on the area and moved to the south near Cherbourg, but once again the site was discovered and bombed — this time while the concrete was still wet.
The plan was changed to build large truck-towed trailers for the missiles. An entire convoy for the missile, men, equipment and fuel required about thirty trucks. The missile was delivered to a staging area on a Vidalwagen and the local crews would fit the warhead. Launch teams would then transfer their missile to their own Meillerwagen and tow it to the launch site. There it was erected onto the launch table, fuelled, and launched.
The missile could be launched practically anywhere, roads running though forests being a particular favourite. The system was so mobile and small that not one Meillerwagen was ever caught in action.
Peenemünde test launch list (until July 1943)
| Rocket number | Date | Burning time (seconds) | Range (kilometers) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | March 16, 1942 | - | 0 | Explosion at liftoff |
| 2 | June 13, 1942 | 36 | 1.3 | Rolled, unstable |
| 3 | August 16, 1942 | 45 | 8.7 | Nose broke off |
| 4 | October 3, 1942 | 58 | 190 | Too steep, success |
| 5 | October 21, 1942 | 84 | 147 | Steam generator misbehaved |
| 6 | November 9, 1942 | 54 | 14 | Vertical, height 67 km |
| 7 | November 28, 1942 | 37 | 8.6 | Tumbled, lost vanes |
| 9 | December 9, 1942 | 4 | 0.1 | Hydrogen peroxide explosion |
| 10 | January 7, 1943 | - | 0 | Explosion on ignition |
| 11 | January 25, 1943 | 64.5 | 105 | Too steep, rolled |
| 12 | February 17, 1943 | 61 | 196 | Too shallow |
| 13 | February 19, 1943 | 18 | 4.8 | Fire in tail |
| 16 | March 3, 1943 | 33 | 1.0 | Vertical, explosion |
| 18 | March 18, 1943 | 60 | 133 | Too steep, rotated |
| 19 | March 25, 1943 | 28 | 1.2 | Tumbled, exploded |
| 20 | April 14, 1943 | 66 | 287 | Fell on land |
| 21 | April 22, 1943 | 59 | 252 | Fell on land |
| 22 | May 14, 1943 | 62 | 250 | Cut-off switch failed |
| 26 | May 26, 1943 | 66.5 | 265 | - |
| 25 | May 26, 1943 | 40 | 27 | Brennschluss (engine cut-off) at 40 s |
| 24 | May 27, 1943 | 55 | 138 | - |
| 23 | June 1, 1943 | 62 | 235 | Premature engine cutoff |
| 29 | June 11, 1943 | 63.5 | 238 | - |
| 31 | June 16, 1943 | 60.5 | 221 | Premature engine cutoff |
| 28 | June 22, 1943 | 62.5 | 75 | exploded after 75 s |
| 30 | June 24, 1943 | 65.1 | 287 | Cut-off switch failed, first launch on Prüfstand X |
| 36 | June 26, 1943 | 64.9 | 235 | - |
| 38 | June 29, 1943 | 15 | 3 | Fell on airport |
| 40 | June 29, 1943 | 63.6 | 236 | Impact not observed |
| 33 | July 1, 1943 | - | - | Engine cutoff at take-off, exploded |
| 41 | July 9, 1943 | 4 | 0.1 | Fell on pump building |
| 34 | July 9, 1943 | - | - | BEngine cutoff at take-off, exploded |
| - | August 12, 1943 | 64 | ? | Successful launch |
| - | October 6, 1943 | 68 | ? | Successful launch, duration 272 s; first launch after raid on August 17, 1943 |
| - | October 21, 1943 | 63 | ? | Successful launch, duration 286 s |
| - | December 4, 1943 | 63 | ? | Successful launch, duration 286 s |
| - | December 10, 1943 | 69 | ? | Successful launch, duration 247 s |
| - | December 21, 1943 | 33 | ? | Only partial success, premature engine cutoff, duration of flight 104 s |
| - | January 7, 1944 | 43 | ? | Exploded 43 s after launch |
| - | January 27, 1944 | ? | ? | First test flight of rocket built in Mittelwerk, failure |
| - | March 2, 1944 | ? | ? | Exploded |
| - | March 11, 1944 | 59 | ? | Flight duration 282 s |
For the period after July 1943 only uncomplete launch logs of experimental A4-launches at Peenemünde are available. Experimental launches continued in spite of air raids on August 17, 1943 and in July/August 1944 until February 21, 1945. A test rocked launched from Peenemünde on June 13, 1944, crashed in Sweden.
- Test range in Peenemunde Test range in Peenemunde
- Failed test at Peenemunde, August of 1943 Failed test at Peenemunde, August of 1943
-
 V-2 rocket being recovered from the Bug river by the Home Army
V-2 rocket being recovered from the Bug river by the Home Army
- Parts of the V-2 rocket recovered from the Bug river by the Home Army Parts of the V-2 rocket recovered from the Bug river by the Home Army
- German WWII leaflet in Polish and German warning the inhabitants of the area of testing site at Blizna of the crashed V-2 rockets German WWII leaflet in Polish and German warning the inhabitants of the area of testing site at Blizna of the crashed V-2 rockets
- Marceli Struszyński, a professor of the Warsaw University of Technology who successfuly analised the composition of fuel used by the V-2 and then passed the results of his research to the UK Marceli Struszyński, a professor of the Warsaw University of Technology who successfuly analised the composition of fuel used by the V-2 and then passed the results of his research to the UK
- Members of the Operation Most III, during which the parts of the captured V-2, as well as the analisis and sketches were transfered from occupied Poland to UK Members of the Operation Most III, during which the parts of the captured V-2, as well as the analisis and sketches were transfered from occupied Poland to UK
- Roman Traeger, a Polish scientist and member of the Polish intelligence service who discovered the Peenemunde test site Roman Traeger, a Polish scientist and member of the Polish intelligence service who discovered the Peenemunde test site
- V-2 ready to use; Holland, December of 1944 V-2 ready to use; Holland, December of 1944
Operational history
V-2 mass production was conducted at the Mittelwerk tunnel system under the Kohnstein mountain, part of the Mittelbau-Dora slave labour camp complex, near Nordhausen, Germany. By late 1943 over 10,500 forced laborers were in Kohnstein and many died due to the conditions (cold and humidity, especially) and heavy labour. For example, 2,900 died between October 1943 and March 1944, but others died during transfers and other work. Put another way, fatalities averaged over 100 per day during certain periods. The majority of the slaves were Russian, Polish and French, although there were also prisoners of war, foreign workers and Germans forced to compulsory work.


The first unit to reach operational status was Batterie 444. On September 2 1944 they formed up to launch attacks on Paris, recently liberated, and eventually set up near Houffalize in Belgium. The next day the 485th moved to The Hague for operations against London. Several launch attempts over the next few days failed, but on the 8th both groups fired successfully.
This was the tip of the iceberg. Over the next few months the total numbers fired were:
- At the Netherlands
- Maastricht 19
A V-2 test rocket fired on 30th May 1944 crashed near the test facility at Sarnaki nad Bugiem and was recovered and secured by Polish resistance (Home Army). On the night of 25/26 July 1944 it was successfully transported to the UK from occupied Poland by a RAF plane (see Operation III Most). Analysis of the captured equipment proved vital in improving the Allies anti-V-2 defences.
On 3 March 1945 the allies attempted to destroy V-2s and launching equipment near The Hague by a large-scale bombardment, but due to navigational errors the Bezuidenhout quarter was destroyed, killing 500 civilians.
The V-2 was militarily ineffective. Its guidance systems were too primitive to hit specific targets, and its costs were approximately equivalent to four-engined bombers, which were more accurate (though only in a relative sense—see discussion in strategic bomber), had longer ranges, carried many more warheads, and were reusable. Nevertheless, it had a considerable psychological effect as, unlike bombing planes or the V1 Flying Bomb, which made a characteristic buzzing sound, the V-2 travelled faster than the speed of sound, with no warning before impact and no possibility of defense. The British were able to redirect V-1's and V-2's aimed at London to less populated areas east of the city by sending false impact reports via the German espionage network in Britain, which was actually controlled by the British. See: Double Cross System.
A submarine towed launch platform was tested successfully, effectively making it the prototype for submarine launched ballistic missiles. The project codename was Prufstand XII. If deployed, it would have allowed a U-boat to launch V-2 missiles against American cities, though only with considerable effort (and likely limited effect).
Twelve dismantled V-2 rockets were shipped to the Japanese by U-boat in dismantled condition. These left Bordeaux in August 1944 on transport U-boats U-219 and U-195 reaching Djakarta in December 1944. A civillian V-2 expert was also a VIP passenger on the U-234 bound for Japan in May 1945 when the war ended in Europe. The fate of these V-2 rockets is unknown.
Post-war V-2 usage
At the end of the war a race started to retrieve as many V-2 rockets and staff as possible. Under Operation Paperclip three hundred trainloads of V-2s and parts were captured and shipped to the United States, as well as 126 of the principal designers, including both Wernher von Braun and Walter Dornberger. Under British supervision, there were also three V-2 rocket launches to demonstrate the launch of V-2 rockets (operation Backfire) in October 1945. For several years afterward, the United States rocketry program made use of the supply of unused V-2 rockets left from the war. Some of these were equipped with a WAC-rocket as a second stage. These rockets were called Bumper. In 1949 such a rocket reached a then-record altitude of 400 km (250 miles) at its launch from White Sands. The Bumper was also the first rocket launched from Cape Canaveral. Many of these rockets were used for peaceful purposes, including upper-atmosphere research.
Von Braun went to work for the US Army's Redstone Arsenal, eventually settling in Huntsville, Alabama in 1950. He quickly became the father of almost all US rocketry, working on the Redstone, Jupiter, Jupiter-C, Pershing, and Saturn rockets.
The USSR also captured a number of V-2s and staff, letting them set up in Germany for a time. In 1946 they were moved to a site near Moscow in the USSR where Groettrup headed up a group of just under 250 engineers. The first Soviet missile was the R-1, an exact copy of the V-2 manufactured in the USSR. Starting with the R-1 (soon followed by its evolved version R-2) the Soviets developed a number of new missile designs which would eventually lead to the Scud missile.
The designs produced by the German team in Moscow were not put directly into production; instead, local designers would incorporate the better features into their own designs. In this way the Soviet Union built up its own rocket design experience. The German team was eventually repatriated in the 1950s after the local design teams had captured all their knowledge.
The British also captured a small number of V-2 missiles, and launched several of them from a site in northern Germany under Operation Backfire. However the engineers involved had already agreed to move to the US when the test firings were complete. The Backfire report however remains the most extensive technical documentation of the rocket, including all support procedures, tailored vehicles and fuel composition.
Technical details
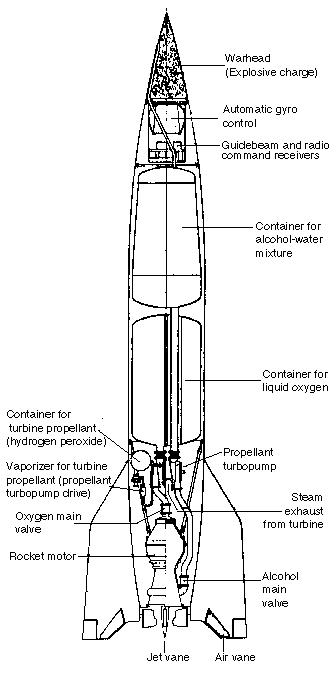
The V-2 had an operational range of about 300 km (200 statute miles) carrying a 1000 kg (2200 lb) warhead. The V-2 had an accuracy circular error probable (CEP) of 11 miles (17 km). This means at a 200-mile (300 km) range, the V-2 would only have a 50% chance of being within an 11-mile (17 km) circle centred on the target. With that kind of accuracy, it could be aimed to hit a city, but not a factory. Modern missiles, the Minuteman for example, have a CEP of 320 feet (100 metres) at a 6,000 mile (10,000 km) range.
The V-2 was propelled by alcohol (ethanol) and water fuel, and the oxidizer was liquid oxygen. The fuel and oxidizer pumps were steam turbines, and the steam was produced by concentrated hydrogen peroxide with calcium permanganate catalyst. The water-alcohol fuel was kept in a tank of aluminium to save weight, which put a high pressure on German war economy, as this metal was rare and valuable.
The alcohol-water fuel was pumped along the double wall of the main combustion burner, so that the chamber would at the same time heat the fuel and be cooled by it so preventing melting due to the 2500–2700 degree Celsius temperature. The fuel was then pumped into the main burner chamber through 1224 nozzles, which assured the correct mixture of alcohol and oxygen at all times. Small holes also permitted some alcohol to escape directly into the combustion chamber, forming a boundary layer that further protected the wall of the chamber, especially at the neck where the chamber was narrowest. This boundary layer ignited in contact with the atmosphere, accounting for the long, diffuse exhaust plume of the V-2. (Later, post-V2 engine designs not employing the boundary layer show a translucent plume with shock diamonds.)
The V-2 was controlled by four external rudders on the tail fins, and four internal rudders, made of graphite, at the exit of the motor. Some later V-2s used "guide beams" (i.e. radio signals transmitted from the ground), to navigate the missile toward its target, but the first models used a simple analog computer that would adjust the azimuth for the rocket, and the flying distance was controlled by the moment of engine cut-off,"Brennschluss", ground controlled by a Doppler system or by different types of on-board integrating accelerometers. The rocket would stop accelerating and soon reach the top of the (approximately parabolic) flight curve.
The painting of the operational V-2s was mostly a camouflage ragged pattern with several variations, but in the end of the war a plain olive green rocket also appeared. During tests, the rocket was painted in a characteristic black/white chessboard pattern which aided in determining if the rocket was spinning around its own longitudinal axis.
Lesser known influences on culture and technology
- The V-2 rocket plays a major part in Thomas Pynchon's novel Gravity's Rainbow.
- The lunar rocket in Hergé's Tintin comic books Destination Moon and Explorers on the Moon looks like a V-2, as do most science fiction rockets of the 1950s. What is unique about Hergé's book is that they also feature the chessboard test-pattern.
- The "rocket-bombs" in George Orwell's Nineteen Eighty-Four may have been analogous to the V2.
- The Canadian Arrow, a competitor for the Ansari X Prize, is based on the V2.
Models
Model rocket V-2s are available in many sizes. For Germans, the 33-cm and 47-cm NORIS models are the best flying versions, because they can be launched without special permission with model rocket engines available in Germany.
Surviving V-2 examples and components
The short overview below includes only four of the at least 20 V-2s still existing as of 2005. For a presumably complete list, consult V2ROCKET.COM's "Surviving A4/V2 Rockets Around the World". Most, but not all, of the listed examples are available on public display.
- one V-2 at the London Science Museum
- one V-2 (painted bright green, and cut through to display the engine and some other interior parts) at the Imperial War Museum, London (on loan from Cranfield University)
- one V-2 (chessboard-painted) at the Kansas Cosmosphere and Space Center in Hutchinson, Kansas
- one V-2 at the National Air and Space Museum, Washington, D.C.
- one V-2 engine at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama
- one V-2 (1944, complete) at the Deutsches Museum in Munich (this example standing next to the Museum's spiral staircase)
- one V-2 engine (1944, cut through to reveal technical details) (also at the Deutches Museum)
- ironically, and unfortunately, the chessboard-painted V-2 at the outdoor exhibit of the Peenemünde Museum in northern Germany is not a genuine rocket, but a replica
See also
References
- King, Benjamin and Timothy J. Kutta. Impact: The History of Germany's V-Weapons in World War II . (Alternately: Impact: An Operational History of Germany's V Weapons in World War II.) Rockville Center, New York: Sarpedon Publishers, 1998. ISBN 1885119518; ISBN 1862270244; ISBN 0306812924.
- Piszkiewicz, Dennis. The Nazi Rocketeers: Dreams of Space and Crimes of War. Westport, Conn.: Praeger, 1995. ISBN 0275952177.
- Dornberger, Walter. V-2. New York: Ballantine Books, 1954
External links
- Encyclopedia Astronautica article on the V-2
- www.v2rocket.com
- V-2 history page – from Canadian Arrow official website
| Aviation lists | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Military | |
| Accidents / incidents | |
| Records | |