This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Ramdrake (talk | contribs) at 18:38, 19 October 2007 (→Late 20th century debate: Removing cite as per talk page). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 18:38, 19 October 2007 by Ramdrake (talk | contribs) (→Late 20th century debate: Removing cite as per talk page)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| The neutrality of this article is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Template:Race and intelligence2
The study of race and intelligence is the controversial study of how human intellectual capacities may vary among the different population groups commonly known as races. This study seeks to identify and explain the differences in manifestations of intelligence (e.g. IQ testing results), as well as the underlying causes of such variance.
Theories about the possibility of a relationship between race and intelligence have been the subject of speculation and debate since the 16th century. The contemporary debate focuses on the nature, causes, and importance, or lack of importance, of ethnic differences in intelligence test scores and other measures of cognitive ability, and whether "race" is a meaningful biological construct with significance other than its correlation to membership of particular ethnic groups. Thus, the question of the relative roles of nature and nurture in causing individual and group differences in cognitive ability is seen as fundamental to understanding the debate.
The modern controversy surrounding intelligence and race focuses on the results of IQ studies conducted during the second half of the 20th century in the United States, Western Europe, and other industrialized nations.
Background information
Much of the research on intelligence currently cited is based on IQ testing in the United States. Modern theories and research on race and intelligence are often grounded in two controversial assumptions:
- that the social categories of race and ethnicity are concordant with genetic categories, such as biogeographic ancestry.
- that intelligence is quantitatively measurable (see psychometrics) by modern tests and is dominated by a unitary general cognitive ability.
While the g-based factor hierarchy is the most widely accepted current view of the structure of abilities, some theorists regard it as misleading. Moreover, a wide range of human abilities-including many that seem to have intellectual components are outside the domain of standard psychometric tests. Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain why average IQ varies among racial-ethnic groups; most of them focus on environment ("nurture") and genetics ("nature"). Certain environmental factors, such as nutrition, are thought to moderate IQ in children, and other influences have been hypothesized, including education level, richness of the early home environment, the existence of caste-like minorities, socio-economic factors, culture, the effort gap, pidgin language barriers, quality of education, health, racism, lack of positive role-models, exposure to violence, the Flynn effect, sociobiological differences and stereotype threat. One focus of the scientific debate is whether group IQ differences also reflect a genetic component. Hereditarianism hypothesizes that a genetic contribution to intelligence could include genes linked to neuron structure or function, brain size or metabolism, or other physiological differences that could vary with biogeographic ancestry. There is also significant debate about exactly how environmental factors play their role in creating the gap and the interrelationships between these factors. Some researchers focus their attention on intervention techniques to close the gap.
The Bell Curve, a controversial book that asserted that the gap in black and white IQ scores was probably, in part, genetic, received a great deal of publicity, including cover stories in Newsweek The New Republic, and The New York Times Book Review.
Invented in the early 20th century, IQ tests have been strongly criticized, but are now considered to be relatively reliable, valid and stable measures of cognitive ability. Some critics question the fairness and validity of cognitive testing and racial categorization, as well as the reliability of the studies and the motives of the authors, on both sides. This has included accusations of bias based on the political ideals of the researchers or the funding agencies, such as the Pioneer Fund. Some critics such as Robert Sternberg, Stephen Jay Gould, Karen Lee and Gloria Ladson-Billings fear the misuse of the research, question its utility, or feel that comparing the intelligence of racial groups is itself unethical.
Robert Sternberg writes that race intelligence research that focuses on a genetic cause for the gap is attempting to show that one group is inferior to another group. The conclusions of some researchers: that racial groups in the US vary in average IQ scores, and the hypothesis that a genetic component may be involved, have led to heated academic debates that have spilled over into the public sphere.
Observations about race and intelligence also have important applications for critics of the media portrayal of different races. Stereotypes in media such as books, music, film, and television can reinforce old racist ideas and may influence the perceived opportunities for success in academics for minority students.
History
Main article: Race and intelligence (history) See also: Race (historical definitions)In the 19th and 20th centuries research on race and intelligence has been used to argue that one race is superior to another, justifying poor outcomes and ill-treatment for the "inferior race". Some early opinions about the differences among races grew out of stereotypes about non-whites developed during the period of colonialism and slavery. Francisco Gil-White, author of Resurrecting Racism: The Modern Attack on Black People Using Phony Science and Stephen Jay Gould author of The Mismeasure of Man have both suggested that some modern research has similar motives.
Scientific racism
Main article: Scientific racismMany studies that purport to be both science-based and attempt to influence public policy have been criticized for scientific racism; the most recent examples of are those of Charles Murray and the late Richard Herrnstein. Melvin Konner, in his book Tangled Wing: Biological Constraints on the Human Spirit Konner accused Murray and Hernstein of trying to make public policy based on speculations about race. He wrote that Rushton's application of a theory drawn from evolutionary biology to the difference between races had no academic legitimacy.
Most social scientists refute at least the first of these two assumptions. In the official statements of position endorsed by the American Sociological Association and the American Anthropological Association, as reported in The New York Times "A view widespread among many social scientists is that race is not a valid biological concept. But biologists, particularly the population geneticists who study genetic variation, have found that there is a structure in the human population. The structure is a family tree showing separate branches for Africans, Caucasians (Europe, the Middle East and the Indian subcontinent), East Asians, Pacific Islanders and American Indians."
Immigration and segregation
The theory that there are differences in the brain sizes and brain structures that pertain to racial and ethnic groups was widely held and studied during the 19th century and early 20th century. Beginning in the 1930s, race difference research and hereditarianism — the belief that genetics are the primary cause of differences in intelligence among human groups — began to fall out of favor in psychology and anthropology after major internal debates. Anthropologists, such as Amanda Thompson, Franz Boas and Elazar Barkan suggested that "Scientific racism" had been used to perpetuate the idea of the intellectual inferiority of African Americans
Late 20th century debate
See also: IQ and the Wealth of NationsThe contemporary debate on race and intelligence can be traced to a controversial article by psychologist Arthur Jensen called "How Much Can We Boost IQ and Scholastic Achievement?" Jensen concluded that it is"a not unreasonable hypothesis that genetic factors are strongly implicated in the average Negro-white intelligence difference" (p. 82) According to Jensen, heritability measures indicate that about 80 percent of the determinance of intelligence is due to genes and about 10 percent to environment. In direct response, Ashley Montagu, former chairman of the anthropology department at Princeton University wrote in his book, Race and IQ (p. 7) that "Professor Jensen makes much of his heritability measures, but the truth is that the so-called heritability coefficient is an especially undependable measure when applied to the human species, an application which has been criticized from its very inception by mathematical geneticists such as R.A. Fisher," and others.
Montagu said:
- Fisher, one of the founders of modern statistics and mathematical genetics, referred to the coefficient of heritability "as one of those unfortunate short-cuts which have emerged in biometry for lack of a more thorough analysis of the data."
In the 1980s William Shockley postulated, based on the research of Cyril Burt, that the higher rate of reproduction among African Americans in the United States was having what he termed a "dysgenic" effect (meaning an opposite of eugenics); especially as influenced by welfare subsidies (e.g., AFDC), which, he opined, unintentionally encouraged childbearing by what he called less productive mothers. Shockley proposed that individuals with IQs below 100 be paid to undergo voluntary sterilization. Press attention returned again to the issue of race and intelligence in 1994 with the publication of The Bell Curve, which included two chapters on the subject of racial difference in intelligence and related life outcomes. In response to The Bell Curve, Stephen Jay Gould updated The Mismeasure of Man in 1996. Among other things, he criticized the IQ test as a measure of intelligence, citing racial and social bias and systematic flaws in the testing process.
Melvin Konner, professor of anthropology and associate professor of psychiatry and neurology at Emory University, called Bell Curve a "deliberate assault on efforts to improve the school performance of African-Americans". "This book presented strong evidence that genes play a role in intelligence but linked it to the unsupported claim that genes explain the small but consistent black-white difference in IQ. The juxtaposition of good argument with a bad one seemed politically motivated, and persuasive refutations soon appeared. Actually, African-Americans have excelled in virtually every enriched environment they have been placed in, most of which they were previously barred from, and this in only the first decade or two of improved but still not equal opportunity. It is likely that the real curves for the two races will one day be superimposable on each other, but this may require decades of change and different environments for different people. Claims about genetic potential are meaningless except in light of this requirement."
Race
Main article: Race| This section may contain material not related to the topic of the article. Please help improve this section or discuss this issue on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Race as biology
In the United States, racial distinctions are generally made on the basis of skin color, facial features, inferred ancestry, national origin, cultural background and self-identification. In an ongoing debate, some geneticists argue race is neither a meaningful concept nor a useful heuristic device, and even that genetic differences among groups are biologically meaningless, on the basis that more genetic variation exists within such races than among them, and that racial traits overlap without discrete boundaries. Lewontin, for example argues that there is no biological basis for race on the basis of research indicating that more genetic variation exists within such races than between them Template:AYref.
Some critics of race may not consider this a problem for race and intelligence inquiries. Jared Diamond, who praises Cavalli-Sforza's genetics research over the decades for "demolishing scientists' attempts to classify human populations into races in the same way that they classify birds and other species into races"(Template:AYref), also argues "in mental ability New Guineans are probably genetically superior to Westerners" due to that intelligence was likely selected for in hunter-gatherer New Guinea societies where the challenges were tribal warfare and food procurement, compared with high population density European civilizations where the major survival pressure was on genes for resisting epidemics Other geneticists, in contrast, argue that categories of self-identified race/ethnicity or biogeographic ancestry are both valid and useful, that these categories correspond with clusters inferred from multilocus genetic data, and that this correspondence implies that genetic factors might contribute to unexplained phenotypic variation between groups.
A survey taken in 1985, asked 1,200 scientists how many disagree with the following proposition: "There are biological races in the species Homo sapiens." The responses were: biologists 16%, developmental psychologists 36%, physical anthropologists 41%, cultural anthropologists 53%. A survey of cultural and physical anthropologists done in 1999 found that the concept of race was rejected by 69% of physical anthropologists and 80% of cultural anthropologists.
Many alleles vary in frequency across (and within) human populations. Most of this variation is selectively neutral, but a significant number show evidence of recent positive selection. These include genes involved in brain development and other neuronal functions, which have variants that have spread to high frequencies under selective pressure and now occur in substantially different frequencies in different global populations. This citation is inadequate.The actual functions of these genes, and their effect, if any, on IQ is unknown.
Race as a social construct
Robert J. Sternberg, Elena L. Grigorenko, and Kenneth K. Kidd write that the overwhelming portion of the literature on intelligence, race, and genetics is based on folk taxonomies rather than scientific analysis. Race, they write, fits into no known genetic pattern. Race is a socially constructed concept, not a biological one. This concept of race serves a social rather than a biological purpose. Different types of parentage have, at various times and places, given rise to racial labeling (e.g., “Aryan race,” “German race,” and “Jewish race”). Hence race is a highly inconsistent concept. In contemporary North American society, Blacks and coloreds are considered to be one “race,” since any individual who possess any degree of nonwhiteness is automatically grouped in the Black category. (see: One drop rule) In other countries different racial groupings are often employed. In Beyond the Bell Curve: Toward a Model of Talent and Character Development Serge Madhere critiques hereditarian assumptions about ability, biology, and ecology. He argues that the measures of ability assessed on IQ tests are essentially measures of literacy, which is largely a socially constructed outcome. This proposition is validated using data from a large national sample of students and hierarchical regression techniques.
The political, social and cultural structure of the United States is still weighted by race. It was only in the 1960s that racial discrimination became illegal in many areas of public and private life, including employment and housing, and some consider discrimination to remain prevalent. The national and state governments of the United States employ racial categorization in the census, law enforcement, and innumerable other ways. Many political organizations intend to represent the interests of specific racial groups. See the articles Race and Race (U.S. Census) for further discussion.
Arthur Jensen writes that claims that race is fictional, that races do not exist in reality, and that they are merely social constructions, which then imply that it is meaningless to inquire about the biological basis of any racial differences, are rooted in five sources which are political rather than scientific: (1) "heaping scorn on the concept of race is deemed an effective way of combating racism", (2) "Neo-Marxist philosophy (which still has exponents in the social sciences and the popular media)" (3) discrediting race itself (not just misconceptions of it) "is seen as a way to advance more harmonious relations among the groups in our society that are commonly perceived as 'racially' different" (4) "universal revulsion to the Holocaust", and (5) frustration with "wrong-headed" popular conceptions about race among population genetics experts lead some to "abandon the concept instead of attempting candidly to make the public aware of how the concept of race is viewed by most present-day scientists".
Intelligence
Main article: Intelligence See also: Intelligence testingIntelligence is usually measured using IQ tests, both in research and practical applications.
IQ
Main article: intelligence quotient See also: general intelligence factorAll such tests are often called "intelligence tests," though the use of the term "intelligence" is itself controversial. A low but significant correlation was found in tests administered to two groups of kindergarten children in a study reported in 1991:
- An equally weighted Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI)
WPPSI short-form (Comprehension, Arithmetic, Block Design, and Picture Completion) was administered to 64 prekindergarten children, while a verbally weighted WPPSI short-form (Comprehension, Arithmetic, Block Design, and Vocabulary) was administered to 63 prekindergarten children. All subjects subsequently were administered school achievement tests at the end of the first- and second-grade years. Low, but significant correlations between the full scale IQ (FSIQ) and achievement test scores were obtained; the Arithmetic and Block Design subtests were the best subtest predictors of school achievement in grades one and two. The predictive validities of the two WPPSI short-forms were found to be essentially equivalent. School grades are the better predicator of later academic success than IQ and the relations may be lower for specific populations. In a sample of 127 students enrolled in a private day school located in a large metropolitan area, the correlations ranged from .11 to .22 with the median of .18.
"Many of the most widely used tests are not intended to measure intelligence itself but some closely related construct: scholastic aptitude, school achievement, specific abilities... . Scores on intelligence-related tests matter, and the stakes can be high," according to the task force appointed by the Board of Scientific Affairs of the American Psychological Association. Such tests are argued to be good measures of the psychometric variable g (for general intelligence factor). While some psychologists regard g as the fundamental measure of intelligence, others emphasize the strengths and weaknesses present in each person's performance on different aspects of the tests.
Although the correlation is fair in some academic areas, the correlation between IQ tests and many real-world results is not inconsistent. For example, the hereditary transmission of wealth via IQ is near zero. As commonly used, "IQ test" denotes tests of cognitive ability, and "IQ" is used as shorthand for scores on tests of cognitive ability. Some psychologists question the validity of IQ testing and say that aspects of intelligence is not reflected in IQ tests. Criticisms of the validity of IQ testing focuses on questions of test bias. Several conclusions about tests of cognitive ability are now largely accepted by intelligence researchers:
- IQ scores measure many, but not all of the qualities that people mean by intelligent or smart. (For example, IQ does not measure creativity, wisdom, or personality.)
- Especially in developing nations, there are many factors that may adversely affect IQ. See Health and intelligence.
Sternberg writes that conventional tests of intelligence can be useful, but only if they are carefully interpreted, taking into account factors such as cross-cultural issues.
Multiple intelligences
Main article: Theory of multiple intelligencesPsychologist Howard Gardner says there are multiple forms of intelligence, which he calls multiple intelligences not often captured by the usual IQ tests. Multiple Intelligences can include the following: linguistic; logical-mathematical; spatial; bodily-kinesthetic; musical; naturalistic; interpersonal and intrapersonal. This raises the possibility that it may not be possible to construct a single meaningful ordering on intelligence.
Another theory is the Triarchic theory of intelligence which was formulated by Robert J. Sternberg. According to this theory the three components of intelligence are analytic intelligence, creative intelligence, and practical intelligence. According to Sternberg, only analytic intelligence is measured by standardized IQ tests.
Research
Main article: Race and intelligence (Research)Test data
Main article: Race and intelligence (test data)The modern controversy surrounding intelligence and race focuses on the results of IQ studies conducted during the 20th century, mainly in the United States and some other industrialized nations. In almost every testing situation where tests were administered and evaluated correctly, the mean IQ of Blacks was approximately one standard deviation below that of Whites.
Attempted world-wide compilations of average IQ by race generally place Ashkenazi Jews and East Asians at the top, followed by Whites, Arabs and Native Americans, sub-Saharan Africans and Australian Aboriginals.
The IQ scores vary greatly among different nations for the same group. Blacks in Africa score much lower than Blacks in the US. However contrary to indications from the IQ and the Wealth of Nations study, the majority of blacks enrolled in Ivy League Universities in the US are either from Africa or the Caribbean. The chairperson of the sociology department at Harvard University stated:
Since they come from majority-black countries, they are less psychologically handicapped by the stigma of race.
Thus this is seen as evidence that racial prejudice combined with the status of being a minority that has been excluded from society does have a significant effect on academic achievement. However, according to the African-American economist Thomas Sowell racism and the legacy of slavery do not stand up under scrutiny of historical facts as explanations to the IQ disparity between Blacks and Whites. He argues that "redneck" black culture is the reason for the low IQ and poor academic performance of black Americans.
Additionally, there are 800 million people in sub-Saharan Africa and the Caribbean - over twenty times the number of blacks in the USA. It is perhaps not surprising therefore that a much larger population produces more Ivy League students.
Gaps are seen in other tests of cognitive ability or aptitude, including university admission exams such as the SAT and GRE as well as employment tests for corporate settings and the military (Roth et al. 2001). Measures of school achievement correlate fairly well with IQ, especially in younger children. In the United States, achievement tests find that by 12th grade Black students are performing on average only as well as White students in 10th grade, and Asian students in 8th grade; Hispanic students do only slightly better than Blacks. Whether the gaps are narrowing or not is debated.
Although most experts still adhere to the findings in IQ and the Wealth of Nations which show differences between ethnic groups of the same race. There is an IQ of 70 for the native African population in Africa. The African American IQ is usually 85 in U.S., Jamaica IQ, 72. The IQ's have been fairly consistent for decades and corresponds with the wealth and well-being of these groups which many historians have noted.
Steve Sailer has states,
that a bad environment can hurt IQ and can be seen in the IQ scores for sub-Saharan African countries. They average only around 70. In contrast, African-Americans average about 85. It appears unlikely that African-Americans’ white admixture can account for most of this 15-point gap because they are only around 17%-18% white on average, according to the latest genetic research. (Thus African-Americans white genes probably couldn't account for more than 3 points of the gap between African-Americans and Africans.) This suggests that the harshness of life in Africa might be cutting ten points or more off African IQ scores.
This also implies that African Americans might be able to achieve higher IQs too, although the environmental gap between white Americans and black Americans appears to be much smaller than between black Americans and black Africans. One proposed avenue for improving African-Americans' IQs is by promoting breastfeeding among blacks mothers, who nurse their babies at much lower rates than whites.
Another researcher Philippe Rushton found African university students averaged an IQ of 84. In some studies, by other researchers, they have scored lower (IQ = 77). In still others of our studies, highly-selected engineering students who took math and science courses in high school scored higher (IQ = 103). Rushton also points out that immigrants regardless of race outperform native populations and adds that in theory Africans would revert back to their normal IQ in future generations if kept in the harsh African environment and cultural setting.
Explanations
Main article: Race and intelligence (Explanations)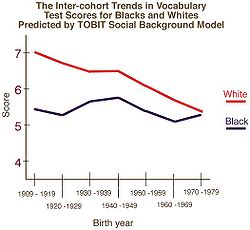

The consensus among intelligence researchers is that IQ differences between individuals of the same race reflect (1) real, (2) functionally/socially significant, and (3) substantial differences in the general intelligence factor. It is a matter of debate whether IQ differences between races in the U.S. are (3a) entirely environmental or (3b) partly genetic. Several published consensus statements agree that the large differences between the average IQ scores of Blacks and Whites in the U.S. cannot be attributed to biases in test construction, nor can they be explained just by simple differences in socio-economic status, however they are still well within the range that may be attributed to other environmental factors. The debate over causal explanations focuses predominately on the IQ gaps seen in developed countries. There is a consensus that IQ in developing countries is depressed due at least in part to poor health and nutrition.
A few of the notable proponents of the partly genetic hypothesis are Raymond B. Cattell, Arthur Jensen and Hans Eysenck.
Rushton and Jensen examined 10 categories of research evidence from around the world to contrast "a hereditarian model" (50% genetic-50% cultural) and a culture-only model (0% genetic-100% cultural). In the article "Thirty Years of Research on Race Differences in Cognitive Ability" published in the APA journal Psychology, Public Policy and Law they cite the following evidence to support the hereditarian model:
1) The Worldwide Pattern of IQ Scores. East Asians average higher on IQ tests than Whites, both in the U. S. and in Asia, even though IQ tests were developed for use in the Euro-American culture. Around the world, the average IQ for East Asians centers around 106; for Whites, about 100; and for Blacks about 85 in the U.S. and 70 in sub-Saharan Africa.
2) Race Differences are Most Pronounced on Tests that Best Measure the General Intelligence Factor (g). Black-White differences, for example, are larger on the Backward Digit Span test than on the less g loaded Forward Digit Span test.
3) The Gene-Environment Architecture of IQ is the Same in all Races, and Race Differences are Most Pronounced on More Heritable Abilities. Studies of Black, White, and East Asian twins, for example, show the heritability of IQ is 50% or higher in all races.
4) Brain Size Differences. Studies using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) find a correlation of brain size with IQ of about 0.40. Larger brains contain more neurons and synapses and process information faster. Race differences in brain size are present at birth. By adulthood, East Asians average 1 cubic inch more cranial capacity than Whites who average 5 cubic inches more than Blacks.
5) Trans-Racial Adoption Studies. Race differences in IQ remain following adoption by White middle class parents. East Asians grow to average higher IQs than Whites while Blacks score lower. The Minnesota Transracial Adoption Study followed children to age 17 and found race differences were even greater than at age 7: White children, 106; Mixed-Race children, 99; and Black children, 89.
6) Racial Admixture Studies. Black children with lighter skin, for example, average higher IQ scores. In South Africa, the IQ of the mixed-race "Colored" population averages 85, intermediate to the African 70 and White 100.
7) IQ Scores of Blacks and Whites Regress toward the Averages of Their Race. Parents pass on only some exceptional genes to offspring so parents with very high IQs tend to have more average children. Black and White children with parents of IQ 115 move to different averages--Blacks toward 85 and Whites to 100.
8) Race Differences in Other "Life-History" Traits. East Asians and Blacks consistently fall at two ends of a continuum with Whites intermediate on 60 measures of maturation, personality, reproduction, and social organization. For example, Black children sit, crawl, walk, and put on their clothes earlier than Whites or East Asians.
9) Race Differences and the Out-of-Africa theory of Human Origins. East Asian-White-Black differences fit the theory that modern humans arose in Africa about 100,000 years ago and expanded northward. During prolonged winters there was evolutionary selection for higher IQ created by problems of raising children, gathering and storing food, gaining shelter, and making clothes.
10) Culture-only theories do not explain the highly consistent pattern of race differences in IQ, especially the East Asian data. No interventions such as ending segregation, introducing school busing, or "Head Start" programs have reduced the gaps as culture-only theory would predict.
Regarding the IQ gaps in the U.S., it has also been suggested that Black culture disfavors academic achievement and fosters an environment that is damaging to IQ (Boykin, 1994). Likewise, it is argued that a persistence of racism reinforces this negative effect. John Ogbu (1978, 1994) has developed a hypothesis that the condition of being a "caste-like minority" affects motivation and achievement, depressing IQ. Many anthropologists have argued that intelligence is a cultural category; some cultures emphasize speed and competition more than others, for example. Even proponents of the view that the IQ gap is caused partly by genetic differences recognize that non-genetic factors are likely involved. Non-genetic biological factors that affect IQ have been proposed. Increased rates of low birth weight babies and lower rates of breastfeeding in Blacks as compared to Whites are some factors of many that have been proposed to affect the IQ gap. The Flynn effect is often cited as evidence that average IQ scores have changed greatly and rapidly, for reasons poorly understood, noting that average IQ in the US may have been below 75 before the start of this effect, and thus some argue that the IQ gap between races could change in the future or is changing, especially if the effect started earlier for Whites.
Interpretations
Main article: Race and intelligence (interpretations)Given the observed differences in IQ scores between certain groups, a great deal of debate revolves around the significance of these observations. Various interpretations of test data lead to a multitude of conflicting conclusions as to which specific explanations the data support.
Some people have attributed differential economic growth between nations to differences in the intelligence of their populations. One example is Richard Lynn's IQ and the Wealth of Nations. The book is sharply criticized in the peer-reviewed paper The Impact of National IQ on Income and Growth. Another peer-reviewed paper, Intelligence, Human Capital, and Economic Growth: An Extreme-Bounds Analysis, finds a strong connection between intelligence and economic growth. It has been argued that East Asian nations underachieve compared to IQ scores.
Jared Diamond's Guns, Germs and Steel instead argues that historical differences in economic and technological development for different areas can be explained by differences in geography (which affects factors like population density and spread of new technology) and differences in available crops and domesticatable animals. However,psychologist John Philippe Rushton suggests these environmental differences may operate in part by selecting for higher levels of IQ There is no evidence to suggest that such selective forces occur in regards to IQ. Consensus at the American Psychological Association is that a partly genetic hypothesis is as of now, inadequate in explaining differences in IQ among population groups.
The human genome and intelligence
- See also The genome and intelligence
Some scholars have proposed that in order to make a racial hypothesis about intelligence the genes for intelligence need to be identified along with their frequencies in the various populations. However recent studies attempting to find regions in the genome relating to intelligence have had little success. A recent study used several hundred people in two groups, one with a very high IQ, average 160, and a control group with an average IQ of 102. The study used 1,842 DNA markers and put them through a five step inspection process to eliminate false positives. By the fifth step the study could not find a single gene that was related to intelligence. Critics of these studies say the failure to find a specific gene associated with intelligence is indicative of the complex nature of intelligence. They contend that intelligence is probably under the influence of several genes. Some estimate that as much as 40% of the genome may contribute to intelligence.
Recently scientists at the University of Chicago identified two genes, microcephalin and ASPM. Mutations in these genes are associated with brain size abnormality, microcephaly . The normal variants are found at high frequencies in Asian and European populations but they are not found among Sub-Saharan Africans. The scientists stated that microcephalin may have arisen some 37,000 years ago coinciding with upper paleolithic transitions in Europe. They also stated that a variant of APSM arose about 5,800 years ago roughly correlating with the development of written language, spread of agriculture and development of cities. They thus believe these two genes conferred some cognitive abilities upon Asians and Europeans. These studies have been criticized saying it was far from clear that the new alleles conferred any cognitive advantage or had spread for that reason.
Other scholars have criticized the University of Chicago scientists because they made claims about these genes without undertaking any direct experimentation to test their hypothesis on increased intelligence and brain size. Subsequently when these experiments were done, no relationship was found between these genes and intelligence or brain size.
In the US, Critics of these studies also say that as long as social and environmental disparities between the races exist it will be impossible to scientifically test whether there are any genetic differences in IQ between the various populations. They propose that if the historical effects of poverty and social bigotry were eliminated and differences in IQ between the races still persisted then there might be some utility in such research.
Theories on the intelligence of Ashkenazi Jews
See also: Ashkenazi intelligenceA link between disease mutations specific to the Ashkenazi Jews and high IQ scores has been suggested by scientists at the University of Utah, who cite evidence that sphingolipid disorders promote the growth and interconnection of brain cells and that mutations in the DNA repair genes, involved in some Ashkenazic diseases, may also unleash growth of neurons. The researchers predict that these disease mutations will enhance IQ in heterotsygotes. This prediction is based on evidence that selection pressure has increased the frequency of the disease mutations in the reproductively isolated Ashkenazi population in medieval times. The hypothesis has not yet been empirically tested.
Ashkenazi Jews have been reported to score 0.75 to 1.0 standard deviations above the general European average, corresponding to an IQ 112-115. According to Richard Lynn the best reading of the IQ of Jews in Britain is 110. Lynn proposes that the overrepresentation of Jews as Nobel Prize Winners and as Fellows of the Royal Society can be partly explained by the higher average Jewish IQ because comparatively small differences in average intelligence can become very large differences in the very high I.Q ranges. Jews are over-represented among Nobel prize-winners by a factor of 8.0 in Britain and 12.3 in the United States.
The evolutionary history of IQ
- See also: Dysgenics
According to the Out of Africa hypothesis, one or more subgroups of early modern humans left Africa between 55,000 and 60,000 years ago to become the ancestors of the non-African populations. Population-level differences in climate-selected traits such as skin color evolved in this time period. Some scholars suggest that a similar time scale applies to the evolution of possible cognitive differences between human populations..
According to Loring Brace “human cognitive capacity, founded on the ability to learn a language, is of equal survival value to all human groups, and consequently there is no valid reason to expect that there should be average differences in intellectual ability among living human populations.”
This claim is disputed by the biochemist Gerhard Meisenberg who thinks that the value of intelligence in survival and reproduction has varied. According to Meisenberg before the advent of modern contraception, usually the wealthy had higher fertility and lower mortality than the poor. In the late 20th century United States, unequal reproductive rates favoring the less intelligent would have lowered the IQ of the population by anywhere between 0.35 and 0.8 points per generation had the environment remained unchanged over time. In order to create an IQ difference of 15 points between two populations in 100,000 years, natural selection would have to drive their IQs apart by only 0.004 points every generation – about 1% of the selective pressure in late 20th-century America. Meisenberg argues that measurements of genetic diversity by the population geneticist Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza indicate that the difference in “genotypic” intelligence between the most divergent human populations caused by random genetic drift should be about 12 IQ points.
Richard Lynn has proposed that the exposure to two recent ice ages, one 77,000-50,000 years ago, and another, more severe one 28,000-10,000 years ago, created evolutionary pressures which increased the intelligence of Europeans and East Asians significantly above other world populations. However, Lynn's views are controversial and the increased intelligence of Europeans and East Asians over other races is a matter of hot dispute.
Human intelligence is related in some manner to the large increase in brain size going up the human evolutionary tree. When the encephalization quotient (EQ) is used to measure brain size in relation to body size, modern humans are three times as encephalized (EQ = 6) as other primates (EQ = 2) and six times the average for all living mammals (EQ = 1, the reference group). According to Gottfredson phylogenetic increase represents a disproportionate expansion of the brain’s prefrontal cortext, which matures last and is most essential for the highest cognitive functions, including weighing alternatives, planning, understanding the temporal order of events (and thus cause-and-effect relations), and making decisions. Moreover, encephalization of the human line proceeded rather quickly, in evolutionary terms, after the first hominids (Australopithicines, EQ = 3) split off from their common ancestor with chimpanzees (EQ = 2) about 5 million years ago. Encephalization was especially rapid during the last 500,000 to one million years, when relative brain size increased from under EQ = 4 for Homo erectus (arguably the first species of Homo) to about EQ = 6 for living humans (the only surviving subspecies of Homo sapiens). Race differences in brain size have been examined in a number of studies. East Asians have an average cranial capacity of 1,364 cm, Whites 1,347 cm and Blacks 1,267 cm and Neanderthals up to 1,750cm. A positive correlation of 0.40 between brain size and intelligence has been found in modern humans.
According to Linda S. Gottfredson technological innovation has been in a significant role in the evolution of human intelligence. Different social groups are differentially exposed to the risk of accidental death in both modern and hunter-gatherer societies. Members of lower social classes are the largest risk. As new technologies have created new physical hazards this disparity has increased. Consequently, new technologies have gradually increased the IQ level of a population which has increased the capacity of the population to produce new innovations and led to further gains in intelligence. According to Gottfredson disparities in innovativeness and exposure to hazards between populations have led to differences in general intelligence between them which is consistent with recent evidence on trends in relative brain size and genetic divergence of human populations.
Cavalli himself has made significant contributions to the fight against racism. On several occasions he publicly debated Arthur Jensen and William Shockley arguing that environmental factors could explain the black white IQ gap .
Prejudice and IQ
A university study in the US was carried out in order to determine whether a relationship existed between prejudice and IQ. Students were given an IQ test and a test that measures racial prejudice. The study found that students who scored lower on IQ tests were more prejudiced.
Controversies
Main article: Race and intelligence (Controversies)Utility of research
Main article: Race and intelligence (Utility of research)In a book review J. Philippe Rushton called Richard Lynn's and Tatu Vanhanen's book IQ And Global Inequality which links GDP with the racial composition of nations as "the most important contribution to economic understanding since Adam Smith".
Theories of race and intelligence have been challenged on grounds of their utility. Critics want to know what purpose such research could serve and why it has been an intense an area of focus for a few researchers. Some defend the research, saying it has egalitarian aims or that it is pure science, others say that the true motivation for the research is the same as that of the eugenics movement and other forms of scientific racism. Even supporters of intelligence research have described such research as analogous to "working with dynamite" or "dangerous play" in sports.
As to whether research in this area is desirable, John C. Loehlin wrote in 1992, "Research on racial differences in intelligence is desirable if the research is appropriately motivated, honestly done, and adequately communicated." Defenders of the research suggest that both scientific curiosity and a desire to draw benefits from the research are appropriate motivations. Researchers such as Richard Lynn have suggested that conclusions from the research can help make political decisions, such as the type of educational opportunities and expectations of achievement policy makers should have for people of different races. Charles Murray, a conservative political pundit at the American Enterprise Institute has used their conclusions to criticize social programs based on racial equality that fail, he claims, to recognize the realities of racial differences.
Sociologist and demographer Reanne Frank says that some race and intelligence research has been abused "The most malignant are the "true believers," who subscribe to the typological distinctions that imply hierarchical rankings of worth across different races. Although this group remains small, the members' work is often widely publicized and well known (e.g., Herrnstein and Murray 1994; Rushton 1991)"
Potential for bias
Main article: Race and intelligence (Potential for bias)Proponents of genetic explanations of race/IQ correlation have often been criticized both of scientific misconduct and of their intimate links with groups that have historic ties to Nazis and eugenics of the early 19th century, such as the Pioneer Fund. The Pioneer Fund has been characterized by the Southern Poverty Law Center as a hate group. Beverly Daniel Tatum writes that dominant cultures often set the parameters by which minority cultures will be judged. Minority groups are labeled as substandard in significant ways, for example blacks have historically been characterized as less intelligent than whites. Tatum suggests that the ability to set these parameters is a form of white privilege.
Proponents of genetic explanations of race/IQ correlation have in turn accused their critics of suppressing scientific debate in the name of political correctness. They claim harassment and interference with both their work and funding.
The preponderance of evidence indicates that IQ tests measuring general intelligence are crossculturally valid. There is little or no evidence of population-specific cultural effects apart from the obvious example of language bias. For example, Robert Sternberg et al. found that the IQ of 12- to 15-year-old Kenyans predicted school grades at about the same level as they do in the West. IQ also predicted university performance equally well in African and non-African engineering students in South Africa in a 2004 study. Salgado et al. (2003) demonstrated the international generalizability of general mental ability across 10 member countries of the European Community and differences in a nation’s culture, religion, language, socioeconomic level or employment legislation did not affect the predictive validity of IQ tests.
Policy implications
- See also: Intelligence and public policy
Public policy implications of IQ and race research are one of the greatest sources of controversy surrounding this issue. Regardless of the source of the gap, most educators agree that it must be addressed. They often advocate equitable funding for education.
Some proponents of a genetic interpretation of the IQ gap, such as Template:A(Y)ref and Template:A(Y)ref, have sometimes argued that their interpretation does not in itself demand any particular policy response: while a conservative/libertarian commentator may feel the results justify, for example, reductions in affirmative action, a liberal commentator may argue from a Rawlsian point of view (that genetic advantages are undeserved and unjust) for substantial affirmative action. Since all races have representatives at all levels of the IQ curve, this means any policy based on low IQ affects members of all races.
While not specifically race-related, policies focused on geographical regions or nations may have disproportionate influences on certain racial groups and on cognitive development. Differences in health care, nutrition, regulation of environmental toxins, and geographic distribution of diseases and control strategies between the developing world and developed nations have all been subjects of policies or policy recommendations (see Health and intelligence).
Finally, Gregory Stock, writes that germinal choice technology may one day be able to select or change directly alleles found to influence intelligence or racially identifying traits (such as skin color; see gene SLC24A5), making them susceptible to biotechnological intervention.
End material
See also
- Ashkenazi intelligence
- Brain to body mass ratio
- Craniometry
- Flynn effect
- Hominid intelligence
- Height and intelligence
- Neuroscience and intelligence
- Race and crime
- Race and intelligence (Explanations)
- Sex and intelligence
- Scientific racism
- The Mismeasure of Man
- Teaching for social justice
- IQ and Global Inequality
Notes
- Andor, L. E., ed. Aptitudes and Abilities of the Black Man in Sub-Saharan Africa: 1784-1963: An Annotated Bibliography. Johannesburg: National Institute for Personnel Research, 1966.
- "Race as Biology Is Fiction, Racism as a Social Problem Is Real: Anthropological and Historical Perspectives on the Social Construction of Race." by Audrey Smedley and Brian D. Smedley
- Thirty Years of Research on Race Differences In Cognitive Ability. p. 240
- Black-White-East Asian IQ differences at least 50% genetic, major law review journal concludes
- Ceci, S. J. (1990). On intelligence more or less: A bioecological treatise on intellectual development. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall
- Intelligence: Knowns and Unknowns
- There are no public-policy implications: A reply to Rushton and Jensen (2005) Robert Sternberg
- Entman, Robert M. and Andrew Rojecki The Black Image in the White Mind: Media and Race in America 2001
- Darwin's Athletes: how sport has damaged Black America and preserved the myth of race By John Milton Hoberman. ISBN 0395822920
- Social Darwinism, Scientific Racism, and the Metaphysics of Race Rutledge M. Dennis The Journal of Negro Education, Vol. 64, No. 3, Myths and Realities: African Americans and the Measurement of Human Abilities (Summer, 1995), pp. 243-252
- A History of Race/ism Produced By: Tim McCaskell Toronto District School Board
- Jalata, Asafa 1954- "Race and Ethnicity in East Africa (review)" Africa Today - Volume 48, Number 4, Winter 2001, pp. 134-136 Indiana University Press
- The Invention of the White Race By Chantal Mouffe, Theodore (Theodore W.) Allen
- Media, Stereotypes and the Perpetuation of Racism in Canada by James Crawford
Indians were seen as a homogeneous group of savages despite the fact that individual groups varied extensively and had several well developed social systems. Black people were also portrayed as savage, uncivilized and having low intelligence. By creating these social constructs, expansion into North America was justified.
- The first Muslim explorers in East Africa wrote that they were shocked by the nudity, paganism, cannibalism, and poverty of the natives. Some claimed Blacks had the nature "of wild animals... most of them go naked... the child does not know his father, and they eat people." Several hundred years later, European explorers had the same impressions. They wrote that Africans seemed to have a very low intelligence and few words to express complex thoughts. They praised some tribes for making fine pottery, forging iron, carving wooden art, and making musical instruments. But more often, they were shocked by the near nakedness of the people, their poor sanitary habits, simple houses, and small villages. They found no wheels for making pots, grinding corn, or for transport, no farm animals, no writing, no money, and no numbering systems. J. Philippe Rushton: Race, Evolution, and Behavior: A Life History Perspective, 2000. p. 8
- However, Rushton points out that the whites who explored China were just as racist as those who explored Africa, but their descriptions were different from what they and the Arabs had written about Africans. When Marco Polo arrived in China in 1275 from his native Italy he found that the Chinese had well built roads, bridges, cities connected by canals, census takers, markets, standardized weights and measures, and not only coins, but paper money as well. Even a postal system existed. All of these made him marvel when he compared the Chinese to what he saw in Europe and the Middle East. Even though he was an Italian, proud of his people and well aware of the greatness of Ancient Rome, Marco Polo wrote: "Surely there is no more intelligent race on earth than the Chinese." Ibid.
-
- "What of the latest currents of thought? Are they likely to lead to, or at least encourage, further distortions of social policy? The indications are not all encouraging. Richard Herrnstein and Charles Murray published a book in 1994 clearly directed at policy, just as Jensen and others had in the 1960s and 1970s. The Bell Curve: Intelligence and Class Structure in American Life (New York: Free Press, 1994) teamed a psychologist with a conservative policy advocate to try to prove that both the class structure and the racial divide in the United States result from genetically determined differences in intelligence and ability."
- "Their general assertions about genes and IQ were not very controversial, but their speculations on race were something else again."
- "Also in the 1990s, Phillipe Rushton has tried to couch racial differences in IQ in a theory drawn from evolutionary biology. This theory takes the concepts of r and K selection, crudely useful when applied to a vast range of living creatures considered on a continuum, and apply it to subtle differences in skull form, mental test results, and sexual behavior within our one species. This theory has no academic legitimacy and little relationship to real evolutionary theory, but it taints the whole Darwinian enterprise, strongly recalling the “scientific anthropology” of the era of slavery."
- "The reality is quite different. As argued by George Armelagos in his Presidential Address to the American Association of Physical Anthropologists (“Race, Reason and Rationale,” Evolutionary Anthropology 4, 1995, pp. 103–109) race itself is a dubious concept for the human species. Obviously it is sociologically meaningful, but even in the social realm it is a constantly moving target with little or no core biological legitimacy."The Tangled Wing Biological Constraints on the Human Spirit Times Books Pub: 2002 ISBN 0-7167-4602-6
- The Tangled Wing: Biological Constraints on the Human Spirit Times Books, Pub Date: Jan. 2002. ISBN 0-7167-4602-6 By Kevin Konner
- Statement on "Race" and Intelligence American Anthropological Association
- ^ 2 Scholarly Articles Diverge On Role of Race in Medicine By NICHOLAS WADE Published: March 20, 2003] New York Times
- Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref
- According to historian of psychology Graham Richards there was widespread critical debate within psychology about the conceptual underpinnings of this early race difference research (Template:AYref). These studies include Estabrooks' (1928) two papers on the limitations of methodology used in the research; Dearborn and Long’s (1934) overview of the criticisms by several psychologists (Garth, Thompson, Peterson, Pinter, Herskovits, Daniel, Price, Wilkerson, Freeman, Rosenthal and C.E. Smith) in a collection they edited and Klineburg, who wrote three major critiques, one in 1928, and two in 1935. Richards also notes that with over a 1000 publications within psychology during the interwar years there had been a large internal debate. Toward the end of the time period almost all those publishing, including most of those who began with a pro-race differences stance, were firmly arguing against race differences research. Richards regards the scientific controversy to be dead at this point, although he also suggests reasons for its re-emergence in the late nineteen sixties.
- Jensen, A. R. (1969). "How Much Can We Boost IQ and Scholastic Achievement". Harvard Educational Review 39: 1-123.
- ^ George Bush: The Unauthorized Biography by Webster Griffin Tarpley and Anton Chaitkin, 1992 Executive Intelligence Review, Chapter 11
- Template:AYref
- The Tangled Wing Biological Constraints on the Human Spirit by Melvin Konner, 2nd edition, p. 428
- Template:AYref, Template:AYref (given in Template:AYref's summary, p.599)
- Template:AYref, Template:AYref (given in Template:AYref's summary, p. 599)
- It is well established that within-population genetic diversity is greatest within Sub-Saharan Africa, and decreases with distance from Africa. One study estimates that only 6.3% of the total human genetic diversity is explained by race. (See: The Biological Meaning of “Race” by Matt Riese) This value is comparable to other reports which find that on average approximately 85% of genetic variation occurs within populations. In a hypothetical situation with two populations and a single gene with two alleles, this is equivalent to allele frequencies of 30% + 70% in one population and 70% + 30% in the other. Thus, using this single gene to classify individuals into populations would result in a 30% misclassification rate.
- Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, The concept and measurement of race and their relationship to public health: a review focused on Brazil and the United States
- (Diamond 1997/99, p.21).
- Template:AYref, Template:AYref. Neil Risch argues: "One could make the same arguments about sex and age! . . you can undermine any definitional system. . . In a recent study. . . we actually had a higher discordance rate between self-reported sex and markers on the X chromosome between genetic structure versus self-description, 99.9% concordance. . . So you could argue that sex is also a problematic category. And there are differences between sex and gender; self-identification may not be correlated with biology perfectly. And there is sexism. And you can talk about age the same way. A person's chronological age does not correspond perfectly with his biological age for a variety of reasons, both inherited and non-inherited. Perhaps just using someone's actual birth year is not a very good way of measuring age. Does that mean we should throw it out? . . . Any category you come up with is going to be imperfect, but that doesn't preclude you from using it or the fact that it has utility" (Template:AYref).
- Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref: "If enough markers are used... individuals can be partitioned into genetic clusters that match major geographic subdivisions of the globe".
- Template:AYref
- Bindon, Jim. University of Alabama. "Post World War II". 2005. August 28, 2006
- How "Caucasoids" Got Such Big Crania and Why They Shrank
- According to a recent review by Template:AYref, seven large-scale studies of positive selection in the human genome have been published. The "advantageous traits" that were being selected for are mostly unknown, but some make inferences based on the known functions of those genes in the regions that show signs of selection.
- Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref. The neural dopamine gene studied in Harpending and Cochran, previously found to occur in substantially different worldwide frequencies, is also tied to behavior, with bearers displaying greater novelty-seeking behavior and being at increased risk for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Harpending and Cochran suggest this gene "may be a model system for understanding the relationship between genetic variation and human cultural diversity," noting high frequencies in South American Indians, such as the Yanomamo (sometimes referred to as "the Fierce People"), intermediate frequencies in Europeans and Africans, and very low frequencies in East Asians and !Kung Bushmen (sometimes referred to as "the Harmless People").
See the NY Times' "Researchers Say Human Brain Is Still Evolving" (September 8, 2005), and "Still Evolving, Human Genes Tell New Story" (March 7, 2006) for discussion of Mekel-Bobrov et al. and Evans et al., and Voight et al. - Intelligence, Race, and Genetics Robert J. Sternberg, Elena L. Grigorenko, and Kenneth K. Kidd Yale University
- 'Beyond the Bell Curve: Toward a Model of Talent and Character Development Serge Madhere The Journal of Negro Education, Vol. 64, No. 3, Myths and Realities: African Americans and the Measurement of Human Abilities (Summer, 1995), pp. 326-339
- Template:AYref
- J Clin Psychol. 1991 Sep;47(5):698-702.
- Predictive validity of two short-forms of the WPPSI: a 3-year follow-up study.
- The Predictive Value of IQ Sternberg, Robert J. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly - Volume 47, Number 1, January 2001, pp. 1-41
- Text of the APA Task Force Report, "Intelligence: Knowns and Unknowns"
- See Template:AYref.
- Template:AYref; Template:AYref; Template:AYref
- Rushton, J. P. (2006). "Lynn Richard, Race Differences in Intelligence: An Evolutionary Analysis, Washington Summit Books, Augusta, GA (2005) ISBN 1-59368-020-1, 318 pages., US$34.95". Personality and Individual Differences. 40 (4): 853–855. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2005.10.004.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help) - Lynn, R. and Vanhanen, T. (2002). IQ and the wealth of nations. Westport, CT: Praeger. ISBN 0-275-97510-X
- Top Colleges Take More Blacks, but Which Ones?
- Shades of gray in black enrollment
- Crippled by Their Culture OpinionJournal, WSJ.com
- http://www.vdare.com/misc/rushton_african_iq.htm
- Convergent Trends in Black-White Test-Score Differentials in the U.S.: A Correction of Richard Lynn Min-Hsiung Huang and Robert M. Hauser 2000
- Reviewed in Template:AYref. Data from the NLSY as reported in figure adapted from Template:AYref, p. 288.
- How Heritability Misleads about Race
- Gene variant may depress IQ of males
- Link between gene and performance IQ
- Gene may affect IQ in males, scientists say Dallas Daily News
- Parents pass on genes for reasoning and memory NewScientist.com
- A World of Difference: Richard Lynn Maps World Intelligence Gene Expression
- Microcephalin, a Gene Regulating Brain Size, Continues to Evolve Adaptively in Humans Gene Expressions
- http://psychology.uwo.ca/faculty/rushtonpdfs/PPPL1.pdf Thirty Years of Research on Race Differences in Cognitive Ability
- http://www.innovations-report.de/html/berichte/studien/bericht-43536.html Black-White-East Asian IQ differences at least 50% genetic, major law review journal concludes
- Thomas Volken, "The Impact of National IQ on Income and Growth."
- Template:AYref
- Richard Nisbett argues in his 2004 The Geography of Thought that some of these regional differences shaped lasting cultural traits, such as the collectivism required by East Asian rice irrigation, compared with the individualism of ancient Greek herding, maritime mercantilism, and money crops wine and olive oil (pp. 34-35).
- This theory is discussed by Template:AYref (pp. 435-437), Template:AYref and Template:AYref in general and by both Template:AYref and Steve Sailer with respect to Guns, Germs, and Steel. See Race and intelligence (Explanations)#Rushton's application of r-K theory. .. Template:AYref state generally that "a number of recent studies have detected more signals of adaptation in non-African populations than in Africans, and some of those studies have conjectured that non-Africans might have experienced greater pressures to adapt to new environments than Africans have" (Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref, Template:AYref).
- {http://www.gifted.uconn.edu/siegle/research/Correlation/Intelligence.pdf Text of the APA consensus statement
- A Genome-Wide Scan of 1842 DNA Markers for Allelic Associations With General Cognitive Ability: A Five-Stage Design Using DNA Pooling and Extreme Selected Groups
- Brain May Still Be Evolving, Studies Hint
- The ongoing adaptive evolution of ASPM and Microcephalin is not explained by increased intelligence
- Normal variants of Microcephalin and ASPM do not account for brain size variability
- The race myth, Joseph Graves, page 183 ISBN 0452286581
- http://homepage.mac.com/harpend/.Public/AshkenaziIQ.jbiosocsci.pdf
- http://homepage.mac.com/harpend/.Public/AshkenaziIQ.jbiosocsci.pdf
- http://www.astarshop.com/j_dis.pdf
- http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6W4M-4JYTRWC-2&_user=10&_coverDate=12%2F31%2F2006&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=b1d721140bda47fb8bca4a1200519d64
- Lynn, R. and Longley, D. (2006). "On the high intelligence and cognitive achievements of Jews in Britain." Intelligence, 34, 541-547.
- http://www.theaustralian.news.com.au/story/0,20867,21692339-601,00.html
- Gerhard Meisenberg: IQ Population Genetics: It’s not as Simple as You Think, pp. 186-189
- http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=1565402
- Ibid. pp. 189-190
- Supra, 67 p. 190
- Lynn, Richard: Race Differences in Intelligence: An Evolutionary Analysis
- http://www.gnxp.com/blog/2006/02/world-of-difference-richard-lynn-maps.php
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=14992214&dopt=Citation
- http://www.udel.edu/educ/gottfredson/reprints/2005accidents&intelligence.pdf
- http://www.udel.edu/educ/gottfredson/30years/Rushton-Jensen30years.pdf
- Neanderthals
- http://cogprints.org/1369/0/IQTAN2.pdf Magnetic Resonance Imaging Brain Size/IQ Relations in Turkish University Students by Tan et. al.
- http://www.udel.edu/educ/gottfredson/reprints/2005accidents&intelligence.pdf
- A Genetic and Cultural Odyssey: The Life and Work of L. Luca Cavalli-Sforza by Linda Stone, pages 76, 168 ISBN 0231133960
- How do you compare pages 28-29 ISBN 0399529519 based on Lapsley and Enright , ' The effect of social desirability, intelligence, and milieu on an American validation of the conservatism scale'
- http://www.vdare.com/rushton/061207_iq.htm
- e.g., Sternberg, 2003, pp. 386-387
- e.g., Sternberg, 2003, pp. 386-387
- Hunt & Carlson, in press
- Frank, Reanne, The Misuse of Biology in Demographic Research on Racial/Ethnic Differences: A Reply to van den Oord and Rowe, Demography - Volume 38, Number 4, November 2001, pp. 563-567
- Tatum, Beverly Daniel (1997). Why are all the black kids sitting together in the cafeteria? And other conversations about race. New York: BasicBooks. ISBN 9780465091270.
- http://www.charlesdarwinresearch.org/PRSL2007.pdf
- Sternberg, R. J., Nokes, C., Geissler, P. W., Prince, R., Okatcha, F., Bundy, D. A. & Grigorenko, E. L. 2001 The relationship between academic and practical intelligence: a case study in Kenya. Intelligence 29, 401–418.
- Construct validity of Raven’s Advanced Progressive Matrices for African and non-African engineering students in South Africa.
- Salgado, J. F., Anderson, N., Moscoso, S., Bertua, C. & Fruyt, F. D. 2003 International validity generalization of GMA and cognitive abilities: a European community meta-analysis. Pers. Psychol. 56, 573–605.
- Achieving Equitable Education in Calhoun County
- Educational Studies: A Jrnl of the American Educ. Studies Assoc.
- For example, the policy recommendations of The Bell Curve were denounced by many. Template:AYref wrote: "We can imagine no recommendation for using the government to manipulate fertility that does not have dangers. But this highlights the problem: The United States already has policies that inadvertently social-engineer who has babies, and it is encouraging the wrong women. If the United States did as much to encourage high-IQ women to have babies as it now does to encourage low-IQ women, it would rightly be described as engaging in aggressive manipulation of fertility. The technically precise description of America's fertility policy is that it subsidizes births among poor women, who are also disproportionately at the low end of the intelligence distribution. We urge generally that these policies, represented by the extensive network of cash and services for low-income women who have babies, be ended. (p. 548)" Two year later the 1996 U.S. welfare reform substantially cut these programs. In a discussion of the future political outcomes of an intellectually stratified society, they stated that they: "fear that a new kind of conservatism is becoming the dominant ideology of the affluent - not in the social tradition of an Edmund Burke or in the economic tradition of an Adam Smith but ’conservatism’ along Latin American lines, where to be conservative has often meant doing whatever is necessary to preserve the mansions on the hills from the menace of the slums below. (p. 518)"Moreover, they fear that an increasing welfare will create a "custodial state": "a high-tech and more lavish version of the Indian reservation of some substantial minority of the nation’s population. They also predict increasing totalitarianism: It is difficult to imagine the United States preserving its heritage of individualism, equal rights before the law, free people running their own lives, once it is accepted that a significant part of the population must be made permanent wards of the states. (p. 526)"
- Template:AYref
- Gregory Stock argues "current debates about whether some of the differences among ethnic and racial groups are cultural or biological will soon become irrelevant, given the coming " (Template:AYref, p. 194; race and intelligence discussed on pp. 44-47).
References
Main article: Race and intelligence (References)External links
Collective Statements
- APA Task Force Examines the Knowns and Unknowns of Intelligence
- Statement on "Race" and Intelligence. American Anthropological Association. Adopted December 1994.
- Mainstream Science on Intelligence. Intelligence, v24 n1 p. 13-23 Jan-Feb 1997
Review Papers
- James Flynn and Charles Murray debate - news summary
- June 2005 issue of Psychology, Public Policy, and Law, Vol. 11, No. 2.
- Thirty Years of Research on Race Differences in Cognitive Ability J. Philippe Rushton & Arthur R. Jensen
- There Are No Public-Policy Implications Robert J. Sternberg
- What if the Hereditarian Hypothesis is True? Linda S. Gottfredson
- Heredity, Environment, and Race Differences in IQ Richard E. Nisbett
- The Cultural Malleability of Intelligence and Its Impact on the Racial/Ethnic Hierarchy Lisa Suzuki & Joshua Aronson
- Wanted: More Race Realism, Less Moralistic Fallacy J. Philippe Rushton & Arthur R. Jensen
- Race, Genetics and IQ Richard E. Nisbett (PDF)
- The Inequality Taboo Charles Murray archived version
- The Black-White Test Score Gap (1998) online (page-image) version of ISBN 0-8157-4609-1
Others
- Crippled by Their Culture - Race doesn't hold back America's black rednecks. Nor does racism by Thomas Sowell
- Race and IQ: Part 1, Part 2, Part 3 by Thomas Sowell
- The Skeptic's Dictionary entry on IQ and race
- (Skeptic Magazine): Two book reviews, by Paul R. Gross and Alondra Oubre, of Sarich’s and Miele’s book, Race: The Reality of Human Differences
- Criticism on source material of Bell Curve book
- Poverty and Brain Development in Early Childhood 1999 report
- Miscellaneous articles by Richard Lynn et al.
- Are IQ Tests Biased?
- Scholars Provide an Overview of Explanations for Black-White Test Score Gap
- School Readiness: Closing Racial and Ethnic Gaps
- A review of the field (Jan. 2006) Kohn, Marek, "This racist undercurrent in the tide of genetic research: As taboos fall away, there's a danger that denial of racial difference will be replaced with uncritical acceptance," The Guardian.
- The Lessons of the Ashkenazim: Groups and Genes, Steven Pinker, June 2006, The New Republic.
- Are all races equally intelligent? -- Or: When is knowledge knowledge? by John J. Ray
- Black-White Gap in IQ Scores Closing, Study Finds
Template:Race and intelligence
| Sex differences in humans | ||
|---|---|---|
| Biology |  | |
| Medicine and Health | ||
| Neuroscience and Psychology | ||
| Sociology | ||