This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Miyokan (talk | contribs) at 03:31, 21 January 2008 (→Imperial Russia). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 03:31, 21 January 2008 by Miyokan (talk | contribs) (→Imperial Russia)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| Russian Federation Российская Федерация Rossiyskaya Federatsiya | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Anthem: Hymn of the Russian Federation | |
 | |
| Capitaland largest city | Moscow |
| Official languages | Russian official throughout nation; thirty others co-official in various regions |
| Demonym(s) | Russian |
| Government | Semi-presidential republic |
| • President | Vladimir Putin |
| • Prime Minister | Viktor Zubkov |
| Founded (862) Arrival of Rurik to Novgorod | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 17,075,400 km (6,592,800 sq mi) (1st) |
| • Water (%) | 13 |
| Population | |
| • 2007 estimate | 142,200,000 (9th) |
| • 2002 census | 145,274,019 |
| • Density | 8.3/km (21.5/sq mi) (209th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2006 estimate |
| • Total | $1.746 trillion (8th) |
| • Per capita | $12,200 (59th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2006 estimate |
| • Total | $987 billion (10th) |
| • Per capita | $6,856 (59th) |
| Gini (2005) | 40.5 Error: Invalid Gini value |
| HDI (2005) | Error: Invalid HDI value (67th) |
| Currency | Ruble (RUB) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 to +12 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 to +13 |
| Calling code | 7 |
| ISO 3166 code | RU |
| Internet TLD | .ru (.su reserved) |
| |
Russia (Template:Lang-ru, Rossiya), also the Russian Federation (Росси́йская Федера́ция, Rossiyskaya Federatsiya; listen), is a transcontinental country extending over much of northern Eurasia. It is a semi-presidential republic comprising 84 federal subjects. Russia shares land borders with the following countries (counter-clockwise from northwest to southeast): Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania (Kaliningrad Oblast), Poland (Kaliningrad Oblast), Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia and North Korea. It is also close to the U.S. state of Alaska, Sweden and Japan across relatively small stretches of water (the Bering Strait, the Baltic Sea, and La Pérouse Strait, respectively).
At 17,075,400 square kilometres (6,592,800 sq mi), Russia is by far the largest country in the world, covering more than an eighth of the Earth’s land area; with 142 million people, it is the ninth largest by population. It extends across the whole of northern Asia and 40% of Europe, spanning 11 time zones and incorporating a great range of environments and landforms. Russia has the world's largest mineral and energy resources, and is considered an energy superpower. It contains approximately one-quarter of the world's unfrozen fresh water and has the world's largest forest reserves.
The nation's history began with that of the East Slavs. The Slavs emerged as a recognizable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD. Founded and ruled by Vikings and their descendants, the first East Slavic state, Kievan Rus', arose in the 9th century and adopted Christianity from the Byzantine Empire in 988, beginning the synthesis of Byzantine and Slavic cultures that defined Russian culture for the next millennium. Kievan Rus' ultimately disintegrated and the Russian lands were divided. The most powerful successor state to Kievan Rus' was Moscow, which gradually came to dominate the cultural and political legacy of Kievan Rus'. By the 18th century, the Grand Duchy of Moscow had expanded through conquest, annexation and exploration to become the huge Russian Empire, stretching from Poland eastward to the Pacific Ocean.
Russia established worldwide power and influence from the times of the Russian Empire to being the preeminent constituent of the Soviet Union, the world's first and largest Communist state, and can boast a long tradition of excellence in every aspect of the arts and sciences. The Russian Federation was founded following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, but is recognized as the continuing legal personality of the Soviet Union. Russia is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council and a leading member of the Commonwealth of Independent States and the G8. It is one of the five recognized nuclear weapons states and possesses the world's largest stockpile of weapons of mass destruction.
Geography
Main article: Geography of RussiaThe Russian Federation stretches across much of the north of the super-continent of Eurasia. Because of its size, Russia displays both monotony and diversity. As with its topography, its climates, vegetation, and soils span vast distances. From north to south the East European Plain is clad sequentially in tundra, coniferous forest (taiga), mixed and broad-leaf forests, grassland (steppe), and semi-desert (fringing the Caspian Sea) as the changes in vegetation reflect the changes in climate. Siberia supports a similar sequence but is taiga. The country contains 23 World Heritage Sites and 39 UNESCO Biosphere reserves.
Topography
The two widest separated points in Russia are about 8,000 km (5,000 mi) apart along a geodesic line. These points are: the boundary with Poland on a 60 km long (40-mi long) spit of land separating the Gulf of Gdańsk from the Vistula Lagoon; and the farthest southeast of the Kurile Islands, a few miles off Hokkaidō Island, Japan. The points which are furthest separated in longitude are 6,600 km (4,100 mi) apart along a geodesic. These points are: in the West, the same spit; in the East, the Big Diomede Island (Ostrov Ratmanova). The Russian Federation spans 11 time zones.
Russia has the world's largest forest reserves and is known as "the lungs of Europe," second only to the Amazon Rainforest in the amount of carbon dioxide it absorbs. It provides a huge amount of oxygen for not just Europe, but the world. With access to three of the world's oceans—the Atlantic, Arctic, and Pacific—Russian fishing fleets are a major contributor to the world's fish supply. The Caspian is the source of what is considered the finest caviar in the world.

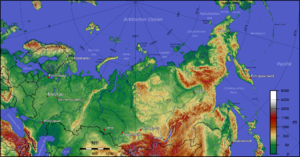
Most of Russia consists of vast stretches of plains that are predominantly steppe to the south and heavily forested to the north, with tundra along the northern coast. Mountain ranges are found along the southern borders, such as the Caucasus (containing Mount Elbrus, Russia's and Europe's highest point at 5,642 m / 18,511 ft) and the Altai, and in the eastern parts, such as the Verkhoyansk Range or the volcanoes on Kamchatka. The Ural Mountains form a north-south range that divides Europe and Asia, rich in mineral resources. Russia possesses 8.9% of the world's arable land.
Russia has an extensive coastline of over 37,000 kilometers (23,000 mi) along the Arctic and Pacific Oceans, as well as the Baltic, Black and Caspian seas. The Barents Sea, White Sea, Kara Sea, Laptev Sea, East Siberian Sea, Bering Sea, Sea of Okhotsk and the Sea of Japan are linked to Russia. Major islands and archipelagos include Novaya Zemlya, the Franz Josef Land, the New Siberian Islands, Wrangel Island, the Kuril Islands and Sakhalin. The Diomede Islands (one controlled by Russia, the other by the United States) are just three kilometers (1.9 mi) apart, and Kunashir Island is about twenty kilometers (12 mi) from Hokkaidō.
Russia has thousands of rivers and inland bodies of water, providing it with one of the world's largest surface water resources. The most prominent of Russia's bodies of fresh water is Lake Baikal, the world's deepest, purest and most capacious freshwater lake. Lake Baikal alone contains over one fifth of the world's fresh surface water. Of its 100,000 rivers, The Volga is the most famous—not only because it is the longest river in Europe but also because of its major role in Russian history. Major lakes include Lake Baikal, Lake Ladoga and Lake Onega. Russia has a wide natural resource base including major deposits of petroleum, natural gas, coal, timber and mineral resources unmatched by any other country.
Climate
The climate of the Russian Federation formed under the influence of several determining factors. The enormous size of the country and the remoteness of many areas from the sea result in the dominance of the continental climate, which is prevalent in European and Asian Russia except for the tundra and the extreme southeast. Mountains in the south obstructing the flow of warm air masses from the Indian Ocean and the plain of the west and north makes the country open to Arctic and Atlantic influences.
Throughout much of the territory there are only two distinct seasons — winter and summer; spring and autumn are usually brief periods of change between extremely low temperatures and extremely high. The coldest month is January (on the shores of the sea—February), the warmest usually is July. Great ranges of temperature are typical. In winter, temperatures get colder both from south to north and from west to east. Summers can be quite hot and humid, even in Siberia. A small part of Black Sea coast around Sochi is considered in Russia to have subtropical climate. The continental interiors are the driest areas.
History
Main article: History of RussiaEarly periods
Main articles: Proto-Indo-Europeans, Scythians, Bosporan Kingdom, and Khazaria
The vast steppes of Southern Russia were home to disunited tribes, such as Proto-Indo-Europeans and Scythians. Remnants of these steppe civilizations were discovered in the course of the 20th century in such places as Ipatovo, Sintashta, Arkaim, and Pazyryk. In the latter part of the eighth century BC, Greek merchants brought classical civilization to the trade emporiums in Tanais and Phanagoria. Between the third and sixth centuries AD, the Bosporan Kingdom, a Hellenistic polity which succeeded the Greek colonies, was overwhelmed by successive waves of nomadic invasions, led by warlike tribes, such as the Huns and Turkic Avars. A Turkic people, the Khazars, ruled the lower Volga basin steppes between the Caspian and Black Seas through to the 8th century.

The ancestors of modern Russians are the Slavic tribes, whose original home is thought by some scholars to have been the wooded areas of the Pripet Marshes. Moving into the lands vacated by the migrating Germanic tribes, the Early East Slavs gradually settled Western Russia in two waves: one moving from Kiev toward present-day Suzdal and Murom and another from Polotsk toward Novgorod and Rostov. From the 7th century onwards, the East Slavs constituted the bulk of the population in Western Russia and slowly but peacefully assimilated the native Finno-Ugric tribes, including the Merya, the Muromians, and the Meshchera.
Kievan Rus
Main article: Kievan Rus
Scandinavian Norsemen, called "Vikings" in Western Europe and "Varangians" in the East, combined piracy and trade in their roamings over much of Northern Europe. In the mid-9th century, they ventured along the waterways extending from the eastern Baltic to the Black and Caspian Seas. According to the earliest Russian chronicle, a Varangian named Rurik was elected ruler (konung or knyaz) of Novgorod around the year 860; his successors moved south and extended their authority to Kiev, which had been previously dominated by the Khazars.
In the tenth to eleventh centuries this state of Kievan Rus became the largest and most prosperous in Europe. In the eleventh and twelfth centuries, constant incursions by nomadic Turkic tribes, such as the Kipchaks and the Pechenegs, caused a massive migration of Slavic populations to the safer, heavily forested regions of the north, particularly to the area known as Zalesye. Like many other parts of Eurasia, these territories were overrun by the Mongols. The invaders, later known as Tatars, formed the state of the Golden Horde, which pillaged the Russian principalities and ruled the southern and central expanses of Russia for over three centuries. Mongol rule retarded the country's economic and social development. However, the Novgorod Republic together with Pskov retained some degree of autonomy during the time of the Mongol yoke and was largely spared the atrocities that affected the rest of the country. Led by Alexander Nevsky, Novgorodians repelled the Germanic crusaders who attempted to colonize the region. Kievan Rus' ultimately disintegrated as a state because of in-fighting between members of the princely family that ruled it collectively. Kiev's dominance waned, to the benefit of Vladimir-Suzdal in the north-east, Novgorod in the north, and Halych-Volhynia in the south-west. Conquest by the Golden Horde in the 13th century was the final blow and resulted in the destruction of Kiev in 1240. Halych-Volhynia was eventually absorbed into the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, while the Mongol-dominated Vladimir-Suzdal and the independent Novgorod Republic, two regions on the periphery of Kiev, established the basis for the modern Russian nation.
Grand Duchy of Moscow and Tsardom of Russia
Main articles: Grand Duchy of Moscow and Tsardom of Russia
The most powerful successor state to Kievan Rus' was Grand Duchy of Moscow. It would annex rivals such as Tver and Novgorod, and eventually become the basis of the modern Russian state. After the downfall of Constantinople in 1453, Moscow claimed succession to the legacy of the Eastern Roman Empire. While still under the domain of the Mongol-Tatars and with their connivance, the Duchy of Moscow (or "Muscovy") began to assert its influence in Western Russia in the early fourteenth century. Assisted by the Russian Orthodox Church and Saint Sergius of Radonezh's spiritual revival, Russia inflicted a defeat on the Mongol-Tatars in the Battle of Kulikovo (1380). Ivan III (Ivan the Great) eventually tossed off the control of the invaders, consolidated surrounding areas under Moscow's dominion and first took the title "grand duke of all the Russias".
In 1547, Ivan IV (Ivan the Terrible) was officially crowned the first Tsar of Russia. During his long reign, Ivan IV annexed the Tatar khanates (Kazan, Astrakhan) along the Volga River and transformed Russia into a multiethnic and multiconfessional state. Ivan IV promulgated a new code of laws (Sudebnik of 1550), established the first Russian feudal representative body (Zemsky Sobor) and introduced local self-management into the rural regions. But Ivan IV's rule was also marked by the long and unsuccessful Livonian War against the coalition of Poland, Lithuania, Sweden for the access to the Baltic coast and sea trade. The military losses, epidemics, and poor harvests weakened the state, and the Crimean Tatars were able to burn down Moscow. The death of Ivan's sons, combined with the famine (1601–1603), led to the civil war and foreign intervention of the Time of Troubles in the early 1600s. By the middle of the seventeenth century there were Russian settlements in Eastern Siberia, on the Chukchi Peninsula, along the Amur River, and on the Pacific coast. The strait between North America and Asia was first sighted by a Russian explorer in 1648.
Imperial Russia
Main article: Russian Empire
Under the Romanov dynasty and Peter I (Peter the Great), the Russian Empire was officially founded. Ruling from 1682 to 1725, Peter defeated Sweden in the Great Northern War, forcing it to cede West Karelia and Ingria (two regions lost by Russia in the Time of Troubles), Estland, and Livland, securing Russia's access to the sea and sea trade. It was in Ingria that Peter founded a new capital, Saint Petersburg. Peter's reforms brought considerable Western European cultural influences to Russia. Catherine II (Catherine the Great), who ruled from 1762 to 1796, continued the efforts at establishing Russia as one of the great powers of Europe. In alliance with Prussia and Austria, Russia stood against Napoleon's France and eliminated its rival Poland-Lithuania in a series of partitions, gaining large areas of territory in the west. As a result of its victories in the Russian-Turkish wars, by the early 19th century Russia had made significant territorial gains in Transcaucasia. Napoleon's invasion failed miserably as obstinate Russian resistance combined with the bitterly cold Russian winter dealt him a disastrous defeat, from which more than 95% of his invading force perished. However, the officers of the Napoleonic wars brought back to Russia the ideas of liberalism and even attempted to curtail the tsar's powers during the abortive Decembrist revolt of 1825, which was followed by several decades of political repression.


The prevalence of serfdom and the conservative policies of Nicolas I impeded the development of Russia in the mid-nineteenth century. Nicholas's successor Alexander II (1855–1881) enacted significant reforms, including the abolition of serfdom in 1861; these "Great Reforms" spurred industrialization. However, many socio-economic conflicts were aggravated during Alexander III’s reign and under his son, Nicholas II. Harsh conditions in factories created mass support for the revolutionary socialist movement. In January, 1905 striking workers peaceably demonstrated for reforms in Saint Petersburg but were fired upon by troops, killing and wounding hundreds. The event, known as "Bloody Sunday", ignited the Russian Revolution of 1905. Although the uprising was swiftly put down by the army and he retained much of his power, Nicholas II was forced to concede major reforms including granting the freedoms of speech and assembly, legalization of political parties and the creation of an elected legislative assembly, the Duma, however basic improvements in the lives of industrial workers were unfulfilled.
Russia entered World War I in the aid of its ally Serbia and fought a war across three fronts. Although the army was far from defeated in 1916, the already existing public distrust of the regime was deepened by the rising costs of war, casualties, and tales of corruption and even treason in high places, leading to the outbreak of the Russian Revolution of 1917. A series of uprisings were organized by workers and peasants throughout the country, as well as by soldiers in the Russian army, who were mainly of peasant origin. Many of the uprisings were organized and led by democratically elected councils called Soviets. The February Revolution overthrew the Russian monarchy, which was replaced by a shaky coalition of political parties that declared itself the Provisional Government. The abdication marked the end of imperial rule in Russia, and Nicholas and his family were imprisoned and later executed during the Civil War. While initially receiving the support of the Soviets, the Provisional Government proved unable to resolve many problems which had led to the February Revolution. The second revolution, the October Revolution, led by Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Provisional Government and created the world’s first Communist state.
Soviet Russia
Main articles: History of the Soviet Union and Russian SFSR
Following the October Revolution, a civil war broke out between the new regime and its opponents, the moderate socialist parties—the Socialist Revolutionaries and Mensheviks— and a loose confederation of counter-revolutionary forces known as the White movement. The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, a peace treaty signed by the Central Powers with Soviet Russia, concluded hostilities between those countries in World War I. Russia lost its Polish and Baltic territories, and Finland by signing the treaty. However, the Allied powers of World War I launched a military intervention in support of anti-Communist forces. Both the Bolsheviks and White movement carried out campaigns of mass arrests, deportations, and executions against each other, known respectively as the Red Terror and White Terror. The Bolsheviks instituted "War Communism" in order to requisition food for the army and cities, resulting in mass starvation and peasant resistance. By 1921, Bolshevik forces brought most of the territories lost from the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk under their control. However, Russia had been at war for 7 years, during which time some 16 million of its people had lost their lives, with the Civil War taking an estimated 7–10 million of them. At the end of the Civil War, the economy and infrastructure were devastated.
Following victory in the Civil War, the Russian SFSR together with three other Soviet republics formed the Soviet Union on December 30, 1922. The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic dominated the Soviet Union for its entire 74-year history; the USSR was often referred to as "Russia" and its people as "Russians." The largest of the republics, Russia contributed over half the population of the Soviet Union. The Bolsheviks introduced free universal health care, education and social-security benefits, as well as the right to work and housing. Women's rights were greatly increased through new laws aimed to wipe away centuries-old inequalities. Notably, Russia became the first country in the world with full freedom of divorce and legalized abortion. After Lenin's death in 1924 a Georgian named Joseph Stalin consolidated power and became dictator.
Stalin launched a command economy, forced rapid industrialization of the largely rural country and collectivization of its agriculture. While the Soviet Union transformed from an agrarian economy to a major industrial powerhouse in a short span of time, hardships and famine ensued for many millions of people as a result of the severe economic upheaval and party policies. At the end of 1930s, Stalin launched the Great Purges, a major campaign of repression against millions of people who were suspected of being a threat to the party were executed or exiled to Gulag labor camps in remote areas of Siberia or Central Asia. A number of ethnic groups in Russia were also forcibly resettled.

On June 22, 1941, Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union, opening the largest theater of the Second World War and beginning what became known in the USSR as the Great Patriotic War, the largest theatre of war in history in terms of numbers of soldiers, equipment and casualties and notorious for its unprecedented ferocity, destruction, and immense loss of life. The conflict became the deadliest in World War II, with over 5.5 million deaths amongst the Axis Forces and 10.7 million Soviet military deaths and civilian deaths were about 15.9 million. 2.8-3.5 million Soviet prisoners of war died in German captivity. Although the German army had considerable success early on, they suffered defeats after reaching the outskirts of Moscow and were dealt their first major defeat at the Battle of Stalingrad in the winter of 1942–1943. Soviet forces drove through Eastern Europe in 1944–45 and captured Berlin in May, 1945. Although the Soviet Union was victorious, an estimated 27 million of its people were killed, accounting for half of all World War II casualties and the vast majority of Allied deaths. The Soviet economy and infrastructure suffered massive devastation. However, the Soviet Union had emerged as an acknowledged superpower. The Red Army had occupied Eastern Europe after the war, including the eastern half of Germany; Stalin installed communist governments in these satellite states. Becoming the world's second nuclear weapons power, the Soviet Union established the Warsaw Pact alliance and entered into a struggle for global dominance with the United States, which became known as the Cold War.
Under Stalin's successor Nikita Khrushchev, the Soviet Union launched the world's first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1 and the Russian astronaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human being to orbit the Earth aboard the first manned spacecraft, Vostok 1. Tensions with the United States heightened when the two rivals clashed over the deployment of the U.S. Jupiter missiles in Turkey and Soviet missiles in Cuba. Following the ousting of Khrushchev, another period of rule by collective leadership ensued until Leonid Brezhnev established himself in the early 1970s as the pre-eminent figure in Soviet politics. Brezhnev's rule oversaw economic stagnation and the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, which dragged on without success and with continuing casualties inflicted by insurgents, and Soviet citizens became increasingly discontented with the war, ultimately leading to the withdrawal of Soviet forces by 1989.
From 1985 onwards, the reformist Mikhail Gorbachev introduced the landmark policies of glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring), in an attempt to modernize the country. Glasnost meant that the harsh restrictions on free speech that had characterized most of the Soviet Union's existence were removed and open political discourse and criticism of the government became possible. Perestroika was a program of economic reforms designed to decentralize the Soviet planned economy. However, the reforms put in motion forces of change that threatened Communist Party hegemony while provoking strong resentment amongst conservatives. The last years of the USSR were characterized by shortages of goods in grocery stores, huge budget deficits and explosive growth in money supply leading to inflation. In August 1991, an unsuccessful military coup against Gorbachev aimed at preserving the Soviet Union instead led to its collapse. In Russia, Boris Yeltsin came to power and declared the end of exclusive Communist rule. The USSR soon splintered into fifteen independent republics and was officially dissolved in December 1991. Boris Yeltsin was elected the President of Russia in June 1991, in the first direct presidential election in Russian history.
Russian Federation
Main article: History of post-Soviet RussiaAfter the disintegration of the USSR, the Russian economy went through a major crisis. In October 1991, Yeltsin announced that Russia would proceed with radical, market-oriented reform along the lines of "shock therapy", as recommended by the United States and International Monetary Fund. However, this policy resulted in economic collapse, with GDP declining by roughly 50 percent between 1990 and 1995 and millions being plunged into poverty. The early and mid-1990s was marked by extreme lawlessness. Criminal gangs and organized crime flourished and murders and other violent crime spiraled out of control. The severe hardships and decline in the standard of living suffered by the population led to a resurgence of support for the Communist Party. In 1993 a constitutional crisis pushed Russia to the brink of civil war. President Boris Yeltsin illegally dissolved the country's legislature which opposed his moves to consolidate power and push forward with unpopular neo-liberal reforms; in response, legislators barricaded themselves inside the White House and major protests against Yeltsin's government resulted in the most deadly street fighting seen in Moscow since the October Revolution. With military support, Yeltsin sent the army to besiege the parliament building and used tanks and artillery to eject the legislators.

The 1990s were plagued by armed ethnic conflicts in the North Caucasus. Such conflicts took a form of separatist Islamist insurrections against federal power (most notably in Chechnya), or of ethnic/clan conflicts between local groups (e.g., in North Ossetia-Alania between Ossetians and Ingushs, or between different clans in Chechnya). Since the Chechen separatists declared independence in the early 1990s, an intermittent guerrilla war (First Chechen War, Second Chechen War) has been fought between disparate Chechen groups and the Russian military. On December 31, 1999 Boris Yeltsin resigned from the presidency, handing the post to the recently appointed prime minister, Vladimir Putin, who then won the 2000 election. Putin won popularity for suppressing the Chechen insurgency, but sporadic violence and acts of terrorism have continued. High oil prices and a cheap ruble followed by increasing domestic demand, consumption and investments has helped the economy grow for eight straight years, alleviating the standard of living and increasing Russia's clout on the world stage. While many reforms made under Putin’s rule have been generally criticized by Western nations as un-democratic, Putin's leadership over the return of stability and progress has won him widespread popularity in Russia.
Government and politics
Main article: Politics of RussiaAccording to the Constitution, which was adopted by national referendum on December 12, 1993 following the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis, Russia is a federation and a presidential republic, wherein the President of Russia is the head of state and the Prime Minister of Russia is the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation.
The president is elected by popular vote for a four-year term (eligible for a second term but constitutionally barred for a third consecutive term); election last held 14 March 2004 (next to be held 2 March 2008). Ministries of the government are composed of the premier and his deputies, ministers, and selected other individuals; all are appointed by the president. The national legislature is the Federal Assembly, which consists of two chambers; the 450-member State Duma and the 176-member Federation Council. According to the Constitution of Russia, constitutional justice in the court is based on the equality of all citizens, judges are independent and subject only to the law, and trials are to be open, and the accused is guaranteed a defense. Leading political parties in Russia include United Russia, the Communist Party, the Liberal Democratic Party of Russia and Fair Russia.
Subdivisions
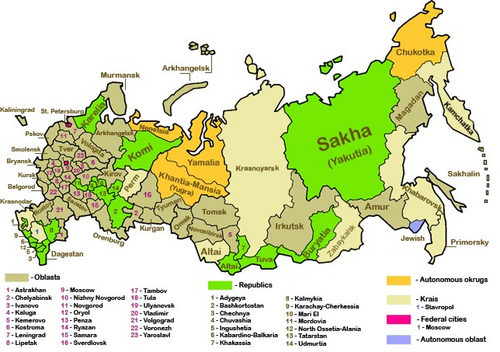
Main article: Subdivisions of Russia- Federal subjects
The Russian Federation comprises 84 federal subjects. These subjects have equal representation—two delegates each—in the Federation Council. However, they differ in the degree of autonomy they enjoy.
- 47 oblasts (provinces): most common type of federal subjects, with federally appointed governor and locally elected legislature.
- 21 republics: nominally autonomous; each has its own constitution, president, and parliament. Republics are allowed to establish their own official language alongside Russian but are represented by the federal government in international affairs. Republics are meant to be home to specific ethnic minorities.
- Eight krais (territories): essentially the same as oblasts. The "territory" designation is historic, originally given to frontier regions and later also to administrative divisions that comprised autonomous okrugs or autonomous oblasts.
- Five autonomous okrugs (autonomous districts): originally autonomous entities within oblasts and krais created for ethnic minorities, their status was elevated to that of federal subjects in the 1990s. With the exception of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, all autonomous okrugs are still administratively subordinated to a krai or an oblast of which they are a part.
- One autonomous oblast (the Jewish Autonomous Oblast): originally autonomous oblasts were administrative units subordinated to krais. In 1990, all of them except the Jewish AO were elevated in status to that of a republic.
- Two federal cities (Moscow and St. Petersburg): major cities that function as separate regions.
- Federal districts and economic regions
Federal subjects are grouped into seven federal districts, each administered by an envoy appointed by the President of Russia. Unlike the federal subjects, the federal districts are not a subnational level of government, but are a level of administration of the federal government. Federal districts' envoys serve as liaisons between the federal subjects and the federal government and are primarily responsible for overseeing the compliance of the federal subjects with the federal laws. For economic and statistical purposes the federal subjects are grouped into twelve economic regions. Economic regions and their parts sharing common economic trends are in turn grouped into economic zones and macrozones.
Foreign relations and military
Main articles: Foreign relations of Russia and Armed Forces of the Russian Federation
The Russian Federation is recognized in international law as continuing the legal personality of the former Soviet Union. Russia continues to implement the international commitments of the USSR, and has assumed the USSR's permanent seat on the UN Security Council, membership in other international organizations, the rights and obligations under international treaties and property and debts. Russia has a multifaceted foreign policy. It maintains diplomatic relations with 178 countries and has 140 embassies. Russia's foreign policy is determined by the President and implemented by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
As one of five permanent members of the UN Security Council, Russia plays a major role in maintaining international peace and security, and plays a major role in resolving international conflicts by participating in the Quartet on the Middle East, the Six-party talks with North Korea, promoting the resolution of the Kosovo conflict and resolving nuclear proliferation issues. Russia is a member of the Group of Eight (G8) industrialized nations, the Council of Europe, OSCE and APEC. Russia usually takes a leading role in regional organizations such as the CIS, EurAsEC, CSTO, and the SCO. President Vladimir Putin has advocated a strategic partnership with close integration in various dimensions including establishment of four common spaces between Russia and the EU. Since the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia has developed a friendlier, albeit volatile relationship with NATO. The NATO-Russia Council was established in 2002 to allow the 26 Allies and Russia to work together as equal partners to pursue opportunities for joint collaboration.

Russia assumed control of Soviet assets abroad and most of the Soviet Union's production facilities and defense industries are located in the country. The Russian military is divided into the Ground Forces, Navy, and Air Force. There are also three independent arms of service: Strategic Rocket Forces, Military Space Forces, and the Airborne Troops. Russia has the largest stockpile of nuclear weapons in the world. It has the second largest fleet of ballistic missile submarines and is the only country apart from the U.S. with a modern strategic bomber force. The country has a large and fully indigenous arms industry, producing all of its own military equipment. Russia is the world's top supplier of weapons, a spot it has held since 2001, accounting for around 30% of worldwide weapons sales and exporting weapons to about 80 countries. Following the Soviet practice, it is mandatory for all male citizens aged 18–27 to be drafted for two years' Armed Forces service, though various problems associated with this is why the armed forces are from 2008 reducing the conscription term from 18 months to 12, and plan to increase contract servicemen to compose 70% of the armed forces by 2010. Defense expenditure has quadrupled over the past six years. Official government military spending for 2007 was $32.4 billion, though various sources, including US intelligence, and the US Department of Defence, have estimated Russia’s military expenditures to be considerably higher. Currently, the military is undergoing a major equipment upgrade with about $200 billion (what equals to about $400 billion in PPP dollars) on procurement of military equipment between 2006 and 2015.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Russia

Since the turn of the century, high oil prices, foreign investment, increasing domestic consumption and political stability have bolstered economic growth. Russia ended 2006 with its eighth straight year of growth, averaging 6.7% annually since the financial crisis of 1998. Russia's 2006 GDP was $1.723 trillion (est. PPP), the 8th highest in the world, with GDP growth of 6.8%. Growth was driven by non-traded services and goods for the domestic market, as opposed to oil or mineral extraction and exports. The International Monetary Fund and World Bank forecast that Russia's GDP will grow by at least 7% in 2007. The Ministry of Economic Development and Trade revised its forecast up and projects that GDP will grow 7.3% in 2007. Approximately 12.5% of Russians were below the federally designated poverty line in 2007, down from 33.5% in 1992. The average salary was $540 (about $920 PPP) per month in August 2007, up from $65 per month in August 1999.
Oil, natural gas, metals, and timber account for more than 80% of exports. Since 2003, exports of natural resources started decreasing in economic importance as the internal market has strengthened considerably. Oil and gas contribute to 5.7% of GDP and the government predicts this will drop to 3.7% of Russia's GDP by 2011. Russia has the world's largest natural gas reserves, the second largest coal reserves and the eighth largest oil reserves. It is the world's leading natural gas exporter and the second leading oil exporter. Russia is well ahead of most other resource-rich countries in its economic development, with a long tradition of education, science, and industry. The importance of oil and gas to the economy led to the creation the Stabilization Fund of the Russian Federation, which takes in revenues from oil and gas exports and helps offset market volatility. As of October 1, 2007, it stands at $147.6 billion.
In the first half of 2007, foreign investment in the Russian economy doubled year-on-year, reaching $60.3 billion. In 2000 total investment in fixed assets was $40 billion, giving growth of 300% by 2006 when it reached $120 billion. A simpler, more streamlined tax code adopted in 2001 reduced the tax burden on people, and dramatically increased state revenue. Russia has a flat personal income tax rate of 13 percent, ranked the second most attractive personal tax system for single managers in the world after the United Arab Emirates according to a 2007 survey by investment services firm Mercer, and its implementation has been so successful that it has been emulated by other countries. The federal budget has run surpluses since 2001 and ended 2006 with a surplus of 9% of GDP. Over the past several years, Russia has used its stabilization fund based on oil taxes to prepay all Soviet-era sovereign debt to Paris Club creditors and the IMF. Oil export earnings have allowed Russia to increase its foreign reserves from $12 billion in 1999 to some $315 billion at the end of 2006, the third largest reserves in the world (as of November 30, 2007, it stands at $463.5 billion). The country is also benefiting from rising oil prices and has been able to substantially reduce its formerly huge foreign debt.
The economic development of the country has been uneven geographically: the Moscow region contributes a disproportionately high amount of the country's GDP. While the huge capital region of Moscow is an affluent metropolis, much of the country, especially indigenous and rural communities in Asian Russia, lags significantly behind. Nevertheless, the middle class has grown from just 8 million in 2000 to 55 million in 2006, estimates Expert, a market research firm in Moscow.
Over the last five years, fixed capital investments have averaged real gains greater than 10% per year and personal incomes have achieved real gains more than 12% per year. During this time, poverty has declined steadily and the middle class has continued to expand. Russia has also improved its international financial position since the 1998 financial crisis. Equal redistribution of capital gains from the natural resource industries to other sectors is still a problem. A principal factor in Russia's growth has been the combination of strong growth in productivity, real wages, and consumption. A skilled work-force, including women and minorities, secular attitudes and mobile class structure has set Russia far apart from the majority of developing nations and even some developed nations.
Despite the country's strong economic performance since 1999, the World Bank lists several challenges facing the Russian economy including diversifying the economy, encouraging the growth of small and medium enterprises, building human capital and improving governance.
Demographics
Main article: Demography of Russia| Ethnic composition (2002) | |
|---|---|
| Russians | 79.8% |
| Tatars | 3.8% |
| Ukrainians | 2.0% |
| Chuvash | 1.1% |
| Chechen | 0.9% |
| Armenians | 0.8% |
| Other/unspecified | 10.3% |

In July 2007, the population of Russia was estimated to be 141,377,752. The Russian Federation is a diverse, multiethnic society, home to as many as 160 different ethnic groups and indigenous peoples. Though Russia's population is comparatively large, its population density is low because of its enormous size; its population is densest in European Russia, near the Ural Mountains, and in the southwest Siberia.
73% of the population live in urban areas. As of the 2002 Census, the two largest cities in Russia are Moscow (10,126,424 inhabitants) and Saint Petersburg (4,661,219). Eleven other cities have between one and two million inhabitants: Chelyabinsk, Kazan, Novosibirsk, Nizhny Novgorod, Omsk, Perm, Rostov-on-Don, Samara, Ufa, Volgograd, and Yekaterinburg. In 2006, 186,380 migrants arrived to the Russian Federation of which 95% came from CIS countries. There are also an estimated 10 million illegal immigrants from the ex-Soviet states in Russia.
According to most sources, Russia's population peaked in 1991 at 148,689,000. In 2006, the federal statistics agency reported that Russia's population shrunk by about 700,000 people, dipping to 142.8 million. The primary causes of Russia's population decrease are a high death rate and low birth rate. While Russia's birth-rate is comparable to that of other European countries (Russia's birth rate is 10.92 per 1000 people compared to the European Union average of 10.00 per 1000) its population declines at much greater rate due to a substantially higher death rate (Russia's death rate is 16.04 per 1000 people compared to the European Union average of 10.00 per 1000).
| Largest cities or towns in Russia 2024 estimate | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Federal subject | Pop. | Rank | Name | Federal subject | Pop. | ||
 Moscow  Saint Petersburg |
1 | Moscow | Moscow | 13,149,803 | 11 | Rostov-on-Don | Rostov Oblast | 1,140,487 |  Novosibirsk  Yekaterinburg |
| 2 | Saint Petersburg | Saint Petersburg | 5,597,763 | 12 | Krasnodar | Krasnodar Krai | 1,138,654 | ||
| 3 | Novosibirsk | Novosibirsk Oblast | 1,633,851 | 13 | Omsk | Omsk Oblast | 1,104,485 | ||
| 4 | Yekaterinburg | Sverdlovsk Oblast | 1,536,183 | 14 | Voronezh | Voronezh Oblast | 1,046,425 | ||
| 5 | Kazan | Tatarstan | 1,318,604 | 15 | Perm | Perm Krai | 1,026,908 | ||
| 6 | Krasnoyarsk | Krasnoyarsk Krai | 1,205,473 | 16 | Volgograd | Volgograd Oblast | 1,018,898 | ||
| 7 | Nizhny Novgorod | Nizhny Novgorod Oblast | 1,204,985 | 17 | Saratov | Saratov Oblast | 887,365 | ||
| 8 | Chelyabinsk | Chelyabinsk Oblast | 1,177,058 | 18 | Tyumen | Tyumen Oblast | 861,098 | ||
| 9 | Ufa | Bashkortostan | 1,163,304 | 19 | Tolyatti | Samara Oblast | 667,956 | ||
| 10 | Samara | Samara Oblast | 1,158,952 | 20 | Makhachkala | Dagestan | 622,091 | ||
Education
Main article: Education in Russia
Russia has a free education system guaranteed to all citizens by the Constitution, and has a literacy rate of 99.4%. The country came first in the world in the 2006 Progress in International Reading Literacy Study conducted by Boston College. Entry to higher education is highly competitive. Universities have been transitioning to a new degree structure similar to that of Britain and the USA; a four year Bachelor's degree and two year Master's degree. As a result of great emphasis on science and technology in education, Russian medical, mathematical, scientific, and space and aviation research is generally of a high order.
The Russian Constitution grants a universal right to higher education free of charge and through competitive entry. The Government allocates funding to pay the tuition fees within an established quota, or number of students for each state institution. This is considered crucial because it provides access to higher education to all skilled students, as opposed to only those who can afford it. In addition, students are provided with a small stipend and free housing. However, the institutions have to be funded entirely from the federal and regional budgets; institutions have found themselves unable to provide adequate teachers' salaries, students' stipends, and to maintain their facilities. To address the issue, many state institutions started to open commercial positions, which have been growing steadily since. Many private higher education institutions have emerged to address the need for a skilled work-force for high-tech and emerging industries and economic sectors.
Health
Russia's constitution guarantees free, universal health care for all citizens. While Russia has more physicians, hospitals, and health care workers than almost any other country in the world, since the collapse of the Soviet Union the health of the Russian population has declined considerably as a result of social, economic, and lifestyle changes. As of 2006, the average life expectancy in Russia is 59.12 years for males and 73.03 years for females. The Russian life expectancy of 65.87 years at birth is 13 years shorter than the overall figure in the European Union. The biggest factor contributing to this relatively low life expectancy for males is a high mortality rate among working-age males from preventable causes (e.g., alcohol poisoning, stress, smoking, traffic accidents, violent crimes). As a result, there are 0.859 males to every female.
Heart diseases account for 56.7% of total deaths, with about 30% involving people still of working age. About 16 million Russians suffer from cardiovascular diseases, placing Russia second in the world, after Ukraine, in this respect. Mortality among Russian men rose by 60% since 1991, four to five times higher than in Europe.
Death rates from homicide, suicide and cancer are also especially high. According to a 2007 survey by Romir Monitoring, 52% of men and 15% of women smoke, and more than 260,000 lives are lost each year as a result of tobacco use. HIV/AIDS, virtually non-existent in the Soviet era, rapidly spread following the collapse, mainly through the explosive growth of intravenous drug use. According to official statistics, there are currently more than 364,000 people in Russia registered with HIV but independent experts place the number significantly higher. In increasing efforts to combat the disease, the government increased spending on HIV control measures 20-fold in 2006. Since the Soviet collapse. there has also been a dramatic rise in both cases of and deaths from tuberculosis, with the disease being particularly widespread amongst prison inmates.
In an effort to stem Russia’s demographic crisis, the government is implementing a number of programs designed to increase the birth rate and attract more migrants to alleviate the problem. The government has doubled monthly child support payments and offered a one-time payment of 250,000 Rubles (around US$10,000) to women who had a second child since 2007. In the first six months of 2007, Russia has seen the highest birth rate since the collapse of the USSR. The First Deputy Prime Minister indicated that the number of childbirths increased 6.5 percent in the first half of 2007, while the number of deaths fell the same 6.5 percent. The First Deputy PM also said about 20 billion rubles (about US$1 billion) will be invested in new prenatal centres in Russia in 2008–2009. Immigration is increasingly seen as necessary to sustain the country's population.
Language
Main article: Russian language
| Languages (2002) | |
|---|---|
| Russian | 142.6 million |
| English | 7.0 million |
| Tatar | 5.3 million |
| German | 2.9 million |
| Ukrainian | 1.8 million |
| Bashkir | 1.4 million |
| Chechen | 1.3 million |
| Chuvash | 1.3 million |
Russia's 160 ethnic groups speak some 100 languages. Russian is the only official state language, but the Constitution gives the individual republics the right to make their native language co-official next to Russian. Despite its wide dispersal, the Russian language is homogeneous throughout Russia. Russian is the most geographically widespread language of Eurasia and the most widely spoken Slavic language. Russian belongs to the Indo-European language family and is one of three (or, according to some authorities, four) living members of the East Slavic languages; the others being Belarusian and Ukrainian (and possibly Rusyn). Written examples of Old East Slavic (Old Russian) are attested from the 10th century onwards.
Over a quarter of the world's scientific literature is published in Russian. Russian is also applied as a means of coding and storage of universal knowledge—60–70% of all world information is published in English and Russian languages. Because of the status of the Soviet Union as a superpower, Russian had great political importance in the 20th century. Hence, the language is still one of the official languages of the United Nations.
Religion
Main article: Religion in Russia
Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, and Judaism are Russia’s traditional religions, deemed part of Russia's "historical heritage" in a law passed in 1997. Estimates of believers widely fluctuate among sources, and some reports put the number of non-believers in Russia as high as 24–48% of the population. Russian Orthodoxy is the dominant religion in Russia. 95% of the registered Orthodox parishes belong to the Russian Orthodox Church while there is a number of smaller Orthodox Churches. However, the vast majority of Orthodox believers do not attend church on a regular basis. Nonetheless, the church is widely respected by both believers and nonbelievers, who see it as a symbol of Russian heritage and culture. Smaller Christian denominations such as Roman Catholics, Armenian Gregorian and various Protestants exist.
The ancestors of today’s Russians adopted Orthodox Christianity in the 10th century. According to a poll by the Russian Public Opinion Research Center, 63% of respondents considered themselves Russian Orthodox, 6% of respondents considered themselves Muslim and less than 1% considered themselves either Buddhist, Catholic, Protestant or Jewish. Another 12% said they believe in God, but did not practice any religion, and 16% said they are non-believers.
It is estimated that Russia is home to some 15–20 million Muslims. Russia also has an estimated 3 million to 4 million Muslim migrants from the ex-Soviet states. Most Muslims live in the Volga-Ural region, as well as in the North Caucasus, Moscow, St. Petersburg and western Siberia. In Russia, there are more than 6,000 mosques (in 1991 it was about 150). Buddhism is traditional for three regions of the Russian Federation: Buryatia, Tuva and Kalmykia. Some residents of the Siberian and Far Eastern regions, Yakutia, Chukotka, etc., practice pantheistic and pagan rites, along with the major religions. Induction into religion takes place primarily along ethnic lines. Slavs are overwhelmingly Orthodox Christian. Turkic speakers are predominantly Muslim, although several Turkic groups in Russia are not.
Culture
Main article: Russian cultureMusic and ballet
Main articles: Russian music and Russian ballet
Russia's large number of ethnic groups have distinctive traditions of folk music. Music in 19th century Russia was defined by the tension between classical composer Mikhail Glinka and his followers, who embraced Russian national identity and added religious and folk elements to their compositions, and the Russian Musical Society led by composers Anton and Nikolay Rubinstein, which was musically conservative. The later Romantic tradition of Tchaikovsky was brought into the 20th century by Sergei Rachmaninoff, one of the last great champions of the Romantic style of European classical music.
World-renowned composers of the 20th century included Scriabin, Stravinsky, Rachmaninoff, Prokofiev, and Shostakovich. During most of the Soviet Era, music was highly scrutinized and kept within a conservative, accessible idiom in conformity with Soviet expectations. Russian conservatories have turned out generations of world-renowned soloists. Among the best known are violinists David Oistrakh and Gidon Kremer, cellist Mstislav Rostropovich, pianists Vladimir Horowitz, Sviatoslav Richter and Emil Gilels, and vocalist Galina Vishnevskaya.
Russian composer Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky composed the world's most famous works of ballet—Swan Lake, The Nutcracker, and Sleeping Beauty. During the early 20th century, Russian dancers Anna Pavlova and Vaslav Nijinsky rose to fame, and impresario Sergei Diaghilev and his Ballets Russes' travels abroad profoundly influenced the development of dance worldwide. Soviet ballet preserved the perfected 19th century traditions, and the Soviet Union's choreography schools produced one internationally famous star after another, including Maya Plisetskaya, Rudolf Nureyev, and Mikhail Baryshnikov. The Bolshoi Ballet in Moscow and the Kirov in St. Petersburg remain famous throughout the world.
Literature
Main article: Russian literature
Russian literature is considered to be among the most influential and developed in the world, contributing much of the world's most famous literary works. Russia's literary history dates back to the 10th century and by the early 19th century a native tradition had emerged, producing some of the greatest writers of all time. This period began with Alexander Pushkin, considered to be the founder of modern Russian literature and often described as the "Russian Shakespeare". Amongst Russia's most renowned poets and writers of the 19th century are Anton Chekhov, Mikhail Lermontov, Leo Tolstoy, Nikolai Gogol, Ivan Turgenev and Fyodor Dostoevsky. Ivan Goncharov, Mikhail Saltykov, Aleksey Pisemsky, and Nikolai Leskov made lasting contributions to Russian prose.
By the 1880s Russian literature had begun to change. The age of the great novelists was over and short fiction and poetry became the dominant genres of Russian literature for the next several decades which became known as the "Silver Age". Previously dominated by realism, symbolism dominated Russian literature in the years between 1893 and 1914. Leading writers of this age include Valery Bryusov, Andrey Bely, Vyacheslav Ivanov, Aleksandr Blok, Dmitry Merezhkovsky, Fyodor Sologub, Anna Akhmatova, Osip Mandelstam, Leonid Andreyev, Ivan Bunin and Maksim Gorky.
Following the Russian Revolution of 1917 and the ensuing civil war, Russian cultural life in was left in chaos. Some established writers left Russia while a new generation of talented writers who had at least some sympathy for the ideals of the revolution was emerging. The most ardent of these joined together in writers organizations with the aim of creating a new and distinctive proletarian (working-class) culture appropriate to the new state. Throughout the 1920s writers enjoyed broad tolerance. In the 1930s censorship over literature was tightened in line with Joseph Stalin's policy of socialist realism. After his death several thaws took place and restrictions on literature were eased. By the 1970s and 1980s, writers were increasingly ignoring the guildlines of socialist realism. The leading writers of the Soviet era included Yevgeny Zamiatin, Isaac Babel, Ilf and Petrov, Yury Olesha, Vladimir Nabokov, Mikhail Bulgakov, Boris Pasternak, Alexander Solzhenitsyn, Vladimir Mayakovski, Mikhail Sholokhov, Yevgeny Yevtushenko and Andrei Voznesensky.
Motion pictures
Main article: Cinema of RussiaWhile in the industrialized nations of the West, motion pictures had first been accepted as a form of cheap recreation and leisure for the working class, Russian filmmaking came to prominence following the 1917 revolution when it explored editing as the primary mode of cinematic expression. Russian and later Soviet cinema was a hotbed of invention in the period immediately following the 1917 revolution, resulting in world-renowned films such as Battleship Potemkin. Soviet-era filmmakers, most notably Sergei Eisenstein and Andrei Tarkovsky, would become some of the world's most innovative and influential directors.
Eisenstein also was a student of filmmaker and theorist Lev Kuleshov, who formulated the groundbreaking editing process called montage at the world's first film school, the All-Union Institute of Cinematography in Moscow. Dziga Vertov, whose kino-glaz (“film-eye”) theory—that the camera, like the human eye, is best used to explore real life—had a huge impact on the development of documentary film making and cinema realism. In 1932, Stalin made Socialist Realism the state policy; this stifled creativity but many Soviet films in this style were artistically successful, including Chapaev, The Cranes Are Flying and Ballad of a Soldier. Leonid Gaidai's comedies of the 1960s and 1970s were immensely popular, with many of the catch phrases still in use today. In 1969, Vladimir Motyl's White Sun of the Desert was released, starting a genre known as 'osterns'. The film is watched by cosmonauts before any trip into space.
The 1980s and 1990s were a period of crisis in Russian cinema. Although Russian filmmakers became free to express themselves, state subsidies were drastically reduced, resulting in fewer films produced. The early years of the 21st century have brought increased viewership and subsequent prosperity to the industry on the back of the economy's rapid development, and production levels are already higher than in Britain and Germany. Russia's total box-office revenue in 2006 was $412 million (by comparison, in 1996 revenues stood at $6 million). Russian cinema continues to receive international recognition. Russian Ark (2002) was the first feature film ever to be shot in a single take.
Sports
Main article: Sport in Russia
Russians have been successful at a number of sports and continuously finishing in the top rankings at the Olympic games. During the Soviet era the national team placed first in the total number of medals won at 14 of its 18 appearances; with these performances, the USSR was the dominant Olympic power of its era. Since the 1952 Olympic Games, Soviet and later Russian athletes have always been in the top three for the number of gold medals collected at the Summer Olympics. The 1980 Summer Olympic Games were held in Moscow while the 2014 Winter Olympics will be hosted by Sochi.
Soviet gymnasts and track-and-field athletes, weight lifters, wrestlers and boxers were consistently among the best in the world. Even since the collapse of the Soviet empire, Russian athletes have continued to dominate international competition in these areas. As in most of the world, football enjoys wide popularity in Russia. Although ice hockey was only introduced during the Soviet era, the national team soon dominated the sport internationally, winning gold at almost all the Olympics and World Championships they contested.
Figure skating is another popular sport; in the 1960s, the Soviet Union rose to become a dominant power in figure skating, especially in pairs skating and ice dancing. At every Winter Olympics from 1964 until the present day, a Soviet or Russian pair has won gold, often considered the longest winning streak in modern sports history. Since the end of the Soviet era, tennis has grown in popularity and Russia has produced a number of famous tennis players. Chess is a widely popular pastime; from 1927, Soviet and Russian chess grandmasters have held the world championship almost continuously.
See also
References
- ^ The World Factbook. "CIA". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". From Article 1: "The names "Russian Federation" and "Russia" shall be equal.". Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- Microsoft® Encarta® Online Encyclopedia 2007. ""Russia"". Retrieved 2007-12-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Library of Congress. "Topography and Drainage". Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- ^ excerpted from Glenn E. Curtis (ed.) (1998). "Russia: A Country Study: Kievan Rus' and Mongol Periods". Washington, DC: Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. Retrieved 2007-07-20.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - "Russia". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- ^ "Russia". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2007-07-03.
- UNESCO World Heritage Centre. "Russian Federation". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- The World Network of Biosphere Reserves - UNESCO. "Russian Federation". Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- Walsh, Nick Paton. "It's Europe's lungs and home to many rare species. But to Russia it's £100bn of wood". Guardian (UK). Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- Fish Industry of Russia - Production, Trade, Markets and Investment. Eurofish, Copenhagen, Denmark. August 2006. p. 211. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- "Russia's rural development program". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- "Lake Baikal—A Touchstone for Global Change and Rift Studies". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- "Lake Baikal". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- "Angara River". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- ^ "Russian Federation: Country Brief". The World Bank. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- ^ "Climate". Library Of Congress. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- Drozdov, V. A. (1992). "Ecological and Geographical Characteristics of the Coastal Zone of the Black Sea" (PDF). GeoJournal. 27.2, pp. 169–178: Springer Netherlands.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: location (link) - Dienekes Pontikos (2004-10-02). "Indo-European Origins in Southeast Europe". Anthropological Research Page. Retrieved 2007-07-20.
- ^ Belinskij, Andrej (March/April 1999). "The 'Princess' of Ipatovo". Archeology. 52 (2). Retrieved 2007-12-26.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Drews, Robert (2004). Early Riders: The beginnings of mounted warfare in Asia and Europe. New York: Routledge. p. 50.
- Koryakova, Dr. Ludmila. "Sintashta-Arkaim Culture". The Center for the Study of the Eurasian Nomads (CSEN). Retrieved 2007-07-20.
- "1998 NOVA documentary: "Ice Mummies: Siberian Ice Maiden"". Transcript. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- Jacobson, Esther (1995). The Art of the Scythians: The Interpenetration of Cultures at the Edge of the Hellenic World. p. 38: Brill. ISBN 9004098569.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Tsetskhladze, Gocha R. (1998). The Greek Colonisation of the Black Sea Area: Historical Interpretation of Archaeology. p. 48: F. Steiner. ISBN 3515073027.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Turchin, Peter (2003). Historical Dynamics: Why States Rise and Fall. pp. 185–186: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691116695.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Christian, David (1998). A History of Russia, Central Asia and Mongolia. pp. 286–288: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 0631208143.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - For a discussion of the origins of Slavs, see Barford, Paul M. The Early Slavs. pp. 15–16: Cornell University Press. ISBN 0801439779.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Christian, David (1998). A History of Russia, Central Asia and Mongolia. pp. 6–7: Blackwell Publishing.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Paszkiewicz, Henry K (1963). The Making of the Russian Nation. p. 262: Darton, Longman & Todd.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - McKitterick, Rosamond (1995). The New Cambridge Medieval History. p. 497: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521364477.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Mongaĭt, Aleksandr Lʹvovich (1959). Archeology in the U.S.S.R. p. 335: Foreign Languages Publishing House.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - See, for instance,. "Viking (Varangian) Oleg". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Obolensky, Dimitri (1994). Byzantium and the Slavs. p. 42: St Vladimir's Seminary Press. ISBN 088141008X.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Thompson, James Westfall (1937). An Introduction to Medieval Europe, 300–1500. p. 268: W. W. Norton & Co. ISBN 0415346991.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: location (link) - Christian, David (1998). A History of Russia, Central Asia and Mongolia. p. 343: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 0631208143.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - "Ukraine: Security Assistance". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Klyuchevsky, Vasily. The course of the Russian history. v.1. ISBN 5-244-00072-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Рыбаков, Б. А. (1948). Ремесло Древней Руси. с.525–533,780–781.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Hamm, Michael Franklin. Kiev: A Portrait, 1800–1917. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691025851.
- May, Dr. Timothy. "Khanate of the Golden Horde". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Solovyov, Sergey (2001). History of Russia from the Earliest Times. pp.562–604, volume 6: AST. ISBN 5170021429.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Skrynnikov, R. (1981). Ivan the Terrible. p.58: Academic Intl Pr (March 1981). p. 219. ISBN 0875690394.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Solovyov, Sergey (2001). History of Russia from the Earliest Times. v.6, pp.751–908: AST. ISBN 5170021429.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Borisenkov E, Pasetski V. The thousand-year annals of the extreme meteorological phenomena. ISBN 5-244-00212-0, p.190
- Solovyov, Sergey (2001). History of Russia from the Earliest Times. v.6, pp.751–809: AST. ISBN 5170021429.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Nighttime temperatures in all summer months, often below freezing, wrecked crops. Borisenkov E, Pasetski V. The thousand-year annals of the extreme meteorological phenomena. ISBN 5-244-00212-0, p.190
- Solovyov, Sergey (2001). History of Russia from the Earliest Times. v.7, pp.461–568: AST. ISBN 5170021429.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Solovyov, Sergey (2001). History of Russia from the Earliest Times. v.9, ch.1: AST. ISBN 5170021429. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Solovyov, Sergey (2001). History of Russia from the Earliest Times. v.15, ch.1: AST.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - "Ruling the Empire". Library of Congress. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Riasanovsky, Nicholas V. (1999). A History of Russia. pp.478-85: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0195121791.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Mawdsley, Evan. The Russian Civil War. ISBN 1841580643.
- ^ Microsoft® Encarta® Online Encyclopedia 2007. "Union of Soviet Socialist Republics". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Cliff, Tony (1984). Class Struggle and Women’s Liberation. pp. 138–139: Bookmarks. ISBN 0906224128.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Erlikman, Vadim (2004). Poteri narodonaseleniia v XX veke : spravochnik. ISBN 5-93165-107-1. Note: Estimates for Soviet World War II casualties vary between sources.
- "Soviet Prisoners of War: Forgotten Nazi Victims of World War II". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Andreev, E. M. (1993). Naselenie Sovetskogo Soiuza, 1922–1991. ISBN 5-02-013479-1.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Harrison, Mark (1998). The Economics of World War II: Six Great Powers in International Comparison. p. 291: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521785030.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - "Reconstruction and Cold War". Library of Congress. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Yegor Gaidar "Beginning of New Phase" (in Russian)
- "Russia: Economic Conditions in Mid-1996". Library of Congress.
- Melvin Fagen. "Russia: Shock Therapy Isn't the Way to Promote Democracy". International Herald Tribune. Retrieved 2008-01-22.
- Elaine Sciolino. "U.S. is abandoning 'shock therapy' for the Russians". The New York Times. Retrieved 2008-01-20.
- Sokolov, Vsevolod (Spring 2004). "From Guns to Briefcases: The Evolution of Russian Organized Crime". World Policy Journal. XXI (No 1).
{{cite journal}}:|issue=has extra text (help) - Sahadi, Jeanne. "Moscow remains the world's most expensive city while London moves up from fifth to second place". CNN.
- ^ "Nuffield Poultry Study Group—Visit to Russia" (PDF). pg 7. The BEMB Research and Education Trust. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Treisman, Daniel. "Is Russia's Experiment with Democracy Over?". UCLA International Institute. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- Stone, Norman. "No wonder they like Putin". The Times. Retrieved 2007-12-31.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 80, para. 1). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 110, para. 1). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 94). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 81, para. 1). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 81, para. 3). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 95, para. 3). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 19, para. 1). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 120, para. 1). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 123, para. 1). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 65, para. 1) In 1993, when the Constitution was adopted, there were 89 subjects listed. Some of them were later merged. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 95, para.2). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов" (ОК 024–95) введённый 1 января 1997 г., в ред. Изменения № 05/2001. Секция I. Федеральные округа (Russian Classificaton of Economic Regions (OK 024–95) of January 1, 1997 as amended by the Amendments #1/1998 through #5/2001. Section I. Federal Districts)
- "Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов" (ОК 024–95) введённый 1 января 1997 г., в ред. Изменения № 05/2001. Секция II. Экономические районы (Russian Classificaton of Economic Regions (OK 024–95) of January 1, 1997 as amended by the Amendments #1/1998 through #5/2001. Section II. Economic Regions)
- "Country Profile: Russia". Foreign & Commonwealth Office of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- ""News From Russia", Issue No. 4". The Embassy of the Russian Federation in the Republic of India. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Kosachev, Konstantin. "Russian Foreign Policy Vertical". Russia In Global Affairs. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Template:Ru icon Interview of official Ambassador of Russian Foreign Ministry on relations with the EU
- "NATO-Russia relations". NATO. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Chapter 2—Investing In Russian Defense Conversion: Obstacles and Opportunities". Federation of American Scientists. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- ^ "Status of Nuclear Powers and Their Nuclear Capabilities". Federation of American Scientists. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "US drives world military spending to record high". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Russia: Assessment, Adam Baltin Interview, Opinion Poll on State of Armed Forces, FBIS: Informatsionno-Analiticheskoye Agentstvo Marketing i Konsalting, 14 March 2006
- "Rice: Russia's Military Moves 'a Problem'". ABC News. Retrieved 2008-01-06.
- "The Military Balance;previous editions", International Institute for Strategic Studies
- "World Wide Military Expenditures". Global Security. Retrieved 2008-01-06.
- "Big rise in Russian military spending raises fears of new challenge to west". Guardian. Retrieved 2008-01-06.
- "Russia's GDP to grow by 7% in 2007: IMF". Russia Today. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Russia's GDP expected to grow 7.3% in 2007 - Kudrin". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Putin says direct investment in Russia totals 3.3% of GDP". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 2008-01-01.
- "Putin's Economy—Eight Years On". russiaprofile.org. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- ^ "Russia fixed asset investment to reach $370 bln by 2010 - Kudrin". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Russia: How Long Can The Fun Last?". BusinessWeek. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Stabilization fund of the Russian Federation" (PDF). Ministry of Finance. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Stabilization Fund of the Russian Federation". Ministry of Finance. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Mayor says foreign investment in Moscow to double in 2007". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Tavernise, Sabrina (March 23, 2002). "Russia Imposes Flat Tax on Income, and Its Coffers Swell". The New York Times. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Rabushka, Alvin. "The Flat Tax at Work in Russia: Year Three". Hoover Institution. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Global personal taxation comparison survey – market rankings". Mercer (consulting firms). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "International Reserves assets of the Russian Federation in 2007". The Central Bank of the Russian Federation. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Russia's foreign debt down 31.3% in Q3—finance ministry". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Russia: How Long Can The Fun Last?". BusinessWeek. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Lipsky, John. "Statement by John Lipsky, First Deputy Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund". Press Release No. 07/126. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Russian Census of 2002". 4.1. National composition of population. Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2008-01-16.
- "Demographics". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "June 1, 2007: A great number of children in Russia remain highly vulnerable". United Nations Children's Fund. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- List of countries by population density
- "Resident population". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "International Migration". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2008-01-13.
- "Russia cracking down on illegal migrants". International Herald Tribune. January 15, 2007.
- "Demographics". Library of Congress. Retrieved 2008-01-16.
- "Resident population". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- The World Factbook. "Rank Order - Birth rate". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- The World Factbook. "Rank Order - Death rate". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Численность постоянного населения Российской Федерации по муниципальным образованиям на 1 января 2024 года". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 43 para. 1). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Russia tops, South Africa last, in literacy study". Reuters. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Smolentseva, Anna. "Bridging the Gap Between Higher and Secondary Education in Russia". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Education System in Russia". studyrussian.com. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Russia Country Guide". EUbusiness.com. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Background Note: Russia". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 2008-01-02.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 43 para. 3). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- ^ "Higher education structure". State University Higher School of Economics. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Higher Education Institutions". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2008-01-01.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 41). Retrieved 2007-12-27.Russian Constitution,
- Field, M. G. The health and demographic crisis in post-Soviet Russia: a two-phase development in "Russia’s Torn Safety Nets", edited by Field M. G., Twigg J. L. (eds). 2000:11–42: St. Martin’s Press.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - "Highlights on Health in the Russian Federation" (PDF). World Health Organization. November 1999. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Leonard, William R (Apr 2002). "Declining growth status of indigenous Siberian children in post-Soviet Russia". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "European Union". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2008-01-20.
- ^ "Heart disease kills 1.3 million annually in Russia - chief cardiologist". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Corruption Pervades Russia's Health System". CBS News. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- ^ "Third of Russians smoke, but half welcome public smoking ban". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "HIV/AIDS in the Russian Federation". The World Bank. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Russian regional HIV vaccine center seeks $40–50 mln from budget". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "119,000 TB cases in Russia - health official". RIA Novosti. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Country Profile: Russia" (PDF). Library of Congress—Federal Research Division. October 2006. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Birth rate in Russia highest in past 15 years—Medvedev (Part 2)". Interfax. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Birth rate hits 15-year high in Russia". RosBusinessConsulting. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "United Nations Expert Group Meeting On International Migration and Development" (PDF). Population Division; Department of Economic and Social Affairs; United Nations Secretariat. 6–8 July 2005. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Russian Census of 2002". 4.3. Population by nationalities and knowledge of Russian; 4.4. Spreading of knowledge of languages (except Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2008-01-16.
- "Russia". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2008-01-15.
- "The Constitution of the Russian Federation". (Article 68, para. 2). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- ^ "Russian". University of Toronto. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Microsoft® Encarta® Online Encyclopedia 2007. "Russian language". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Russian language course". Russian Language Centre — Official Website, Moscow State University. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Bell, Imogen. "Eastern Europe, Russia and Central Asia". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Zuckerman, Phil (2005). Atheism: Contemporary Rates and Patterns, chapter in The Cambridge Companion to Atheism, ed. by Michael Martin. Cambridge University Press.
- "Religion In Russia". Embassy of the Russian Federation. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "[[:Template:Ru icon]]Сведения о религиозных организациях, зарегистрированных в Российской Федерации По данным Федеральной регистрационной службы". December 2006. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
{{cite web}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - ^ Microsoft® Encarta® Online Encyclopedia 2007. "Russia". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "[[:Template:Ru icon]]Опубликована подробная сравнительная статистика религиозности в России и Польше". religare.ru. 6 June 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
{{cite web}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - "Fact Box: Muslims In Russia". Radio Free Europe. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Page, Jeremy. "The rise of Russian Muslims worries Orthodox Church". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|published=ignored (help) - ^ "Russia's Islamic rebirth adds tension". Financial Times. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Mainville, Michael (November 19, 2006). "Russia has a Muslim dilemma". Page A - 17. San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Nettleton, Steve. "Prayers for Ivolginsky". CNN. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- ^ "Russia". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- Garafola, Lynn. Diaghilev's Ballets Russes. Oxford University Press. p. 576. ISBN 0195057015.
- Cashin, Kathryn Karrh. "Alexander Pushkin's Influence on Russian Ballet - Chapter Five: Pushkin, Soviet Ballet, and Afterward" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "A Tale of Two Operas". Petersburg City. Retrieved 2008-01-11.
- Microsoft® Encarta® Online Encyclopedia 2007. "Russian Literature". Retrieved 2008-01-07.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Kelly, Catriona. Russian Literature: A Very Short Introduction (Very Short Introductions) (Paperback). Oxford Paperbacks. ISBN 0192801449.
- "History of the motion picture: The Soviet Union". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2008-01-07.
- ^ "Russia". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- {{cite web|url=http://filmlinc.com/wrt/onsale/russian08/whitesunofthedesert.html%7Cpublisher=Film Society of Lincoln Center|title=White Sun of the Desert / Beloe solntse pustyni|accessdate=2008-01-18
- ^ Dzieciolowski, Zygmunt. "Kinoeye: Russia's reviving film industry". Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Russian Entertainment & Media Industry worth $27.9 bn by 2011". PricewaterhouseCoopers. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Summer Olympics Through The Years". Information Please. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "The main game in a dragon's lair". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- ^ "Russia". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
- "Winter Olympics Through The Years". Information Please. Retrieved 2007-12-27.
External links
- Interfax.com—News agency based in Moscow
- Russia Profile—In-depth coverage of international, cultural, business and political events in Russia
- RussiaMap.org—Maps of Russia
- Government resources
- Russian News Agency Ria Novosti
- Duma—Official site of the parliamentary lower house Template:Ru icon
- Federative Council—Official site of the parliamentary upper house
- Kremlin—Official presidential site
- Gov.ru—Official governmental portal Template:Ru icon
- Russian Federation Today—Official issue of the Federal Assembly Template:Ru icon
- Ministry of Foreign affairs
- Russian Federal Customs Service
- Central Bank of Russia
| International organisations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Template:Slavic-speaking nations
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: