This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Hollis01 (talk | contribs) at 20:27, 18 February 2008. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 20:27, 18 February 2008 by Hollis01 (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)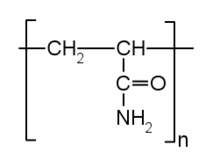
Polyacrylamide is a polymer (-CH2CHCONH2-) formed from acrylamide subunits that can also be readily cross-linked. Acrylamide needs to be handled using good laboratory practices (GLP) to avoid poisonous exposure since it is a neurotoxin. Polyacrylamide is not toxic, but unpolymerized acrylamide can be present in the polymerized acrylamide. Therefore it is recommended to handle it with caution. In the cross-linked form, it is highly water-absorbent, forming a soft gel used in such applications as polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and in manufacturing soft contact lenses. In the straight-chain form, it is also used as a thickener and suspending agent. More recently, it has been used as a subdermal filler for aesthetic facial surgery (see Aquamid).
One of the largest uses for polyacrylamide is flocculate or coagulate solids in a liquid. THis process applies to waste water treatment, and processes like paper making. Most polyacrylimide is supplied in a liquid form. THe liquid is subcatogorized as solution and emulsion polymer.
Emulsion polymers require specialized equipment like a vortiblend polymer feed system to activate invert the emulsion to an active form and create the right ratio of polymer to water. More can be learned about chemfeed and polymer activation at this chemfeed wiki or at www.vortiblend.com.
It has also been advertised as a soil conditioner called Krilium by Monsanto in the 1950s and today "MP", which is stated to be a "unique formulation of PAM (water-soluble polyacrylamide)". The anionic form of polyacrylamide is frequently used as a soil conditioner on farmland and construction sites for erosion control.
The polymer is also used to make Gro-Beast toys, which expand when placed in water, as the Test Tube Aliens.
The non-ionic form of Polyacrylamide has found an important role in the potable water treatment industry. Trivalent metal salts like ferric chloride and aluminum chloride are bridged by the long polymer chains of polyacrylamide. This results in significant enhancement of the flocculation rate. This allows water treatment plants to greately improve the removal of total organic content (TOC) from raw water.
Anionic Polyacrylamide is a super absorbent polymer. It is most often seen in a white crystal form. It is considered environmentally friendly because it has been shown to be non-toxic to plants and animals. Anionic Polyacrylamide is a soil-binding agent whose primary use is in staging areas; rough grading areas and soil stockpiles. It can also be used in borrowed areas after final grade and before final seeding.
Anionic Polyacrylamide when used is mixed with sand 1 to 1 ratio and broadcast directly on the ground.
Anionic Polyacrylamide is most often sold under the brand name of Soiloc-PAM.
Some research indicates that polyacrylamide can degrade under normal environmental conditions, releasing acrylamide, a known nerve toxin.
See also
- Sodium polyacrylate, a similar material
External links
This article about polymer science is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |