This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Landon1980 (talk | contribs) at 04:56, 16 July 2008 (Undid revision 225954745 by 4.226.125.144 (talk)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 04:56, 16 July 2008 by Landon1980 (talk | contribs) (Undid revision 225954745 by 4.226.125.144 (talk))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) "KKK" redirects here. For other uses, see KKK (disambiguation). | |
| In Existence | |
|---|---|
| 1st Klan | 1865-1870s |
| 2nd Klan | 1915-1944 |
| 3rd Klan | 1945-Present |
| Members | |
| 1st Klan | 550,000 |
| 2nd Klan | 4,000,000 (1924 Peak) |
| 3rd Klan | 8,000 |
| Properties | |
| Origin | United States of America |
| Political ideology | White supremacy |
| Political position | Far right |
| The 3rd Klan is decentralized, with approx. 179 chapters. | |
Ku Klux Klan (KKK) is the name of several past and present secret organizations in the United States, generally in the southern states, that are best known for advocating white supremacy and acting as vigilantes while hidden behind conic masks and white robes. The first KKK arose in the turmoil after the Civil War. It utilized terrorism, violence, and lynching to intimidate and oppress African Americans, Jews, and other racial and religious minorities.
The first Klan was founded in 1866 by veterans of the Confederate Army. Its purpose was to restore white supremacy in the aftermath of the American Civil War. The Klan resisted Reconstruction by intimidating "carpetbaggers", "scalawags" and freedmen. The KKK quickly adopted violent methods. The increase in murders finally resulted in a backlash among Southern elites who viewed the Klan's excesses as an excuse for federal troops to continue occupation. The organization declined from 1868 to 1870 and was destroyed by President Ulysses S. Grant's prosecution and enforcement under the Civil Rights Act of 1871.
In 1915, the second Klan was founded. It grew rapidly in another period of postwar social tensions. After WWI, many Americans coped with booming growth rates in major cities, where numerous waves of immigrants from southern and eastern Europe and the Great Migration of Southern blacks and whites were being absorbed. After WWI, labor tensions rose as veterans tried to reenter the work force. In reaction to these new groups of immigrants and migrants, the second KKK preached racism, anti-Catholicism, anti-Communism, nativism, and anti-Semitism. Some local groups took part in lynchings, attacks on private houses and public property, and other violent activities. Members used ceremonial cross burning to intimidate victims and demonstrate its power. Murders and violence by the Klan were most numerous in the South, which had a tradition of lawlessness.
The film The Birth of a Nation and the sensationalized newspaper coverage of the trial, conviction and lynching of Leo Frank of Georgia sparked the Klan's revival. The second Klan was a formal fraternal organization, with a national and state structure. At its peak in the mid-1920s, the organization included about 15% of the nation's eligible population, approximately 4–5 million men. The Klan's popularity fell rapidly during the Great Depression, and membership fell further during World War II.
The name Ku Klux Klan has since been used by many independent groups opposing the Civil Rights Movement and desegregation, especially in the 1950s and 1960s. During this period, they often acted with impunity by alliances with Southern police departments, as during the reign of Bull Connor in Birmingham, Alabama; or governor's offices, as with George Wallace of Alabama. Several members of KKK-affiliated groups were convicted of manslaughter and murder in the deaths of civil rights workers and children in the bombing of the 16th Street Baptist Church in Alabama, the assassination of NAACP organizer Medgar Evers, and the murders of three civil rights workers in Mississippi. Today, researchers estimate there may be more than 150 Klan chapters with 5,000-8,000 members nationwide. The U.S. government classifies them as hate groups, with operations in separated small local units.
First Klan 1865-1874
Creation
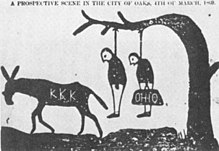


As W.E.B. DuBois noted, "It is always difficult to stop war, and doubly difficult to stop civil war... In the case of civil war, where the contending parties must rest face to face after peace, there can be no quick and perfect peace." As reported by Mississippi Governor Sharkey in 1866, disorder, lack of control and lawlessness were widespread; in some states armed bands of Confederate soldiers roamed at will. Southerners seemed to take out on blacks all their wrath at the Federal government. They casually attacked and killed blacks whose bodies were left on the roads.
The original Ku Klux Klan was created in the aftermath of the American Civil War by six educated, middle-class Confederate veterans on December 24, 1865. from Pulaski, Tennessee. They made up the name by combining the Greek "kyklos" (κυκλος,circle) with "clan" It was one among a number of secret, oath-bound organizations, including the Southern Cross in New Orleans (1865), and the Knights of the White Camellia.
In an 1867 meeting in Nashville, Tennessee, Klan members gathered to try to create a hierarchical organization with local chapters reporting eventually up to national headquarters. As most of them were veterans, they were used to such organization. Former Confederate Brigadier General George Gordon put the proposals together in what was called the "Prescript." The Prescript suggested elements of white supremacy belief. For instance, an applicant should be asked if he was in favor of "a white man's government", "the reenfranchisement and emancipation of the white men of the South, and the restitution of the Southern people to all their rights." Despite Gordon's work, local Klan units never accepted the Prescript and continued to operate autonomously. There were never hierarchical levels or state headquarters.
Gordon supposedly told former slave trader and Confederate General Nathan Bedford Forrest in Memphis, Tennessee, about the Klan. Forrest allegedly responded, "That's a good thing; that's a damn good thing. We can use that to keep the niggers in their place." A few weeks later, Forrest was selected as Imperial Wizard, the Klan's national leader, though he always denied leadership.
In effect, the Klan defended the interest of the planter class and Democratic Party by working to curb the education, economic advancement, voting rights, and right to keep and bear arms of blacks. The Ku Klux Klan soon spread into nearly every southern state, launching a "reign of terror" against Republican leaders both black and white. Those political leaders assassinated during the campaign included Arkansas Congressman James M. Hinds, three members of the South Carolina legislature, and several men who served in constitutional conventions."
In an 1868 newspaper interview, Forrest stated the Klan's primary opposition was to the Loyal Leagues, Republican state governments, people like Tennessee governor Brownlow and other carpetbaggers and scalawags. He claimed that many southerners believed blacks were voting for the Republican Party because they were being hoodwinked by the Loyal Leagues. One Alabama newspaper editor declared "The League is nothing more than a nigger Ku Klux Klan." At the local level, however, old feuds and grudges were the cause of numerous attacks, and Klan members worked for their own dominance in the disrupted postwar society.
As historian Elaine Frantz Parsons discovered,
Lifting the Klan mask revealed a chaotic multitude of antiblack vigilante groups, disgruntled poor white farmers, wartime guerrilla bands, displaced Democratic politicians, illegal whiskey distillers, coercive moral reformers, sadists, rapists, white workmen fearful of black competition, employers trying to enforce labor discipline, common thieves, neighbors with decades-old grudges, and even a few freedmen and white Republicans who allied with Democratic whites or had criminal agendas of their own. Indeed, all they had in common, besides being overwhelmingly white, southern, and Democratic, was that they called themselves, or were called, Klansmen.
As historian Eric Foner observed,
In effect, the Klan was a military force serving the interests of the Democratic party, the planter class, and all those who desired restoration of white supremacy. Its purposes were political, but political in the broadest sense, for it sought to affect power relations, both public and private, throughout Southern society. It aimed to reverse the interlocking changes sweeping over the South during Reconstruction: to destroy the Republican party's infrastructure, undermine the Reconstruction state, reestablish control of the black labor force, and restore racial subordination in every aspect of Southern life.
Activities
Klan members adopted masks and robes that hid their identities and added to the drama of their night rides, their chosen time for attacks. Many of them operated in small towns and rural areas where people otherwise knew each other's faces, and sometimes still recognized the attackers. "The kind of thing that men are afraid or ashamed to do openly, and by day, they accomplish secretly, masked, and at night." With this method both the high and the low could be attacked. The Ku Klux Klan night riders "sometimes claimed to be ghosts of Confederate soldiers so, as they claimed, to frighten superstitious blacks. Few freedmen took such nonsense seriously."
The Klan raided black members of the Loyal Leagues and intimidated southern Republicans and Freedmen's Bureau workers. When they killed black political leaders, they also took heads of families, leaders in churches and community groups, because people had many roles. Agents of the Freedmen's Bureau reported weekly assaults and murders of blacks. "Armed guerilla warfare killed thousands of Negroes; political riots were staged; their causes or occasions were always obscure, their results always certain: ten to one hundred times as many Negroes were killed as whites." Masked men shot into houses and burned them, sometimes with the occupants still inside. They drove successful black farmers off their land. General Canby reported that in North and South Carolina, in 18 months ending in June 1867, there were 197 murders and 548 cases of aggravated assault.
Klan violence worked to suppress black voting. As examples, over 2,000 persons were killed, wounded and otherwise injured in Louisiana within a few weeks prior to the Presidential election of November 1868. Although St. Landry Parish had a registered Republican majority of 1,071, after the murders, no Republicans voted in the fall elections. White Democrats cast the full vote of the parish for Grant's opponent. The KKK killed and wounded more than 200 black Republicans, hunting and chasing them through the woods. Thirteen captives were taken from jail and shot; a half-buried pile of 25 bodies was found in the woods. The KKK made people vote Democratic and gave them certificates of the fact.
In the April 1868 Georgia gubernatorial election, Columbia County cast 1,222 votes for Republican Rufus Bullock. By the November presidential election, however, Klan intimidation led to suppression of the Republican vote and only one person voted for Ulysses S. Grant.
Klansmen killed more than 150 African Americans in a county in Florida, and hundreds more in other counties. Freedmen's Bureau records provided a detailed recounting of beatings and murders of freedmen and their white allies by Klansmen.
Milder encounters also occurred. In Mississippi, according to the Congressional inquiry
One of these teachers (Miss Allen of Illinois), whose school was at Cotton Gin Port in Monroe County, was visited ... between one and two o'clock in the morning on March 1871, by about fifty men mounted and disguised. Each man wore a long white robe and his face was covered by a loose mask with scarlet stripes. She was ordered to get up and dress which she did at once and then admitted to her room the captain and lieutenant who in addition to the usual disguise had long horns on their heads and a sort of device in front. The lieutenant had a pistol in his hand and he and the captain sat down while eight or ten men stood inside the door and the porch was full. They treated her "gentlemanly and quietly" but complained of the heavy school-tax, said she must stop teaching and go away and warned her that they never gave a second notice. She heeded the warning and left the county.

By 1868, two years after the Klan's creation, its activity was beginning to decrease. Members were hiding behind Klan masks and robes as a way to avoid prosecution for free-lance violence. Many influential southern Democrats feared that Klan lawlessness provided an excuse for the federal government to retain its power over the South, and they began to turn against it. There were outlandish claims made, such as Georgian B.H. Hill stating "that some of these outrages were actually perpetrated by the political friends of the parties slain."
Decline and suppression
Although Forrest boasted the Klan was a nationwide organization of 550,000 men and he could muster 40,000 Klansmen with five days' notice, as a secret or "invisible" group, it had no membership rosters, no chapters, no local officers, making it difficult for observers to judge its membership. It had created a sensation by the dramatic nature of its masked forays and many murders.
One Klan official complained his, "so-called 'Chief'-ship was purely nominal, I having not the least authority over the reckless young country boys who were most active in 'night-riding,' whipping, etc., all of which was outside of the intent and constitution of the Klan..."
A federal grand jury in 1869 determined the Klan was a "terrorist organization." It issued hundreds of indictments for crimes of violence and terrorism. Klan members were prosecuted, and many fled jurisdiction, particularly in South Carolina. Many people not formally inducted into the Klan had used the Klan's uniform for anonymity, to hide their identities when carrying out acts of violence. Forrest ordered the Klan to disband in 1869, stating it was "being perverted from its original honorable and patriotic purposes, becoming injurious instead of subservient to the public peace." Historian Stanley Horn writes "generally speaking, the Klan's end was more in the form of spotty, slow, and gradual disintegration than a formal and decisive disbandment." A reporter in Georgia wrote in January 1870, "A true statement of the case is not that the Ku Klux are an organized band of licensed criminals, but that men who commit crimes call themselves Ku Klux."

While people used the Klan as a mask for nonpolitical crimes, state and local governments seldom acted against them. African Americans were kept off juries. In lynching cases, all-white juries almost never indicted Ku Klux Klan members. When there was a rare indictment, juries were unlikely to vote for conviction. In part, jury members feared reprisals from local Klansmen.
Others may have agreed with lynching as a way of keeping dominance over black men. In many states, officials were reluctant to use black militia against the Klan from fear that race tensions would be raised. When Republican Governor of North Carolina William Woods Holden called out the militia against the Klan in 1870, it added to his unpopularity. Combined with violence and fraud at the polls, in the election, the Republicans lost their majority in the state legislature. Disaffection with Holden's actions led to white Democratic legislators' impeaching Holden and removing him from office, but their reasons were numerous.
Resistance
Union Army veterans in mountainous Blount County, Alabama, organized 'the anti-Ku Klux.' They put an end to violence by threatening Klansmen with reprisals unless they stopped whipping Unionists and burning black churches and schools. Armed blacks formed their own defense in Bennettsville, South Carolina and patrolled the streets to protect their homes.
National sentiment gathered to crack down on the Klan, even though some Democrats at the national level questioned whether the Klan existed or was a creation of nervous Southern Republican governors. Many southern states began to pass anti-Klan legislation.
In January 1871, Pennsylvania Republican Senator John Scott convened a Congressional committee which took testimony from 52 witnesses about Klan atrocities. They accumulated 12 volumes of horrifying testimony. In February, former Union General and Congressman Benjamin Franklin Butler of Massachusetts introduced the Ku Klux Klan Act. This added to the enmity southern white Democrats bore toward him. While the bill was being considered, further violence in the South swung support for its passage. The Governor of South Carolina appealed for federal troops to assist his keeping control. A riot and massacre in a Meridian, Mississippi, courthouse were reported, from which a black state representative escaped only by taking to the woods.

In 1871, President Ulysses S. Grant signed Butler's legislation. The Ku Klux Klan Act was used by the Federal government together with the 1870 Force Act to enforce the civil rights provisions for individuals under the constitution. Under the Klan Act, Federal troops were used for enforcement, and Klansmen were prosecuted in Federal court. More African Americans served on juries in Federal court than were selected for local or state juries, so had a chance to participate in the process. In the crackdown, hundreds of Klan members were fined or imprisoned. In South Carolina, habeas corpus was suspended in nine counties. The Klan was destroyed in South Carolina and decimated throughout the rest of the South, where it had already been in decline. Attorney General Amos Tappan Ackerman led the prosecutions. "By 1872, the Klan as an organization was broken." In some areas, other local paramilitary organizations such as the White League, Red Shirts, saber clubs, and rifle clubs continued intimidation and murder of black voters. Although destroyed, the Klan achieved many of its goals, such as suppressing suffrage for Southern blacks and driving a wedge between poor whites and blacks.
Ku Klux Klan Act of 1871 – via Wikisource.
Despite suppression of the Klan, violence continued against African Americans as whites struggled for power. On Easter Sunday 1873, black citizens fought a mixed political and racial battle against white militia in Colfax, Louisiana. The ostensible cause was an election contested at both the state and local levels. Each man elected sheriff claimed the local office. When black Republicans gathered at the courthouse, white militia collected to force them to leave. Estimates of African Americans killed overnight and into the next day were 105 to 280. Some bodies were hidden in the woods or thrown in the river; others buried before state and Federal troops arrived. African-American legislator John G. Lewis remarked, "They attempted (armed self-defense) in Colfax. The result was that on Easter Sunday of 1873, when the sun went down that night, it went down on the corpses of two hundred and eighty negroes." The Colfax Massacre had the highest fatalities of any incident of racial violence during Reconstruction.
Shortly after, in United States v. Cruikshank (1875), the Supreme Court ruled that the few convictions achieved after the Colfax Massacre were faulty. It ruled that the Force Act of 1870 did not give the Federal government power to regulate private actions, but only those by state governments. The result was that as the century went on, African Americans were at the mercy of hostile state governments to intervene against private violence and paramilitary groups.
In 1882, long after the Klan was destroyed, the Supreme Court ruled in United States v. Harris that the Klan Act was partially unconstitutional. It ruled that Congress's power under the Fourteenth Amendment did not extend to regulate against private conspiracies.
As 20th century Supreme Court rulings extended Federal enforcement of citizens' civil rights, the Force Act and the Klan Act were used by 20th c. Federal prosecutors as the basis for investigation and indictments in the 1964 murders of Chaney, Goodman, and Schwerner; and the 1965 murder of Viola Liuzzo. They were also the basis of prosecution in 1991 in Bray v. Alexandria Women's Health Clinic.
Disfranchisement and Great Migration
Main article: Disfranchisement after the Civil WarThe nadir of American race relations is often placed from the end of reconstruction to the 1910s, especially in the South. Once white Democrats regained political power in state legislatures in the 1870s, they passed bills directed at restricting voter registration by blacks and poor whites. Continued low cotton prices, agricultural depression and labor shortages in the South contributed to social tensions. According to Tuskegee Institute, the 1890s was also the peak decade for lynchings, with most of them directed against African Americans in the South. The lynchings were a byproduct of political tensions as white Democrats tried to strip blacks from voter rolls and suppress voting. Some of the violence was directed at trying to break up interracial coalitions that came to power in state legislatures in 1894, with alliances of Populist and Republican parties. In 1896 the Democrats used fraud, violence and intimidation to suppress voting by poor classes, and regained power.
From 1890 to 1908, ten of eleven southern states ratified new constitutions or amendments that completed disfranchisement of most African Americans and many poor whites. The constitutions had provisions making voter registration more complicated: such as poll taxes, residency requirements, recordkeeping, and literacy tests, which were often subjectively applied. In addition, in voting sometimes multiple ballot boxes were used. The result was that blacks and poor whites in most southern states were deprived of suffrage, representation at any level of government, local elected offices, and the right to serve on juries (usually restricted to voters). In most of the South, sweeping disfranchisement and white one-party government lasted until African Americans' leadership and activism in the Civil Rights Movement gained passage of Federal civil rights legislation in 1964 and 1965.
Beginning in 1910 and going through 1940, tens of thousands of African Americans decided to leave the South and its violence and segregation, in a movement known as the Great Migration. They went to northern and midwestern cities for jobs, better education for their children, a chance to vote, and the hopes of living with less violence. Northern industry recruited black workers because of a shortage of labor for expanding industries: for instance, the Pennsylvania Railroad hired 12,000 men, all but 2,000 of them from Florida and Georgia.

The second Klan 1915-1944
Creation
The second Klan rose in response to urbanization and industrialization, massive immigration from eastern and southern Europe, the Great Migration of African Americans to the North, and the migration of African Americans and whites from rural areas to Southern cities. The Klan grew most in cities which had high growth rates between 1910 and 1930, such as Detroit, Memphis, Dayton, Atlanta, Dallas, and Houston.
Its growth was also affected by mobilization for WWI and postwar tensions, especially in the cities where strangers came up against each other more often. Southern whites resented the arming of black soldiers. Black veterans did not want to go back to second class status.
This Klan modeled itself after other fraternal organizations created in the early decades of the 20th century. Organizers signed up hundreds of new members, who paid initiation fees and bought KKK costumes. The organizer kept half the money and sent the rest to state or national officials. When the organizer was done with an area, he organized a huge rally, often with burning crosses and perhaps presenting a Bible to a local Protestant minister. He then left town with the money. The local units operated like many fraternal organizations and occasionally brought in speakers. State and national officials had little or no control over the locals and rarely attempted to forge political activist groups. Stanley Horn, a Southern historian sympathetic to the first Klan, was careful in an oral interview to distinguish it from the later "spurious Ku Klux organization which was in ill-repute — and, of course, had no connection whatsoever with the Klan of Reconstruction days."
The accumulating social tensions of rapid change were sparked by events in 1915:
- The film The Birth of a Nation was released, mythologizing and glorifying the first Klan.
- Leo Frank, a Jewish man accused of the rape and murder of a young white girl named Mary Phagan, was tried, convicted and lynched near Atlanta against a backdrop of media frenzy.
- The second Ku Klux Klan was founded in Atlanta with a new anti-immigrant, anti-Catholic, and anti-Semitic agenda. The bulk of the founders were from an Atlanta-area organization calling itself the Knights of Mary Phagan that had organized around the Frank trial. The new organization emulated the fictionalized version of the Klan presented in The Birth of a Nation.

Director D. W. Griffith's The Birth of a Nation glorified the original Klan. His film was based on the book and play The Clansman and the book The Leopard's Spots, both by Thomas Dixon. Dixon said his purpose was "to revolutionize northern sentiment by a presentation of history that would transform every man in my audience into a good Democrat!" The film created a nationwide Klan craze. At the official premier in Atlanta, members of the Klan rode up and down the street in front of the theater.
Much of the modern Klan's iconography, including the standardized white costume and the lighted cross, are derived from the film. Its imagery was based on Dixon's romanticized concept of old Scotland, as portrayed in the novels and poetry of Sir Walter Scott. The film's influence and popularity were enhanced by a widely reported endorsement by historian and U.S. President Woodrow Wilson.

The Birth of a Nation included extensive quotations from Woodrow Wilson's History of the American People, as if to give it a stronger basis. On seeing the film in a special White House screening, Wilson allegedly said, "It is like writing history with lightning, and my only regret is that it is all so terribly true." Given Wilson's views on race and the Klan, his statement was taken as supportive of the film. In later correspondence with Griffith, Wilson confirmed his enthusiasm. Wilson's remarks immediately became controversial. Wilson tried to remain aloof, but finally, on April 30, he issued a non-denial denial. Historian Arthur Link quotes Wilson's aide, Joseph Tumulty, who said, "the President was entirely unaware of the nature of the play before it was presented and at no time has expressed his approbation of it."

Another event that influenced the Klan was sensational coverage of the trial, conviction and lynching of a Jewish factory manager from Atlanta named Leo Frank. In lurid newspaper accounts, Frank was accused of the rape and murder of Mary Phagan, a girl employed at his factory. After a trial in Georgia in which a mob daily surrounded the courtroom, Frank was convicted. Because of the armed mob, the judge asked Frank and his counsel to stay away when the verdict was announced. Frank's appeals failed. Supreme Court Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes dissented from other justices and condemned the mob's intimidation of the jury as the court's failing to provide due process to the defendant. After the governor commuted Frank's sentence to life imprisonment, a mob calling itself the Knights of Mary Phagan kidnapped Frank from prison and lynched him.
The Frank trial was used skillfully by Georgia politician and publisher Thomas E. Watson, the editor for The Jeffersonian magazine. He was a leader in recreating the Klan and was later elected to the U.S. Senate. The new Klan was inaugurated in 1915 at a meeting led by William J. Simmons on top of Stone Mountain. A few aging members of the original Klan attended, along with members of the self-named Knights of Mary Phagan.
Simmons claimed to have been inspired by the original Klan's "Prescripts," written in 1867 by Confederate veteran George Gordon to try to create a national organization. These were never adopted by the Klan, however. The Prescript stated the Klan's purposes in idealistic terms, hiding the fact that they committed vigilante violence and murder from behind masks.
"The Klan's resurgence in the 1920s partially stemmed from the extreme militant wing of the temperance movement. In Arkansas, as elsewhere, the newly formed Ku Klux Klan marked bootleggers as one of the groups that needed to be purged from a morally upright community. In 1922, 200 Klansmen torched saloons that had sprung up in Union County in the wake of the oil discovery boom. The national Klan office ended up in Dallas, Texas, but Little Rock was the home of the Women of the Ku Klux Klan. The first head of this female auxiliary was a former president of the Arkansas WCTU."
In 1921, the Klan arrived in Oregon from central California and established the state's first klavern in Medford. In a state with one of the country's highest percentages of white residents, the Klan attracted up to 14,000 members and established 58 klaverns by the end of 1922. Given small population of non-white minorities outside Portland, the Oregon Klan directed attention almost exclusively against Catholics, who numbered about 8% of the population. In 1922, the Masonic Grand Lodge of Oregon sponsored a bill to require all school-age children to attend public schools. With support of the Klan and Democrat Governor Walter M. Pierce, endorsed by the Klan, the Compulsory Education Law was passed with a majority of votes. Its primary purpose was to shut down Catholic schools in Oregon, but it also affected other private and military schools. It was challenged in court and struck down by the United States Supreme Court Pierce v. Society of Sisters (1925) before it went into effect.
One historian contends that the KKK’s "support for Prohibition represented the single most important bond between Klansmen throughout the nation." Membership in the Klan and other prohibition groups overlapped, and they often coordinated activities. For example, Edward Young Clarke, a top leader of the Klan, raised funds for both the Klan and the Anti-Saloon League. A man with his own demons, Clarke was indicted in 1923 for violations of the Mann Act.
Members

A significant characteristic of the second Klan was that it was an organization based in urban areas, reflecting the major shifts of population to cities in both the North and the South. In Michigan, for instance, 40,000 members lived in Detroit, where they made up more than half of the state's membership. Most Klansmen were lower to middle-class whites who were trying to protect their jobs and housing from the waves of newcomers to the industrial cities: immigrants from southern and eastern Europe, who tended to be Catholic and Jewish in numbers higher than earlier groups of immigrants; and black and white migrants from the South. As new populations poured into cities, rapidly changing neighborhoods created social tensions. Because of the rapid pace of population growth in industrializing cities such as Detroit and Chicago, the Klan grew rapidly in the U.S. Midwest. The Klan also grew in booming Southern cities such as Dallas and Houston.
For some states, historians have obtained membership rosters of some local units and matched the names against city directory and local records to create statistical profiles of the membership. Big city newspapers were often hostile and ridiculed Klansmen as ignorant farmers. Detailed analysis from Indiana showed the rural stereotype was false for that state:
Indiana's Klansmen represented a wide cross section of society: they were not disproportionately urban or rural, nor were they significantly more or less likely than other members of society to be from the working class, middle class, or professional ranks. Klansmen were Protestants, of course, but they cannot be described exclusively or even predominantly as fundamentalists. In reality, their religious affiliations mirrored the whole of white Protestant society, including those who did not belong to any church.
The Klan attracted people but did not hold most. Membership turned over rapidly as people found it was not the group they wanted. Millions joined, and at its peak in the 1920s, the organization included about 15% of the nation's eligible population. Lessening of social tensions contributed to decline.
Activities

In reaction to social changes, the Klan adopted anti-Jewish, anti-Catholic, anti-Communist and anti-immigrant slants. The social unrest of the postwar period included labor strikes over low wages and working conditions in many industrial cities, often led by immigrants, who also organized unions. Klan members worried about labor organizers and socialist leanings of some of the immigrants, which added to the tensions. They also resented upwardly mobile ethnic Catholics. At the same time, in cities Klan members were themselves working in industrial environments and often struggled with working conditions.
Klan groups lynched and murdered Black soldiers returning from World War I while they were still in military uniforms. The Klan warned Blacks that they must respect the rights of the white race "in whose country they are permitted to reside." The number of lynchings escalated, and from 1918 to 1927, 416 African Americans were killed, mostly in the South.
In Florida, when two black men attempted to vote in November 1920 in Ocoee, Orange County, the Klan attacked the black community. In the ensuing violence, six black residents and two whites were killed, and twenty five black homes, two churches, and a fraternal lodge were destroyed.
Although Klan members were concentrated in the South, Midwest and west, there were some members in New England, too. Klan members torched an African American school in Scituate, Rhode Island.
In the 1920s and 1930s, a violent and zealous faction of the Klan called the Black Legion was active in the Midwestern U.S.. The Legion wore black uniforms and targeted and assassinated communists and socialists.
In southern cities such as Birmingham, Alabama, Klan members kept control of access to the better-paying industrial jobs but opposed unions. During the 1930s and 1940s, Klan leaders urged members to disrupt the Congress of Industrial Organizations(CIO), which advocated industrial unions and was open to African-American members. With access to dynamite and skills from their jobs in mining and steel, in the late 1940s some Klan members in Birmingham began using bombings to intimidate upwardly mobile blacks who moved into middle-class neighborhoods. "By mid-1949, there were so many charred house carcasses that the area was informally named Dynamite Hill." Independent Klan groups remained active in Birmingham and were deeply engaged in violent opposition to the Civil Rights Movement.
Political influence

The Klan had major political influence in several states and was influential mostly in the center of the country. The Klan spread from the South into the Midwest and Northern states, and into Canada where there was a large movement against Catholic immigrants. At its peak, Klan membership exceeded four million and comprised 20% of the adult white male population in many broad geographic regions, with 40% in some areas. Most of the membership resided in Midwestern states.
The KKK controlled Southern legislatures and the governments of Tennessee, Indiana, Oklahoma, and Oregon. In Indiana, Republican Klansman Edward Jackson was elected governor in 1924.
In another well-known example from the same year, the Klan decided to make Anaheim, California, into a model Klan city. It secretly took over the City Council, but the city conducted a special recall election and Klan members were voted out.
Klan delegates played a significant role at the path-setting 1924 Democratic National Convention in New York City, often called the "Klanbake Convention." The convention initially pitted Klan-backed candidate William Gibbs McAdoo against Catholic New York Governor Al Smith. After days of stalemates and rioting, both candidates withdrew in favor of a compromise. Klan delegates defeated a Democratic Party platform plank that would have condemned their organization. On July 4 1924, thousands of Klansmen celebrated victory on a nearby field in New Jersey by burning effigies of Smith and by burning crosses.
In some states, such as Alabama, the KKK worked for political and social reform. The state's Klansmen were among the foremost advocates of better public schools, effective prohibition enforcement, expanded road construction, and other "progressive" political measures. In many ways these reforms benefited lower class white people. By 1925, the Klan was a political force in the state, as leaders like J. Thomas Heflin, David Bibb Graves, and Hugo Black manipulated the KKK membership against the power of Black Belt planters who had long dominated the state.
Black was elected senator in 1926 and later became a Supreme Court Justice. In 1926, with Klan support, a former Klan chapter head named Bibb Graves won the Alabama governor's office. He pushed for increased education funding, better public health, new highway construction, and pro-labor legislation. Because the Alabama state legislature refused to redistrict until 1972, however, even the Klan was unable to break the planters' and rural areas' hold on power.
Resistance and Decline
Many groups and leaders, including prominent Protestant ministers such as Reinhold Niebuhr in Detroit, spoke up against the Klan. To blunt attacks against Jewish Americans and conduct public education, the Jewish Anti-Defamation League was formed after the lynching of Leo Frank. When one civic group began to publish Klan membership lists, the number of members quickly declined. The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People carried on public education about Klan activities and lobbied against Klan abuses in Congress. After its peak in 1925, Klan membership began to decline rapidly in most areas of the Midwest.
In Alabama, KKK vigilantes, thinking they had governmental protection, launched a wave of physical terror in 1927, targeting both blacks and whites for violating racial norms and perceived moral lapses. The state's conservative elite counterattacked. Grover C. Hall, Sr., editor of the Montgomery Advertiser, began a series of editorials and articles attacking the Klan for their "racial and religious intolerance." Hall won a Pulitzer Prize for his crusade. Other newspapers kept up a steady, loud attack on the Klan as violent and "un-American." Sheriffs cracked down. In the 1928 presidential election, the state voted for the Democratic candidate Al Smith, although he was Catholic. Klan membership in Alabama dropped to less than six thousand by 1930. Small independent units continued to be active in Birmingham, where in the late 1940s, members started a program of bombings against the homes of upwardly mobile African Americans. KKK activism increased against the civil rights movement in the 1950s and 1960s. (see below.)
When the Grand Dragon of Indiana and fourteen states, David Stephenson, was convicted of the rape and murder of Madge Oberholtzer, the Klan declined further. Stephenson was convicted in a sensational trial. According to historian Leonard Moore, a leadership failure caused the organization's collapse:
Stephenson and the other salesmen and office seekers who maneuvered for control of Indiana's Invisible Empire lacked both the ability and the desire to use the political system to carry out the Klan's stated goals. They were disinterested in, or perhaps even unaware of, grass roots concerns within the movement. For them, the Klan had been nothing more than a means for gaining wealth and power. These marginal men had risen to the top of the hooded order because, until it became a political force, the Klan had never required strong, dedicated leadership. More established and experienced politicians who endorsed the Klan, or who pursued some of the interests of their Klan constituents, also accomplished little. Factionalism created one barrier, but many politicians had supported the Klan simply out of expedience. When charges of crime and corruption began to taint the movement, those concerned about their political futures had even less reason to work on the Klan's behalf.
Imperial Wizard Hiram Wesley Evans sold the organization in 1939 to James Colescott, an Indiana veterinarian, and Samuel Green, an Atlanta obstetrician, but they were unable to staunch the exodus of members. The Klan's image was further damaged by Colescott's association with Nazi-sympathizer organizations, the Klan's involvement in the 1943 Detroit Race Riot, and efforts to disrupt the American war effort during World War II. In 1944, the IRS filed a lien for $685,000 in back taxes against the Klan, and Colescott was forced to dissolve the organization in 1944.

After WWII, folklorist and author Stetson Kennedy infiltrated the Klan and provided information to media and law enforcement agencies. He also provided secret code words to the writers of the Superman radio program, resulting in episodes in which Superman took on the KKK. Kennedy's intention to strip away the Klan's mystique and trivialize the Klan's rituals and code words may have contributed to the decline in Klan recruiting and membership. In the 1950s, Kennedy wrote a bestselling book about his experiences, which further damaged the Klan.
The following table shows the change in the Klan's estimated membership over time. (The years given in the table represent approximate time periods.)
| year | membership |
|---|---|
| 1920 | 4,000,000 |
| 1924 | 6,000,000 |
| 1930 | 30,000 |
| 1980 | 5,000 |
| 2006 | 3,000 |
Later Klans, 1950 through 1960s
The name "Ku Klux Klan" began to be used by several independent groups. Beginning in the 1950s, individual Klan groups began to resist the Civil Rights Movement by bombing houses in transitional neighborhoods and the houses of activists, as well as by physical violence, intimidation and assassination. In Birmingham, Alabama, during the tenure of Bull Connor, Klan groups were closely allied with police and operated with impunity. There were so many bombings of homes by Klan groups that the city's nickname was "Bombingham". In states such as Alabama and Mississippi, Klan members had alliances with governors' administrations.
Many murders went unreported and unprosecuted. Continuing disfranchisement of blacks meant that most could not serve on juries, which were all white. According to a report from the Southern Regional Council in Atlanta, the homes of forty black Southern families were bombed during 1951 and 1952. Some were social activists whose work exposed them to danger, but most were either people who refused to bow to racist convention or were innocent bystanders, unsuspecting victims of random terrorism."
Among the more notorious murders by Klan members:
- The 1951 Christmas Eve bombing of the home of NAACP activists Harry and Harriette Moore in Mims, Florida, resulting in both their deaths.
- The 1957 murder of Willie Edwards, Jr. Klansmen forced Edwards to jump to his death from a bridge into the Alabama River.
- The 1963 assassination of NAACP organizer Medgar Evers in Mississippi. In 1994, former Ku Klux Klansman Byron De La Beckwith was convicted.
- The 1963 bombing of the 16th Street Baptist Church in Birmingham, Alabama, which killed four black girls. The perpetrators were Klan members Robert Chambliss, convicted in 1977, Thomas Blanton and Bobby Frank Cherry, convicted in 2001 and 2002. The fourth suspect, Herman Cash, died before he was indicted.
- The 1964 murders of three civil rights workers Chaney, Goodman, and Schwerner in Mississippi. In June 2005, Klan member Edgar Ray Killen was convicted of manslaughter.
- The 1964 murder of two black teenagers, Henry Hezekiah Dee and Charles Eddie Moore in Mississippi. In August 2007, based on the confession of Klansman Charles Marcus Edwards, James Ford Seale, a reputed Ku Klux Klansman, was convicted. Seale was sentenced to serve three life sentences. Seale was a former Mississippi policeman and sheriff's deputy.

- The 1965 Alabama murder of Viola Liuzzo. She was a Southern-raised Detroit mother of five in the state to attend a civil rights march. At the time of her murder Liuzzo was transporting Civil Rights Marchers.
- The 1966 firebombing death of NAACP leader Vernon Dahmer Sr., 58, in Mississippi. In 1998 former Ku Klux Klan wizard Sam Bowers was convicted of his murder and sentenced to life. Two other Klan members were indicted with Bowers, but one died before trial, and the other's indictment was dismissed.
There was also resistance to Klan violence. In a 1958 North Carolina incident, the Klan burned crosses at the homes of two Lumbee Native Americans who had associated with white people and threatened to return with more men. When they held a nighttime rally nearby, they found themselves surrounded by hundreds of armed Lumbees. Gunfire was exchanged, and the Klan was routed at what became known as the Battle of Hayes Pond.
When Freedom Riders arrived in Birmingham, Alabama, the police commissioner Bull Connor gave Klan members fifteen minutes to attack the riders before sending in the police. When local and state authorities failed to protect them, the federal government established more effective intervention.
While the FBI had paid informants in the Klan, for instance in Birmingham, Alabama in the early 1960s, their relations with local law enforcement and the Klan were often ambiguous. The head of the FBI J. Edgar Hoover, appeared more concerned about Communist links to civil rights activists than about controlling Klan excesses. In 1964, the FBI's COINTELPRO program began attempts to infiltrate and disrupt civil rights groups.
1970s to present
Once African Americans secured Federal legislation to protect civil and voting rights, the Klans shifted focus to opposing court-ordered busing to desegregate schools, affirmative action, and more open immigration. For instance, in 1971, Klansmen used bombs to destroy ten school buses in Pontiac, Michigan. Klansman David Duke was active in South Boston during the school busing crisis of 1974. Duke was leader of the Knights of the Ku Klux Klan from 1974 until he resigned from the Klan in 1978.
Jerry Thompson, a newspaper reporter who infiltrated the Klan in 1979, reported the FBI's COINTELPRO efforts were highly successful. Rival Klan factions accused each other's leaders of being FBI informants. Bill Wilkinson of the Invisible Empire, Knights of the Ku Klux Klan, was later revealed to have been working for the FBI. During Thompson's brief membership, his truck was shot at, he was yelled at by black children, and a Klan rally he attended turned into a riot when black soldiers on an adjacent military base taunted the Klansmen. Attempts by the Klan to march were often met with counterprotests and sometimes violence.
After Michael Donald was lynched in 1981 in Alabama, the FBI was involved in investigating his death. Two local Klansmen were convicted of having a role. Henry Hays was sentenced to death. With the support of Morris Dees and Joseph J. Levin at the Southern Poverty Law Center (SPLC), Michael's mother Beulah Mae Donald decided to use this case to try and destroy the Ku Klux Klan in Alabama. Her civil suit against the United Klans of America took place in February 1987. The all-white jury found the Klan responsible for the lynching of Michael Donald and ordered it to pay $7 million USD. To pay the suit, the Klan had to hand over all its assets, including the national headquarters in Tuscaloosa.
After exhausting the appeals process, Henry Hayes was executed for Donald's death in Alabama on 6th June, 1997. It was the first time since 1913 that a white man had been executed in Alabama for a crime against an African American.
The journalist Thompson related that Klan leaders who appeared indifferent to the threat of arrest showed great concern about a series of civil lawsuits filed by the Southern Poverty Law Center for damages in the millions of dollars. These were filed after Klansmen shot into a group of African Americans. Klansmen curtailed activities to conserve money for defense against the suits. Plaintiffs' success in these lawsuits virtually bankrupted the Klan, which has ceased to function as a national organization.
The Klan itself used lawsuits as tools. They filed a libel suit to prevent publication of a paperback edition of Thompson's book. The publisher canceled.
The present Ku Klux Klan is no longer one organization, but is made up of small independent chapters across the United States. The formation of independent chapters has made the KKK groups more difficult to infiltrate and researchers find it hard to estimate their numbers.
KKK members have increased somewhat in recent years, but membership is estimated at 5,000 to 8,000 among an estimated 179 chapters. The latest recruitment drives have used issues such as people's anxieties about illegal immigration, urban crime and same-sex marriage.
The only known former member of the Klan to hold a federal office currently in the United States is Democratic Senator Robert Byrd of West Virginia, who says he "deeply regrets" having joined the Klan over half a century ago, when he was about 24 years old.
Some of the larger KKK organizations in operation include:
- Bayou Knights of the Ku Klux Klan, prevalent in Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisiana and other areas of the Southeastern U.S.
- Church of the American Knights of the Ku Klux Klan
- Imperial Klans of America
- Knights of the White Kamelia
- Knights of the Ku Klux Klan, headed by national director and self-claimed pastor Thom Robb, and based in Zinc, Arkansas. They claim to be biggest Klan organization in America today. Spokesmen refer to it as a "sixth era Klan," and it continues to be a racist group.
Numerous smaller groups use the Klan name. Estimates are that about two-thirds of KKK members are concentrated in the South, with another third situated primarily in the lower Midwest.
Many Klan groups have formed strong alliances with other white supremacist groups like the Neo-Nazis. Some Klan groups have become increasingly "Nazified" adopting the look and emblems of the Nazi skinheads.
Although there are numerous KKK groups, the media and popular discourse generally refer to the Klan for expediency.
The ACLU has provided legal support to various factions of the KKK in defense of their First Amendment rights to hold public rallies, parades, and marches, and their right to field political candidates.
Vocabulary
Membership in the Klan is secret. Like many fraternal organizations, the Klan has signs which members can use to recognize one another. A member may use the acronym AYAK (Are you a Klansman?) in conversation to surreptitiously identify himself to another potential member. The response AKIA (A Klansman I am) completes the greeting.
Throughout its varied history, the Klan has coined many words beginning with "KL" including:
- Klabee: treasurers
- Kleagle: recruiter
- Klecktoken: initiation fee
- Kligrapp: secretary
- Klonvocation: gathering
- Kloran: ritual book
- Kloreroe: delegate
- Kludd: chaplain
All of the above terminology was created by William Simmons, as part of his 1915 revival of the Klan. The Reconstruction-era Klan used different titles; the only titles to carry over were "Wizard" (or Imperial Wizard) for the overall leader of the Klan, "Night Hawk" for the official in charge of security, and a few others, mostly for regional officers of the organization.
Popular culture references
The KKK figured prominently in the Sherlock Holmes story, "The Five Orange Pips", first published in 1891. More recently, the KKK has served as an antagonist in several movies and television shows. The 2000 film O Brother, Where Art Thou? included a scene shot as a KKK rally, featuring a cross burning, a lynching, and a musical performance of a traditional American song called "Oh Death". In the opening scenes of the 2003 movie Bad Boys II, a Klan rally is featured, including a cross burning. In the TV show South Park, a character has appeared dressed as a Klansman numerous times.
See also
- American Protective Association
- Christian terrorism
- Cross burning
- Grand Wizard
- History of the United States (1865-1918)
- Imperial Klans of America
- Jim Crow laws
- Johnny Lee Clary
- Klanbake
- Kleagle
- Kloran
- Knights of the Golden Circle
- Knights of the White Camelia
- Ku Klux Klan regalia and insignia
- Leaders of the Ku Klux Klan
- Notable alleged Ku Klux Klan members in national politics
- Silent Brotherhood
- The Leopard's Spots
- Timeline of racial tension in Omaha, Nebraska
- United Klans of America
- White Knights of the Ku Klux Klan
- Wide Awakes
- WKKK, KKK auxiliaries
Notes
- http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,898581-2,00.html
- Jackson 1992 ed., pp. 241-242.
- According to the 1920 census, the population of white males 18 years and older was about 31 million, but many of these men would have been ineligible for membership because they were immigrants, Jews, or Roman Catholics. Klan membership peaked at about 4-5 million: "The Ku Klux Klan, a brief biography". The African American Registry.
- Lay, Shawn. "Ku Klux Klan in the Twentieth Century". The New Georgia Encyclopedia. Coker College.
- ^ McWhorter 2001.
- W.E.B. Du Bois, Black Reconstruction in America: 1860-1880, New York: Oxford University Press, 1935; reprint, The Free Press, 1998, pp.671-675
- Horn 1939, p. 9. The founders were John C. Lester, John B. Kennedy, James R. Crowe, Frank O. McCord, Richard R. Reed, and J. Calvin Jones
- Horn 1939, p. 11, states that Reed proposed "κύκλος" ("kyklos") and Kennedy added "clan." Wade 1987, p. 33 says Kennedy came up with both words, but Crowe suggested transforming "κύκλος" into "kuklux."
- W.E.B. Du Bois, Black Reconstruction in America: 1860-1880, New York: Oxford University Press, 1935; reprint, The Free Press, 1998, pp.679-680
- "Ku Klux Klan, Organization and Principles, 1868". State University of New York at Albany.
- Horn 1939. Horn casts doubt on some other aspects of the story.
- Foner 1989, p. 426.
- Foner 1989, p. 342.
- Cincinnati 'Commercial', August 28 1868, quoted in Wade 1987. Full text of the interview on wikisource.
- Horn 1939, p. 27.
- Parsons 2005, p. 816.
- Foner 1989, pp. 425-426.
- W.E.B. Du Bois, Black Reconstruction in America: 1860-1880, New York: Oxford University Press, 1935; reprint, The Free Press, 1998, pp.677-678
- Eric Foner, Reconstruction: America's Unfinished Revolution, 1863-1877, New York: Perennial Classics, 1989; reprinted 2002, p.432
- A special report prepared by the Southern Poverty Law Center. "A Hundred Years of Terror". Indiana University-Purdue University Indianapolis.
- W.E.B. Du Bois, Black Reconstruction in America: 1860-1880, New York: Oxford University Press, 1935; reprint, The Free Press, 1998, pp.674-675
- W.E.B. Du Bois, Black Reconstruction in America: 1860-1880, New York: Oxford University Press, 1935; reprint, The Free Press, 1998, pp.680-681
- Bryant, Jonathan M. "Ku Klux Klan in the Reconstruction Era". The New Georgia Encyclopedia. Georgia Southern University.
- The Invisible Empire: The Ku Klux Klan in Florida by Michael Newton, pp. 1-30. Newton quotes from the Testimony Taken by the Joint Select Committee to Enquire into the Condition of Affairs in the Late Insurrectionary States. Vol. 13. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1872. Among historians of the Klan, this volume is also known as "The KKK testimony."
- Rhodes 1920, pp. 157-158.
- ^ Horn 1939, p. 375.
- ^ Wade 1987, p. 102.
- White Terror: The Ku Klux Klan Conspiracy and Southern Reconstruction by Allen W. Trelease (Louisiana State University Press: 1995)
- Trelease 1995.
- quotes from Wade 1987.
- Horn 1939, p. 360.
- Horn 1939, p. 362.
- ^ Wormser, Richard. "The Rise and Fall of Jim Crow — The Enforcement Acts (1870-1871)". Public Broadcasting Service.
- Wade 1987, p. 85.
- Foner 1989, p. 435.
- Wade 1987.
- Horn 1939, p. 373.
- Wade 1987, p. 88.
- Wade 1987, p. 109, writes that by ca. 1871-1874, "For many, the lapse of the enforcement acts was justified since their reason for being — the Ku-Klux Klan — had been effectively smashed as a result of the dramatic showdown in South Carolina." Klan "costumes or regalia" disappeared by the early 1870s (Wade 1987, p. 109). The fact that the Klan did not exist for decades was shown when Simmons's 1915 recreation of the Klan attracted only two aging "former Reconstruction Klansmen." All other members were new.(Wade 1987, p. 144).
- "The Rise and Fall of Jim Crow: The Enforcement Acts, 1870-1871", Public Broadcast Service, accessed 5 Apr 2008
- Wade 1987, pp. 109-110.
- Foner 1989, p. 437, and KKK Hearings, 46th Congress, 2d Session, Senate Report 693, and Taylor 1974, p. 268-270.
- Balkin, Jack M. (2002). "History Lesson" (PDF). Yale University.
- Simon, Dennis M. "The Civil Rights Movement, 1964-1968". Southern Methodist University.
- "Viola Liuzzo". Spartacus Educational.
- Richard H. Pildes, "Democracy, Anti-Democracy, and the Canon", Constitutional Commentary, Vol.17, 2000, p.27, accessed 10 Mar 2008
- Richard H. Pildes, "Democracy, Anti-Democracy, and the Canon", Constitutional Commentary, Vol.17, 2000, pp.12-13, 27, accessed 10 Mar 2008
- Maxine D. Rogers, Larry E. Rivers, David R. Colburn, R. Tom Dye, and William W. Rogers, Documented History of the Incident Which Occurred at Rosewood, Florida in January 1923, Florida: Dec 1993, p.2, accessed 28 Mar 2008
- Jackson 1967, p. 241.
- Maxine D. Rogers, et.al., Documented History of Rosewood, Florida in January 1923, op.cit., pp.4-6, accessed 28 Mar 2008
- An Interview with Stanley F. Horn - Oral History Interviews of the Forest History Society
- Dray 2002.
- Dray 2002, p. 198. Griffith quickly relayed the comment to the press, where it was widely reported. In subsequent correspondence, Wilson discussed Griffith's filmmaking in a positive tone, without challenging use of his statement.
- Wade 1987, p. 137.
- Letter from J. M. Tumulty, secretary to President Wilson, to the Boston branch of the NAACP, quoted in Link, Wilson.
- The Ku Klux Klan and Related American Racialist and Antisemitic Organizations: A History and Analysis by Chester L Quarles, Page 219. The second Klan's constitution and preamble, reprinted in Quarles book, stated the second Klan was indebted to the original Klan's Prescripts.
- Lender et al 1928, p. 33.
- Prendergast 1987, pp. 25-52, 27.
- Barr 1999, p. 370.
- "A Wizard's Indictment". TIME. March 10, 1923.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Jackson, 1992.
- Moore 1991.
- Maxine D. Rogers, et.al., Documented History of Rosewood, Florida in January 1923, op.cit., p.6, accessed 28 Mar 2008
- Franklin 1992, p.145
- Maxine D. Rogers, et.al., Documented History of Rosewood, Florida in January 1923, op.cit., p.7, accessed 28 Mar 2008
- Maxine D. Rogers, et.al., Documented History of Rosewood, Florida in January 1923, op.cit., p.7, accessed 28 Mar 2008
- Smith, Robert L. (April 26, 1999). "In the 1920s, the Klan ruled the countryside". The Providence Journal.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Diane McWhorter, Carry Me Home: Birmingham, Alabama, The Climactic Battle of the Civil Rights Revolution, New York: Touchstone Book, 2002, p.75
- Weedmark, Kevin. "When the KKK rode high across the Prairies". Moosomin World-Spectator.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - It's been seventy years since Anaheim booted the Klan, reprinted from the Los Angeles Times
- Feldman 1999.
- Rogers et al, pp. 432-433.
- Rogers et al, p. 433.
- Moore 1991, p.186.
- von Busack, Richard. "Superman Versus the KKK". MetroActive.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Kennedy 1990.
- "The Ku Klux Klan, a brief biography". The African American Registry. and Lay, Shawn. "Ku Klux Klan in the Twentieth Century". The New Georgia Encyclopedia. Coker College.
- Egerton 1994, pp. 562-563.
- "Who Was Harry T. Moore?" — The Palm Beach Post, 16 August, 1999
- Cox, Major W. (March 2, 1999). "Justice Still Absent in Bridge Death". Montgomery Advertiser.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Axtman, Kris (June 23, 2005). "Mississippi verdict greeted by a generation gap". The Christian Science Monitor.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Mitchell, Jerry. "Seale gets 3 life terms for '64 murders". USA Today.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - "Reputed Klansman, Ex-Cop, and Sheriff's Deputy Indicted For The 1964 Murders of Two Young African-American Men in Mississippi; U.S. v. James Ford Seale". January 24, 2007. Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- Ingalls 1979; Graham, Nicholas (January 2005). "January 1958 -- The Lumbees face the Klan". University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
- Thompson 1982.
- "Ku Klux Klan". Spartacus Educational, accessed 22 Apr 2008.
- "Ku Klux Klan". Spartacus Educational.
- About the Ku Klux Klan, Anti-Defamation League, 2002. According to the report, the KKK's estimated size then was "No more than a few thousand, organized into slightly more than 100 units."
- Brad Knickerbocker (9 Feb 2007). "Anti-Immigrant Sentiments Fuel Ku Klux Klan Resurgence". Christian Science Monitor.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Church of the American Knights of the KKK". Anti-Defamation League. October 22, 1999.
- "Active U.S. Hate Groups". Intelligence Report. Southern Poverty Law Center.
- "About the Ku Klux Klan". Anti-Defamation League.
- Ku Klux Klan - Affiliations Anti-Defamation League.
- "A Visual Database of Extremist Symbols, Logos and Tattoos". Anti-Defamation League.
- Axelrod 1997, p. 160.
References
- Axelrod, Alan (1997). The International Encyclopedia of Secret Societies & Fraternal Orders. New York: Facts On File.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Barr, Andrew (1999). Drink: A Social History of America. New York: Carroll & Graf.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Dray, Philip (2002). At the Hands of Persons Unknown: The Lynching of Black America. New York: Random House.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Egerton, John (1994). Speak Now Against the Day: The Generation Before the Civil Rights Movement in the South. Alfred and Knopf Inc.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Feldman, Glenn (1999). Politics, Society, and the Klan in Alabama, 1915-1949. Tuscaloosa, Alabama: University of Alabama Press.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Foner, Eric (1989). Reconstruction: America's Unfinished Revolution, 1863-1877. Perennial (HarperCollins).
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Franklin, John Hope (1992). Race and History: Selected Essays 1938-1988. Louisiana State University Press.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Horn, Stanley F. (1939). Invisible Empire: The Story of the Ku Klux Klan, 1866-1871. Montclair, New Jersey: Patterson Smith Publishing Corporation.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)
- Horn, born in 1889, was a Southern historian who was sympathetic to the first Klan, which, in an 1976 oral interview, he was careful to distinguish from the later "spurious Ku Klux organization which was in ill-repute—and, of course, had no connection whatsoever with the Klan of Reconstruction days."
- Ingalls, Robert P. (1979). Hoods: The Story of the Ku Klux Klan. New York: G.P. Putnam's Sons.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Jackson, Kenneth T. (1967; 1992 edition). The Ku Klux Klan in the City, 1915-1930. Oxford University Press.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|year=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameters:|locationNew York=and|coauthors=(help)CS1 maint: year (link) - Kennedy, Stetson (1990). The Klan Unmasked. University Press of Florida.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Lender, Mark E. (1982). Drinking in America. New York: Free Press.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Levitt, Stephen D. (2005). Freakonomics: A Rogue Economist Explores the Hidden Side of Everything. New York: William Morrow.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - McWhorter, Diane (2001). Carry Me Home: Birmingham, Alabama, The Climactic Battle of the Civil Rights Revolution. New York: Simon & Schuster.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Moore, Leonard J. (1991). Citizen Klansmen: The Ku Klux Klan in Indiana, 1921-1928. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Newton, Michael (1991). The Ku Klux Klan: An Encyclopedia. New York & London: Garland Publishing.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Parsons, Elaine Frantz (2005). "Midnight Rangers: Costume and Performance in the Reconstruction-Era Ku Klux Klan". The Journal of American History. 92 (3): 811–836.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|month=and|coauthors=(help) - Template:Harvard reference.
- Rhodes, James Ford (1920). History of the United States from the Compromise of 1850 to the McKinley-Bryan Campaign of 1896. Vol. 7.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)
- Winner of the Pulitzer Prize.
- Rogers, William (1994). Alabama: The History of a Deep South State. Tuscaloosa, Alabama: University of Alabama Press.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Steinberg, Alfred (1962). The man from Missouri; the life and times of Harry S. Truman. New York: Putnam. OCLC 466366.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Taylor, Joe G. (1974). Louisiana Reconstructed, 1863-1877. Baton Rouge.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Thompson, Jerry (1982). My Life in the Klan. New York: Putnam. ISBN 0399126953.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Trelease, Allen W. (1995). White Terror: The Ku Klux Klan Conspiracy and Southern Reconstruction. Louisiana State University Press.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)
- First published in 1971 and based on massive research in primary sources, this is the most comprehensive treatment of the Klan and its relationship to post-Civil War Reconstruction. Includes narrative research on other night-riding groups. Details close link between Klan and late 19th century and early 20th century Democratic Party.
- Wade, Wyn Craig (1987). The Fiery Cross: The Ku Klux Klan in America. New York: Simon and Schuster.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)
- An unsympathetic account of both Klans, with a dedication to "my Kentucky grandmother ... a fierce and steadfast Radical Republican from the wane of Reconstruction until her death nearly a century later."
Further reading
- Blee, Kathleen M. (1992). Women of the Klan. University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-07876-4.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - "White supremacist groups flourishing". The Associated Press.
External links
- Klan Tableau,A film documenting William Christenberry's Klan Tableau in Washington, D.C. (Includes interview with Christenberry.)
- Ku Klux Klan: A Secret History, a TV documentary on the KKK.
- The History of the Original Ku Klux Klan — by an anonymous author sympathetic to the original Klan.
- The Southern Poverty Law Center Report
- The ADL on the KKK
- MIPT Terrorist Knowledge Base for the KKK
- Proceedings of the Second Imperial Klonvocation (1924)
- In 1999, South Carolina town defines the KKK as terrorist
- A long interview with Stanley F. Horn, author of Invisible Empire: The Story of the Ku Klux Klan, 1866-1871.
- Full text of the Klan Act of 1871 (simplified version)
- The Protestant "Kluxing" of Cañyon City, Colorado — (Cañyon City Public Library)
- The Ku Klux Klan website
Template:White supremacist organizations
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
Categories: