This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Squash Racket (talk | contribs) at 17:46, 1 August 2008 (→Conquest of Transylvania and integration into the Kingdom of Hungary: adding referenced information (Columbia Encyclopedia)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 17:46, 1 August 2008 by Squash Racket (talk | contribs) (→Conquest of Transylvania and integration into the Kingdom of Hungary: adding referenced information (Columbia Encyclopedia))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)

Transylvania (Template:Lang-ro or Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help); Template:Lang-hu; Template:Audio-de, see also other denominations) is a Central European region located in the eastern half of the Carpathian Basin, in present-day central Romania. Bounded in the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historic Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains however, since 1919, Transylvania also encompasses, in the north-west, parts of the historical regions of Crişana and Maramureş (see also Partium), and in the west, eastern-(Romanian) Banat.
After forming part of Hungary (11th–16th century), it was an autonomous principality within the Ottoman Empire (16th–17th century) and then once again became part of Hungary at the end of the 17th century; later it was incorporated into Romania (1918–20).
Outside Romania, it is strongly associated with the novel Dracula, while within Romania and Hungary the region is known for the scenic beauty of its Carpathian landscape and its rich history.
Etymology

Transylvania was first referred to in a Medieval Latin document in 1075 as ultra silvam, meaning "exceedingly forested" (ultra meaning "excessively or beyond what is common" and the accusative case of sylva (sylvam) meaning "wood or forest").
The modern English name is probably taken from the Hungarian Erdély, which is derived from Erdő-elve meaning "beyond the forest" (a meaning first referred to in its Medieval Latin version in a 12th century document - Gesta Hungarorum). "Transylvania" means "beyond the forest" (trans meaning "across, over, beyond").
The German name Siebenbürgen means "seven fortresses", after the seven (ethnic German) Transylvanian Saxons' cities in the region (Kronstadt, Schäßburg, Mediasch, Hermannstadt, Mühlbach, Bistritz and Klausenburg). This is also the origin of many other language's name for the region, such as the Polish siedmiogród.
The origin of the Romanian name Ardeal is controversial. The first known occurrence of the Romanian name appeared in a document in 1432 as Ardeliu. It may be a result of an elision from the Romanian words aur and deal ("gold" and "hill", respectively), resulting in Ardeal from the composed word Aur-deal. It may also take its origin from the Khazar word “Ardil-land” (Hebrew „Eretz Ardil”, „ארדיל”), from the Celtic "Arduenna" (forest), reflected in other names such as Arda, Ardal, Ardistan, Ardiche, Ardennes, Ardelt and Ardilla, or from the Sanskrit Har-Deal. Another hypothesis is that the name is borrowing of the Hungarian name Erdély, as is the Romanian name Ardyalo - in old Hungarian, Erdély was pronounced as Erdél. The initial e- in Hungarian occasionally changes to a in Romanian (cf. Hung. egres "gooseberry" and Egyed, which became agriş and Adjud in Romanian).
See also other languages.
History
Main article: History of TransylvaniaIn its early history, the territory of Transylvania belonged to a variety of empires and states, including Dacia, the Roman Empire, the Hun Empire and the Gepid Kingdom. There were also periods when autonomus political entities raised under the control of the Byzantine and the Bulgarian Empire. As a political entity, (Southern) Transylvania is mentioned from the 12th century as a county(Alba) of the Kingdom of Hungary (M. princeps ultrasilvanus - comes Bellegratae). Transylvania's seven counties were brought under the voivode's (count of Alba Iulia) rule in 1263. It then became an autonomous principality under nominal Ottoman suzerainty in 1571. A few centuries later, in 1688, it was added to the expanding territories of Habsburg Monarchy, then became again a part of the Kingdom of Hungary within the newly established Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1867. Since World War I, it has been part of Romania, apart from a brief period of Hungarian occupation during World War II.
Cluj-Napoca is today considered to be the region's spiritual capital, although Transylvania was also ruled from Alba Iulia during its period as an autonomous principality within the Ottoman Empire, and from Sibiu, where the Habsburg governor was located from 1711 to 1848. The seat of the Transylvanian Diet was itself moved to Sibiu for some time in the 19th century.
Since medieval times, the population of the region has been a mixture of ethnic Romanians (historically known as Vlachs), Hungarians, the ethnic Hungarian Székely people, Germans (known as Saxons), Armenians (especially in Gherla (Armenopolis), Gheorgheni and Tarnaveni), Jews and Roma (known as Gypsies or "tatars" - Tatern in Transylvanian Saxon or tătăraşi in Romanian).
The Roman province of Dacia, 105-271
The Kingdom of Dacia was in existence at least as early as the beginning of the 2nd century BC, and it reached its maximum extent under the rule of Burebista. The area now constituting Transylvania was the political center of the ancient kingdom, where several important fortified cities were built, among them Sarmizegetusa, near today's Hunedoara.
In 101-102 and 105-106, Roman forces under the Emperor Trajan fought a series of military campaigns to subjugate Dacia. After the suicide of the Dacian ruler Decebalus, parts of Dacia were incorporated into the Roman Empire. According to Eutropius Breviarium historiae Romanae, after Decebals death the romans destroyed and killed allmost the whole local population. Dacia had to be repopulated all over again, ("ex toto Orbe Romano"), from the whole Roman Empire. Hadrian (117-135) the current territory of Transylvania was included in Dacia Superior. During Antoninus Pius (138-161) the same territory was included in the provinces Dacia Porolissensis (capital at Porolissum) and Dacia Apulensis (capital at Apulum).The Romans built mines, roads and forts in the province. Colonists from other Roman provinces were brought in to settle the land and cities like Apulum (now Alba Iulia), Napoca (now Cluj-Napoca), Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa and Aquae appeared. During the Roman administration also Christianity entered the current territory of Transylvania from the neighbouring Roman provinces where according to the tradition of the Romanian Orthodox Church St. Peter preached.
Due to increasing pressure from the Visigoths, the Romans abandoned the province during the reign of the Emperor Aurelian in 271. As across much of Europe, a period of chaos and conquests followed after the collapse of Roman rule. However, as shown by the archeological research, many of the Roman cities continued to exist, building fortifications. Also Christianity survived as proved by the many artifacts discovered. Among the most famous is the donarium from Biertan (4th century) having the inscription 'Ego Zenovius votvm posui' (I, Zenovie, offered this). The territory fell under the control of the Visigoths and Carpians until they were in turn displaced and subdued by the Huns in 376, under the leadership of their infamous warlord Attila. After the disintegration of Attila's empire, the Huns were succeeded by Gepids of Eurasian Avar descent. The region was also influenced during this period by massive Slavic immigration.
At the beginning of the 9th century, Transylvania, along with eastern Pannonia, was under the control of the First Bulgarian Empire. After a brief period of Bulgarian rule, the territory, was partially under Byzantine control.
Between 10th-12th centuries A.D. Transylvania was slowly conquered by the Magyar tribes, during a period of 300 years. . The most powerfull local leaders who opposed the Magyars were Gelou / Gelu, Glad and Menumorut. .
Conquest of Transylvania and integration into the Kingdom of Hungary
According to the Columbia Encyclopedia the Magyar tribes first entered the region in the 5th century. At the beginning of the 9th century the Hungarian tribes were located in the north of the Black Sea. In 895 as a result of a planned 'conquest' and a massive withdrawal caused by a Bulgarian-Pecheneg attack they established in the Upper-Tisza region and Transylvania and started to expand their territories towards west only in 899. According to Gesta Hungarorum describing among others the conquest of Transylvania, three statal structures ruled by Menumorut, Glad and Gelu were encountered and defeated by the Magyars.
Gelou (Gelu in Romanian, Gyalu in Hungarian) leader of the Vlachs (ancient Romanians) in Transylvania was ruling over the Middle part of Transylvania and had his capital at Dăbâca. He was defeated by the warriors of the Magyar chieftain Tétény (also called Töhötöm; in the original Latin: Tuhutum) sometime during the 10th century.
Glad (Bulgarian and Serbian Cyrillic: Глад) rulled over the South-West of Trabsylvania, having authority over the Slavs and Vlachs, which consisted most of the population of mentioned regions at the time. He was, according to the Gesta Hungarorum, a voivod (dux) from Bundyn (Vidin), ruler of the territory of Banat, during the 9th and 10th centuries. He also ruled part of south Transylvania, and Vidin region, and was a local governor or vassal of the First Bulgarian Empire under Bulgarian tsar Simeon. Glad was defeated by the Hungarians during the 10th century. One of his descendants, Ahtum, was a duke of Banat and the last ruler who opposed to the establishment of the Hungarian Kingdom in the 11th century, but he was too, defeated by the Hungarian Crown.
Menumorut, a vassal of Byzantium ruled the lands between the River Tisza and the Ygfon Forest in the direction of Ultrasilvania (Transylvania), from the Mureş river to the Someş river. He declined the request of the Magyar ruler Árpád (907) to cede his territory between the Someş river and the Meses Mountains, and in the negotiations with the ambassadors Usubuu and Veluc of Árpád he invoked the sovereignty of the Byzantine Emperor Leo VI the Wise. The Magyars first besieged the citadel of Zotmar (Romanian: Satu Mare, Hungarian: Szatmár) and then Menumorut's castle in Bihar, and were able to defeat him. The Gesta Hungarorum then retells the story of Menumorut. In the second telling, he married his daughter into the Árpád dynasty. Her son Taksony, the grandson of Menumorut, became ruler of the Magyars and father of Mihály and Géza, whose son Vajk became the first King of Hungary in 1001 under the Christian baptismal name Stephen.
The early 11th century was marked by the conflict between King Stephen I of Hungary and his uncle Gyula, the ruler of Transylvania. The Hungarian ruler was successful in these wars, and Transylvania was incorporated into the Christian Kingdom of Hungary. The Transylvanian Christian bishopric and the comitatus system were organised. By the early 11th century the ethnic Hungarian Székely were established in southeastern Transylvania as a border population of ready warriors, and in the 12th and 13th centuries, the areas in the south and northeast were settled by German colonists called Saxons. Romanians maintained control over a few autonomous regions called 'terrae': Fagaras, Amlas. Hateg, Maramures, Lapus. However the autonomy was taken by the end of Árpád dynasty in 1301.
In 1241-1242, during the Mongol invasion of Europe, Transylvania was among the territories devastated by the Golden Horde. A large portion of the population perished. This was followed by a second Mongol invasion in 1285, led by Nogai Khan.
Following this devastation, Transylvania was reorganized according to a class system of Estates, which established privileged groups (universitates) with power and influence in economic and political life, as well as along ethnic lines. The first Estate was the lay and ecclesiastic aristocracy, ethnically heterogeneous, but undergoing a process of homogenization around its Hungarian nucleus. The other Estates were Saxons, Szeklers and Romanians (or Vlachs - Universitas Valachorum), all with an ethnic and ethno-linguistic basis (Universis nobilibus, Saxonibus, Syculis et Olachis). The general assembly (congregatio generalis) of the four Estates had few genuine legislative powers in Transylvania, but it sometimes took measures regarding order in the country.

A key figure to emerge in Transylvania in the first half of the 15th century was John Hunyadi/János Hunyadi/Iancu de Hunedoara, a native of Transylvania born in a family of Romanian origins. . He was one of the greatest military figures of the time, being Hungarian general, voivode of Transylvania and then governor of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1446 to 1452. He was a Transylvanian noble of Romanian origin some sources indicating him as the son of Voicu/Vajk, a Romanian boyar from Wallachia though other sources are telling that his father was a Transylvanian Vlach/Romanian. Hungarian historians claim that his mother was Erzsébet Morzsinay the daughter of a Hungarian noble family. His fame was built in the effective wars of defence against the Turkish attacks, waged from 1439. With his private mercenary army John rapidly rose to the heights of power. His military campaigns against the Ottoman Empire brought him the status of Transylvanian governor in 1446 and papal recognition as the Prince of Transylvania in 1448. Continuing his military activity, he won an important victory at Belgrade in 1456, which halted the Ottomans advance for several decades, but died shortly afterwards during an epidemic.
After the suppression of the Budai Nagy Antal-revolt in 1437, the political system was based on Unio Trium Nationum (The Union of the Three Nations). According to the Union, which was explicitly directed against serfs and other peasants, society was ruled by three privileged Estates of the nobility (mostly ethnic Hungarians), the Székelys, also an ethnic Hungarian people who primarily served as warriors, and the ethnic German, Saxon burghers.
The only possibility for Romanians to retain or access nobility in Hungarian Transylvania was through conversion to Catholicism. Some Orthodox Romanian nobles converted, becoming integrated into the Hungarian nobility. These circumstances marked the beginning of a conflict between ethnic Hungarian Catholics and ethnic Romanian Orthodox in the territory of Transylvania which in some regions remains unresolved to this very day.
Transylvania as an Independent Principality
The 16th century in Southeastern Europe was marked by the struggle between the Muslim Ottoman Empire and the Catholic Habsburg Empire. After the Ottoman Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent overran central Hungary (see Ottoman Hungary), Transylvania became a semi-independent principality where Austrian and Turkish influences vied for supremacy for nearly two centuries. It is this period of independence and Turkish influence that contributed to Transylvania being seen as exotic in the eyes of Victorians such as Bram Stoker, whose novel Dracula was published in 1897.

Due to the fact that Transylvania was now beyond the reach of Catholic religious authority, Protestant preaching such as Lutheranism and Calvinism were able to flourish in the region. In 1568 the Edict of Turda proclaimed four religious expressions in Transylvania - Catholicism, Lutheranism, Calvinism and Unitarianism, while Orthodoxy, which was the confession of the Romanian population, was proclaimed as "tolerated" (tolerata).
The Báthory family began to rule Transylvania as princes under the Ottomans in 1571, and briefly under Habsburg suzerainty until 1600. The latter period of their rule saw a four-sided conflict in Transylvania involving the Transylvanian Báthorys, the emerging Austrian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Romanian voivoideship (province) of Wallachia. This included a brief period of Romanian rule after the conquest of the territory by Wallachian voivod Michael the Brave. As he subsequently extended his rule over Moldavia, Michael the Brave unified for the first time in history all the territories where Romanians lived, rebuilding the mainland of the ancient Kingdom of Dacia

The Calvinist magnate of Bihar county Stephen Bocskai managed to obtain, through the Peace of Vienna (June 23, 1606), religious liberty and political autonomy for the region, the restoration of all confiscated estates, the repeal of all "unrighteous" judgments, as well as his own recognition as independent sovereign prince of an enlarged Transylvania. Under Bocskai's successors, most notably Gabriel Bethlen and George I Rákóczi, Transylvania passed through a golden age for many religious movements and for the arts and culture. Transylvania became one of the few European States where Roman Catholics, Calvinists, Lutherans and Unitarians lived in peace, although Orthodox Romanians continued to be denied equal recognition.
This golden age and relative independence of Transylvania ended with the reign of George II Rákóczi. The prince, coveting the Polish crown, allied with Sweden and invaded Poland in spite of the Turkish Porte clearly prohibiting any military action. Rákóczi's defeat in Poland, combined with the subsequent invasions of Transylvania by the Turks and their Crimean Tatar allies, the ensuing loss of territory (most importantly, the loss of the most important Transylvanian stronghold, Oradea) and diminishing manpower led to the complete subordination of Transylvania, which now became a powerless vassal of the Ottoman Empire.
Within the Habsburg Empire

After the defeat of the Ottomans at the Battle of Vienna in 1683, the Habsburgs gradually began to impose their rule on the formerly autonomous Transylvania. Apart from strengthening the central government and administration, the Habsburgs also promoted the Roman Catholic Church, both as a uniting force and also as an instrument to reduce the influence of the Protestant nobility. In addition, they tried to persuade Romanian Orthodox clergymen to join the Greek (Byzantine Rite) Catholic Church in union with Rome. As a response to this policy, several peaceful movements of the Romanian Orthodox population advocated for freedom of worship for all the Transylvanian population, most notably being the movements led by Visarion Sarai, Nicolae Oprea Miclăuş and Sofronie of Cioara.
From 1711 onward, the princes of Transylvania were replaced with Austrian governors and in 1765 Transylvania was declared a grand principality.
The revolutionary year 1848 was marked by a great struggle between the Hungarians, the Romanians and the Habsburg Empire. Warfare erupted in November with both Romanian and Saxon troops, under Austrian command, battling the Hungarians led by the Polish born general Józef Bem. He carried out a sweeping offensive through Transylvania, and Avram Iancu managed to retreat to the harsh terrain of the Apuseni Mountains, mounting a guerrilla campaign on Bem's forces. After the intervention by the armies of Tsar Nicholas I of Russia, Bem's army was defeated decisively at the Battle of Timişoara (Temesvár, Hun.) on 9 August 1849.
Having quashed the revolution, Austria imposed a repressive regime on Hungary, ruled Transylvania directly through a military governor and granted citizenship to the Romanians.
The 300-year long special separate status came to an end by the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, which established the dual monarchy and reincorporated Transylvania into the Kingdom of Hungary. On 20 June 1867, the Diet was dissolved by royal decree, and an ordinance abrogated the legislative acts of the Cluj-Napoca provincial assembly. The department of the interior inherited the responsibilities of the Transylvanian Gubernium, and the government reserved the right to name Transylvania's royal magistrates as well the Saxon bailiff of the Universitas Saxorum. Hungarian legislation also came to supersede the Austrian code of civil procedure, penal law, commercial law, and regulations for bills of exchange. The new unity of Austria-Hungary created a process of Magyarization affecting Transylvania's Romanians and German Saxons.
Part of Romania

Since the Austro-Hungarian empire had begun to disintegrate after the end of World War I, the nationalities living inside proclaimed their independence from the empire. The 1228-member National Assembly of Romanians of Transylvania and Hungary, headed by leaders of Transylvania's Romanian National Party and Social Democratic Party, passed a resolution calling for unification of all Romanians in a single state on 1 December in Alba Iulia. This was approved by the National Council of the Germans from Transylvania and the Council of the Danube Swabians from the Banat, on 15 December in Mediaş. In response, the Hungarian General Assembly of Cluj reaffirmed the loyalty of Hungarians from Transylvania to Hungary on December 22, 1918. (See also: Union of Transylvania with Romania)
The Treaty of Versailles placed Transylvania under the sovereignty of Romania, an ally of the Triple Entente, and after the defeat in 1919 of Béla Kun's Hungarian Soviet Republic by the Romanian army the Treaty of St. Germain (1919) and the Treaty of Trianon (signed in June 1920) further elaborated the status of Transylvania and defined the new border between the states of Hungary and Romania. King Ferdinand I of Romania and Queen Maria of Romania were crowned at Alba Iulia in 1922 as King and Queen of all Romania.
In August 1940, the second Vienna Award granted the northern half of Transylvania to Hungary. After the Treaty of Paris (1947), at the end of World War II, the territory was returned to Romania. The post-WWII borders with Hungary, agreed on at the Treaty of Paris, were identical with those set out in 1920.
After World War II and especially after the fall of Communism, Transylvania lost almost all of the German-speaking population, most of them left for Germany.
A Hungarian minority group is pressing for greater autonomy in that region where its members outnumber Romanians. There are tensions in Transylvania between Romanians and ethnic Hungarians who want autonomy. The Hungarians say they are the target of attacks by Romanian politicians and news organizations. They say the aim is to forcibly assimilate the Hungarian minority of 1.7 million people, or 7.1 percent of the Romanian population.
The Szekler National Council is a local Hungarian group founded in 2003 with autonomy as its stated goal. Unlike the Kosovars, the Szeklers are asking for autonomy within Romania rather than complete independence, leaving foreign policy and national defense in the hands of the government in Bucharest.
A new and more radical organization, the Hungarian Civic Party, has risen to challenge the establishment Hungarian party and has advocated for the autonomy of the Szekler region. .
The Hungarian politician, László Tőkés, one of the party leaders, is pressing for greater autonomy, saying that Romanian and Hungarian authorities have to reach an agreement regarding the statute of the Hungarian community, the Szeckler county respectively. .
Historical coat of arms of Transylvania
Main article: Coat of arms of TransylvaniaThe first heraldic representation of Transylvania is found on the coat of arms of Michael the Brave. Besides the Walachian eagle and the Moldavian auroch, Transylvania is here represented by two afronted lions holding a sword (elements referring to the Dacian Kingdom), standing upon seven hills.
The Diet of 1659 codified the representation of the privileged nations in Transylvania's coat of arms. It depicts:
- A black turul on a blue background, representing the medieval nobility, which was mainly Magyar.
- The Sun and the Moon representing the Székelys.
- Seven red towers on a yellow background representing the seven fortified cities of the Transylvanian Saxons
(The red dividing band was originally not part of the coat of arms.)
-
 Coat of arms of Michael the Brave, ruller of Transylvania, Wallachia and Moldova, 1600
Coat of arms of Michael the Brave, ruller of Transylvania, Wallachia and Moldova, 1600
-
 Coat of Arms of 1659
Coat of Arms of 1659
-
 Landesfarben of Transylvania in Austria-Hungary, reflecting the tinctures of the coat-of-arms
Landesfarben of Transylvania in Austria-Hungary, reflecting the tinctures of the coat-of-arms
- As part of the coat of arms of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 As part of the coat of arms of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920
-
 As in the coat of arms of Romania at present
As in the coat of arms of Romania at present
Geography and ethnography

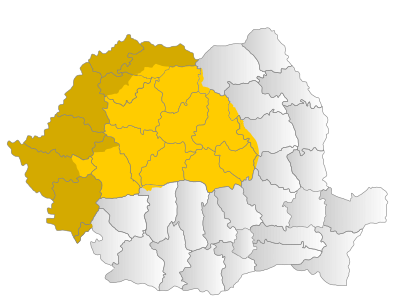
The Transylvanian plateau, 300 to 500 metres (1,000-1,600 feet) high, is drained by the Mureş, Someş, Criş, and Olt rivers, as well as other tributaries of the Danube. This core of historical Transylvania roughly corresponds with nine counties of modern Romania. Other areas to the west and north, which also united with Romania in 1918 (inside the border established by peace treaties in 1919-20), are since that time widely considered part of Transylvania.
See also Administrative divisions of the Kingdom of Hungary. In common reference, the Western border of Transylvania has come to be identified with the present Romanian-Hungarian border, settled in the Treaty of Trianon, although geographically the two are not identical.
Administrative divisions
 Bihor
Arad
Timiș
Caraș-Severin
Hunedoara
Satu Mare
Sălaj
Alba
Sibiu
Brașov
Covasna
Harghita
Mureș
Cluj
Bistrița-Năsăud
Maramureș
Bihor
Arad
Timiș
Caraș-Severin
Hunedoara
Satu Mare
Sălaj
Alba
Sibiu
Brașov
Covasna
Harghita
Mureș
Cluj
Bistrița-Năsăud
Maramureș
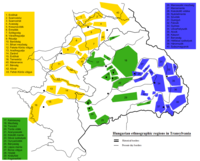
Light yellow – historical region of Transylvania
Dark yellow – historical regions of Banat, Crișana and Maramureș
Grey – historical regions of Wallachia, Moldavia and Dobruja
The historical region granted to Romania in 1920 covered 23 counties including nearly 102,200 km² (102,787 - 103,093 in Hungarian sources and 102,200 in contemporany Romanian documents) now due to the several administrative reorganisations Transylvania covers 16 present-day counties (Romanian: judeţ) which include nearly 99,837 km² of central and northwest Romania. The 16 counties are:
- Alba
- Arad
- Bihor
- Bistriţa-Năsăud
- Braşov
- Caraş-Severin
- Cluj
- Covasna
- Harghita
- Hunedoara
- Maramureş
- Mureş
- Sălaj
- Satu Mare
- Sibiu
- Timiş
The most populous cities are:
- Cluj-Napoca (318,027)
- Timişoara (317,651)
- Braşov (283,901)
- Oradea (206,527)
- Arad (172,824)
- Sibiu (155,045)
- Târgu Mureş (149,577)
- Baia Mare (137,976)
- Satu Mare (115,630)
Population
Historic definitions of Transylvania vary geographically. The 2002 Romanian census classified Transylvania as the entire region of Romania west of the Carpathians. This region has a population of 7,221,733, with a large Romanian majority (75,9%). There are also sizeable Hungarian (20%), Roma (3.3%), German (0.7%) and Serb (0.1%) communities. The ethnic Hungarian population of Transylvania, largely composed of Székely, form a majority in the counties of Covasna and Harghita.
The percentage of Romanian majority has increased since the union of Transylvania with Romania after World War I in 1918 (the 1910 Census indicates a total population of 5,262,495, Romanians 53.8%; Hungarians 31.6%; Germans 10.7%). This is due to the emigration of non-Romanian peoples, assimilation and internal migration within Romania (estimates show that between 1945 and 1977, some 630,000 people moved from the Old Kingdom to Transylvania, and 280,000 from Transylvania to the Old Kingdom, most notably to Bucharest). The assimilation process for Hungarians slowed during the first stages of the communist era, when most of the region's ethnic Hungarian population was granted nominal political autonomy, but accelerated under the Ceauşescu regime.
For people connected to Transylvania's cultural life see: List of Transylvanians.
Economy
Main article: Economy of TransylaniaTransylvania is rich in mineral resources, notably lignite, iron, lead, manganese, gold, copper, natural gas, salt and sulfur.
There are large iron and steel, chemical, and textile industries. Stock raising, agriculture, wine production and fruit growing are important occupations. Timber is another valuable resource.
Transylvania accounts for around 35% of Romania's GDP, and has a GDP per capita (PPP) of around $11,500, around 10% higher than the Romanian average.
Tourist attractions
- The medieval cities of Alba Iulia, Cluj-Napoca, Sibiu (European Capital Of Culture-2007) , Târgu Mureş and Sighişoara
- The city of Braşov and the nearby Poiana Braşov ski resort
- The city of Hunedoara with the 14th century Hunyadi Castle
- The citadel and the Art Nouveau city centre of Oradea
- The Wooden Churches of the Maramureş region
- The Dacian Fortresses of the Orăştie Mountains, including Sarmizegetusa
- The Saxon fortified churches
- Hungarian traditions and folk culture
- The cafe culture , street theatre and cosmopolitan society of Sibiu
- Orthodox Cathedral in Timişoara Orthodox Cathedral in Timişoara
-
 Arad cultural center
Arad cultural center
-
 Wooden church in Maramureş
Wooden church in Maramureş
- Orthodox Cathedral in Cluj-Napoca Orthodox Cathedral in Cluj-Napoca
-
 Arad Evangelical church
Arad Evangelical church
-
 Bran Castle
Bran Castle
- Black Church in Braşov Black Church in Braşov
- Braşov Council Square (Piaţa Sfatului) Braşov Council Square (Piaţa Sfatului)
-
 Catholic Church in Cluj-Napoca
Catholic Church in Cluj-Napoca
-
 The Theatre in Oradea
The Theatre in Oradea
-
 The town hall in Oradea
The town hall in Oradea
-
 Dacia Hotel in Satu Mare
Dacia Hotel in Satu Mare
-
 View of Sibiu
View of Sibiu
-
 Sighişoara clock tower
Sighişoara clock tower
-
 View of Sighişoara
View of Sighişoara
-
 The Catholic Cathedral in Timişoara
The Catholic Cathedral in Timişoara
Transylvania in fiction
Main article: Transylvania in fictionTransylvania's long history of Muslim Turkish influence, as well as its late industrialization (which meant that in the late 19th century, Transylvania was still mostly covered with wilderness), created an orientalist fascination with the region by a number of notable Victorian writers. Following the publication of Emily Gerard's The Land Beyond the Forest (1888), Bram Stoker wrote his gothic horror novel Dracula in 1897, using Transylvania as a setting. Due to the success of the latter work, Transylvania became associated in the English-speaking world with vampires. Since then it has been represented in fiction and literature as a land of mystery and magic. For example, in Paulo Coelho's novel The Witch of Portobello, the main character, Sherine Khalil, is described as a Transylvanian orphan with a Romani mother, in an effort to add to the character's exotic mystique. The so-called Transylvanian trilogy of historical novels by Miklos Banffy, The Writing on the Wall, is an extended treatment of the 19th and early 20th century social and political history of the country.
References
- "Transylvania". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. 2008. Retrieved 2008-08-01.
- Transylvania Society of Dracula Information
- Romania Transylvania
- Pascu, Ştefan (1972), Voievodatul Transilvaniei, vol. I, p. 22
- Béla Köpeczi (editor). "History of Transylvania". Atlantic Research and Publications, Inc. Retrieved 2007-01-29.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - 6. SOUTHERN TRANSYLVANIA UNDER BULGAR RULE
- "Szekler". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. 2008. Retrieved 2008-06-30.
- Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh Edition
- Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh Edition
- ^ "Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge". p. 1457. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
- "Transylvania". Columbia Encyclopedia. 2008. Retrieved 2008-08-01.
- ^ "János Hunyadi". Encyclopædia Britannica Inc. 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|encyclopedia=ignored (help) - ^ "János Hunyadi". Encarta. 2008. Retrieved 2008-08-01.
- "Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge". p. 705. Retrieved 2008-08-01.
- "Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge". p. 1458. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
- "Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages, Andre Vauchez, Richard Barrie Dobson, Adrian Walford, Michael Lapidge". p. 1458. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
- Enea Silvius Piccolomini, (Pope Pius II), In Europa - Historia Austrialis, BAV, URB, LAT. 405, ff.245, IIII kal. Aprilis MCCCCLVIII, Ex Urbe Roma
- "Jean W. Sedlar, East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000-1500, Uniiversity of Washington Press, 1994". Retrieved 2008-07-31.
- "A Hunyadiaktól karácsonyig" (in Hungarian). Zoltán Balassa. Retrieved 2008-04-25.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Romania Confronts Transylvanian Separatism
- ELENI COUNDOURIOTIS, Dracula and the Idea of Europe
- Rezachevici, Constantin, Mihai Viteazul et la "Dacie" de Sigismund Báthory en 1595, Ed. Argessis, 2003, 12, p.155-164
- "December 1 - Romania National Day". Honorary Consul of Romania in Boston. Retrieved 2008-01-12.
- Bachman, Robert D. (1989). "Romania: A Country Study". Retrieved 2008-01-12.
- "Trianon, Treaty of". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2008-01-12.
- "BREAKAWAY ROLE MODEL - Romania: The Magyars in Székely Land". Der Spiegel. 2008-02-22. Retrieved 2008-07-29.
- ^ "Kosovo's Actions Hearten a Hungarian Enclave". The New York Times. 2008-04-07. Retrieved 2008-06-30.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Hungarians and Romanians At Odds in Transylvania". The New York Times. 1997-12-26. Retrieved 2008-08-01.
- "Magyar Autonomy, An Issue Romania Needs To Deal With". Mediafax. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
- 2002 Census official results:
- Ethnocultural Diversity Resource Centre database:
- Varga, E. Árpád, Hungarians in Transylvania between 1870 and 1995, Translation by Tamás Sályi, Budapest, March 1999 , p. 27.
Another novel featuring transyvania would be 'The Sight,' by author David Clement-Davies.
Further reading
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. {{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)- Patrick Leigh Fermor, Between the Woods and the Water (New York Review of Books Classics, 2005; ISBN 1-59017-166-7). Fermor travelled across Transylvania in the summer of 1934, and wrote about it in this account first published more than 50 years later, in 1986.
- Zoltán Farkas and Judit Sós, Transylvania Guidebook
External links
- RTI Radio - Radio Transsylvania International
- Tolerant Transylvania - Why Transylvania will not become another Kosovo, Katherine Lovatt, in Central Europe Review, Vol 1, No 14 27 September 1999.
- The History Of Transylvania And The Transylvanian Saxons by Dr. Konrad Gündisch, Oldenburg, Germany
- Template:De icon Historical Literature about Transilvania and Neighbouring Territories by Klaus Popa, Germany
- Transylvania, its Products and its People, by Charles Boner, 1865
- Template:Hu icon Transylvanian Family History Database
| Banat |
|
|---|---|
| Dobruja |
|
| Moldavia |
|
| Transylvania | |
| Wallachia | |
| |