This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Anonimu (talk | contribs) at 18:26, 9 July 2009 (everyon could write whatever he wanted, not just Romanian or Moldovan). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 18:26, 9 July 2009 by Anonimu (talk | contribs) (everyon could write whatever he wanted, not just Romanian or Moldovan)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| Autonomous Territorial Unit of Gagauzia (Gagauz Yeri)Gagauz-Yeri Găgăuzia Гагаузия | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Anthem: Gagauziya Milli Marşı | |
 Location of Gagauzia (purple) Location of Gagauzia (purple) | |
| Capitaland largest city | Comrat |
| Official languages | Gagauz, Moldovan, Russian |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Mihail Formuzal (2006-) |
| • Chairman of the People's Assembly | Ana Harlamenco (2008-) |
| Autonomous region of Moldova | |
| • Created | April 23 1994 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,832 km (707 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • 1996¹ estimate | 155,700 |
| • Density | 85/km (220.1/sq mi) |
| Currency | Moldovan leu (MDL) |
Gagauzia (Gagauz: Gagauziya or Gagauz-Yeri; Moldovan/Romanian: Găgăuzia; Template:Lang-ru), formally known as the Autonomous Territorial Unit of Găgăuzia (Gagauz Yeri) (Gagauz: Avtonom Territorial Bölümlüü Gagauz Yeri, Moldovan/Romanian: Unitatea Teritorială Autonomă Găgăuzia, Russian: Автономное территориальное образование Гагаузия / Avtonomnoye territorial'noye obrazobaniye), is an autonomous region of Moldova. Its name derives from the word "Gagauz", which in turn derived from the name Gok-oguz used to describe descendants of the Turkic Oghuz tribe. Crimean Tatars and Uyghurs used gok to mean "sky" or "sky blue", so Gok-oguz literally meant "sky-blue Oghuz".
History
The Gagauz people descend from the Seljuk Turks that settled in Dobruja, together with the Pechenegs, Uz (Oghuz) and Cuman (Kipchak) people that followed the Anatolian Seljuk Sultan Izzeddin Keykavus II (1236–76). More specifically, one clan of Oghuz Turks migrated to the Balkans during the inter-tribal conflicts with other Turks. This Oghuz Turk clan converted from Islam to Orthodox Christianity after settling in the Eastern Balkans (in Bulgaria) and were called Gagauz Turks.
Russian Empire
In 1812, Bessarabia, previously the eastern half of the Principality of Moldavia, became part of the Russian Empire, and Nogai tribes that inhabited several villages in south Bessarabia (or Budjak) were forced to leave. Between 1812 and 1846, Russians settled the Gagauz people from what is nowadays eastern Bulgaria (which remained under Ottoman Empire) to the orthodox Bessarabia, mainly in the settlements vacated by the Nogai tribes. They settled there in parallel with Bessarabian Bulgarians in Avdarma, Comrat, Congaz, Tomai, Cişmichioi, and other former Nogai villages. Some Gagauz were also settled in the part of the Principality of Moldavia that did not come under Russian control in 1812, but within several years village by village moved to the compact area they inhabit today in the south of Bessarabia.
With the exception of a five-day de facto independence in the winter of 1906, when a peasant uprising declared an autonomous Republic of Comrat, Gagauzians have been ruled by the Russian Empire (1812-1917), Romania (1918-1940 and 1941-1944), the Soviet Union (1940-1941 and 1944-1991), and Moldova (1917-1918 and 1991 to date).
USSR
Gagauzian nationalism remained an intellectual movement during the 1980s, but strengthened by the end of the decade, as the Soviet Union began to embrace democratic ideals. In 1988, activists from the local intelligentsia aligned with other ethnic minorities to create a movement known as the "Gagauz People". A year later, the "Gagauz People" held its first assembly in which a resolution was passed to demand the creation an autonomous territory in southern Moldova, with the city of Comrat as its capital. The Gagauzian national movement intensified when Romanian was accepted as the official language of the Republic of Moldova in August 1989, replacing Russian, the official language of the USSR. A part of the multiethnic population of southern Moldova regarded this decision with concern, precipitating a lack of confidence in the central government in Chişinău. The Gagauzians were also worried about the implications for them if Moldova reunited with Romania, as seemed likely at the time. In August 1990, Comrat declared itself an autonomous republic, but the Moldovan government annulled the declaration as unconstitutional. At that time, Stepan Topal emerged as the leader of the Gagauz national movement.
Independent Moldova
Support for the Soviet Union remained high, with a referendum in March 1991 returning an almost unanimous vote in favour of remaining part of the USSR. The referendum, however, was boycotted by Moldovans in Gagauzia, as well as in the rest of Moldova. Many Gagauz supported the Moscow coup attempt in August 1991, and Gagauzia declared itself independent on 19 August 1991, followed in September by Transnistria, thus further straining relations with Chişinău. However, when the Moldovan parliament voted on whether Moldova should become independent on 27 August 1991, six of the twelve Gagauz deputies in Moldovan parliament voted in favour, while the other six did not participate. As a consequence, the Moldovan government toned down its pro-Romanian stance and paid more attention to minority rights.
In February 1994, President Mircea Snegur promised the Gagauz autonomy, but he was against outright independence. He was also opposed to the suggestion that Moldova become a federal state made up of three republics, Moldova, Gagauzia, and Transnistria.
In 1994, the Parliament of Moldova awarded to "the people of Gagauzia" (through the adoption of the new Constitution of Moldova) the right of "external self-determination", should the status of the country change. In other words, if the case was that Moldova decided to join another country (by all accounts, that would be Romania), then Gagauzians would be entitled to decide, by means of a self-determination referendum, whether to remain part of the new state or not. On December 23 1994, the Parliament of the Republic of Moldova accepted the "Law on the Special Legal Status of Gagauzia" (Gagauz: Gagauz Yeri), resolving the dispute peacefully. This date is now a Gagauzian holiday. Gagauzia is now a "national-territorial autonomous unit" with three official languages, Moldovan, Gagauz, and Russian.
Three cities and twenty-three communes were included in the Autonomous Gagauz Territory: all localities with over 50% Gagauz, and those localities with between 40% and 50% Gagauz which expressed their desire to be included as a result of referendums to determine Gagauzia's borders. In 1995, Georgi Tabunshik was elected to serve as the Governor (Moldovan: Guvernator, Gagauz: Bashkan) of Gagauzia for a four-year term, as were the deputies of the local parliament, "The People's Assembly", with Peter Pashali as chairman.
Dumitru Croitor won the 1999 Governor elections and began to make use of the rights granted to the Governor by the 1994 agreement. The central authorities of Moldova proved unwilling to accept the results initiating a lengthy stand-off between the autonomy and Chişinău. Finally Croitor resigned in 2002 due to the pressure from the Moldovan government which accused him of abuse of authority, relations with the separatist authorities of Transnistria and other charges. The central electoral commission of Gagauzia did not register Croitor as a candidate for the post of the Governor in the subsequent elections and Gheorgi Tabunshik was elected in what was described as unfair elections.
Geography
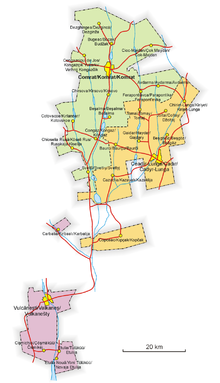
Gagauzia consists of a main central part around the cities Comrat and Ceadîr-Lunga (Gagauz: Çadır-Lunga); one larger enclave around the city of Vulcăneşti; and two smaller enclaves, the villages of Copceac and Carbalia.
Administrative divisions
Gagauzia consists of one municipality, two cities, and twenty-three communes containing a total of thirty-two localities.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| if different from official name. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Politics
The autonomy of Gagauzia is guaranteed by the Moldovan constitution and regulated by the 1994 Gagauz Autonomy Act. If Moldova decided to unite with Romania, Gagauzia would have the right of self-determination. The Gagauzian People's Assembly (Adunarea Populară; Gagauz: Halk Topluşu) has a mandate for lawmaking powers within its own jurisdiction. This includes laws on education, culture, local development, budgetary and taxation issues, social security, and questions of territorial administration. The People's Assembly also has two special powers: it may participate in the formulation of Moldova's internal and foreign policy; and, should central regulations interfere with the jurisdiction of Gagauz-Yeri, it has the right of appeal to Moldova's Constitutional Court.
The highest official of Gagauzia, who heads the executive power structure, is the Governor of Gagauzia (Moldovan: Guvernatorul Găgăuziei; Gagauz: Bashkan). He or she is elected by popular suffrage for a four-year term. He has power over all public administrative bodies of Gagauzia, and is also a member of the Government of the Republic of Moldova. Eligibility for governorship requires fluency in the Gagauz language, Moldovan citizenship, and a minimum age of 35 years.
Permanent executive power in Gagauz-Yeri is exercised by the Executive Committee (Comitetul Executivor Bakannik Komiteti). Its members are appointed by the Governor, or by a simple majority vote in the Assembly at its first session. The Committee ensures the application of the laws of the Republic of Moldova and those of the Assembly of Gagauz-Yeri.
As part of its autonomy, Gagauzia has its own police force.
"The Peoples Movement Gagauz Khalky" is a Gagauz separatist political party.
| Politics of Europe | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other entities | |
| Other entities | |
Economy
The base of the Gagauzian economy is agriculture, particularly viticulture. The main export products are wine, sunflower oil, non-alcoholic beverages, wool, leather and textiles. There are twelve wineries, processing over 400,000 tonnes annually. There are also two oil factories, two carpet factories, one meat factory, and one non-alcoholic beverages factory.
Transport
There are 451 kilometers of roads in Gagauzia, of which 82% are paved. Turkey loaned Moldova 35 million dollars to improve Gagauzia's road network.
Demographics
According to the 2004 census, Gagauzia had a population of 155,646, of which 58,190 lived in cities and 97,456 in rural communities.
Ethnic composition
- 127,835 (82.13%) Gagauz
- 8,013 (5.15%) Bulgarians
- 7,481 (4.83%) Moldovans
- 5,941 (3.82%) Russians
- 4,919 (3.16%) Ukrainians
- 486 (0.31%) Gypsies
- 38 (0.02%) Romanians
- 28 (0.02%) Poles
- 17 (0.01%) Jews
- 878 (0.56%) others
- 10 (0.01%) non-declared
Note: There is an ongoing controversy, whether Romanians and Moldovans are the same ethnic group. In the census every citizen had to write in either Moldovan, Romanian, Ukrainian, Russian, Bulgarian, Gagauz, Pole etc. Accordingly, one couldn't declare himself both Moldovan and Romanian. The combined figure for Moldovans (Romanians) is 7,519 (4.85%).
Culture and education
Gagauzia has fifty-five schools, the Comrat Pedagogical College (high school+two years over high school), and Comrat State University (Universitatea de Stat din Comrat ). Turkey financed the creation of a Turkish cultural centre (Türk İşbirliği Ve Kalkınma İdaresi Başkanlığı) and a Turkish library (Atatürk Kütüphanesi). In the village of Beşalma, there is a Gagauz historical and ethnographical museum established by Dmitrii Kara Coban.
See also
- Conflict in Transnistria and Gagauzia
- List of Chairmen of the Gagauzian People's Assembly
- Turks of Romania
References
- Information on previous elections of Governor of Gagauz ATU Template:En icon Template:Ru icon Template:Ro icon)
- Moldova Strategic Conflict Assessment (SCA), Stuart Hensel, Economist Intelligence Unit.
- Template:Ro icon Organic Law No. 292-XIV (see Annex 4), Republic of Moldova, 19 February 1999.
- East - West Working Group. Levente Benkö. Autonomy in Gagauzia: A Precedent for Central and Eastern Europe?
- "Opinion on the Law on Modification and Addition in the Constitution of the Republic of Moldova in Particular Concerning the Status of Gagauzia". Council of Europe. 2002. Retrieved 2007-11-24.
- Template:Ro icon Moldovan law on the special legal status of Gagauzia
- Population Census of 2004, National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova. Accessed on July 5, 2009
- Comrat, str. Galaţan, 17, tel: (0-298) 2-43-45
Further reading
- Chinn, Jeff (1998). "Territorial autonomy in Gagauzia". Nationalities Papers. 26 (1): 87–101. doi:10.1080/00905999808408552.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|laydate=,|quotes=,|laysource=, and|laysummary=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
External links
- www.comrat.md - Official website of Comrat - the capital of Gagauzia
- www.gagauzia.md - Official website of Gagauzia
- www.edingagauz.com - Newspaper of Social Movement "Edinaya Gagauzia"
- www.kdu.md - Komrat Devlet Universiteti (Comrat State University)
- www.gagauz.tv - «Gagauziya Radio Televizionu»
- Weather forecast for Comrat
- Images of Gagauzia
- ww.budjak.com - Gagauzia news
- Mari Kiz, Gagauzian folk music
- The law on the special legal status of Gagauzia
- Moldova: The Example Of Gagauz-Yeri As An 'Unfrozen Conflict' Region
- News in Gagauz
- moldovarious.com - Social, cultural and political life in Gagauzia
| Geographic locale | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||