This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Edgar181 (talk | contribs) at 13:30, 26 July 2009 (unneeded - NDGA now a disambig). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 13:30, 26 July 2009 by Edgar181 (talk | contribs) (unneeded - NDGA now a disambig)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)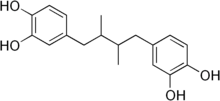 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 4,4'-(2,3-dimethylbutane-1,4-diyl)dibenzene-1,2-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.185 |
| MeSH | Nordihydroguaiaretic+acid |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C18H22O4 |
| Molar mass | 302.365 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Nordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA) is a potent antioxidant compound found in the long-lived creosote bush. It is believed that NDGA reduces cell damage by free radicals, so under the free-radical theory of aging, could be responsible for the bush's long life. A 1986 study involved feeding female mosquitos NDGA to test the effect on their average life span. While the usual mosquito life span was 29 days, the NDGA-fed mosquitos lived an average of 45 days—an increase of 50 percent. Nordihydroguaiaretic acid is also published as lengthening the lifespan of mice
The plant has been used to treat a variety of illnesses including infertility, rheumatism, arthritis, diabetes, gallbladder and kidney stones, pain and inflammation but its use is controversial. It was widely used during the 1950s as a food preservative and to preserve natural fibers but was later banned after reports of toxicity during the early 1960s. Recently, it has been used as a nutritional supplement, however renal and hepatotoxicity are reported for chronic use of creosote bush and NDGA.
References
- Richie JP Jr, Mills BJ, Lang CA. "Dietary nordihydroguaiaretic acid increases the life span of the mosquito." Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Oct;183(1):81-5
- Adapted from Arteaga S, Andrade-Cetto A, Cardenas R. "Larrea tridentata (Creosote bush), an abundant plant of Mexican and US-American deserts and its metabolite nordihydroguaiaretic acid." J Ethnopharmacol. 2005 Apr 26;98(3):231-9