This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Edgar181 (talk | contribs) at 18:48, 21 June 2011 (Disambiguate Telluride to Telluride (chemistry) using popups). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 18:48, 21 June 2011 by Edgar181 (talk | contribs) (Disambiguate Telluride to Telluride (chemistry) using popups)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Cadmium(II) iodide | |
| Other names Cadmium diiodide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.294 |
| EC Number |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | CdI2 |
| Molar mass | 366.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | white to pale yellow crystals |
| Density | 5.640 g/cm, solid |
| Melting point | 387 °C (729 °F; 660 K) |
| Boiling point | 742 °C (1,368 °F; 1,015 K) |
| Solubility in water | 787 g/L (0 °C) 847 g/L (20 °C) 1250 g/L (100 °C) |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, acetone, ether and ammonia |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Trigonal, hP3, space group P3m1, No. 164 |
| Coordination geometry | octahedral |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | cadmium fluoride cadmium chloride cadmium bromide |
| Other cations | zinc iodide mercury(II) iodide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Cadmium iodide, CdI2, is a chemical compound of cadmium and iodine. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects.
Uses
Cadmium iodide is used in lithography, photography, electroplating and the manufacturing of phosphors.
Preparation
Cadmium iodide is prepared by the addition of cadmium metal, or its oxide, hydroxide or carbonate to hydroiodic acid.
Also, the compound can be made by heating cadmium with iodine.
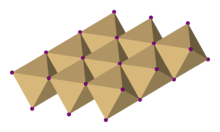
Crystal structure
In cadmium iodide the iodide anions form a hexagonal close packed arrangement while the cadmium cations fill all of the octahedral sites in alternate layers. The resultant structure consists of a layered lattice. This same basic structure is found in many other salts and minerals. Cadmium iodide is mostly ionically bonded but with partial covalent character.
Cadmium iodide's crystal structure is the prototype on which the crystal structures many other compounds can be considered to be based. Compounds with any of the following characteristics tend to adopt the CdI2 structure:
- Iodides of moderately polarising cations; bromides and chlorides of strongly polarising cations
- Hydroxides of dications, i.e. compounds with the general formula M(OH)2
- Sulfides, selenides and tellurides (chalcogenides) of tetracations, i.e. compounds with the general formula MX2, where X = S, Se, Te
Compounds with the CdI2 crystal structure

Iodides
MgI2, TiI2, VI2, MnI2, FeI2, CoI2, CaI2, PdI2, PbI2.
Chlorides and bromides
MgBr2, TiBr2, VBr2, MnBr2, FeBr2, CoBr2.
Hydroxides of M
Chalcogenides of M
TiS2, ZrS2, SnS2, α-TaS2, PtS2;
SiTe2, TiTe2, CoTe2, NiTe2, PdTe2, PtTe2.
Others
References
- Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0070494398
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 1211–1212. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
| Cadmium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Cadmium(I) | |
| Cadmium(II) | |