This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 00:25, 1 July 2011 (Updating {{drugbox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 00:25, 1 July 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{drugbox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Pharmaceutical compound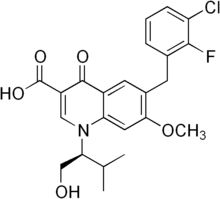 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H23ClFNO5 |
| Molar mass | 447.883 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Elvitegravir (EVG) is an investigational new drug for the treatment of HIV infection. It acts as an integrase inhibitor. It is undergoing Phase III clinical trial conducted by the pharmaceutical company Gilead Sciences, which licensed EVG from Japan Tobacco in March 2008.
According to the results of the phase II clinical trial, patients taking once-daily elvitegravir boosted by ritonavir had greater reductions in viral load after 24 weeks compared to individuals randomized to receive a ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor.
References
- Gilead Press Release Phase III Clinical Trial of Elvitegravir July 22, 2008
- Gilead Press Release Gilead and Japan Tobacco Sign Licensing Agreement for Novel HIV Integrase Inhibitor March 22, 2008
- Shimura K, Kodama E, Sakagami Y; et al. (2007). "Broad Anti-Retroviral Activity and Resistance Profile of a Novel Human Immunodeficiency Virus Integrase Inhibitor, Elvitegravir (JTK-303/GS-9137)". J Virol. 82 (2): 764. doi:10.1128/JVI.01534-07. PMC 2224569. PMID 17977962.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Stellbrink HJ (2007). "Antiviral drugs in the treatment of AIDS: what is in the pipeline ?". Eur. J. Med. Res. 12 (9): 483–95. PMID 17933730.
- Thaczuk, Derek and Carter, Micheal. ICAAC: Best response to elvitegravir seen when used with T-20 and other active agents Aidsmap.com. 19 Sept. 2007.
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |