This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 14:41, 7 August 2011 (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:Wi). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:41, 7 August 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:Wi)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)- For the genus of grass skipper butterflies, see Chalcone (butterfly).
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 1,3-Diphenyl-2-propen-1-one | |
| Other names
Chalcone Chalkone Benzylideneacetophenone Phenyl styryl ketone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.119 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C15H12O |
| Molar mass | 208.26 g/mol |
| Density | 1.071 g/cm |
| Melting point | 55–57 °C |
| Boiling point | 345-348 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Chalcone is an aromatic ketone and an enone that forms the central core for a variety of important biological compounds, which are known collectively as chalcones or chalconoids.
Chemical synthesis
Chalcones can be prepared by an aldol condensation between a benzaldehyde and an acetophenone in the presence of sodium hydroxide as a catalyst.
This reaction has been found to work without any solvent at all - a solid-state reaction. The reaction between substituted benzaldehydes and acetophenones has been used to demonstrate green chemistry in undergraduate chemistry education. In a study investigating green chemistry synthesis, chalcones were also synthesized from the same starting materials in high temperature water (200 to 350 °C).
Chemical reactions
An example is the carbonyl reduction of chalcone by tributyltin hydride :
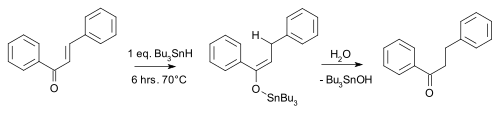 |
| Conjugate reduction chalcone |
|---|
An asymmetric version of this reaction has also been developed .
See also
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2028.
- Toda, F., et al., J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I, 1990, 3207.
- Palleros, D. R., J. Chem. Educ., 81, 1345 (2004).
- Comisar, C. M. and Savage, P. E. Green Chem., 6 (2004), 227 - 231. doi:10.1039/b314622g
- Leusink, A.J.; Noltes, J.G. (1966). "Reaction of organotin hydrides with α,β-unsaturated ketones". Tetrahedron Letters. 7 (20): 2221. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)72405-1.
- Moritani, Yasunori; Appella, Daniel H.; Jurkauskas, Valdas; Buchwald, Stephen L. (2000). "Synthesis of β-Alkyl Cyclopentanones in High Enantiomeric Excess via Copper-Catalyzed Asymmetric Conjugate Reduction". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 122 (28): 6797. doi:10.1021/ja0009525.
