This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 15:31, 8 August 2011 (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:Wi). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 15:31, 8 August 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:Wi)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)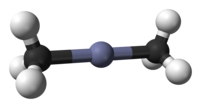
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name dimethylzinc | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.077 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | Zn(CH3)2 |
| Molar mass | 95.478 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Dimethylzinc, also known as Zinc methyl, DMZ, or DMZn is a colorless mobile liquid Zn(CH3)2, formed by the action of methyl iodide on zinc at elevated temperature or on zinc sodium alloy.
- 2Zn + 2CH3I → Zn(CH3)2 + ZnI2
The sodium assists the reaction of the zinc with the methyl iodide. Zinc iodide is formed as a byproduct.
It has a disagreeable odor, and is spontaneously flammable in air. It has been of great importance in the synthesis of organic compounds. It is soluble in alkanes and often sold as a solution in hexanes. It belongs to the large series of similar compounds such as diethylzinc.
History
This substance was first prepared by Edward Frankland during his work with Robert Bunsen in 1849 at the University of Marburg. After heating a mixture of zinc and methyl iodide in an airtight vessel a flame bursted out after the seal was broken. In laboratory scale the synthesis method did not change till today, except that copper or copper compounds are used to activate the zinc.
Dimethyl zinc was used for a long time to introduce methyl groups into organic molecules or to synthesize organometalic compounds containing methyl groups. Grignard reagents, (organo-magnesium compounds), which are easier to handle and less flammable replaced organo-zinc compounds in most laboratory syntheses. Due to differences in reactivity (as well as in reaction by-products) between organo-zinc compounds and Grignard reagents, organo-zinc compounds may be preferred in some syntheses.
References
- E. Frankland (1849). "Notiz über eine neue Reihe organischer Körper, welche Metalle, Phosphor u. s. w. enthalten". Liebig's Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie. 71 (2): 213–216. doi:10.1002/jlac.18490710206.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |