This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 20:17, 9 August 2011 (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:Wi). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 20:17, 9 August 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:Wi)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)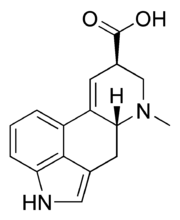 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 7-Methyl- 4,6,6a,7,8,9- hexahydro- indolo quinoline- 9-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names 6-Methyl- 9,10- didehydroergoline- 8-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.302 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C16H16N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 268.316 g·mol |
| Melting point | 238 - 240 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Lysergic acid, also known as D-lysergic acid and (+)-lysergic acid, is a precursor for a wide range of ergoline alkaloids that are produced by the ergot fungus and some plants. Amides of lysergic acid, lysergamides, are widely used as pharmaceuticals and as psychedelic drugs (LSD). Lysergic acid is usually produced by hydrolysis of lysergamides, but can also be synthesized in the laboratory by a complex total synthesis. Lysergic acid monohydrate crystallizes in very thin hexagonal leaflets when recrystallized from water. Lysergic acid monohydrate, when dried (140 °C at 2 mmHg or 270 Pa) forms anhydrous lysergic acid. Lysergic acid is a chiral compound with two stereocenters. The isomer with inverted configuration at carbon atom 8 close to the carboxy group is called isolysergic acid. Inversion at carbon 5 close to the nitrogen atom leads to L-lysergic acid and L-isolysergic acid, respectively. Lysergic acid is listed as a Table I precursor under the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances.

See also
- Lysergic acid diethylamide (also known as LSD/Acid)
- Lysergic acid amide (LSA/Ergine)
- Ergoline
- Lysergamides
References
- List of Precursors and Chemicals Frequently Used in the Illicit Manufacture of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Under International Control, International Narcotics Control Board
This hallucinogen-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |