This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 05:11, 13 September 2011 (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:WikiProject_Chemicals|error). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 05:11, 13 September 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:WikiProject_Chemicals|error)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)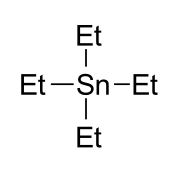
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Tetraethyltin | |
| Other names Tetraethyl tin | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | TET |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.007 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Tetraethyltin |
| PubChem CID | |
| UN number | 3384 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H20Sn |
| Molar mass | 234.958 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.187 g cm |
| Melting point | −112 °C (−170 °F; 161 K) |
| Boiling point | 181 °C (358 °F; 454 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | 53 °C |
| Related compounds | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Tetraethyltin or tetraethyl tin is a chemical compound with formula C
8H
20Sn and molecular structure (CH3CH2)4Sn, that is, a tin atom attached to four ethyl groups. It is an important example of an organotin compound, often abbreviated as TET.
Tetraethyltin is a colourless flammable liquid, soluble in diethyl ether and insoluble in water, that freezes at -112°C and boils at 181°C. It is used in the electronics industry.
Tetraethyltin can be obtained by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with tin(IV) chloride:
- SnCl4 + 4 (C2H5)MgBr → (CH3CH2)4Sn + 4 MgBrCl
The same reaction can be used to obtain tetra-n-propyltin and tetra-n-butyltin.
Tetraethyltin is converted in the body to the more toxic triethyltin.
See also
References
- ^ G. J. M. Van Der Kerk and J. G. A. Luijten (1956), "Tetraethyltin". Organic Syntheses, volume 36, page 86; Coll. Vol. 4, p.881 (1963)
- SAFC corp, tetraethyltin catalog page. Accessed on 2011-01-18.
- Jill E. Cremer (1958), "The biochemistry of organotin compounds. The conversion of tetraethyltin into triethyltin in mammals". Biochem J. volume 68, issue 4, pages 685–692. PMID 1200418
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |