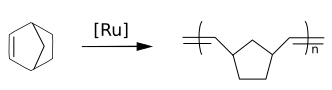This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Amirobot (talk | contribs) at 06:40, 15 September 2011 (r2.7.1) (robot Adding: it:Norbornene). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 06:40, 15 September 2011 by Amirobot (talk | contribs) (r2.7.1) (robot Adding: it:Norbornene)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name Bicyclohept-2-ene | |||
| Other names
Norbornylene Norcamphene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.152 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C7H10 | ||
| Molar mass | 94.157 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 | ||
| Flash point | −15 °C | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
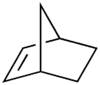
Norbornene or norbornylene or norcamphene is a bridged cyclic hydrocarbon. It is a white solid with a pungent sour odor. The molecule consists of a cyclohexene ring bridged with a methylene group in the para position. The molecule carries a double bond which induces significant ring strain and significant reactivity.
Norbornene, like many of its derivatives, is made by a Diels-Alder reaction of cyclopentadiene and ethylene. Related bicyclics are norbornadiene which has the same carbon skeleton but with two double bonds and norbornane which is completely saturated without double bonds.
Norbornene undergoes an acid-catalyzed hydration reaction with water to form norborneol. This reaction is of great interest to chemists studying non-classical ions.
Polynorbornenes
Norbornenes are important monomers in ring-opening metathesis polymerizations (ROMP) with for instance the Grubbs' catalyst. Polynorbornenes are polymers with high glass transition temperatures and high optical clarity.
In addition to ROMP polymerization, norbornene monomers also undergo vinyl-addition polymerization.
Ethylidene norbornene is a related monomer derived from cyclopentadiene and butadiene.
Practical uses
Norbornene does not have as many practical uses as ethylene or other commodity chemicals. It is utilized to make pharmaceutical intermediates, pesticide compounds, specialty fragrances and in general organic synthesis. When combined with ethylene, norbornene will react and turn into a cyclic olefin copolymer.
Polynorbornene, known under Norsorex, a brand from Astrotech Advanced Elastomerproducts GmbH since 2008, is used mainly in the rubber industry for anti-vibration (rail, building, industry), anti-impact (personal protective equipment, shoe parts, bumpers) and grip improvement (toy tires, racing tires, transmission systems, transports systems for copiers, feeders, etc.)
- Reachable performances: Loss factors (tan delta) larger than 3, rebounds of less than 1%, tear strengths of 50 N/mm², friction coefficients of 2 and more, Shore hardness between 4 and 90 Shore A.
- Second main application: oil-binding system with absorption capability of hydrocarbons, 10 times of own weight
References
- Norbornene MSDS
- Paul Binger, Petra Wedemann, and Udo H. Brinker. "Cyclopropene: A New Simple Synthesis and its Diels-Alder Reaction with Cyclopentadiene". Organic Syntheses
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collected Volumes, vol. 10, p. 231. - Masaji Oda, Takeshi Kawase, Tomoaki Okada, and Tetsuya Enomoto. "2-Cyclohexene-1,4-dione". Organic Syntheses
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link); Collected Volumes, vol. 9, p. 186.