This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 14:47, 22 October 2011 (Updating {{drugbox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'CAS_number_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:47, 22 October 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{drugbox}} (changes to verified fields - updated 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'CAS_number_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Pharmaceutical compound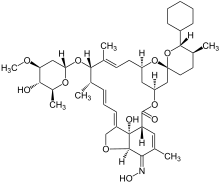 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Revolution, Stronghold |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATCvet code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.250.168 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C43H63NO11 |
| Molar mass | 769.96 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Selamectin (trade names Revolution, Stronghold) is a topical parasiticide and antihelminthic used on dogs and cats, distributed by Pfizer. It prevents heartworms, fleas, ear mites, sarcoptic mange (scabies), and certain types of ticks in dogs, and prevents heartworms, fleas, ear mites, hookworms, and roundworms in cats. Selamectin is not approved for human use.
Usage
Selamectin is generally prescribed for cats and smaller indoor dogs due to studies that have shown it does not work as well to prevent heartworms as some of the oral preventatives.
The drug is applied topically. It is waterfast, and does not lose its effectiveness with bathing. It is packaged according to its varying dosage sizes, and is applied once monthly.
Mode of action
Selamectin disables parasites by replacing glutamate in their muscle synapses; glutamate is the amino acid which normally interacts with the receptors that open chloride channels into the muscle. Selamectin interferes with this process; it activates the chloride current without desensitization, allowing chloride ions to enter the nerve cells and causing neuromuscular paralysis, impaired muscular contraction, and eventual death.
The substance fights both internal and surface parasitic infection. Absorbed into the body through the skin and hair follicles, it travels through the bloodstream, intestines, and sebaceous glands; parasites ingest the drug when they feed on the animal's blood.
Side effects
Selamectin has been found to be safe and effective in a 2003 review.
Selamectin has high safety ratings, with less than 1% of pets displaying side effects. In cases where side effects do occur, they most often include passing irritation or hair loss at the application site. Symptoms beyond these (such as drooling, rapid breathing, lack of coordination, vomiting, or diarrhea) could indicate the existence of a serious underlying cause, requiring immediate veterinary care.
Similar products
Main rival products for dogs include ivermectin (trade names Stromectol, Ivermec and others) or milbemycin oxime (Interceptor) for heartworms, fipronil (Frontline) or lufenuron (Program) for fleas, or the combination milbemycin oxime/lufenuron (Sentinel) for both.
References
- "Label for Revolution (selamectin topical solution) Topical Parasiticide for Dogs and Cats". Pfizer Canada Inc. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
- Pipano, E. (2003). "Recent Developments In The Control Of Ectoparasites And Endoparasites Of Dogs And Cats With Selamectin". Israel Journal of Veterianry Medicine. 58 (2–3). Archived from the original on April 14, 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)