This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Beetstra (talk | contribs) at 09:02, 31 October 2011 (Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'ChEMBL', 'CASNo').). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 09:02, 31 October 2011 by Beetstra (talk | contribs) (Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'ChEMBL', 'CASNo').)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)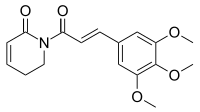
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 1--5,6-dihydropyridin-2(1H)-one | |
| Other names Piplartine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.243.690 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C17H19NO5 |
| Molar mass | 317.341 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Piperlongumine (PL) is a natural product constituent of the fruit of the Long pepper (Piper longum), a pepper plant found in southern India and southeast Asia.
Piperlongumine may have anti-cancer properties. It selectively targets and kills cancer cells but leaving normal cells unharmed. "In mice injected with human bladder, breast, lung, or melanoma cancer cells, PL inhibited tumor growth but showed no toxicity in normal mice. In a tougher test of mice that developed breast cancer spontaneously, PL blocked both tumor growth and metastasis."
References
- ^ Raj, Lakshmi; Ide, Takao; Gurkar, Aditi U.; Foley, Michael; Schenone, Monica; Li, Xiaoyu; Tolliday, Nicola J.; Golub, Todd R.; Carr, Steven A. (2011). "Selective killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targeting the stress response to ROS". Nature. 475 (7355): 231–234. doi:10.1038/nature10167. PMID 21753854.
- "Novel Compound Selectively Kills Cancer Cells by Blocking Their Response to Oxidative Stress". ScienceDaily. July 2011.