This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Smokefoot (talk | contribs) at 15:29, 25 January 2014 (a ref). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 15:29, 25 January 2014 by Smokefoot (talk | contribs) (a ref)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)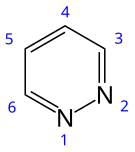
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name Pyridazine | |||
| Other names 1,2-diazine, orthodiazine, oizine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.478 | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C4H4N2 | ||
| Molar mass | 80.09 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.107 g/cm | ||
| Melting point | −8 °C (18 °F; 265 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 208 °C (406 °F; 481 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Pyridazine is a heteroaromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C4H4N2, sometimes called 1,2-diazine. It contains a six-membered ring with two adjacent nitrogen atoms. It is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 208 °C.
The pyridazine structure is found within a number of herbicides such as credazine, pyridafol and pyridate. It is also found within the structure of several drugs such as cefozopran, cadralazine, minaprine, pipofezine, hydralazine, and cilazapril. These heterocycles are often prepared via condensation of 1,4-diketones or 4-ketoacids and hydrazine]].
References
- M. Tišler, B. Stanovnik "Pyridazines" Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry, Volume 9, 1968, Pages 211-320. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60374-8