This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Enthusiast01 (talk | contribs) at 04:28, 9 May 2014 (→Consequences). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 04:28, 9 May 2014 by Enthusiast01 (talk | contribs) (→Consequences)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) This article is about the act of adultery or extramarital sex. For other uses, see Adultery (disambiguation). For a broad overview, see Religion and sexuality.| Family law |
|---|
| Family |
| Marriage and other unions and status |
| Validity of marriages |
| Dissolution of marriages |
Children's issues
|
| Private international law |
|
Family and criminal code (or criminal law) |
Adultery (anglicised from Latin adulterium) is extramarital sex that is considered objectionable on social, religious, moral or legal grounds. What sexual activities constitute adultery vary widely, as do the religious and legal consequences of such acts. The concept exists in many societies, though the definition and consequences vary, but the concept is similar in Islam, Christianity and Judaism.
Historically, adultery has been considered a very serious offense by many cultures, with the act of a man having sexual relations with another man's wife most often incurring very severe punishment for both the wife and her lover, including the death penalty, mutilation or torture. Such punishments have gradually fallen into disfavor, especially from the 19th century onwards. In most Western countries, adultery is no longer a criminal offense. Nevertheless, even in jurisdictions where adultery is not a criminal offense, it may still have legal consequences, particularly in divorce cases. For example, where there is fault-based family law, it almost always constitutes grounds for divorce; depending on jurisdiction, it may be a factor to consider in a property settlement, the custody of children, the denial of alimony etc. Moreover, adultery can affect the social status of those involved, and result in social ostracism in some parts of the world.
In countries where adultery is illegal, punishments range from fines to caning and even the death penalty. In the 21st century, criminal laws against adultery have become controversial, with international organizations calling for their abolition, especially in the light of several high profile stoning cases that have occurred in certain countries. The head of the U.N. expert body charged with identifying ways to eliminate laws that discriminate against women or are discriminatory to them in terms of implementation or impact, Kamala Chandrakiran, has stated that: "Adultery must not be classified as a criminal offence at all". A joint statement by the United Nations Working Group on discrimination against women in law and in practice states that: "Adultery as a criminal offence violates women’s human rights".
Some ultra-conservative Islamic societies with sharia law may implement stoning as punishment for adultery. Most countries that criminalize adultery are those where the dominant religion is Islam, and several Sub-Saharan African Christian-majority countries, but there are some notable exceptions to this rule, namely Philippines, South Korea, Taiwan, and several US states.
Overview
The application of the term to the act appears to arise from the idea that "criminal intercourse with a married woman ... tended to adulterate the issue of an innocent husband ... and to expose him to support and provide for another man's ". Thus, the "purity" of the children of a marriage is corrupted, and the inheritance is altered. The law often uses the word "adulterate" to describe contamination of food and the like.
Three 1990s studies in the United States, using nationally representative samples, have found that about 10–15% of women and 20–25% of men admitted to having engaged in extramarital sex. Other studies in the US have higher numbers (see United States below).
Definitions and legal constructs
In the traditional English common law, adultery was a felony. Although the legal definition of adultery differs in nearly every legal system, the common theme is sexual relations outside of marriage, in one form or another.
Adultery involving a married woman and a man other than her husband was considered a very serious crime; in 1707, English Lord Chief Justice John Holt stated that a man having sexual relations with another man's wife was "the highest invasion of property" and claimed, in regard to the aggrieved husband, that "a man cannot receive a higher provocation".
The Encyclopedia of Diderot & d'Alembert, Vol. 1 (1751), also equated adultery to theft writing that "adultery is, after homicide, the most punishable of all crimes, because it is the most cruel of all thefts, and an outrage capable of inciting murders and the most deplorable excesses."
Legal definitions of adultery vary. For example, New York defines an adulterer as a person who "engages in sexual intercourse with another person at a time when he has a living spouse, or the other person has a living spouse." North Carolina defines adultery as occurring when any man and woman "lewdly and lasciviously associate, bed, and cohabit together." Minnesota law provides: "when a married woman has sexual intercourse with a man other than her husband, whether married or not, both are guilty of adultery." In the 2003 New Hampshire Supreme Court case Blanchflower v. Blanchflower, it was held that female same-sex sexual relations did not constitute sexual intercourse, based on a 1961 definition from Webster's Third New International Dictionary; and thereby an accused wife in a divorce case was found not guilty of adultery. In 2001, Virginia prosecuted an attorney, John R. Bushey, for adultery, a case that ended in a guilty plea and a $125 fine. Adultery is against the governing law of the U.S. military.
In common-law countries, adultery was also known as criminal conversation. This became the name of the civil tort arising from adultery, being based upon compensation for the other spouse's injury. Criminal conversation was usually referred to by lawyers as crim. con., and was abolished in England in 1857, and the Republic of Ireland in 1976. Another tort, alienation of affection, arises when one spouse deserts the other for a third person. This act was also known as desertion, which was often a crime as well. A small number of jurisdictions still allow suits for criminal conversation and/or alienation of affection. In the United States, seven states still maintain this tort.
A marriage in which both spouses agree ahead of time to accept sexual relations by either partner with others is sometimes referred to as an open marriage or the Swinging lifestyle. Both are a form of non-monogamy, and the spouses would not view the sexual relations as adultery. However, irrespective of the stated views of the partners, extra-marital relations could still be considered adultery and a crime in some legal jurisdictions.
In Canada, though the written definition in the Divorce Act refers to extramarital relations with someone of the opposite sex, a British Columbia judge used the Civil Marriage Act in a 2005 case to grant a woman a divorce from her husband who had cheated on her with another man, which the judge felt was equal reasoning to dissolve the union.
In the United Kingdom, case law restricts the definition of adultery to penetrative sexual intercourse between a man and a woman, no matter the gender of the spouses in the marriage, although infidelity with a person of the same gender can be grounds for a divorce as unreasonable behavior; this situation was discussed at length during debates on the Marriage (Same-Sex Couples) Bill.
In India, adultery is the sexual intercourse of a man with a married woman without the consent of her husband when such sexual intercourse does not amount to rape. It is a non-cognizable, non-bailable criminal offence. A police officer cannot arrest a person without a warrant in a case of adultery as adultery is a non-cognizable offence.
Legal issues regarding paternity
Further information: Paternity (law)
Historically, paternity of children born out of adultery has been seen as a major issue. Modern advances such as reliable contraception and paternity testing have changed the situation (in Western countries). Most countries nevertheless have a legal presumption that a woman's husband is the father of her children who were born during that marriage. Although this is often merely a rebuttable presumption, many jurisdictions have laws which restrict the possibility of legal rebuttal (for instance by creating a legal time limit during which paternity may be challenged - such as a certain number of years from the birth of the child). Establishing correct paternity may have major legal implications, for instance in regard to inheritance.
Children born out of adultery suffered, until recently, adverse legal and social consequences. In France, for instance, a law that stated that the inheritance rights of a child born under such circumstances were, on the part of the married parent, half of what they would have been under ordinary circumstances, remained in force until 2001, when France was forced to change it by a ruling of the European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) (and in 2013 the ECtHR also ruled that the new 2001 regulations must be also applied to children born before 2001).
There has been, in recent years, a trend of legally favoring the right to a relation between the child and its biological father, rather than preserving the appearances of the 'social' family. In 2010, the ECtHR ruled in favor of a German man who had fathered twins with a married woman, granting him right of contact with the twins, despite the fact that the mother and her husband had forbidden him to see the children.
Prevalence
Durex's Global Sex Survey found that worldwide 22% of people surveyed admitted to have had extramarital sex. A 2005 scientific review of international published studies of paternal discrepancy found a range in incidence from 0.8% to 30% (median 3.7%), suggesting that the widely quoted figure of 10% of non-paternal events is an overestimate.
In the United States Alfred Kinsey found in his studies that 50% of males and 26% of females had extramarital sex at least once during their lifetime. Depending on studies, it was estimated that 26–50% of men and 21–38% women, or 22.7% of men and 11.6% of women, had extramarital sex. Other authors say that between 20% and 25% of Americans had sex with someone other than their spouse.
Cultural and religious traditions
Relationships (Outline) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Types
|
|||||||||
| Activities | |||||||||
| Endings | |||||||||
| Emotions and feelings | |||||||||
| Practices | |||||||||
| Abuse | |||||||||

Greco-Roman world
In the Greco-Roman world there were stringent laws against adultery, but these applied to sexual intercourse with a married woman. In the early Roman Law the jus tori belonged to the husband. It was therefore not a crime against the wife for a husband to have sex with a slave or an unmarried woman.
It is well known that the Roman husband often took advantage of his legal immunity. Thus we are told by the historian Spartianus that Verus, the imperial colleague of Marcus Aurelius, did not hesitate to declare to his reproaching wife: "Uxor enim dignitatis nomen est, non voluptatis." ('Wife' connotes rank, not sexual pleasure, or more literally "Wife is the name of dignity, not bliss") (Verus, V).
Later in Roman history, as William E.H. Lecky has shown, the idea that the husband owed a fidelity similar to that demanded of the wife must have gained ground, at least in theory. Lecky gathers from the legal maxim of Ulpian: "It seems most unfair for a man to require from a wife the chastity he does not himself practice".
The lending of wives practiced among some people was, as Plutarch tells us, encouraged also by Lycurgus, though from a motive other than that which actuated the practice (Plutarch, Lycurgus, XXIX). The recognized license of the Greek husband may be seen in the following passage of the Oration against Neaera, the author of which is uncertain, though it has been attributed to Demosthenes:
- We keep mistresses for our pleasures, concubines for constant attendance, and wives to bear us legitimate children and to be our faithful housekeepers. Yet, because of the wrong done to the husband only, the Athenian lawgiver Solon allowed any man to kill an adulterer whom he had taken in the act. (Plutarch, Solon)
The Roman Lex Julia, Lex Iulia de Adulteriis Coercendis (17 BC), punished adultery with banishment The two guilty parties were sent to different islands ("dummodo in diversas insulas relegentur"), and part of their property was confiscated. Fathers were permitted to kill daughters and their partners in adultery. Husbands could kill the partners under certain circumstances and were required to divorce adulterous wives.
Abrahamic religions
See also: Extramarital sex § Religions, and Fornication § ReligionsBiblical sources
Main article: Thou shalt not commit adultery
The Hebrew Bible (the Tanakh or Old Testament) prohibits adultery in the seventh of the Ten Commandments (Exodus 20:12) (sixth Commandments in Christian enumeration and in verse Exodus 20:14). Adultery in traditional Judaism applies unequally to both parties.
For instance, the Old Testament book of Leviticus prescribes capital punishment for adultery between a man and married woman, though not for adultery between a woman and a married man.
And the man that committeth adultery with another man's wife, even he that committeth adultery with his neighbour's wife, the adulterer and the adulteress shall surely be put to death. (Lev. 20:10).
Furthermore, Deuteronomic code prescribes stoning not only for female extramarital sex, but also for female premarital sex in the case where the woman lies about her virginity.
If any man take a wife, and go in unto her, … and say, / I took this woman, and when I came to her, I found her not a maid. / … But if this thing be true, and the tokens of virginity be not found for the damsel: / Then they shall bring out the damsel to the door of her father's house, and the men of her city shall stone her with stones that she die. (Deut. 22:13-21).
It also prescribes the same for engaged women who lie with another man, under the premise that if she allows the action without protesting, this indicates willingness.
If a damsel that is a virgin be betrothed unto an husband, and a man find her in the city, and lie with her; / Then ye shall bring them both out unto the gate of that city, and ye shall stone them with stones that they die; the damsel, because she cried not, being in the city. (Deut. 22:23-24).
Book of Mormon sources
The Book of Mormon also prohibits adultery. For instance, Abinadi cites the Ten Commandments when he accuses Noah's priests of sexual immorality. When Jesus Christ visits the Americas he reinforces the law and teaches them the higher law (also found in the New Testament):
- Behold, it is written by them of old time, that thou shalt not commit adultery; but I say unto you, that whosoever looketh on a woman, to lust after her, hath committed adultery already in his heart.
Book of Mormon prophets and civil leaders often list adultery as an illegal activity along with murder, robbing, and stealing.
Christianity
See also: Extramarital sex § Christianity, Christian views on marriage, Christian views on divorce, and Pauline privilegeAdultery is considered by Christians to be immoral and a sin, based primarily on passages like 1 Corinthians 6:9–10. Although 1 Corinthians 6:11 does say that "and that is what some of you were. But you were washed", it still acknowledges adultery to be immoral and a sin. The sixth commandment (seventh in some traditions) ("Thou shalt not commit adultery") is also a basis, but see also Biblical law in Christianity.
Jesus taught that indulgence in adulterous thoughts could be just as harmful to the soul as actual adultery, and it is clear that both carry the same weight of guilt:
- But I tell you that anyone who looks at a woman lustfully has already committed adultery with her in his heart. (Matthew 5:28)
and He also says:
- But I tell you that anyone who divorces his wife, except for marital unfaithfulness, causes her to become an adulteress, and anyone who marries the divorced woman commits adultery.(Matthew 5:32)
However, Christ also showed forbearance to those committing adultery, although still commanding repentance, perhaps most famously in the story related in the Eighth Chapter of John:
Then the scribes and Pharisees brought to Him a woman caught in adultery. And when they had set her in the midst, they said to Him, “Teacher, this woman was caught in adultery, in the very act. Now Moses, in the law, commanded us that such should be stoned. But what do You say?” This they said, testing Him, that they might have something of which to accuse Him. But Jesus stooped down and wrote on the ground with His finger, as though He did not hear.
So when they continued asking Him, He raised Himself up and said to them, “He who is without sin among you, let him throw a stone at her first.” And again He stooped down and wrote on the ground. Then those who heard it, being convicted by their conscience, went out one by one, beginning with the oldest even to the last. And Jesus was left alone, and the woman standing in the midst. When Jesus had raised Himself up and saw no one but the woman, He said to her, “Woman, where are those accusers of yours? Has no one condemned you?”
She said, “No one, Lord.”
And Jesus said to her, “Neither do I condemn you; go and sin no more.” ~John 8: 3-11
Some churches have interpreted adultery to include all sexual relationships outside of marriage, regardless of the marital status of the participants.
Judaism
Adultery in traditional Judaism applies to both parties, but depends on the marital status of the woman (Lev. 20:10). Though the Torah prescribes the death penalty for adultery, the legal procedural requirements were very exacting and required the testimony of two eyewitnesses of good character for conviction. The defendant also must have been warned immediately before performing the act. A death sentence could be issued only during the period when the Holy Temple stood, and only so long as the Supreme Torah Court convened in its chamber within the Temple complex. Today, therefore, no death penalty applies. The death penalty for adultery was strangulation, except in the case of a woman who was the daughter of a Kohain (Aaronic priestly caste), which was specifically mentioned by Scripture by the death penalty of burning (pouring molten lead down the throat). Ipso facto, there never was mentioned in Pharisaic or Rabbinic Judaism sources a punishment of stoning for adulterers as mentioned in John 8.
At the civil level, however, Jewish law (halakha) forbids a man to continue living with an adulterous wife, and he is obliged to divorce her. Also, an adulteress is not permitted to marry the adulterer, but, to avoid any doubt as to her status as being free to marry another or that of her children, many authorities say he must give her a divorce as if they were married.
According to Judaism, the Seven laws of Noah apply to all of humankind; these laws prohibit adultery with another man's wife.
Islam
Main article: Zina (Arabic) See also: Extramarital sex § IslamZina (زنا) is an Arabic term for illegal intercourse; premarital or extramarital. Various conditions and punishments have been attributed to adultery.
Under Muslim law, adultery in general is sexual intercourse by a person (whether man or woman) with someone to whom they are not married. Adultery is a violation of the marital contract and one of the major sins condemned by Allah in the Qur'an:
Qur'anic verses prohibiting adultery include:
- "Do not go near to adultery. Surely it is a shameful deed and evil, opening roads (to other evils)."
- "Say, 'Verily, my Lord has prohibited the shameful deeds, be it open or secret, sins and trespasses against the truth and reason."'
Punishments are reserved to the legal authorities and false accusations are to be punished severely. It has been said that these legal procedural requirements were instituted to protect women from slander and false accusations: i.e. four witnesses of good character are required for conviction, who were present at that time and saw the deed taking place; and if they saw it they were not of good moral character, as they were looking at naked adults; thus no one can get convicted of adultery unless both of the accused also agree and give their confession under oath four times.
The punishment prescribed by the Qur'an is flogging 100 times in public for those found guilty. According to the prophet Muhammad, an unmarried person who commits adultery or fornication is punished by flogging 100 times; a married person, however, may receive the heavier punishment of stoning to death if convicted of adultery. A survey conducted by the Pew Research Center found support for stoning as a punishment for adultery mostly in Arab countries, such as in Egypt (82% of respondents in favor of the punishment) and Jordan (70% in favor), as well as Pakistan (82% favor), whereas Nigeria (56% in favor) and in Indonesia (42% in favor) opinion is more divided, perhaps due to diverging traditions and differing interpretations of Sharia.
Other historical practices


In Native American cultures, severe penalties could be imposed on an adulterous wife by her husband. In many instances she was made to endure a bodily mutilation which would, in the mind of the aggrieved husband, prevent her from ever being a temptation to other men again. Among the Aztecs, wives caught in adultery were occasionally impaled, although the more usual punishment was to be stoned to death.
The Laws of Manu of ancient India, for example, said: "though destitute of virtue or seeking pleasure elsewhere, or devoid of good qualities, yet a husband must be constantly worshiped as a god by a faithful wife"; on the other, hand, "if a wife, proud of the greatness of her relatives or excellence, violates the duty which she owes to her lord, the king shall cause her to be devoured by dogs in a place frequented by many."
In England and its successor states, it has been high treason to engage in adultery with the King's wife, his eldest son's wife and his eldest unmarried daughter. The jurist Sir William Blackstone writes that "the plain intention of this law is to guard the Blood Royal from any suspicion of bastardy, whereby the succession to the Crown might be rendered dubious." Adultery was a serious issue when it came to succession to the crown. Philip IV of France had all three of his daughters-in-law imprisoned, two (Margaret of Burgundy and Blanche of Burgundy) on the grounds of adultery and the third (Joan of Burgundy) for being aware of their adulterous behaviour. The two brothers accused of being lovers of the king's daughters-in-law were executed immediately after being arrested. The wife of Philip IV's eldest son bore a daughter, the future Joan II of Navarre, whose paternity and succession rights were disputed all her life.
Consequences
Law
See also: Extramarital sex § LawAfrica
Adultery is a crime in many African countries, often with harsh penalties, especially in countries with a Muslim majority. For instance, stoning sentences have been given in Sudan and Somalia.
Asia
In some East Asian countries or regions, including North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan, adultery continues to be a crime. In the Philippines, adultery (defined as consensual sexual intercourse between a married woman and a man who is not her husband) and a related act of concubinage (a man cohabiting with a woman who is not his wife), are considered crimes under the Revised Penal Code of the Philippines. Adultery is not a crime in mainland China, but constitutes grounds for divorce.
In Pakistan, adultery is a crime under the Hudood Ordinance. The Ordinance sets a maximum penalty of death, although only imprisonment and corporal punishment have ever actually been imposed. The Ordinance has been particularly controversial because it requires a woman making an accusation of rape to provide extremely strong evidence to avoid being charged with adultery herself. A conviction for rape is only possible with evidence from no fewer than four witnesses. In recent years high-profile rape cases in Pakistan have given the Ordinance more exposure than similar laws in other countries. Similar laws exist in some other Muslim countries, such as Saudi Arabia.
In Indian law, adultery is defined as sex between a man and a woman without the consent of the woman's husband. The man is prosecutable and can be sentenced for up to five years (even if he himself was unmarried) whereas the married woman cannot be jailed. Men have called the law gender discrimination in that women cannot be prosecuted for adultery and the National Commission of Women has criticized the British era law of being anti-feminist as it treats women as the property of their husbands and has consequentially recommended deletion of the law or reducing it to a civil offense. The Government is yet to act. Extramarital sex without the consent of one's partner can be a valid grounds for monetary penalty on government employees, as ruled by the Central Administrative Tribunal.
In Southwest Asia, adultery has attracted severe sanctions, including death penalty. In some places, such as Saudi Arabia, the method of punishment for adultery is stoning to death. Proving adultery under Muslim law can be a very difficult task as it requires the accuser to produce four eyewitnesses to the act of sexual intercourse, each of whom should have a good reputation for truthfulness and honesty. The criminal standards do not apply in the application of social and family consequences of adultery, where the standards of proof are not as exacting. Sandra Mackey, author of The Saudis: Inside the Desert Kingdom, stated in 1987 that in Saudi Arabia, "unlike the tribal rights of a father to put to death a daughter who has violated her chastity, death sentences under Koranic law are extremely rare."
Europe
Adultery is not a crime in European countries. Until quite recently however, several Western countries had anti-adultery laws on their books. Among the last European countries to decriminalize adultery were Italy (1969), Portugal (1974), France (1975), Spain (1981), Greece (1983), Belgium (1987) and Austria (1997). Before the 20th century, adultery was often punished harshly. In Scandinavia, in the 17th century, adultery and bigamy were subject to the death penalty, although few people were actually executed.
In most Communist countries adultery was not a criminal offense, although there were exceptions, most notably Romania, where adultery remained a crime until 2006.
In Turkey adultery was decriminalized in 1996/1998 because the law was deemed discriminatory as it differentiated between women and men. In 2004, there were new discussions about re-criminalizing adultery, this time through a gender-neutral offense. The plans were dropped, and it has been suggested that the objections from the European Union played a role.
The European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) has had the opportunity to rule in recent years on several cases involving the legitimacy of firing a person from their job due to adultery. These cases dealt with people working for religious organizations and raised the question of the balancing of the right of a person to respect for their private life (recognized in the EU) and the right of religious communities to be protected against undue interference by the State (recognized also in the EU). These situations must be analyzed with regard to their specific circumstances, in each case. The ECtHR had ruled both in favor of the religious organization (in the case of Obst) and in favor of the fired person (in the case of Schüth).
United States
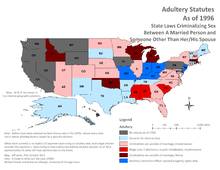


In the United States, laws vary from state to state. As at 2014, adultery is a criminal offense in 21 states. In those states where adultery is still on the statute books (although prosecutions are rare), penalties vary from life sentence (Michigan) to a $10 fine (Maryland) to a Class B misdemeanor (New York) to a Class I felony (Wisconsin). In South Carolina, the fine for adultery is up to $500 and/or imprisonment for no more than one year , yet the divorce laws codified at South Carolina Code Section 20-3-60(A) deny alimony to the adulterous spouse, which in some cases can cost the adulterous spouse millions of dollars in future income. Other states where adultery is an offence include Massachusetts, Idaho, Oklahoma. Massachusetts, Idaho, Michigan, Oklahoma and Wisconsin consider adultery a felony, while in the other states it is a misdemeanor. In 2010, West Virginia repealed its adultery law. Colorado repealed its adultery law in 2013.
In the last conviction for adultery in Massachusetts in 1983, it was held that the statute was constitutional and that "no fundamental personal privacy right implicit in the concept of ordered liberty guaranteed by the United States Constitution bars the criminal prosecution of such persons ." Whether a conviction under this statue would be possible today (especially after Lawrence v. Texas (2003)) is not known.
In Utah adultery is a class B misdemeanor. The adultery law only applies to the married party (the law states that "A married person commits adultery when he voluntarily has sexual intercourse with a person other than his spouse.") However, Utah also has a fornication law that applies to any unmarried person (also a class B misdemeanor).
In Florida "Living in open adultery" (Art 798.01) as well as "Lewd and lascivious behavior"(Art 798.02) which includes, among others, a man and a woman who "not being married to each other, lewdly and lasciviously associate and cohabit together" are both misdemeanors of the second degree.
South Carolina's adultery law came into spotlight in 2009, when then governor Mark Sanford admitted to his extramarital affair. He was not prosecuted for it; it is not clear whether South Carolina could prosecute a crime that occurred in another jurisdiction (Argentina in this case); furthermore, under South Carolina law adultery involves either "the living together and carnal intercourse with each other" or, if those involved do not live together "habitual carnal intercourse with each other" which is more difficult to prove.
In Alabama "A person commits adultery when he engages in sexual intercourse with another person who is not his spouse and lives in cohabitation with that other person when he or that other person is married." Adultery is a Class B misdemeanor.
Up until the mid 20th century most US states (especially Southern and Northeastern states) had laws against fornication, adultery or cohabitation. These laws have gradually been abolished or struck down by courts as unconstitutional.
Pennsylvania abolished its 270-year-old laws against fornication and adultery in a sweeping recodification of its criminal laws in 1973.
In the U.S. Military, adultery is a potential court-martial offense. The enforceability of adultery laws in the United States is unclear following Supreme Court decisions since 1965 relating to privacy and sexual intimacy of consenting adults. However, occasional prosecutions do occur.
Seven US states (Hawaii, Illinois, North Carolina, Mississippi, New Mexico, South Dakota, and Utah) allow the possibility of the tort action of alienation of affections (brought by a deserted spouse against a third party alleged to be responsible for the failure of the marriage). In a highly publicized case in 2010, a woman in North Carolina won a $9 million suit against her husband's mistress.
Criticism of adultery laws
See also: Alienation of affections § CriticismPolitical arguments
Laws against adultery have been named as invasive and incompatible with principles of limited government. Much of the criticism comes from libertarianism, the consensus among whose adherents is that government must not intrude into daily personal lives and that such disputes are to be settled privately rather than prosecuted and penalized by public entities. It is also argued that adultery laws are rooted in religious doctrines; which should not be the case for laws in a secular state.
Opponents of adultery laws regard them as painfully archaic, believing they represent sanctions reminiscent of nineteenth-century novels. They further object to the legislation of morality, especially a morality so steeped in religious doctrine. Support for the preservation of the adultery laws comes from religious groups and from political parties who feel quite independent of morality, that the government has reason to concern itself with the consensual sexual activity of its citizens … The crucial question is: when, if ever, is the government justified to interfere in consensual bedroom affairs?
There is a history of adultery laws being abused. In Somerset, England, a somewhat common practice was for husbands to encourage their wives to seduce another man, who they would then sue or blackmail, under laws prohibiting men from having sex with women married to other men.
Historical context
Historically, in most cultures, laws against adultery were enacted only to prevent women—and not men—from having sexual relations with anyone other than their spouses, whose property they were deemed. Among many cultures the penalty was—and to this day still is, as noted below—capital punishment. At the same time, men were free to maintain sexual relations with any women (polygyny) provided that the women didn't already have husbands or "owners." Indeed, בעל (ba`al), Hebrew for husband, used throughout the Bible, is synonymous with owner. These laws were enacted in fear of cuckoldry and thus sexual jealousy. Many indigenous customs, such as female genital mutilation and even menstrual taboos, have been theorized to have originated as preventive measures against cuckolding. This arrangement has been deplored by many modern intellectuals.
Laws against adultery based upon the idea that woman is a chattel, so that to make love to a married woman is to deprive the husband of her services. It is the frankest and most crass statement of a slave-situation. To us, every woman … has … an absolute right to travel in her own orbit. There is no reason why she should not be the ideal hausfrau, if that chance to be her will. But society has no right to insist upon that standard. It was, for practical reasons, almost necessary to set up such taboos in small communities, savage tribes, where the wife was nothing but a general servant, where the safety of the people depended upon a high birth-rate. But to-day woman is economically independent, becomes more so every year. The result is that she instantly asserts her right to have as many or as few men or babies as she wants or can get; and she defies the world to interfere with her. More power to her!
Violence against women
Opponents of adultery laws argue that these laws maintain social norms which justify violence, discrimination and oppression of women; in the form of state sanctioned forms of violence such as stoning, flogging or hanging for adultery; or in the form of individual acts of violence committed against women by husbands or relatives, such as honor killings, crimes of passion, and beatings. UN Women has called for the decriminalization of adultery. A Joint Statement by the United Nations Working Group on discrimination against women in law and in practice in 2012 stated:
- "The United Nations Working Group on discrimination against women in law and in practice is deeply concerned at the criminalization and penalization of adultery whose enforcement leads to discrimination and violence against women."
Use of limited resources of the criminal law enforcement
An argument against the criminal status of adultery is that the resources of the law enforcement are limited, and that they should be used carefully; by investing them in the investigation and prosecution of adultery (which is very difficult) the curbing of serious violent crimes may suffer.
The importance of consent as the basis of sexual offenses legislation
Human rights organizations have stated that legislation on sexual crimes must be based on consent, and must recognize consent as central, and not trivialize its importance; doing otherwise can lead to legal, social or ethical abuses. Amnesty international, when condemning stoning legislation that targets adultery, among other acts, has referred to "acts which should never be criminalized in the first place, including consensual sexual relations between adults". Salil Shetty, Amnesty International’s Secretary General, said: "It is unbelievable that in the twenty-first century some countries are condoning child marriage and marital rape while others are outlawing abortion, sex outside marriage and same-sex sexual activity – even punishable by death." The My Body My Rights campaign has condemned state control over individual sexual and reproductive decisions; stating "All over the world, people are coerced, criminalized and discriminated against, simply for making choices about their bodies and their lives".
Other consequences
General
For various reasons, most couples who marry do so with the expectation of fidelity. Adultery is often seen as a breach of trust and of the commitment that had been made during the act of marriage. Adultery can be emotionally traumatic for both spouses and often results in divorce. However, in a new work, The New Rules by Dr Catherine Hakim, a French sociologist and author, refers to the UK arguing that a "sour and rigid English view" of infidelity as opposed to the 'wonderful French way' of male infidelity is condemning millions of people to live frustrated "celibate" lives with their spouses. She argues that there is such a thing as a "successful affair" in which both parties are happier but no one gets hurt: "Sex is no more a moral issue than eating a good meal," she writes. "The fact that we eat most meals at home with spouses and partners does not preclude eating out in restaurants to sample different cuisines and ambiences, with friends or colleagues."
Adultery may lead to ostracization from certain religious or social groups.
Adultery can also lead to feelings of guilt and jealousy in the person with whom the affair is being committed. In some cases, this "third person" may encourage divorce (either openly or subtly). If the cheating spouse has hinted at divorce in order to continue the affair, the third person may feel deceived if that does not happen. They may simply withdraw with ongoing feelings of guilt, carry on an obsession with their lover, may choose to reveal the affair, or in rare cases commit violence or other crimes.
Since adultery can lead to divorce, it may have long-term consequences for children in the family. Children of divorcees are twice as likely to have problems as adults with mental illness, substance abuse, and failed relationships, though heritable factors, such as a tendency toward anxiety and depression, are likely the root cause of both the infidelity of the parent and the later struggles of the child. While there is correlation, there is no evidence that divorces causes children to have struggles in later life.
If adultery leads to divorce, it also carries higher financial burdens. For example, living expenses and taxes are generally cheaper for married couples than for divorced couples. Legal fees can add up into the tens of thousands of dollars. Divorced spouses may not qualify for benefits such as health insurance, which must then be paid out-of-pocket.
Sexually transmitted infections
Further information: Sexually transmitted diseaseLike any sexual contact, adultery may result in sexually-transmitted diseases (STD). Since most married couples do not routinely use barrier contraceptives, STDs can easily be transmitted from one spouse to another in this way. This can be a public health issue in regions of the world where STDs are common, but addressing this issue is very difficult due to legal and social barriers - to openly talk about this situation would mean to acknowledge that adultery (often) takes place, something that is taboo in certain cultures, especially those strongly influenced by religion. In addition, dealing with the issue of barrier contraception in marriage in cultures where women have very few rights is difficult: the power of women to negotiate safer sex (or sex in general) with their husbands is often limited. The World Health Organisation (WHO) found that women in violent relations were at increased risk of HIV/AIDS, because they found it very difficult to negotiate safe sex with their partners, or to ask medical advice if they though to have been infected.
Violence

Historically, female adultery often resulted in extreme violence, including murder (of the woman, her lover, or both, committed by her husband). Today domestic violence is outlawed in the Western World, but this is not the case in many developing countries.
Honor killings
Main article: Honor killingHonor killings are often connected to accusations of adultery. Honor killings continue to be legal in parts of the world.
According to the report of the Special Rapporteur submitted to the 58th session of the United Nations Commission on Human Rights (2002) concerning cultural practices in the family that reflect violence against women (E/CN.4/2002/83):
- The Special Rapporteur indicated that there had been contradictory decisions with regard to the honour defense in Brazil, and that legislative provisions allowing for partial or complete defense in that context could be found in the penal codes of Argentina, Ecuador, Egypt, Guatemala, Iran, Israel, Jordan, Peru, Syria, Venezuela and the Palestinian National Authority.
Part of article 340 of the Penal Code of Jordan states that "he who discovers his wife or one of his female relatives committing adultery and kills, wounds, or injures one of them, is exempted from any penalty."
Until 2009, in Syria, it was legal for a husband to kill or injure his wife or his female relatives caught in flagrante delicto committing adultery or other illegitimate sexual acts. The law has changed to allow the perpetrator to only "benefit from the attenuating circumstances, provided that he serves a prison term of no less than two years in the case of killing." Other articles also provide for reduced sentences. Article 192 states that a judge may opt for reduced punishments (such as short-term imprisonment) if the killing was done with an honorable intent. Article 242 says that a judge may reduce a sentence for murders that were done in rage and caused by an illegal act committed by the victim.
According to the UN in 2002:
- "The report of the Special Rapporteur ... concerning cultural practices in the family that are violent towards women (E/CN.4/2002/83), indicated that honour killings had been reported in Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Morocco, Pakistan, the Syrian Arab Republic, Turkey, Yemen, and other Mediterranean and Persian Gulf countries, and that they had also taken place in western countries such as France, Germany and the United Kingdom, within migrant communities."
Stoning
Main article: StoningStoning, or lapidation, refers to a form of capital punishment whereby an organized group throws stones at an individual until the person dies, or (in ancient Judaism) the condemned person is pushed from a platform set high enough above a stone floor that the fall would probably result in instantaneous death.
Stoning continues to be practiced today, in parts of the world. Recently, several people have been sentenced to death by stoning after being accused of adultery in Iran, Somalia, Afghanistan, Sudan, Mali, and Pakistan by tribal courts.
Flogging
Main articles: Flogging and Judicial corporal punishmentIn some jurisdictions flogging is a punishment for adultery. There are also incidents of extrajudicial floggings, ordered by informal religious courts. In 2011, a 14-year-old girl in Bangladesh died after being publicly lashed, when she was accused of having an affair with a married man. Her punishment was ordered by villagers under Sharia law.
In fiction

The theme of adultery has been used in many literary works, and has served as a theme for some notable books, such as Anna Karenina, Madame Bovary, Lady Chatterley's Lover, The Scarlet Letter. Adultery has also been the theme of many movies.
See also
- Adultery in literature
- Affair
- Crime of passion
- Cuckold
- Emotional affair
- Family therapy (Relationship counseling)
- Fornication
- Honor killing
- Incest
- Incidence of monogamy
- Jesus and the woman taken in adultery
- Mistress
- On-again, off-again relationship
- Open marriage
- Polygyny threshold model
- Polyamory
- Sexual jealousy in humans
- Swinging
References
- "Encyclopædia Britannica Online, "Adultery"". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- The doctrine and law of marriage, adultery, and divorce
- The Age, 7 May 2014 - Aceh Woman gangraped by vigilantes for alleged adultery now to be flogged
- "IPS – Adultery Laws Unfairly Target Women, U.N. Says | Inter Press Service". Ipsnews.net. 2012-10-24. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "DisplayNews". Ohchr.org. 2012-10-18. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- Modern Perspectives on Islamic Law - Page 217, E. Ann Black, Hossein Esmaeili, Nadirsyah Hosen - 2013
- Evans v. Murff, 135 F. Supp. 907, 911 (1955).
- E.g., U.S. Code, Title 21, Chapter 1: Adulterated or Misbranded Foods or Drugs.
- Clements, M. (1994, August 7). Sex in America today: A new national survey reveals how our attitudes are changing. Parade Magazine, 4–6.
- Laumann, E. O.; Gagnon, J. H.; Michael, R. T.; Michaels, S. (1994). The social organization of sexuality: Sexual practices in the United States. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-46957-3.
- ^ Wiederman, M. W. (1997). "Extramarital sex: Prevalence and correlates in a national survey". Journal of Sex Research. 34 (2): 167–174. doi:10.1080/00224499709551881. JSTOR 3813564.
- Judging Evil: Rethinking the Law of Murder and Manslaughter - Samuel H. Pillsbury - Google Cărţi. Books.google.ro. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- http://quod.lib.umich.edu/cgi/t/text/text-idx?c=did;cc=did;rgn=main;view=text;idno=did2222.0000.328
- "New York Penal Law Section 255.17". Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- "North Carolina Statute 14-184". Archived from the original on 25 June 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Minnesota Statute section 609.36". Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- Appel, Jacob M. (October 6, 2009). "Hate the Husband? Sue the Mistress!". Huffingtonpost.com. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- Michelle Boorstein (August 25, 2004). "Virginia Adultery Case Goes from Notable to Nonevent". The Washington Post. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Rod Powers. "Adultery in the Military". about.com. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- Black's Law Dictionary, 4th ed. 1957.
- Black's Law Dictionary, 4th ed. 1957, citing Young v. Young, 236 Ala. 627, 184 So. 187. 190.
- Black's Law Dictionary.
- "Criminal Conversation: North Carolina Laws and Defense". Haas McNeil & Associates, P.A. Archived from the original on 2008-06-04. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- http://edition.cnn.com/2009/LIVING/12/08/cheating.spouses.lawsuits/
- Tina Stowell, Baroness Stowell of Beeston, Lords Spokesperson for Women and Equalities (8–9 July 2013). http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/ld201314/ldhansrd/lhan31.pdf (PDF). Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). Vol. 747. House of Lords. col. 145–147.
{{cite book}}:|chapter-url=missing title (help) - Adultery : Indian Legal Perspectives
- http://www.biojuris.com/natural/3-2-0.html
- http://hudoc.echr.coe.int/sites/eng/pages/search.aspx?i=001-116716#{%22itemid%22:}
- http://sim.law.uu.nl/SIM/CaseLaw/hof.nsf/d0cd2c2c444d8d94c12567c2002de990/db5e85a236de283dc1257803004974b7?OpenDocument
- "The Global Sex Survey 2005". durex.com. Archived from the original on 2008-04-30. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- "The Global Sex Survey 2005, full report" (PDF). durex.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-02-16. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- Non-paternity event.
- "Kinsey Study Data [Research Program]". The Kinsey Institute. Archived from the original on 26 July 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - K H Choi, J A Catania, and M M Dolcini (December 1994). "Extramarital sex and HIV risk behavior among US adults: results from the National AIDS Behavioral Survey". Am J Public Health. 84 (12). Am J Public Health. 1994 December; 84(12): 2003–2007: 2003–7. doi:10.2105/ajph.84.12.2003. PMC 1615405. PMID 7998648.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Atkins, D. C.; Baucom, D. H.; Jacobson, N. S. (2001). "Understanding Infidelity: Correlates in a National Random Sample". Journal of Family Psychology. 15 (4): 735–749. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.15.4.735. PMID 11770478.
- Dig., XLVIII, ad leg. Jul.
- Codex Justin., Digest, XLVIII, 5–13; Lecky, History of European Morals, II, 313.
- ^ "The Julian marriage laws". Unrv.com. Retrieved 2010-11-29.
- Mosiah 13:22
- 3 Nephi 12:27
- Alma 30:10
- "Guide to the Scriptures: Adultery". lds.org. Retrieved 2014-05-02.
- Maimonidies, Book of the Commandments, Prohibition 392 and the note at the end of Prohibition 347, Hebrew translation and notes by Rabbi Joseph Kapach, Mossad Harav Kook, Jerusalem 1971
- Maimonides Mishneh Torah: Laws of Sanhedrin 14:11
- Talmud Bavli: Tractate Ketuvoth 30a,b
- Talmud Bavli: Tractate Sanhedrin, folio 52b, towards the bottom
- Lev. 21:9
- The Jewish Way in Love & Marriage, Rabbi Maurice Lamm, Harper & Row, San Francisco,1980
- Maimonides, Mishneh Torah, Judges, Laws of Kings and Wars, Chapter 7 (Shabse Frankel edition, Jerusalem - B'nai B'rak, 5762 (c.2008, copyright 1998))
- Online Qur'an Project Chapter 24.
- "American Muslims need to speak out against violations of Islamic Shariah law". Asmasociety.org. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- Hadith Muslim 17:4192. Also, see the following: Bukhari 6:60:79, Bukhari 83:37, Muslim 17:4196, Muslim 17:4206, Muslim 17:4209, Ibn Ishaq 970.
- "Muslim Publics Divided on Hamas and Hezbollah Retrieved 2011-06-02". Pewglobal.org. 2010-12-02. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- Schoolcraft, Historical and Statistical Information Respecting the History, Condition and Prospects of the Indian Tribes of the United States, I, 236; V, 683, 684, 686.
- H.H. Bancroft, The Native Races of the Pacific States of North America, I, 514.
- ABA aug Journal 1969, p.738
- Laws of Manu, V, 154; VIII, 371.
- McCracken, 171.
- David Smith in Johannesburg (2012-05-31). "Sudanese woman sentenced to stoning death over adultery claims | World news". London: theguardian.com. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "Africa | Stoning victim 'begged for mercy'". BBC News. 2008-11-04. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "Criminal Code of the Republic of China, Article 239". Retrieved 2013-05-04.
- "Marriage Law of the People's Republic of China , Article 32". Retrieved 2011-10-25.(中华人民共和国婚姻法第三十二条)
- Hudood laws open to change in Pakistan, July 2005
- "Adultery: Indian Law perspective". Gangothri.org. 2013-04-10. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "Adultery law biased against men, says Supreme Court"The Times of India
- 'Adultery law must apply equally to men and women' at www.rediff.com
- "NCW rejects proposal to punish women for adultery" The Hindu
- "CAT penalises cop living with lover-Delhi-Cities" The Times of India
- Mackey, Sandra. The Saudis: Inside the Desert Kingdom. Updated Edition. Norton Paperback. W.W. Norton and Company, New York. 2002 (first edition: 1987). p. 271 ISBN 0-393-32417-6 pbk.
- http://books.google.ro/books?id=HartNkkDBssC&printsec=frontcover&hl=ro&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false
- http://books.google.ro/books?id=XE97ryf8noAC&pg=PA25&lpg=PA25&dq=Recent+Social+Trends+in+France,+1960-1990&source=bl&ots=uNGmU1r8CD&sig=5qKlBaI_HsxFSMeJxmXgkPWZOHA&hl=ro&sa=X&ei=POUDU6HbB6eDywOXhIGoBw&ved=0CDEQ6AEwAQ#v=onepage&q=Recent%20Social%20Trends%20in%20France%2C%201960-1990&f=false
- ^ http://books.google.ro/books?id=QeuBc1ryQz8C&printsec=frontcover&hl=ro&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false
- http://books.google.ro/books?id=Ad0_J6T-YDQC&printsec=frontcover&hl=ro&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false
- http://books.google.ro/books?id=_gsfAQAAIAAJ&q=%22The+Cornell+Law+Quarterly%22,+volume+50&dq=%22The+Cornell+Law+Quarterly%22,+volume+50&hl=ro&sa=X&ei=KO0DU_frPIbnygP6qYHoBg&ved=0CC0Q6AEwAA
- http://www.impowr.org/content/summary-adultery-romania
- "Turkey signals U-turn on adultery". BBC News. 2004-09-14.
- http://books.google.ro/books?id=pnGwP9-FhxYC&printsec=frontcover&hl=ro&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false
- http://hudoc.echr.coe.int/sites/eng-press/pages/search.aspx?i=003-3272505-3650095#{%22itemid%22:}
- Lee, Jolie (2014-04-17). "New Hampshire Senate votes to repeal anti-adultery law". USA Today.
- Adultery could mean life, court finds at web.archive.org.
- "Section 10-501 - Adultery. :: 2010 Maryland Code :: US Codes and Statutes :: US Law :: Justia". Law.justia.com. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "New York Penal Law Section 255.17". Retrieved 2011-10-25.
- http://www.legis.state.wi.us/statutes/Stat0944.pdf
- South Carolina Code of Laws, Section 16
- South Carolina Code of Laws, Section 20
- By Ethan Bronner (2012-11-15). "Mass. among 23 states where adultery is a crime, but rarely prosecuted - Nation". The Boston Globe. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- http://www.legis.state.wv.us/bill_status/bills_history.cfm?year=2010&sessiontype=RS&input=457
- The Associated Press (2013-03-22). "Bill to repeal of Colorado adultery law signed". The Denver Post. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "STOWELL, COMMONWEALTH vs., 389 Mass. 171". Masscases.com. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "Section 103 Adultery. :: Chapter 7 Offenses Against the Family :: Title 76 Utah Criminal Code :: 2011 Utah Code :: Utah Code :: US Codes and Statutes :: US Law :: Justia". Law.justia.com. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "Utah State Legislature". Le.utah.gov. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "Chapter 798 - ADULTERY; COHABITATION :: Florida CRIMES :: 2005 Florida Code :: Florida Code :: US Codes and Statutes :: US Law :: Justia". Law.justia.com. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "South Carolina Legislature Mobile". Scstatehouse.gov. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- http://law.onecle.com/alabama/criminal-code/13A-13-2.html
- February 11, 2009, 6:00 PM (2009-02-11). "N.C. Cohabitation Law Struck Down". CBS News. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - By Joanna Grossman FindLaw Columnist Special to CNN.com (2005-01-25). "CNN.com - Virginia strikes down state fornication law - Jan 25, 2005". Articles.cnn.com. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help); no-break space character in|author=at position 3 (help) - Michael, Jenny (2005-02-28). "Judge rules state adultery law unconstitutional". Bismarcktribune.com. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- Pennsylvania Politics Today and Yesterday: The Tolerable Accommodation - Paul B. Beers - Google Books. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- See, e.g., Lawrence v. Texas.
- Jonathan Turley, Of Lust and the Law, The Washington Post, September 5, 2004, p. B1.
- http://edition.cnn.com/2009/LIVING/12/08/cheating.spouses.lawsuits/
- http://abcnews.go.com/Business/TheLaw/wife-wins-million-husbands-alleged-mistress/story?id=10151957
- http://www.upi.com/Top_News/US/2010/03/22/Woman-wins-alienation-of-affection-case/UPI-83231269299182/
- Weissler, Benjamin. "Government and the Bedroom." July 13, 2012. Yale Undergraduate Law Review.
- Ley, David. "Kinky Cuckolding Fetish Goes Mainstream". Psychology Today. June 24, 2010.
- "Female genital mutilation", World Health Organization, February 2010.
- Strassman, B.I. (1992) ‘The function of menstrual taboos among the Dogon: defense against cuckoldry?’ Human Nature 2: 89-131
- Crowley, Aleister (1996), "1:41, The New Comment", The Law is for All, Tempe, AZ: New Falcon Publications
- ^ http://www.ohchr.org/EN/NewsEvents/Pages/DisplayNews.aspx?NewsID=12672&
- ^ http://www.endvawnow.org/en/articles/738-decriminalization-of-adultery-and-defenses.html
- Suffolk law review, The Validity of Criminal Adultery Prohibitions After Lawrence v.Texas; pg. 859 "Lack of enforcement suggests the prevailing view that police resources are better spent elsewhere."
- http://www.amnesty.org/en/for-media/press-releases/afghanistan-reject-stoning-flogging-amputation-and-other-taliban-era-punish
- https://www.amnesty.org/en/news/sexual-and-reproductive-rights-under-threat-worldwide-2014-03-06
- http://www.amnesty.org/en/library/info/ACT35/001/2014/en
- "Encyclopædia Britannica Online, "Adultery"". Britannica.com. Archived from the original on 27 April 2011. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "About.com Divorce Support, "Why Does Infidelity Often Lead to Divorce?"". About.com. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- Mother Tongue (2012-08-20). "Puritan view of adultery turns Brits into 'caged animals' says academic". London: Telegraph. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- Women as Guardians of Purity
- "Signs of a Cheating Husband". Beatingjealousy.com. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- "Are You the Other Woman in an Affair". Essortment.com. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- "Getting Over an Affair as the Other Woman". Truthaboutdeception.com. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- "Amy Fisher". trutv.com. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- "nasponline.org, Divorce: A Parents' Guide for Supporting Children". nasponline.org. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- ^ "divorcehq.com, "Comparison of the Average Cost of Divorce Fees"". divorcehq.com. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- "attorneys.com, "The Hidden Costs of Divorce"". attorneys.com. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- "divorcehq.com, "Divorce and COBRA"". divorcehq.com. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- "family.jrank.org, "Birth Control – Contraceptive Methods, Sociocultural and Historical Aspects"". jrank.com. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- http://upetd.up.ac.za/thesis/available/etd-12032012-153412/unrestricted/dissertation.pdf
- http://www.aids2031.org/pdfs/safe%20and%20consensual%20sex%20are%20women%20empowered%20enough%20to%20negotiate.pdf
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1831928/
- http://www.who.int/hac/techguidance/pht/InfoBulletinIntimatePartnerViolenceFinal.pdf
- ^ "Working towards the elimination of crimes against women committed in the name of honour" (PDF). Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights. Retrieved 2008-02-08.
- Altstein,Howard;Simon, Rita James (2003). Global perspectives on social issues: marriage and divorce. Lexington, Mass: Lexington Books. p. 11. ISBN 0-7391-0588-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "The Secretary Generals database on violence against women". Sgdatabase.unwomen.org. 2012-05-29. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- "Syria: No Exceptions for Honor Killings". Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 2011-12-08.
- "Abu-Ghanem women speak out against serial 'honor killings'". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 25 February 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-23.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Rapps, Dennis; Weinberg, Lewin (December 1999). "Examining Halcha, Jewish issues and secular law". Jewish Law:Legal briefs. Ira Kasdan. Archived from the original on 5 November 2009. Retrieved 2009-10-09.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Examples include:
- "Somali woman stoned for adultery". BBC News. 2009-11-18. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- Robert Tait and Noushin Hoseiny (2008-07-21). "Eight women and a man face stoning in Iran for adultery". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- "Two Men Stoned to Death for Adultery in Iran".
- "Taliban 'kill adulterous Afghan couple'". BBC News. 2010-08-16.
- http://www.rawa.org/temp/runews/2011/01/27/woman-stoned-to-death-in-north-afghanistan.html
- Smith, David (2012-05-31). "Sudanese woman sentenced to stoning death over adultery claims". The Guardian. London.
- http://edition.cnn.com/2012/08/02/world/africa/mali-couple-stoned/index.html
- http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2010/jul/18/couple-sentenced-pakistan
- http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-pacific-10890137
- http://edition.cnn.com/2014/05/01/world/asia/brunei-sharia-law/
- http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-south-asia-12344959
- http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-south-asia-12398757
Further reading
- McCracken, Peggy (1998). The romance of adultery: queenship and sexual transgression in Old French literature. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 0-8122-3432-4.
- Mathews, J. Dating a Married Man: Memoirs from the "Other Women. 2008. ISBN 1-4404-5004-8.
- Best Practices: Progressive Family Laws in Muslim Countries (August 2005)
- Hamowy, Ronald. Medicine and the Crimination of Sin: "Self-Abuse" in 19th Century America. pp2/3
- Moultrup, David J. (1990). Husbands, Wives & Lovers. New York: Guilford Press.
- Glass, S. P., and Wright, T. L. (1992). Justifications for extramarital relationships: The association between attitudes, behaviors, and gender. Journal of Sex Research, 29, 361–387.
- Jack Goody A Comparative Approach to Incest and Adultery The British Journal of Sociology, Vol. 7, No. 4 (Dec., 1956), pp. 286–305 doi:10.2307/586694.
- Pittman, F. (1989). Private Lies. New York: W. W. Norton Co.
- Rubin, A. M., and Adams, J. R. (1986). Outcomes of sexually open marriages. Journal of Sex Research, 22, 311–319.
- Vaughan, P. (1989). The Monogamy Myth. New York: New Market Press.
- Blow, Adrian J.; Hartnett, Kelley (April 2005). Infidelity in Committed Relationships I: A Methodological Review. Journal of Marital and Family Therapy. INFIDELITY IN COMMITTED RELATIONSHIPS I: A METHODOLOGICAL REVIEW | Journal of Marital & Family Therapy | Find Articles at BNET at www.findarticles.com
- Blow, Adrian J; Hartnett, Kelley (April 2005). Infidelity in Committed Relationships II: A Substantive Review. Journal of Marital and Family Therapy. INFIDELITY IN COMMITTED RELATIONSHIPS II: A SUBSTANTIVE REVIEW | Journal of Marital and Family Therapy | Find Articles at BNET at www.findarticles.com
- Donaldson, Geoff. "The Gay Times of Dustin and Thomas". Dan's Publishing. 2-10. 2009.
| Sexual ethics | |
|---|---|
| Human sexuality | |
| Child sexuality | |
| Sexual abuse | |
| Age of consent (reform) | |
