This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 41.56.63.230 (talk) at 11:55, 19 December 2014 (→See also). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 11:55, 19 December 2014 by 41.56.63.230 (talk) (→See also)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)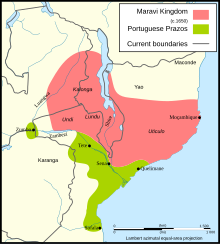
Maravi was a kingdom established by ] and straddled the current borders of Malawi, Mozambique and Zambia, in the 16th century. The present-day name "Malawi" is said to derive from "Maravi" which itself means "fire flames".
At its greatest extent, the state included territory from the Tumbuka and Tonga areas to the north to the Lower Shire in the south, and west to Luangwa and Zambezi valleys. Maravi's rulers belonged to the Mwale matriclan and held the title Kalonga. They ruled from Manthimba, the secular/administrative capital, and were the driving force behind the state's establishment. Meanwhile, the patrilineal Banda clan, which traditionally provided healers, sages and metallurgists, took care of religious affairs from their capital Mankhamba near Nthakataka.
After contact with the Portuguese, trade intensified. It included such items as beads of the Khami type and Chinese porcelain imported via Portuguese intermediaries. In the 19th century, the state declined and the Maravi were frequently raided by their neighbors the Yao and captured for sale as slaves. David Livingstone visited Lake Nyasa in 1859, and Protestant missionaries soon followed.
"Maravi" is therefore a general name of the peoples of Malawi, Zambia, Mozambique and the eastern part of Zimbawe. Chewa, which is also referred to as Nyanja and is the official language of Malawi and Zambia and to some extent Mozambique, is the language that emerged from this Sotho empire and this can be seen by its similarity to Sepedi (Northern Sotho) that is spoken in south Africa as well as the surnames of the Nyanja people - which reflect this Sotho ancestry.
However, what is interesting to note is that Chewa or Nyanja is not an original language. It is a language that contains a number of Bantu languages. Though its foundation is Sotho, it has, however, taken up a lot of Zulu and has been influenced by such languages as Lomwe, Cite error: There are <ref> tags on this page without content in them (see the help page).Shona, Tumbuka, and Tonga.Portuguese in Mozambique and English in Malawi, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
See also
The rulers of Maravi were the Mogale kings, whose name became corrupted to Mwale, just as many other Sotho and Zulu-based words in Chewa (Nyanja) had become - such as ku-kumana for uku-xumana, where the click sound is lost.
External links
This African history–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This Malawi-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This Mozambique-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |