This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Emily Temple-Wood (NIOSH) (talk | contribs) at 20:44, 31 January 2015 (add PEL). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 20:44, 31 January 2015 by Emily Temple-Wood (NIOSH) (talk | contribs) (add PEL)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)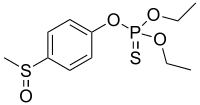 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name O,O-Diethyl O- phosphorothioate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.741 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C11H17O4PS2 |
| Molar mass | 308.35 g·mol |
| Appearance | Brown liquid or yellow oil |
| Hazards | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
| PEL (Permissible) | none |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Fensulfothion is an insecticide and nematicide. It is highly toxic and listed as an extremely hazardous substance. It is widely used on corn, onions, rutabagas, pineapple, bananas, sugar cane, sugar beets, pea nuts, etc.
External Links
References
- Fensulfothion, NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0284". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Fensulfothion, alanwood.net
- Appendix A List of Extremely Hazardous Chemicals
- Sunil Paul, MM; Aravind, UK; Pramod, G; Aravindakumar, CT (April 2013). "Oxidative degradation of fensulfothion by hydroxyl radical in aqueous medium". Chemosphere. 91 (3): 295–301. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.033. PMID 23273737.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |