This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Mark (talk | contribs) at 01:07, 24 July 2006 (Reverted edits by 81.170.36.130 (talk) to last version by Daniel Quinlan). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 01:07, 24 July 2006 by Mark (talk | contribs) (Reverted edits by 81.170.36.130 (talk) to last version by Daniel Quinlan)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)- For other places with the same name, see Lebanon (disambiguation).
33°51′39″N 35°51′28″E / 33.86083°N 35.85778°E / 33.86083; 35.85778
| الجمهوريّة اللبنانيّة Al-Jumhūriyyah al-Lubnāniyyah Republic of Lebanon | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Coat of arms of Lebanon
Coat of arms
Flag
Coat of arms of Lebanon
Coat of arms
| |
| Motto: Transliteration: Kūllūnā li-l-waṭan, li-l-'ula wa-l-'allam (Translation: "Us all! For our Nation, for our Emblem and Glory!") | |
| Anthem: Kulluna lil-watan lil 'ula lil-'alam | |
 | |
| Capitaland largest city | Beirut |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Government | Republic |
| • President | Émile Lahoud |
| • Prime Minister | Fouad Siniora |
| Independence From France | |
| • Declared | November 26, 1941 |
| • Recognised | November 22 1943 |
| • | currency = Pound (LL) |
| • Water (%) | 1.6% |
| Population | |
| • 2006 estimate | 3,874,050 (129th) |
| • 1970 census | 2,126,325 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2005 estimate |
| • Total | $19.49 billion (103rd) |
| • Per capita | $5,100 (90th) |
| HDI (2003) | 0.759 high (81st) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 |
| Calling code | 961 |
| ISO 3166 code | LB |
| Internet TLD | .lb |
Lebanon (Arabic: لبنان Lubnān), officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a small, largely mountainous country in the Middle East, located at the eastern edge of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Syria to the north and east, and Israel to the south, with a narrow coastline along its western edge. The flag of Lebanon features the Lebanon Cedar in green against a white backdrop, with two quarter-height horizontal red stripes on the top and bottom.
The name Lebanon (also "Loubnan" or "Lebnan") is derived from the Semitic root "LVN", meaning "white", a reference to snow-capped Mount Lebanon. In British English, the country has often traditionally been referred to with the definite article as the Lebanon, like the Ukraine or the Gambia, derived from the literal translation from the Hebrew "HaLevanon" (e.g Deuteronomy 3:25)
Recently, the Israeli–Lebanese conflict has continued with mounting military and civilian casualties on both sides; as other nations rush to evacuate their citizens, the UN warns of a possible upcoming Lebanese refugee crisis.
History
Main article: History of LebanonGain and loss of independence
The country gained independence in 1943, and French troops withdrew in 1946. Lebanon's history from independence has been marked by alternating periods of political stability and turmoil (including a civil conflict in 1958) interspersed with prosperity built on Beirut's position as a regional center for finance and trade.
The 1975-1990 war
Main article: Lebanese Civil WarUntil the outbreak of the Lebanese Civil War, Beirut, the capital of Lebanon, was noted for its wide boulevards, French-style architecture, and modernity, and was called "the Paris of the Middle East." Lebanon as a whole was known as the Switzerland of the Middle East (Swisra Ash Shark), enjoying a similar conflict-free status as Costa Rica in Central America and (until recently) Uruguay in South America.
- The term "civil war" is not adequate due to the complexity and foreign (Israeli-Palestinian-Syrian) military forces' role in the 1975-1990 war.
Beginning of the war
After the 1948 Arab-Israeli conflict, Lebanon became home to more than 110,000 Palestinian refugees who had fled from Israel. More Palestinian refugees arrived after the 1967 Arab-Israeli war and Black September. By 1975 they numbered more than 300,000 with Yassir Arafat's Palestine Liberation Organization in charge of their political and military activities. During the early 1970s, difficulties arose over the increase of Palestinian refugees in the south. Initially, fighting began between these Palestinians (referred to as "anti-Lebanese militias" by some) and the indigenous Lebanese "leftists" (the communists and socialist parties). As the fighting intensified, the sides involved became more distinct. On one side was the Christian resistance led first by Bachir Gemayel and later by Samir Geagea. The other side comprised a coalition of Palestinian refugees, Sunni Muslim, and Druze forces who were united in their detestation of the 1943 National Pact. The (civil) war left the nation with no effective central government.
Syrian intervention
In June, 1976 Syria sent 40,000 troops into Lebanon to prevent the Maronite militias from being overrun by Palestinian forces. Together the Syrians and Maronites pushed the Palestinians out of Beirut and into southern Lebanon. Over the next few years, shifting political climates resulted in Syria being allied with the Palestinians and some of the Maronites allied with Israel. Syrian forces remained in Lebanon, effectively dominating its government until 2005.
First Israeli invasion and occupation
After numerous cross-border attacks by Palestinian terrorist groups in southern Lebanon against civilians in Israeli territory, the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) invaded on March 14, 1978 in what was titled the Litani River Operation. A few days later, the United Nations Security Council passed resolutions 425 and 426, calling for the withdrawal of Israeli forces, removal of the militant Palestinian forces, and establishing an international peace-keeping force in southern Lebanon, the United Nations Interim Force In Lebanon (UNIFIL). In 2000 Israel completed the withdrawal of its troops, and turned over control of southern Lebanon to the pro-Israeli South Lebanon Army. Pro-Palestinian forces remained in the region in violation of the UN cease fire agreement.
Second Israeli invasion and occupation
The armed forces of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) continued to use Lebanon as a base to attack Israel with rockets and artillery, and on June 6, 1982 Israel again invaded Lebanon with the objective of evicting the PLO. Israeli forces occupied areas from the southern Lebanese border with Israel northward into areas of Beirut. During this invasion the Phalangist militia, under the command of Elie Hobeika, moved into the Sabra and Shatila refugee camps, and committed the first Sabra and Shatila massacre. Israel's plans for Lebanon suffered a severe setback on September 14, 1982, with the assassination of the Phalangist leader and President-elect Bachir Gemayel, who was regarded as secretly sympathetic to Israel. Hezbollah, a Lebanese Shia Islamic military and political group, formed from 1982 to combat the Israeli occupation.
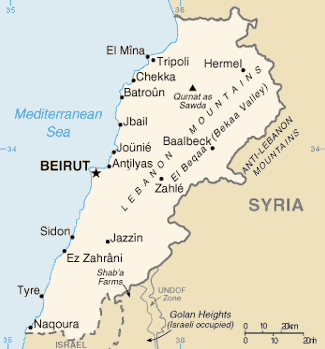
Israel withdrew from the "security zone" in the spring of 2000, under the Prime Minister Ehud Barak, who formerly ruled over the security zone as Chief of Staff. Israel continues to control a small area called Shebaa Farms, which Lebanon and Syria claim to be Lebanese territory but Israel insists to be former Syrian territory with the same status as the Golan Heights. The United Nations has determined that Shebaa Farms is not part of Lebanon. The UN Secretary-General concluded that, as of 16 June, 2000, Israel had withdrawn its forces from Lebanon in accordance with UN Security Council Resolution 425 of 1978, bringing, in the UN's opinion, closure to the 1982 invasion.
Despite common belief, there has been no formal declaration of war between Lebanon and Israel throughout the past conflicts, although on 13 July 2006 officials in both countries called recent engagements "act of war". The two countries do not maintain any open ties and rely on third parties to be intermediaries in any disputes.
International mediation
A multinational force landed in Beirut on August 20, 1982 to oversee the PLO withdrawal from Lebanon, and US mediation resulted in the evacuation of Syrian troops and PLO fighters from Beirut.
This period saw the rise of radicalism among the country's factions, and a number of landmark terrorist attacks against American forces, including the destruction of the US Embassy by a truck bomb and an even deadlier attack on the US Marines barracks.
1988 and 1989 saw unprecedented chaos. The Parliament failed to elect a successor to President Amine Gemayel (who had replaced his slain brother Bachir in 1982), whose term expired on 23 September. Fifteen minutes before his term expired, Gemayel appointed an interim administration headed by the army commander, General Michel Aoun. His predecessor, Selim al-Hoss, refused to accept his dismissal in Aoun's favour. Lebanon was thus left with no president, two rival governments that feuded for power, and more than 40 private militias.
End of the war
The 1989 Arab League-sponsored Taif Agreement marked the final stages of the military war, but neither the end of the Syrian occupation nor the economic war against Lebanon. It is estimated that during the 15 year military war more than 100,000 were killed, and 100,000 maimed. The legitimacy of the Taif agreement was contested by a portion of the population who viewed it as means to institutionalize a confessional political system. Popular protests occurred intermittently between 1989 and 1990 in support of the stand taken by the 1989 interim prime minister in Lebanon, General Michel Aoun. The General Michel Aoun demanded the withdrawal of Syrian and Israeli forces as a condition to having free parliamentary elections; the goal of the then-interim government. He contested these two occupations as justified by so-called “internal confessional conflict”, which was more of a series of foreign military manipulations. In October 1990 the Syrian occupation drove the head of the interim government, the General Aoun, into exile to Paris and the Lebanese patriotic movement he led moved underground until the Syrian withdrawal in 2005.
On May 25 2000, Israel unilaterally completed its withdrawal from the south of Lebanon in accordance with UN Security Council Resolution 425 of 1978. On September 2, 2004, the United Nations Security Council, recalling previous resolutions, especially 425 (1978), 520 (1982) and 1553 (July 2004), approved Resolution 1559, sponsored by the US and France. The resolution suggests that "all foreign forces should withdraw from Lebanon" to allow for free elections. Although not explicitly mentioned, the aim of the resolution was to invoke a withdrawal of Syrian forces. The enactors of the Taif agreement however did not enact the clause asking the Syrian occupation to withdraw from Lebanon, or heed the UN Security Council’s decision. The Lebanese patriotic movement has intensively lobbied for the withdrawal of the Syrian army from Lebanon since 1989 in governments throughout the western world. This withdrawal was catalyzed in its final stage by the assassination of Prime Minister Hariri in 2005.
Reconstruction
The country is recovering from the effects of the war, with foreign investment and tourism on the rise. Syrian forces occupied large areas of the country until April 2005 (see Cedar Revolution below), and Iran exercises heavy influence over Hezbollah forces in the Beqaa Valley and Southern Lebanon. Nevertheless, areas of Lebanon and Beirut in particular are moving toward a sense of normality and stability. Lebanese civil society enjoys significantly more freedoms than elsewhere in the Arab world. After twelve years, the reconstruction of downtown Beirut is largely complete. Lebanon's telecommunication rehabilitation is well underway, and in 2004 and 2005 foreign investment in the country topped $1 billion. Solidere has also announced many projects that will be complete in 2007.
Cedar Revolution (Uprising of Independence)
Main article: Cedar RevolutionNote: International media coined the term "Cedar Revolution", but Lebanese media also uses the term "Intifada (uprising) of Independence."
Hariri assassination
On February 14 2005, after 10 days of relative political stability, Lebanon was shaken by the assassination of former Prime Minister Rafik Hariri in a car bomb explosion. It is widely believed that Syria was responsible for the attack, due to its extensive military and intelligence presence in Lebanon, and to the public rift between Hariri and Damascus over the Syrian-backed constitutional amendment extending pro-Syrian President Lahoud's term in office. Syria, however, denies any involvement. Some sources also suggest a cover up of criminal evidence by Lebanese authorities, or that Israel's Mossad was somehow involved to inflame the Syrian-Lebanese situation. The timing of this bomb coincided with the announcement of the provisional Election results in Iraq released the previous day, in which the US backed candidate failed to win, and so may also have been timed to distract from that event.
On June 2 2005, the journalist and historian Samir Kassir, also a founding member of the Democratic Left Movement was assassinated by a car bomb.
Less than one month later, on June 21 2005, George Hawi, the former Secretary General of the Lebanese Communist Party was also assassinated by a car bomb in Beirut.
On September 25 2005, there was a failed assassination attempt on a Lebanese Broadcasting Corporation news anchor, in which May Chidiac lost her left leg below the knee and received severe injuries to her left arm, later resulting in the amputation of her left hand. Since then, May Chidiac won the UNESCO/Guillermo Cano World Press Freedom Prize 2006.
On December 12 2005, the journalist Gebran Tueni, editor-in-chief and CEO of the An-Nahar newspaper, was assassinated by a car bomb in the suburbs of Beirut.
Demonstrations
The assassination of Hariri resulted in huge anti-Syrian protests by Lebanese citizens in Beirut demanding the resignation of the pro-Syrian government. Following the examples of the Rose Revolution and Orange Revolution in 2004, the popular action was dubbed the "Cedar Revolution" by the US State Department, a name which quickly caught on among the international media. On February 28, 2005, with over 70,000 people demonstrating in Martyrs' Square, Prime Minister Omar Karami and his Cabinet resigned. They remained in office temporarily in a caretaker role prior to the appointment of replacements, as outlined by the constitution.
In response, Hezbollah organized a large counter-demonstration of 1.2 million people , staged on March 8 in Beirut, supporting Syria and accusing Israel and the United States of meddling in internal Lebanese affairs.
On March 14, one month after Hariri's assassination, throngs of people rallied in Martyrs' Square in Lebanon with up to 1.5 million people, . Protestors of all sects (even including a number of Shiites) marched demanding the truth about Hariri's murder and independence from Syrian occupation. The march reiterated their desire for a sovereign, democratic, and unified country, free of Syria's hegemony.
In the weeks following the demonstrations, bombs were detonated in Christian areas near Beirut. Although the damage was mostly material, these acts demonstrate the danger of Lebanon relapsing into sectarian strife.
Eventually, and under pressure from the international community, Syria withdrew its 15,000-strong army troops from Lebanon. The last Syrian uniformed soldier left Lebanon on April 26, 2005. On April 27, 2005, the Lebanese celebrated their first free-from-Syria day.
Parliamentary elections
After weeks of unsuccessful negotiations to form a new government, Prime Minister Omar Karami resigned the post for the third time in his political career on 13 April 2005. Two days later, Najib Mikati, a US-educated millionaire businessman and former Minister of Transportation and Public Works, was appointed Prime Minister-designate. A moderate pro-Syrian, Mikati secured the post through the support of the Opposition, which had previously boycotted such negotiations.
During the first parliamentary elections held after Syria's withdrawal from Lebanon in May 2005, the anti-Syrian coalition of Sunni Muslim, Druze and Christian parties led by Saad Hariri, son of assassinated ex-Prime Minister Rafik Hariri, won a majority of seats in the new Parliament.
The combinations were interesting in that in some areas the anti-Syrian coalition allied with Hezbollah and others with Amal. They did not win the two-thirds majority required to force the resignation of Syrian-appointed President Lahoud voted for by Rafic Hariri parliamentary bloc, due to the unexpectedly strong showing of retired army general Michel Aoun's Free Patriotic Movement party in Mount Lebanon. Aoun is arguably the strongest Christian figure in the new parliament: known previously for his anti-Syrian sentiment, Aoun aligned with politicians who were friendly to the Syrians in the past decade: Soleiman Franjieh Jr and Michel Murr. Their alliance dominated the north and the Metn District of Mount Lebanon. Saad Hariri and Walid Joumblat joined forces with the two staunchly pro-Syrian Shiite movements, Hezbollah and Amal, to secure major wins in the South, Bekaa, and Baabda-Aley district of Mount Lebanon. This alliance proved temporary and the last vestiges of civility between Joumblatt, who has called for the disarmament of Hezbollah, and the Shi'ite coalition came crashing down in December 2005. On February 6, 2006, Hezbollah signed a memorandum of understanding with Michel Aoun.
New government
After the elections, Hariri's Future Movement party, now the country's dominant political force, nominated Fouad Siniora, a former Finance Minister, to be Prime Minister. His newly formed representative government has obtained the vote of confidence from the parliament despite the lack of representation of Gen. Aoun.
On July 18, 2005, Lebanon's newly elected parliament, dominated by an anti-Syrian coalition, approved a motion to free Samir Geagea, who had spent most of the past 11 years in solitary confinement in an underground cell with no access to news. The motion was endorsed by pro-Syrian Lebanese President Emile Lahoud the next day. The following months proved the government's inability to begin the economic and political reforms promised to the people. Little has been done to pull the country out of the economic crisis in which it lingers still. Whilst the government loses credibility, the opposition, mainly comprised of Amal and Hezbollah (who are part of the government) and Gen. Aoun, is growing in popularity, even amongst other comunities than Christians and Shi'as. Since the beginning of May, a series of demonstrations and strikes began to appear, proof of the people's discontent.
Criminal investigation
On September 1, 2005, four current and former officials of Lebanon -- the former head of General Security Maj Gen Jamil Sayyad, the former chief of police Maj Gen Ali Hajj, the former military intelligence chief Brig Gen Raymond Azar, and the commander of the Republican Guard Brig Gen Mustafa Hamdan -- were charged in connection with Hariri's assassination.
On October 21, Detlev Mehlis, lead investigator in the UN Hariri Probe, released the report of the investigation. The report said that "many leads point to the direct involvement of Syrian Officials".
Following the appointment of Mehlis' successor, the Belgian Serge Brammertz, in January 2006 the investigation has taken a different course after the new investigator decided to throw out evidence upon which Melhis had earlier relied. Brammertz' investigation has been conducted in a far more discreet manner and has been marked by a considerable more positive tone between the UN team and Damascus. Brammertz' 30-page report of June 2006 accused no specific party of perpetrating the crime, while asking for the investigation's mandate to be extended for another year .
Withdrawal of Syrian troops
Major General Jamil Sayyed, the top Syrian ally in the Lebanese security forces, resigned on April 25, 2005. The following day the last 250 Syrian troops withdrew from Lebanon.
During the departure ceremonies, Syria's Chief of Staff Gen Ali Habib said that Syria's president had decided to recall his troops after the Lebanese army had been "rebuilt on sound national foundations and became capable of protecting the state."
UN forces led by Senegalese Brig Gen Mouhamadou Kandji were sent to Lebanon to verify the military withdrawal which was mandated by UN Security Council Resolution 1559.
2006 Conflict with Israel
Main article: 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict| This article documents a current event. Information may change rapidly as the event progresses, and initial news reports may be unreliable. The latest updates to this article may not reflect the most current information. Feel free to improve this article or discuss changes on the talk page, but please note that updates without valid and reliable references will be removed. (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
The 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict or 2006 Hezbollah-Israel conflict is a series of ongoing military actions and clashes in northern Israel and southern and central Lebanon between Hezbollah's armed wing and the Israeli Military. Israeli shelling and airstrikes have resulted in the significant destruction of Lebanese infrastructure beyond just Hezbollah outposts, namely the main Beirut airport and national highway system. This has caused much difficulty for the international community to respond with humanitarian aid to people not involved with Hezbollah. The Israeli state has told Lebanese civilians to leave southern Lebanon so that they can continue shelling and airstrikes and hopefully pinpoint Hezbollah outposts and bunkers without hurting innocent people.
A Precursor to the Violence
As of June 8 2006, a senior Palestinian security official close to the Hamas government, Jamal Abu Samhadana, was killed in an Israeli air strike, sparking angry demonstrations in Rafah, southern Gaza Strip. For many months, the Israelis have regularly shelled open areas such as fields and orchards in an effort to prevent Palestinian militants using them to fire their missiles into nearby Israeli territory.
On June 9 2006, eight civilians on a beach near Beit Lahiya - seven of whom belonged to the same family and three of whom were children - were killed and dozens of others wounded in an explosion on the beach of Beit Lahya in northern Gaza Strip. The Palestinians held Israel responsible for the incident, but Israel denied any involvement. Four other people were also killed in separate Israeli air strikes in northern Gaza Strip, Palestinians said.
The military wing of the Palestinian militant group Hamas said it will no longer respect a self-imposed truce that had held since February 2005.. In a statement on its website, the Izzedine al-Qassam Brigade said Israeli "massacres" had spurred the decision. Hamas said it fired rockets at Israel for the first time since its truce 16 months ago, in response to the deaths. . Israel, which has been shelling open areas of northern Gaza to prevent rocket attacks, promised to investigate the deaths. "If innocent civilians have been killed by an Israeli shell, that is totally unacceptable," said government spokesman Mark Regev. "If people have to pay a price with their careers because of negligence or some other factor, that will be done ..."
Jordan spoke of the killings as a crime which would further increase tensions, while Turkey said they were a severe blow to efforts to bring peace. Five Israeli human rights organisations demanded an urgent to end the killing of Palestinian civilians by Israeli security forces. A joint statement put out by the organisations says that since October 2000 at least 1,647 Palestinians - nearly half the number killed by Israeli troops - had been taking no part in fighting at the time of their deaths. The groups said 704 under-18s had been killed by Israeli troops and blamed "illegal expansion of Israel's open-fire regulations, double messages regarding the use of force... and failure to conduct independent investigations".
An Israeli army spokesman said chief of staff Dan Halutz had ordered an immediate stop to all artillery shelling of Gaza while an investigation was carried out into the incident. Speaking before the Hamas statement, Mr Abbas condemned the Israeli strikes in Gaza. "What the Israeli occupation forces are doing in the Gaza Strip constitutes a war of extermination and bloody massacres against our people," he said. UN Secretary General Kofi Annan said he was "deeply disturbed" by the killings and called for a full investigation. The foreign ministers of Russia and the UK also condemned the strike .
On June 11 2006, eleven Palestinians including nine civilians were killed in an Israeli missile attack on a vehicle carrying militants on their way to fire rockets .
On June 26 2006, several Palestinian militias claimed responsibility for the attack of a Israeli military post, killing two soldiers and kidnapping the Corporal Gilad Shalit . The kidnappers called for Israel to release hundreds of imprisoned Palestinians under the age of 18. Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Olmert denied any negotiations and alternatively, in response to the two killed soldiers and the one kidnapped, called for a military operation in Gaza to extract the kidnapped soldier.
The Current Situation
- See also: Israel's unilateral disengagement plan
On 12 July 2006, Hezbollah's armed wing militants crossed into Israel and captured two Israeli soldiers. Israel responded in southern Lebanon with warplanes, tanks and gunboats, and said eight of its soldiers had been killed in the violence. Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Olmert called the soldiers' capture "an act of war," and his Cabinet prepared to approve more military action in Lebanon . Lebanese Prime Minister Fouad Siniora said Beirut did not condone the cross-border Hezbollah attack against Israel, in which two Israel Defense Forces soldiers were kidnapped and seven others killed . Israel then responded with Operation Just Reward, later renamed Operation Change of Direction. The Israeli military strikes have claimed the lives of over 300 Lebanese civilians and wounded at least 600. The Israeli operation has resulted in the destruction of a large percentage of the Lebanese civil infrastructure including Lebanons only international airport, certain sea ports, many roads, dozens of bridges on the Beirut - Damascus international highway and on other major roads linking various parts of Lebanon, a lighthouse, wheat silo, petrol stations, factories and fuel storage tanks. Israel claimed the targeting of the infrastructure was to disrupt the supply of arms from Syria and Iran, believed to be the sponsors of Hezbollah. More than half a million civilians from Lebanon have fled their homes. In Israel, 1.5 million Israeli civilians are taking shelter in underground bomb shelters fearing rocket attacks by Hezbollah. The indiscriminant and ineffective volley of Qassam, Katyusha and RAAD missiles from Southern Lebanon have only claimed the lives of over 30 Israelis, 2 Israeli Arabs and has wounded over 400 others. The level of destruction that has hit Lebanon has been described by the country's Prime Minister Fuad Seniora as "unimaginable". Seniora sent a desperate cry for the world to help stop the violence, and pressure Hezbollah and Israel into an immediate ceasefire so that peaceful negotiations might occur. Israel has said it will only consider a ceasefire offered by the Lebanese government if two goals are met – the removal and disarmament of Hezbollah, and the return of the kidnapped soldiers. Although the government of Lebanon has appealed to the United Nations for aid in an immediate cease fire, several key countries of the United Nations Security Council, including those in the G8 refuse to support such a move.
Politics
| Politics of Lebanon |
|---|
 |
|
|
| Constitution Human rights |
| Executive |
| Legislature |
| Subdivisions |
| Elections |
|
Foreign relations
|
Lebanon is a republic in which the three highest offices are reserved for members of specific religious groups:
- the President must be a Maronite Catholic Christian.
- the Prime Minister must be a Sunni Muslim, and
- the Speaker of the Parliament must be a Shi'a Muslim.
This arrangement is part of the "National Pact" (Arabic: الميثاق الوطني - al Mithaq al Watani), an unwritten agreement which was established in 1943 during meetings between Lebanon's first president (a Maronite) and its first prime minister (a Sunni), although it was not formalized in the Lebanese Constitution until 1990, following the Taif Agreement. The pact included a promise by the Christians not to seek French protection and to accept Lebanon's "Arab face", and a Muslim promise to recognize independence and legitimacy of the Lebanese state in its 1920 boundaries and to renounce aspirations for union with Syria. This pact was thought at the time to be an interim compromise, necessary until Lebanon formed its own sense of a national identity. Its continued existence and the fallout from subsequent civil wars continue to dominate politics in Lebanon.
The pact also stipulated that seats in the Parliament would be allocated by religion and region, in a ratio of 6 Christians to 5 Muslims, a ratio based on the 1932 census, which was taken at a time when Christians still had a slight majority. The Taif Agreement adjusted the ratio to grant equal representation to followers of the two religions.
The Constitution grants the people the right to change their government. However, from the mid-1970s until the parliamentary elections in 1992, civil war precluded the exercise of political rights. According to the constitution, direct elections must be held for the parliament every four years. The last parliament election was in 2000; the election due to be held in 2004 was postponed for one year.
The parliament composition is based more on ethnic and religious identities rather than ideological features. The distribution of parliament seats has been modified recently.
Template:Parliament of Lebanon The Parliament elects the President of the republic to a six-year term. Consecutive terms for the president are forbidden. This constitutional rule has been bypassed by ad-hoc amendment twice in recent history, however, at the urging of the Syrian government. Elias Hrawi's term, which was due to end in 1995, was extended for three years. This procedure was repeated in 2004 to allow Emile Lahoud to remain in office until 2007. Pro-democracy campaigners denounced the moves.
The last presidential election was in 1998. The President appoints the Prime Minister on the nomination of the Parliament. Lebanon has numerous political parties, but their role is less important than in most parliamentary systems. Most represent, in practice if not in theory, sectarian interests; many are little more than ad-hoc lists of candidates endorsed by a well-known national or local figure. Electoral tickets are often formed on a constituency-by-constituency basis by negotiation among local leaders of clans, religious groups, and political parties; these loose coalitions generally exist only for the election and rarely form cohesive blocs in the Parliament subsequently.
Lebanon's judicial system is based on the Napoleonic Code. Juries are not used in trials. The Lebanese court system has three levels - courts of first instance, courts of appeal, and the court of cassation. There also is a system of religious courts having jurisdiction over personal status matters within their own communities, with rules on matters such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance. Lebanese law does not provide for Civil marriage (although it recognizes such marriages contracted abroad); efforts by former President Elias Hrawi to legalize civil marriage in the late 1990s floundered on objections mostly from Muslim clerics.
Administrative divisions
Lebanon is divided into six governorates (mohafazat, singular - mohafazah), which are further subdivided into 25 districts (Aqdya, singular - qadaa), also divided into several municipalities englobing a group of cities or villages.

Geography
Main article: Geography of LebanonA Middle Eastern country, Lebanon is bordered on the west by the Mediterranean (Coast: 225 km; and to the east by the Syro-African Depression. Lebanon borders Syria for 375 kilometres to the north and to the east and Israel for 79 kilometres to the south. The border with Israel has been approved by the United Nations (see Blue Line (Lebanon)), although a small piece of land called Shebaa Farms located in the Golan Heights is claimed by Lebanon but occupied by Israel, who claim that it is actually Syrian land. The UN has officially declared this region to be Syrian and not Lebanese territory, but Hezbollah occasionally launches attacks against Israeli positions within it, under the banner of freeing Lebanese territory.
Economy
Main article: Economy of LebanonLebanon has a competitive and free market regime and a strong laissez-faire commercial tradition. The Lebanese economy is service-oriented; main growth sectors include banking and tourism. There are no restrictions on foreign exchange or capital movement, and bank secrecy is strictly enforced. There are practically no restrictions on foreign investment.
The 1975-1991 civil war seriously damaged Lebanon's economic infrastructure, cut national output by half, and all but ended Lebanon's position as a Middle Eastern entrepot and banking hub. Peace has enabled the central government to restore control in Beirut, begin collecting taxes, and regain access to key port and government facilities. Economic recovery has been helped by a financially sound banking system and resilient small- and medium-scale manufacturers, with family remittances, banking services, manufactured and farm exports, and international aid as the main sources of foreign exchange.
Lebanon has witnessed a growth in the past couple of years. Bank assets have reached over 70 billion dollars. Even though Lebanon was down 10% in the tourism sector in 2005, more than 1.2 million tourists visited Lebanon. Market capitialization is at an all time high. Capitialization reached over $7 billion at the end of January 2006. However, a major economic decline is expected as a result of the Israeli strike of July 2006.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of LebanonThe population of Lebanon is composed of three predominant ethnic groups and religions: Muslims (Shi'ites, Sunnis, Alawites), Druze, and Christians (mostly Maronite Catholics, Melkite Greek Catholics, Armenian Catholics, some Syrian, Chaldean and Latin Rite Catholics, Arabic-speaking Greek Orthodox, Armenian Apostolic, Syrian Orthodox, and a few Assyrians, Copts and Protestants). No official census has been taken since 1932, reflecting the political sensitivity in Lebanon over confessional (religious) balance. It is estimated that about 60% of the resident population are Muslims; the rest are Christians. There used to be a small minority of Jews, mostly living in the eastern region of Beirut. Also, a small community (less than 1%) of Kurds (also known as Mhallamis or Mardins) live in Lebanon. There are approximately 15 million people of Lebanese descent, mainly Christians, spread all over the world, Brazil being the country with the biggest Lebanese community abroad. Lebanese are of mixed descent. They possess Phoenicican, Aramaic/Syriac, Greek, Roman, European (Crusaders, mainly French) and Arabic elements. While 360,000 Palestinian refugees have registered in Lebanon with the United Nations Relief and Works Agency (UNRWA) since 1948, estimates of those remaining range between 180,000 and 250,000.
The urban population, concentrated mainly in Beirut and Mount Lebanon, is noted for its commercial enterprise. A century and a half of migration and return have produced Lebanese commercial networks around the globe from North and South America to Europe, the Persian Gulf, and Africa. Lebanon has a high proportion of skilled labor compared with many other Middle Eastern countries.
Education
Main article: Education in LebanonHistory of Education in Lebanon:
The first two ministries to be established for education in Lebanon were the Ministry of Education and Higher Education, and the Ministry of Vocational and Technical Training, to enrich the Lebanese educational system. In 1946, after independence (26 November, 1941) the Lebanese government replaced the old curriculum program, coming from the French mandate, by new ones and the Arabic language was imposed upon all schools as a primary language, mandatory in the different phases of education. The government also left students the freedom to choose a second or third language (French, English, etc…). Then in 1968 and 1971, the curriculum was changed again. Each step of the educational phases was specified with a defined goal and the contents of the public examinations were also particularized. Before the war, in 1975, Lebanon held one of the highest literacy rates in the Arab world. Over 80% of the Lebanese people could read and write. But ever since then, Lebanon has been in a state of chaos that has consumed its people, all due to the civil war and foreign intervention that took place. When the war was declared ‘over’, the Lebanese took a start on rebuilding their cultural society in the educational domain and encouraging education through free and facilitated methods.
Schools in Lebanon:
Lebanese schools are divided into three categories-private, public, and mid-private. Private schools are the educational institutions owned and operated by other than a government authority. Public schools, on the other hand, are under government authority (Ministry of Education) and free, supported by tax money. The Ministry of education provides all the public schools with the books needed, for each educational level, for negligible prices and often for free. Mid-private schools, mainly parochial schools- such as the ‘Ecoles des Saint Coeurs’, are those that operate as private schools yet charge fees like public schools. The rest of the tuition fee is subsidized by the government.
All Lebanese schools are required by the government to follow a prescribed curriculum designed by the Ministry of Education. Private schools may also add more courses to their curriculum with approval from the Ministry of Education. Computer lessons, for example, are now very common in many schools although they are not a part of the traditional mandatory curriculum. For the schools without computer facilities, any student interested may take up computer courses at private institutions or centers available in almost all the Lebanese districts.
Public schools altogether amount to a total of 192 high schools and 1,125 elementary schools. Of the high schools, 16 are strictly for boys, 12 are girl schools, and 164 are mixed. In the elementary school, a total of 238,556 students are enrolled and taught by 24,463 teachers. In all the schools, pupils receive their instructions from the teachers of each subject taught and not one classroom teacher. In each class room there is about 25 pupils (some public schools may have up to 40 pupils due to the lack of teachers). The main subjects taught would be Mathematics, Sciences, History, Civics, Geography, Arabic, and French/English/both. Other rotating teachers within the school teach Physical education, Art, library use (not available in all), and in private schools, mainly, counselors.
Curriculum in Lebanese Schools:
Altogether public, private, and mid-private schools must follow a uniform curriculum set by the Council of education and Ministry of Education. The private and mid-private schools may include another system such as the American-program (freshman instead of baccalaureate level), but the Ministry officials supervise all. The main curriculum program in schools includes four phases of education:
- Kindergarten
- Elementary/Primary - Five years, for children age 6-11
- Intermediate - Four years, student takes exam to receive 'intermediate certification'
- Secondary - Three years, student takes official exams to get 'Baccalaureate Certificate' in Mathematics, Experimental Science or Philosophy.
By law, the four phases mentioned are free and compulsory to all the Lebanese students studying in the public schools. But, the ‘compulsory’ part indicated by law is not put into practice presently. Yet, it will soon be carried out in a way that every child must be registered in a school, whether it is public, private, or mid-private.
Universities and Colleges:
In Lebanon, the educational levels after high school could be university, college, institutes, or high technical schools. But either way, the years differ within each, depending on the professions or majors chosen by the students.
Lebanon has 15 universities of which the American University of Beirut (AUB) and the Lebanese American University (LAU) are internationally acknowledged. AUB is the first English university to open in Lebanon, while the first university to open was the French, Université Saint Joseph. The 15 universities, public or private, are mainly in Arabic, french, or English since the most widely used languages in Lebanon are: Arabic (official), French (official), English, and Armenian. Four of them are French, seven English, and one Armenian. Almost all these colleges teach in Arabic too since it is so common, but the second chosen language (English, French, and Armenian) is used as a basis for their programs.
In the English universities, students graduating from an American-system high school program, enter as freshman students in order to get their baccalaureate equivalence from the Lebanese Ministry of Higher Education. Otherwise, they cannot take part in any course-study. Also, they should have already sat for the foreign exams, SAT I, SAT II, and TOEFL, instead of the official exams. Any student in private school and university can sit for any foreign exam they choose, whether it is SAT, Toefl, GCSE, or even ‘A’-levels. In any way, there are private institutions that provide the students with these exams.
Transportation
Main article: Transportation in LebanonCulture
Lebanon has been a major crossroads of civilizations for millennia, so it is unsurprising that this small country possesses an extraordinarily rich and vibrant culture. Lebanon's wide array of ethnic and religious groups contributes to the country's rich cuisine, musical and literary traditions, and festivals. Beirut in particular has a very vibrant arts scene, with numerous performances, exhibits, fashion shows, and concerts held throughout the year in its galleries, museums, theaters, and public spaces. Lebanese society is modern, educated, and perhaps comparable to European societies of the Mediterranean. Most Lebanese are bilingual, speaking Arabic and French, this is why Lebanon is a member state of the Organisation Internationale de la Francophonie; however, English has become popular, especially among university students. The country is not only where Christianity intermingles with Islam, but Lebanon is also an Arab gateway to Europe and a European bridge to the Arab world.
Lebanon also hosts several prestigious universities, including the Lebanese University, the American University of Beirut, the Université Saint-Joseph, and the Lebanese American University.
Several international festivals are held in Lebanon, featuring world-renowned artists and drawing crowds from Lebanon and abroad. Among the most famous are the summer festivals at Baalbek, Beiteddine, and Byblos.
See also
- Communications in Lebanon
- List of Lebanon-related topics: an attempt to list every Lebanon-related article on Misplaced Pages.
- List of Lebanese people: a list of well-known Lebanese people, including some foreigners of Lebanese ancestry.
- Military of Lebanon
- South Lebanon conflict
- Transportation in Lebanon
References
- "Israel for rules change in south Lebanon". United Press International. 2006-07-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel to Lebanon: No to ceasefire". Ynetnews.com. 2006-07-16.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
- Fisk, Robert. Pity the Nation: The Abduction of Lebanon. New York: Nation Books, 2002.
- Holst, Sanford. Phoenicians: Lebanon's Epic Heritage. Los Angeles: Cambridge and Boston Press, 2005.
- Riley-Smith, Johnathan. The Oxford Illustrated History of the Crusades. New York: Oxford University Press, 2001.
- Salibi, Kamal. A House of Many Mansions: The History of Lebanon Reconsidered. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1990.
- Also see references for History of Lebanon
External links
| This page or section may contain link spam masquerading as content. Spam on Misplaced Pages consists of external links mainly intended to promote a website. If you are familiar with the content of the external links, please help by removing promotional links in accordance with Misplaced Pages:External links. |
Web portals
- Bluleb - Lebanese Web Portal
- Naharnet
- LebanonLinks.com - Lebanon Links Lebanon Portal since 1997, Directory, Search Engine and Resource information for Lebanon.
Government
- The Lebanese Governmental Portal for Information & Forms
- Official site of the President of the Lebanese Republic
- Official site of The Lebanese Parliament Template:Ar icon
- Central Administration for Statistics
- Ministry of Tourism
- Internal Security Forces
- The Lebanese Armed Forces
- General-security.gov.lb
- Lebanon Customs site
- Central Bank of Lebanon
- Beirut Stock Exchange
- Embassy of Lebanon, Washington, D.C.
News
- The Daily Star national daily newspaper in English
- Electronic Lebanon online news
- Tayyar news website Template:Ar icon
- An-Nahar national daily newspaper Template:Ar icon
- Al-Mustaqbal national daily newspaper Template:Ar icon
- As-Safir national daily newspaper Template:Ar icon
- AL-Balad national daily newspaper Template:Ar icon
- Addiyar national daily newspaper Template:Ar icon
- Ya Libnan independent news in English
- L'Orient - Le Jour national daily newspaper in French Template:Fr icon
- NewsXS aggregated news headlines and rss-feed
- United Nations - Mehlis Report official report of the investigation into Hariri's assassination
- Vote961 Lebanon News aggregates news from various sources on-the-fly using AJAX.
- Libnanews: news from Lebanon (in french)
- Save Leb: News and information on the current attacks against Lebanon
- Russia Might Get Involved in the Middle East Conflict
- Diplomacy Monitor - Documents Affecting Lebanon
Culture and education
- UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Lebanon
- Al-Bustan Festival, Beit Meri
- Baalbek Festival
- Beiteddine Festival
- Byblos Festival
- The National Museum of Beirut
Tourism
- Info Lebanon Information about Lebanon, Both Touristic and Historic.
- Discover Lebanon
- Destination Lebanon
- Rediscover Lebanon
- MEA-Middle East Airlines
General information
- Civil War 1975 to 1990 & War on Lebanon 2006 Pictures
- Movie Clip: Lebanese Civil War 7 minutes
- Lebanon - Al Mashriq Extensive information about Lebanon, including maps and pictures.
- Lebanon at the The World Factbook
- LebWeb.com - The Lebanon Guide Lebanon directory, Lebanon news, Lebanon web resources.
- Open Directory Project - Lebanon directory project
- Go-Leb! Proud to be Lebanese -Lebanon Lebanese directory of links
- US State Department - Lebanon includes Background Notes, Country Study and major reports
Lebanese people
- The Center for Democracy in Lebanon
- Lebanon White Pages (leb.org)|Find Lebanese
- Window in Lebanon (The First Lebanese Blog in French)
- Lebanese Families and Maronite History
- Helem (Lebanese GLBT association)
- Mazenkerblog (Mazen is still drawing under the bombs !)
| Middle East | |
|---|---|
| Countries | |
| Society | |
| Demographics | |
| Culture | |
| Countries and territories of the Mediterranean Sea | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states | |
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other territories |
|
| Marginal seas | |