This is an old revision of this page, as edited by AnomieBOT (talk | contribs) at 13:37, 8 December 2015 (Dating maintenance tags: {{Update inline}}). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 13:37, 8 December 2015 by AnomieBOT (talk | contribs) (Dating maintenance tags: {{Update inline}})(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Ethnic group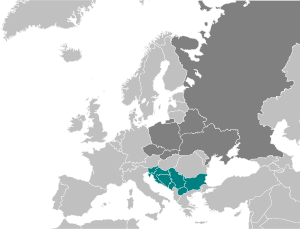 South Slavic countries Other Slavic countries South Slavic countries Other Slavic countries | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| Majority: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Slovenia. Minority: Albania, Greece, Republic of Kosovo (disputed status), Romania, Turkey, Italy, Hungary, Austria. | |
| Languages | |
| East South Slavic languages: Bulgarian, Macedonian West South Slavic languages: Serbo-Croatian, Slovene | |
| Religion | |
| Orthodox Christianity, Catholic Church, Islam | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Other Slavs (particularly East Slavs) |
The South Slavs are a subgroup of Slavic peoples who speak the South Slavic languages.
They inhabit a contiguous region in the Balkan Peninsula, southern Pannonian Plain and eastern Alps, and are geographically separated from the body of West Slavic and East Slavic people by the Romanians, Hungarians, and Austrians. The South Slavs include the Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes. They are the main population of the Central and Southern European countries of Bulgaria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Republic of Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia and Slovenia. Their territories are separated from the rest of the Slavic nations since the 15th century by the modern non-Slavic states of Austria, Hungary, Romania and Moldova, leading to a differing historical progression for the South Slav nations in relation to the West and East Slavs.
In the 20th century the country of Yugoslavia (lit. "South Slavia") merged the vast region to which most South Slavic nations are autochthonous (with the key exception of Bulgaria and the Bulgarians) into a single state. The concept of Yugoslavia, as a single state for all South Slavic peoples, emerged in the late 17th century and gained prominence through the Illyrian movement of the 19th century. The name was coined as a combination of the Slavic words jug (south) and sloveni (Slavs).
History
Early accounts
Main article: Early SlavsLittle is known about the Slavs before the 5th century. Their history prior to this can only be tentatively hypothesized via pre-Indo-European archeological and linguistic studies. Much of what we know about their history after the 6th century is from the works of Byzantine historians. In his work De Bellis, Procopius portrays the Sclavini (supposed to be Slavs) as unusually tall and strong, with a tan complexion and reddish-blonde hair, living a rugged and primitive life. They lived in huts, often distant from one another and often changed their place of abode. They were not ruled by a single leader, but for a long time lived in a "democracy". John of Ephesus, in his Ecclesiastical History portrays the Slavs as extremely violent people. They probably believed in many Gods, but Procopius suggests they believed in one, perhaps supreme god. He has often been identified as Perun, the creator of lightning. The Slavs went into battle on foot, charging straight at their enemy, armed with spears and small shields, but they did not wear armour.
This information is supplanted by Pseudo-Maurice's work Strategikon, describing the Slavs as a numerous but disorganised and leaderless people, resistant to hardship and not allowing themselves to be enslaved or conquered. The lack of understanding may be attributed to matrilineal succession practiced among Southern Slavs.

They made their homes in forests, by rivers and wetlands. Jordanes states that the Slavs "have their homelands on the Danube, not far from the northern bank." Subsequent information about early Slavic states and the Slavs' interaction with the Greeks comes from De Administrando Imperio by Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus, the compilations of Miracles of Saint Demetrius, History by Theophylact Simocatta and the Royal Frankish Annals.
Migrations and postulated homeland
Further information: Slavic settlement of the Eastern AlpsScholars have traditionally placed the Slavic Urheimat in the Pripet marshes of Ukraine, or alternatively between the Bug and the Dniepr. In the 5th century Slavs are mentioned as living north of the Danube in the written sources from that era. From the 5th century, they supposedly spread outward in all directions. The Balkans was one of the regions which lay in the path of the expanding Slavs.
Regarding the Slavs mentioned by 6th-century Byzantine chroniclers, Florin Curta states that their 'homeland' was north of the Danube and not in the Belorussian-Ukrainian borderlands. He clarifies that their itinerant form of agriculture (they lacked the knowledge of crop rotation) "may have encouraged mobility on a micro regional scale". Material culture from the Danube suggests that there was an evolution of Slavic society between the early 7th century and the 8th century. As the Byzantines re-asserted the Danubian defences in the mid 6th century, the Slavs' yield of pillaged goods dropped. As a reaction to this economic isolation, and external threats (e.g. from Avars and Byzantines), political and military mobilisation occurred. Archeological sites from the late 7th century show that the earlier settlements which were merely a non-specific collection of hamlets began to evolve into larger communities with differentiated areas (e.g. designated areas for public feasts as well as an 'industrial' area for craftsmanship). As community elites rose to prominence, they came to "embody a collective interest and responsibility" for the group. "If that group identity can be called ethnicity, and if that ethnicity can be called Slavic, then it certainly formed in the shadow of Justinian's forts, not in the Pripet marshes."
The Byzantines broadly grouped the numerous Slav tribes into two groups: the Sclaveni and Antes. They are both first encountered in the lower Danube region. Some, such as Bulgarian scholar Vasil Zlatarski, suggest that the first group settled the western Balkans, becoming one of the forerunners of the linguistic group that became the Bosnians, Serbs and Croats, whilst offshoots of the Antes settled the eastern regions (roughly speaking), becoming one of the ancestors of the Bulgarians. From the Danube, they commenced raiding the Byzantine Empire from the 520s, on an annual basis. They spread about destruction, taking loot and herds of cattle, seizing prisoners and taking fortresses. Often, the Byzantine Empire was stretched defending its rich Asian provinces from Arabs, Persians and Turks. This meant that even numerically small, disorganised early Slavic raids were capable of causing much disruption, but could not capture the larger, fortified cities.
Large scale Slavic settlement in the Balkans begins in the late 570s and early 580s. Menander, a late 6th-century historian speaks of 100,000 Slavs pouring into Thrace (though likely with some exaggeration) and Illyricum, taking cities and settling down. These large scale population movements are associated with the arrival to the area of the Avars, a nomadic Turkic group that had lost a war against other nomads further east, and settled in the Carpathian basin, subjugating the many small Slavic tribes. They were also facilitated by the fact that the Byzantine Empire was embroiled in a series of wars with Sassanid Persia at the time and was unable to send troops to the Balkans.
By the 580s, as the Slav communities on the Danube became larger and more organized, and as the Avars exerted their influence, raids became larger and resulted in permanent settlement. Most scholars consider the period of 581-584 as the beginning of large scale Slavic settlement in the Balkans. Around this time, the chronicle known as the Miracles of Saint Demetrius speaks of large-scale Slavic settlement in the area around Thessaloniki, although the Slavs never managed to take the city itself. In 591, the Byzantines ended their war with the Persians and a serious attempt to restore the northern border was made by the emperor Maurice, a skilled strategist. Although largely successful, Maurice did not manage to completely eliminate the Avars, and was eventually deposed and murdered in 602 (in part due to his refusal to ransom a large number of captives who were then slaughtered by the Avars). War with the Persians soon broke out again, and the northern border collapsed once more.

The Avars arrived in Europe in the late 550s. Although their identity would not last, the Avars greatly impacted the events of the Balkans. They settled the Carpathian plain, west of the main Slavic settlements. They crushed the Gepid Kingdom (a Germanic tribe) and pushed the Lombards into Italy, essentially opening up the western Balkans. They asserted their authority over many Slavs, who were divided into numerous petty tribes. Many Slavs were relocated to the Avar base in the Carpathian basin and were galvanized into an effective infantry force. Other Slavic tribes continued to raid independently, sometime coordinating attacks as allies of the Avars. Others still spilled into Imperial lands as they fled from the Avars. The Avars and their Slavic allies tended to focus on the western Balkans, whilst independent Slavic tribes predominated in the east. Following the unsuccessful siege of Constantinople in 626, the Avars' reputation diminished, and the confederacy was troubled by civil wars between the Avars and their Bulgar and Slav clients. Their rule contracted to the region of the Carpathian basin. Archaeological evidence show that there was intermixing of Slavic, Avar and even Gepid cultures, suggesting that the later Avars were an amalgamation of different peoples. The Avar Khanate finally collapsed after ongoing defeats at the hands of Franks, Bulgars and Slavs (c. 810), and the Avars ceased to exist. What remained of the Avars was absorbed by the Slavs and Bulgars.
In "De Administrando Imperio", Byzantine emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus mentions the White Croatia (originally Βελοχρωβάτοι i Χρωβάτοι) as the place from which, in the 7th century, part of Croatian tribes started their journey to Balkans (more specific, today's Croatia and Bosnia-Herzegovina) after they were invited there by the Byzantine Empire (emperor Flavius Heraclius Augustus) to protect its borders.The earliest Croatian state was the Principality of Dalmatia. Prince Trpimir of Dalmatia was called Duke of Croats in 852. In 925 Croatian Duke of Dalmatia Tomislav of Trpimir united all Croats and elevated Croatia into kingdom. He organized a state by annexing the Principality of Pannonia as well as maintaining close ties with Pagania and Zahumlje.
By 700 AD, Slavs had settled in most of the Balkans, from Austria to the Peloponnese, and from the Adriatic to the Black seas, with the exception of the coastal areas and certain mountainous regions of the Greek peninsula. The settlement pattern was far from uniform however, with major routes (such as the Morava valley) experiencing greater settlement. Far fewer numbers of Slavs appear to have settled in those parts of Greece where Slavs did settle, and in remote mountainous regions such as Bosnia, Herzegovina and Montenegro. However, archaeological traces of Slavic penetration into the Balkans is scant, especially in the period prior to the 8th century. This has led scholars to cast doubt on the accuracy of the historical sources, often describing large scale settlements by the Slavs throughout the Balkans, including southern Greece.
Interaction with the Balkan population
Prior to the advent of Roman rule, a number of native or autochthonous populations had lived in the Balkans since ancient times. South of the Jireček line were the Greeks. To the north, there were Illyrians in the western portion (Illyricum), Thracians in Thrace (modern Bulgaria and eastern Macedonia), and Dacians in Moesia (northern Bulgaria and northeastern Serbia) and Dacia (modern Romania). They were mainly tribalistic and generally lacked awareness of any greater ethno-political affiliations. Over the classical ages, they were at times invaded, conquered and influenced by Celts, Greeks and Romans. Roman influence, however, was initially limited to cities later concentrated along the Dalmatian coast, later spreading to a few scattered cities inside the Balkan interior particularly along the river Danube (Sirmium, Belgrade, Niš). Roman citizens from throughout the empire settled in these cities and in the adjacent countryside. The vast hinterland was still populated by indigenous peoples who likely retained their own tribalistic character.
Following the fall of Rome and numerous barbarian raids, the population in the Balkans dropped, as did commerce and general standards of living. Many people were killed, or taken prisoner by invaders. This demographic decline was particularly attributed to a drop in the number of indigenous peasants living in rural areas. They were the most vulnerable to raids and were also hardest hit by the financial crises that plagued the falling empire. However, the Balkans were not desolate; considerable numbers of indigenous people simply remained. Only certain areas tended to be affected by the raids (e.g. lands around major land routes, such as the Morava corridor). The pre-Slavic inhabitants sought refuge inside fortified cities and islands, whilst others fled to remote mountains and forests, joining their non-Romanized kin and adopting a transhumant pastoral lifestyle. The larger cities were able to persevere, even flourish, through the hard times. Archaeological evidence suggests that the culture in the cities changed whereby Roman-style forums and large public buildings were abandoned and cities were modified (i.e. built on top of hills or cliff-tops and fortified by walls). The centerpiece of such cities was the church. This transformation from a Roman culture to a Byzantine culture was paralleled by a rise of a new ruling class: the old land-owning aristocracy gave way to rule by military elites and the clergy.
In addition to the autochthons, there were remnants of previous invaders such as "Huns" and various Germanic peoples when the Slavs arrived. Sarmatian tribes (such as the Iazyges) are recorded to have still lived in the Banat region of the Danube.
As the Slavs spread south into the Balkans, they interacted with the numerous peoples and cultures already there. Since their lifestyle revolved around agriculture, they preferentially settled rural lands along the major highway networks which they moved along. Whilst they could not take the larger fortified towns, they looted the countryside and captured many prisoners. In his Strategikon, Pseudo-Maurice noted that it was commonplace for Slavs to accept newly acquired prisoners into their ranks. Despite Byzantine accounts of "pillaging" and "looting", it is possible that many indigenous peoples voluntarily assimilated with the Slavs. The Slavs lacked an organised, centrally ruled organisation which actually hastened the process of willful Slavicisation. The strongest evidence for such a co-existence is from archaeological remains along the Danube and Dacia known as the Ipoteşti-Cândeşti culture. Here, the villages dating back to the 6th century represent a continuity with the earlier Slavic Pen'kovka culture; modified by admixture with Daco-Getic, Daco-Roman and/or Byzantine elements within the same village. Such interactions awarded the pre-Slavic populace protection within the ranks of a dominant, new tribe. In return, they contributed to the genetic and cultural development the South Slavs. This phenomenon ultimately led to an exchange of various loan-words. For example, the Slavic name for "Greeks", Grci, is derived from the Latin Graecus presumably encountered through the local Romanised populace. Conversely, the Vlachs borrowed many Slavic words, especially pertaining to agricultural terms. Whether any of the original Thracian or Illyrian culture and language remained by the time Slavs arrived is a matter of debate. It is a difficult issue to analyse because of the overriding Greek and Roman influence in the region. However, what is certain is that the Thracian and Illyrian identities disappear from history during this period.
Over time, due to the larger number of Slavs, the descendants most of the indigenous populations of the Balkans were Slavicized, an exception being Greece, where the smaller number Slavs scattered there came to be Hellenized over succeeding centuries (aided in time by more Greeks returning to Greece in the 9th century and the role of the church and administration). The Romance speakers within the fortified Dalmatian cities managed to retain their culture and language for a long time, as Dalmatian Romance was spoken until the high Middle Ages. However, they too were eventually assimilated into the body of Slavs. In contrast, the Romano-Dacians in Wallachia managed to maintain their Latin-based language, despite much Slavic influence. After centuries of peaceful co-existence, the groups fused to form the Romanians.
Relationship with Byzantium
Further information: SclaviniaeByzantine literary accounts (i.e., John of Ephesus, etc.) mention the Slavs raiding areas of Greece during the 580s. According to later sources such as The Miracles of Saint Demetrius, the Drougoubitai, Sagoudatai, Belegezitai, Baiounetai, and Berzetai laid siege to Thessaloniki in 614–616. However, this particular event was in actuality of local significance. A combined effort of the Avars and Slavs two years later also failed to take the city. In 626, a combined Avar, Bulgar and Slav army besieged Constantinople. The siege was broken, which had repercussions upon the power and prestige of the Avar khanate. Slavic pressure on Thessaloniki ebbed after 617/618, until the Siege of Thessalonica (676–678) by a coalition of Rynchinoi, Sagoudatai, Drougoubitai and Stroumanoi attacked. This time, the Belegezites also known as the Velegeziti did not participate and in fact supplied the besieged citizens of Thessaloniki with grain.
A number of medieval sources attest to the presence of Slavs in Greece. While en route to the Holy Land in 732, Willibald "reached the city of Monemvasia, in the land of Slavinia". This particular passage from the Vita Willibaldi is interpreted as an indication of a Slavic presence in the hinterland of the Peloponnese. In reference to the plague of 744–747, Constantine VII wrote during the 10th century that "the entire country was Slavonized". Another source for the period, the Chronicle of Monemvasia speaks of Slavs overrunning the western Peloponnese, but of the eastern Peloponnese, together with Athens, remaining in Byzantine hands throughout this period. However, such sources are far from ideal, and their reliability is debated. For example, while the Byzantinist Peter Charanis believes the Chronicle of Monemvasia to be a reliable account, other scholars point out that it greatly overstates the impact of the Slavic and Avar raids of Greece during this time.
Max Vasmer, a prominent linguist and Indo-Europeanist, complements late medieval historical accounts by listing 429 Slavic toponyms from the Peloponnese alone. To what extent the presence of these toponyms reflects compact Slavic settlement is a matter of some debate, and might represent an accumulative strata of toponyms rather than being attributed to the earliest settlement phase
Though medieval chroniclers attest to Slavic "hordes" occupying Byzantine territories, archaeological evidence of actual Slavic presence and its dating is today debated. Florin Curta points out that evidence of substantial Slavic presence does not appear before the 7th century and remains qualitatively different from the "Slavic culture" found north of the Danube. Some authors point to the rapid adoption of local Balkanic cultures by early Slav-speaking groups in specific areas such as Dalmatia. There, investigations of burial graves and cemetery types indicate an uninterrupted continuity of traditions from late antiquity, reflecting a contiguous demographic spread that chronologically matches with the arrival of Slavic-speaking groups. Furthermore, when medieval sources speak of places "going to the Slavs", this could primarily mean that Byzantine authority disappeared, not that these regions had witnessed large-scale migration; doubtless many local people simply governed themselves. Indeed, in the wake of Roman collapse, communities in the Balkan interior and hinterland essentially "became Slavs" by creating new identities and adopting a new language, oriented toward east-central Europe rather than the Graeco-Mediterranean world. As Timothy Gregory surmises:
T E Gregory, A History of Byzantium. Wiley-Blackwell, 2010. Pg 169"It is now generally agreed that the people who lived in the Balkans after the Slavic "invasions" were probably for the most part the same as those who had lived there earlier, although the creation of new political groups and arrival of small immigrants caused people to look at themselves as distinct from their neighbours, including the Byzantines".
Relations between the Slavs and Greeks were probably peaceful apart from the (supposed) initial settlement and intermittent uprisings. Being agriculturalists, the Slavs probably traded with the Greeks inside towns. Furthermore, the Slavs surely did not occupy the whole interior or eliminate the Greek population; some Greek villages continued to exist in the interior, probably governing themselves, possibly paying tribute to the Slavs. Some villages were probably mixed, and quite possibly some degree of Hellenization of the Slavs by the Greeks of the Peloponnese had already begun during this period, before re-Hellenization was completed by the Byzantine emperors.
When the Byzantines were not fighting in their eastern territories, they were able to slowly regain imperial control. This was achieved through its theme system, referring to an administrative province on which an army corps was centered, under the control of a strategos ("general"). The theme system first appeared in the early 7th century, during the reign of the Emperor Heraclius, and as the Byzantine Empire recovered, it was imposed on all areas that came under Byzantine control. The first Balkan theme created was that in Thrace, in 680 AD. By 695, a second theme, that of "Hellas" (or "Helladikoi"), was established, probably in eastern central Greece. Subduing the Slavs in these themes was simply a matter of accommodating the needs of the Slavic elites and providing them with incentives for their inclusion into the imperial administration.
It was not until 100 years later that a third theme would be established. In 782–784, the eunuch general Staurakios campaigned from Thessaloniki, south to Thessaly and into the Peloponnese. He captured many Slavs and transferred them elsewhere, mostly Anatolia (these Slavs were dubbed Slavesians). However it is not known whether any territory was restored to imperial authority as result of this campaign, though it is likely some was. Sometime between 790 and 802, the theme of Macedonia was created, centered on Adrianople (i.e., east of the actual geographic entity). A serious and successful recovery began under Nicephorus I (802–811). In 805, the theme of the Peloponnese was created. According to the Chronicle of Monemvasia in 805 the Byzantine governor of Corinth went to war with the Slavs, obliterated them, and allowed the original inhabitants to claim their own; the city of Patras was recovered and the region re-settled with Greeks. In the 9th century, new themes continued to arise, although many were small and were carved out of original, larger themes. New themes in the 9th century included those of Thessalonica, Dyrrhachium, Strymon, and Nicopolis. From these themes, Byzantine laws and culture flowed into the interior. By the end of the 9th century most of Greece was culturally and administratively Greek again, with the exception of a few small Slavic tribes in the mountains such as the Melingoi and Ezeritai. Although they were to remain relatively autonomous until Ottoman times, such tribes were the exception rather than the rule.

Apart from military expeditions against Slavs, the re-Hellenization process begun under Nicephorus I involved (often forcible) transfer of peoples. Many Slavs were moved to other parts of the empire, such as Anatolia and made to serve in the military. In return, many Greeks from Sicily and Asia Minor were brought to the interior of Greece, to increase the number of defenders at the Emperor's disposal and dilute the concentration of Slavs. Even non-Greeks were transferred to the Balkans, such as Armenians. As more of the peripheral territories of the Byzantine Empire were lost in the following centuries, e.g., Sicily, southern Italy and Asia Minor, their Greek-speakers made their own way back to Greece. That the re-Hellenization of Greece through population transfers and cultural activities of the Church was successful suggests Slavs found themselves in the midst of many Greeks. It is doubtful that such large number could have been transplanted into Greece in the 9th century; thus there surely had been many Greeks remaining in Greece and continuing to speak Greek throughout the period of Slavic occupation. The success of re-Hellenization also suggests the number of Slavs in Greece was far smaller than the numbers found in the former Yugoslavia and Bulgaria. For example, Bulgaria could not be Hellenized when Byzantine administration was established over the Bulgarians in 1018 to last for well over a century, until 1186.
Eventually, the Byzantines recovered the imperial border north all the way to today's region of Macedonia (which would serve as the northern border of the Byzantine Empire until 1018), although independent Slavic villages remained. As the Slavs supposedly occupied the entire Balkan interior, Constantinople was effectively cut off from the Dalmatian cities under its (nominal) control. Thus Dalmatia came to have closer ties with the Italian Peninsula, because of ability to maintain contact by sea (however, this too, was troubled by Slavic pirates). Additionally, Constantinople was cut off from Rome, which contributed to the growing cultural and political separation between the two centers of European Christendom.
Control of the Slavic tribes was nominal, as they retained their own culture and language. However, the Slavic tribes of Macedonia never formed their own empire or state, and the area often switched between Greek (Byzantine), Bulgarian, Serbian and temporarily even Norman control. The Byzantines were unable to completely Hellenize Macedonia because their progress north was blocked by the Bulgarian Empire, and later by the Serbian Kingdom, which were both Slavic states. However, Byzantine culture nonetheless flowed further north, seen to this day as Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia, and Serbia are part of the Orthodox world. Even in Dalmatia, where Byzantine influence was supplanted by Venice and Rome, the influence of Byzantine culture persists.
Sclaviniaes
Main article: SclaviniaeDuring the early Middle Ages, the Byzantine historians categorized the numerous Slavic tribal unions on the early Medieval Balkans as 'Sclavinias' and often associated them with particular tribes. The Slavs were self-governing in their extended families and districts, and their tribal organization was sufficiently strong to abolish Byzantine rule in the Balkans. These Slavs however did not have sufficient state-building skills, they failed to unite them and during the 8th century they were reconquered by the Byzantines. Some contemporary Macedonian historians have seen one of these tribal unions, referred to by the Byzantines as Sclaviniai as proto–state indicative of the formation of a separate Slavic Macedonian state, but this claim is extremely doubtful, more they also spread into Thrace and Moesia, which are now not seen as part of the today Macedonia. On the other hand, according to Florin Curta describes the great Slavic invasion of the 6th and 7th century on the Balkans as a historical exaggeration. Thus, the construction of the first South Slavic states was organized by the Croats, Serbs and Bulgars and the local (Slavic) population in today Republic of Macedonia was first conquered by the Bulgars in the middle of the 9th century.
Ottoman period
So long as the non-Slavic Byzantine Empire was strong it served as an effective buffer to Ottoman incursions into southeastern Europe and in turn the lands of the South Slavs. Eventually its power waned in the face of conquests by other powers, and the rising Turkish Empire found one weakness after another in southeastern Europe.
The Ottomans captured Thessaloniki from the Venetians in 1387. The Ottoman victory at Kosovo in 1389 effectively marked the end of Serbian power in the region, making possible the Ottoman expansion into Europe. Stefan Lazarević of Serbia became a vassal of the Ottoman Empire. The Battle of Nicopolis in 1396, widely regarded as the last large-scale crusade of the Middle Ages, failed to stop the advance of the victorious Ottoman Turks and put an end to the Second Bulgarian Empire.
Modern era
South Slavic peoples
South Slavs are divided along linguistic lines into two groups — eastern and western.
List of the South Slavic peoples and ethnic groups, including population estimation figures (2001):
- Serbs = 10 to 10,500,000
- Bulgarians = 9,000,000
- Croats = 6,000,000 to 7,500,000
- Bosniaks = 3,500,000
- Slovenes = 2,500,000
- Macedonians = 2,200,000
- Montenegrins = 340,000
- Yugoslavs, Muslims by nationality, and other minor ethnic groups
All together: about 40 million including other minor groups
Countries
There are seven countries in which South Slavs are the main population:
 Bulgaria (85% Bulgarians)
Bulgaria (85% Bulgarians) Serbia (83% Serbs, 2% Bosniaks, 0.8% Croats, 0.5% Montenegrins)
Serbia (83% Serbs, 2% Bosniaks, 0.8% Croats, 0.5% Montenegrins) Croatia (90% Croats, 4% Serbs)
Croatia (90% Croats, 4% Serbs) Bosnia and Herzegovina (48% Bosniaks, 37% Serbs, 15% Croats)
Bosnia and Herzegovina (48% Bosniaks, 37% Serbs, 15% Croats) North Macedonia (64% ethnic Macedonians, 2% Serbs, 1% Bosniaks)
North Macedonia (64% ethnic Macedonians, 2% Serbs, 1% Bosniaks) Slovenia (83% Slovenes, 2% Serbs, 2% Croats, 1% Bosniaks)
Slovenia (83% Slovenes, 2% Serbs, 2% Croats, 1% Bosniaks) Montenegro (45% Montenegrins, 29% Serbs, 13% Bosniaks and Muslims by nationality, 1% Croats)
Montenegro (45% Montenegrins, 29% Serbs, 13% Bosniaks and Muslims by nationality, 1% Croats)
In addition, there are local South Slavic minorities in non-Slavic neighbouring countries such as:
- Albania: (Bulgarians, Macedonians, Serbs, Montenegrins)
- Austria: (Croats, Slovenes)*
- Greece: (Slavic-speakers of Greek Macedonia, Pomaks)
- Hungary: (Croats, Serbs, Slovenes, Bulgarians)
- Italy: (Slovenes, Croats)
- Romania: (Croats, Bulgarians, Serbs, Macedonians),
- Turkey: (Bulgarians, Bosniaks, Macedonians)
Cities
| Cities with South Slavic majority (100,000+ residents) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | Population | Municipality | Source | Image |
| 1,233,796 | 1,659,440 | (Census Bureau of Serbia; 2011) | 
| |
| 1,204,685 | 1,359,520 | (Census Bureau of Bulgaria; 2011) | 
| |
| 792,875 | 1,110,517 | (Census Bureau of Croatia; 2011) | 
| |
| 510,000 | 668,518 | (Census Bureau of the Republic of Macedonia; 2006) | 
| |
| 338,153 | 403,153 | (Census Bureau of Bulgaria; 2011) | 
| |
| 334,870 | 343,704 | (Census Bureau of Bulgaria; 2011) | 
| |
| 327,124 | 452,000 | (Census Bureau of Bosnia and Herzegovina; 2010) | 
| |
| 277,522 | 341,625 | (Census Bureau of Serbia; 2011) | 
| |
| 272,220 | (Census Bureau of Slovenia; 2011) | 
| ||
| 225,000 | (Census Bureau of Bosnia and Herzegovina; 2008) | 
| ||
| 200,271 | 212,902 | (Census Bureau of Bulgaria; 2011) | 
| |
| 187,544 | 260,237 | (Census Bureau of Serbia; 2011) | 
| |
| 165,883 | 349,314 | (Census Bureau of Croatia; 2011) | 
| |
| 157,947 | (Census Bureau of Slovenia; 2010) | 
| ||
| 151,312 | (Census Bureau of Montenegro; 2011) | 
| ||
| 150,835 | 179,417 | (Census Bureau of Serbia; 2011) | 
| |
| 149,642 | (Census Bureau of Bulgaria; 2011) | 
| ||
| 138,272 | (Census Bureau of Bulgaria; 2011) | 
| ||
| 127,498 | (Census Bureau of Croatia; 2011) | 
| ||
| 106,954 | (Census Bureau of Bulgaria; 2011) | 
| ||
| 105,681 | 141,554 | (Census Bureau of Serbia; 2011) | 
| |
Regional groups and other subdivisions
Please note that some of the subdivisions remain debatable, particularly for smaller groups and national minorities in former Yugoslavia.
Besides ethnic groups, South Slavs often identify themselves with the geographical region in which they live. Some of the major regional South Slavic groups include: Zagorci, Istrani, Dalmatinci, Slavonci, Bosanci, Hercegovci, Posavljaci, Krajišnici, Semberci, Srbijanci, Šumadinci, Mačvani, Moravci, Vojvođani, Sremci, Bačvani, Banaćani, Sandžaklije, Kosovci, Brđani, Bokelji, Zećani, Torlatsi, Shopi, Pelagonci, Tikvešjani, Trakiytsi, Dobrudzhantsi, Balkandzhii, Aegean Macedonians, Mijaks, Mariovans, Miziytsi, Pirintsi, Rodoptsi, Bessarabians, Carinthians, Styrians, Carniolans, Prekmurians, Venetians, Palćene, Burgenlanders, Janjevci, Molisans, Krashovans, Šokci, Resians, and many others.
Religion
The religious and cultural diversity of the region the South Slavs inhabit has had a considerable influence on their religion. Originally a polytheistic pagan people, the South Slavs have also preserved many of their ancient rituals and traditional folklore, often intermixing and combining it with the religion they later converted to.
Today, the majority of South Slavs are Orthodox Christians- the most Bulgarians, Macedonians, Serbs and Montenegrins, whilst most Slovenes and Croats are Roman Catholics. Bosniaks, other minor ethnic groups (Gorani, Muslims by nationality) and sub-groups (Torbesh and Pomaks) are Muslims. Some South Slavs are atheist, agnostic and/or non-religious.
South Slavic ethnic groups by religion:
- Mainly Roman Catholics
Language
Main article: South Slavic languagesSouth Slavic standard languages are:
In addition, there are also other South Slavic languages which do not constitute official status in any republic, but have recognised standard formats and are widely used by their speakers. The most common of these is Bunjevac. In addition, the Šokac language was formerly listed in the census conducted during the Austro-Hungarian administration. Today, Montenegrin is also in the accelerated process of being codified in Montenegro. It is slowly being revised, embracing local speech, following the lines taken for Bosnian following the independence of Bosnia and Herzegovina from Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
The division of standard languages is orthogonal to the division based on genetic-dialectological criteria. Naming local dialects is made difficult by the fact that Slovenes from Austria and Italy are linked with their most remote South Slavic peoples - the Pomaks and Bulgarians of European Turkey - by a historical dialect continuum. In the 9th century all Slavic dialects formed one dialect continuum, which was subsequently broken after the arrival of Magyars in the area of middle Danube; the subsequent spread of the Germanic, Greek and Romance speakers separated the South Slavic group from West and East Slavic groups leaving it roughly its present-day areal distribution.
Furthermore, as a result of migrations caused by the invasion of Ottoman Turks, dialect continuum was broken in numerous places especially in the so-called "Central South Slavic" area, where some Slavic dialects like Čakavian and Kajkavian were suppressed at the expense of Štokavian, and some "transitional" dialects like Torlakian, originally belonging to West South Slavic group, but having experienced numerous shared innovations with Bularo-Macedonian dialects belonging to East South Slavic.
Major Slavic dialectal groupings are
- Kajkavian - named after the interrogative "kaj", the local word for "what", this dialect is spoken in Croatia and is closely related to the Slovene language (also a "kaj" language).
- Čakavian - named after the interrogative ča, the local word for "what", also an exclusively Croatian dialect
- Štokavian - the largest and most complex dialect chain, named after "što" - the local word for "what" - itself varies with increased distance. Its subdialect, Neoštokavian, is used as the base for standard Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, Montenegrin and Bunjevac, though in a bit different form (in yat reflex, cf. below)
- Torlakian - a non-standard dialect chain separating Western South Slavic and Eastern South Slavic language groups with radical differences, spoken in southern Serbia (including Kosovo), northern Macedonia and north-western Bulgaria, and by all Slavic ethnic groups local to the region, its features include a mixture of the western and eastern linguistic trends. It is also spoken by the Krashovan community in Romania, reflecting their previous geographical settlement.
- Macedonian - spoken across most of Macedonia. The standard Macedonian is based on the West-central subdialect. Several regional dialects exist.
- Shop dialect - a western Bulgarian dialect group bordering with Torlakian areas to its northwest, with Macedonian to its southwest and East Bulgarian to its east.
- East Bulgarian - the standard language of Bulgaria based on the central regions. Several regional dialects exist.
- Slavic (Greece) - spoken by the Slavic population of Greece, most notably by the Pomaks of Thrace. Often disputed as to whether belonging to Macedonian or Bulgarian, this non-standard language has its dialects sparse but varied according to geographical distribution; with the dialects of Thrace (Trakiya) being closer to Bulgarian, and the dialects of Florina (Lerin) and Edessa (Voden) being closer to Macedonian.
- Flazdian or Flazdim is a southern-Slavic dialect spoken in north of Albania.
The dialects are often further subclassified on arbitrary isoglosses, such as the reflex of Common Slavic yat phoneme which had various reflexes in various Slavic dialects. Yat reflex is noted as a major distinction between Serbian and Croatian - while the former has two distinct variants, based on so-called Ekavian /e/ and Ijekavian /ie̯/ reflexes, the standard Croatian is based exclusively on the Ijekavian reflex /ie̯/.
Genetics
"Molecular anthropology" can reveal patterns of prehistoric demographic expansions in addition to analysing the "genetic relatedness" between extant population groups.
Genetic Structuring and Population Affinities
Various methods have been employed for this and consequently produced slightly different results
Early Studies
The earliest studies looked at 'classical markers', i.e. protein and blood group polymorphisms. Such work, e.g. that of Luca Cavali-Sforza and his team, showed that Europeans might cluster into several groups: (1) "Germanic" (Germans, Austrians) (2) "Scandinavian" (Swedes, Norwegians) (3) "Celtic" (Irish, Scottish) (4) south-western European (Spanish, French, Italian) (4) eastern European (Russian, Hungarian, Ukrainian). The analyses found that Yugoslavs did not group into any of the above clusters, but formed a group of their own; a result he attributed to their internal heterogeneity. Bulgarians were not tested in his study.
Y-DNA
Aggregated results of Y-DNA (e.g. by way of Principal Component Analysis (PCA)) have tended to show that most southern Slavs (i.e. Serbians, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Bosnians, Bulgarians, and some Croats) cluster tightly together (characterised by high frequencies of Hg E1b and I2). Western Croats and Slovenians are usually not within this tight South Slavic cluster (due to low E1b levels and comparatively higher R1a and R1b). Non-Slavic Romanians also cluster with the South Slavic group in the Bosch study.
mtDNA
In comparison, mtDNA haplogroups show far more uniform frequency distributions throughout Europe. For example, a study by Bosch et al. showed that mtDNA samples from all southern Slavs as well as Romanians, Albanians and Greeks, clustered together, and separately from those of Turkish groups. Nevertheless, higher resolution studies have detected that South Slavs can be differentiated from other southern Europeans, including Albanian, Greek and Italian neighbours. Even individual South Slavic groups have revealed distinctive combinations of mtDNA subclusters and sequence types.
Autosomal DNA
Whilst useful in postulating population migrations and expansions, mtDNA and Y-DNA do not demonstrate the totality of "genetic make-up", but rather a very small portion of it, namely, a single line of patrilineage (Y-DNA) and matrilineage (mtDNA). Moreoever, given its propensity to drift, population expansions in more recent prehistory can completely overwrite previous patterns. However, the majority of genetic history lies in the thousands of "classical markers" (blood group systems, protein polymorphisms), as well as non-coding single nucleotide polymorphism and STR sequences in autosomal DNA (atDNA), which is representative of the one's entire ancestry . Several loci, such as the β-globin gene, have been dated to 800, 000 years ago. By contrast, the coalescence time of all mtDNA and Y-DNA haplogroups reaches back to a maximum of 200, 000 years
Most of the larger sequences in atDNA undergo recombination, thus direct information about ancestral inheritance is difficult to ascertain. However, inferences on the overall genetic substructure and relatedness between populations is best achieved by analysing the hundreds of thousands of loci within atDNA. One recent study by two research teams has shown that:
- There are no clear clusters or groups within the European population
- Except for "genetic outliers" such as Saami, Finns, Basques and Sardinians, Europeans are somewhat genetically homogeneous
- Individual population groups are often closely related to their immediate neighbours (irrespective of language or ethnicity)
- There is a southern to northern genetic cline, and populations in southern Europe are older and more genetically diverse than those in northern Europe.
Gallery
- Personalities
- Sights
- National costumes
-
 Children in national costumes in Občice, Slovenia.
Children in national costumes in Občice, Slovenia.
-
 Girls with Miljevci dress in Visovac, Croatia.
Girls with Miljevci dress in Visovac, Croatia.
-
Girls with Sarajevan dress, from Bosnia.
-
 King Nikola I of Montenegro in national dress.
King Nikola I of Montenegro in national dress.
-
 Girls from Mariovo, Macedonia.
Girls from Mariovo, Macedonia.
-
Children in national costumes from Šumadija, Serbia.
-
 Bulgarian folk group from Momchilovtsi, Bulgaria.
Bulgarian folk group from Momchilovtsi, Bulgaria.
See also
References
- John of Ephesus, Ecclesiastical History, VI. 25, 6th century AD: "That same year, being the third after the death of king Justin, was famous also for the invasion of an accursed people, called Slavonians, who overran the whole of Greece, and the country of the Thessalonians, and all Thrace, and captured the cities, and took numerous forts, and devastated and burnt, and reduced the people to slavery, and made themselves masters of the whole country, and settled in it by main force, and dwelt in it as though it had been their own without fear. And four years have now elapsed, and still, because the king is engaged in the war with the Persians, and has sent all his forces to the East, they live at their ease in the land, and dwell in it, and spread themselves far and wide as far as God permits them, and ravage and burn and take captive. And to such an extent do they carry their ravages, that they have even ridden up to the outer wall of the city, and driven away all the king's herds of horses, many thousands in number, and whatever else they could find. And even to this day, being the year 895 (AD 584), they still encamp and dwell there, and live in peace in the Roman territories, free from anxiety and fear, and lead captive and slay and burn..."
- Aron, Albert J. iTraces of Matriarchy in Germanic Hero-lore. pp. 13–14.
- French, Marilyn (2002). From Eve to Dawn: A History of Women in the World. McArthur.
- Fouracre, Paul. The Cambridge Medieval History, Volume I.
- ^ Fine (1983), p. 25
- Curta 2006, p. 56: "The Slavic "homeland," at least for the sixth-century authors who wrote about the Slavs, was north of the Lower Danube, not in the Belorussian-Ukrainian borderlands."
- Curta 2006, p. 61
- ^ Hupchick, Dennis P. The Balkans: From Constantinople to Communism. Palgrave Macmillan, 2004. ISBN 1-4039-6417-3
- Robert Donia, John VA Fine (2005). Bosnia and Hercegovina: A Tradition Betrayed. Columbia University Press. Retrieved 30 October 2012., p. 14-16, 1995,
- Fine 1983, p. 26
- ^ Fine, 1983, p. 29
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 31
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 30
- Fine, 1983, p. 32
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 33
- Fine 1983, p. 43
- Fine 1983, p. 36
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 37
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 64
- Fine 1983, p. 38
- Curta 2001, pp. 307-308: "Furthermore, the archaeological evidence discussed in this chapter does not match any long-distance migratory pattern. Assemblages in the Lower Danube area, both east and south of the Carpathian mountains, antedate those of the alleged Slavic Urheimat in the Zhitomir Polesie, on which Irina Rusanova based her theory of the Prague-Korchak-Zhitomir type."
- Fine 1983, p. 9
- Fine 1983, p. 10
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 12
- ^ Curta 2006, p.
- Fine 1983, p. 57
- Fine 1983, p. 27
- Fine 1983, p. 41
- Fine 1983, p. 35
- Fine 1991, p. 41: "Between 614 and 616, at the same time that the Avars were leading their major offensive against Dalmatia, The Miracles of Saint Demetrius describes the attacks by five Slavic tribes by sea in small boats along the coasts of Thessaly, western Anatolia, and various Greek islands. They then decided to capture Thessaloniki in a combined land and sea attack. Under the walls of the city they camped with whole families. They were led by a chief (the Greek title used is exarch) named Chatzon."
- Curta 2001, p. 108: "I suggest therefore that in describing a local event – the attack of the Drugubites, Sagudates, Belegezites, Baiunetes, and Berzetes on Thessalonica – of relatively minor significance, the author of Book II framed it against a broader historical and administrative background, in order to make it appear as of greater importance. When all the other provinces and cities were falling, Thessalonica alone, under the protection of St Demetrius, was capable of resistance."
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 62
- Davis, Jack L. and Alcock, Susan E. Sandy Pylos: An Archaeological History from Nestor to Navarino. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1998, p. 215.
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 61
- Mee, Christopher; Patrick, Michael Atherton; Forbes, Hamish Alexander (1997). A Rough and Rocky Place: The Landscape and Settlement History of the Methana Peninsula, Greece: Results of the Methana Survey Project, sponsored by the British School at Athens and the University of Liverpool. Liverpool, United Kingdom: Liverpool University Press.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Max Vasmer (1941). "Die Slaven in Griechenland". Berlin: Verlag der Akademie der Wissenschaften.
- Vacalopoulos, Apostolos E. (translated by Ian Moles). Origins of the Greek Nation: The Byzantine Period, 1204–1461. New Jersey: Rutgers University Press, 1970, p. 6.
- ^ Curta 2001, p. 308
- Ante Milošević. O kontinuitetu kasnoantičkih proizvoda u materijalnoj kulturi ranoga srednjeg vijeka na prostoru Dalmacije, Starohrvatska spomenička baština. Rađanje prvog hrvatskog kulturnog pejzaža. Exegi monumentum, Znanstvena izdanja 3, Zagreb, 1996, UDK 930.85(497.5), ISBN 953-6100-25-8. p. 39.
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 63
- Danijel Dzino. Becoming Slav, Becoming Croat. Pg 218
- Hupchick, Dennis. The Balkans: From Constantinople to Communism. Palgrave Macmillan, 2004. ISBN 1-4039-6417-3
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 70
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 79
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 80
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 82
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 83
- Fine, 1983, p. 81
- Fine 1983, p. 66
- ^ Fine 1983, p. 65
- Macedonia and the Macedonians: A History, Andrew Rossos, Hoover Press, 2008, ISBN 081794883X, Macedonia c. 600-c. 850
- The New Cambridge Medieval History: Volume 1, C.500-c.700. Cambridge University Press, 2005, ISBN 9780521362917, p. 538.
- The Former Yugoslavia's Diverse Peoples:, Matjaž Klemenčič, Mitja Žagar, ABC-CLIO, 2004, ISBN 1576072940, pp. 26-27.
- The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century," John Van Antwerp Fine, University of Michigan Press, 1991, ISBN 0472081497, pp. 36-37.
- Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Macedonia, Dimitar Bechev, Scarecrow Press, 2009, ISBN 0810862956, p. I-II.
- The Macedonians: Their Past and Present, Ernest N. Damianopoulos, Palgrave Macmillan, 2012, ISBN 1137011904, p. 210.
- The National Question in Yugoslavia: Origins, History, Politics, Ivo Banac, Cornell University Press, 1988, ISBN 0801494931, p. 33.
- Mile Nedeljković. Leksikon naroda Sveta. Beograd, 2001.
- "The World Factbook". cia.gov.
- http://media.popis2011.stat.rs/2011/prvi_rezultati.pdf
- 2011 census
- Rębała et al. 2007.
- Novembre J, Johnson T, Bryc K; Bryc; Kutalik; Boyko; Auton; Indap; King; Bergmann; Nelson; Stephens; Bustamante; et al. (November 2008), "Genes mirror geography within Europe", Nature, 456 (7218): 98–101, Bibcode:2008Natur.456...98N, doi:10.1038/nature07331, PMC 2735096, PMID 18758442
{{citation}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author2=(help); Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Lao O, Lu TT, Nothnagel M; et al. (August 2008), "Correlation between genetic and geographic structure in Europe", Curr. Biol., 18 (16): 1241–8, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2008.07.049, PMID 18691889, retrieved 22 July 2009
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Sources
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (1983), The Early Medieval Balkans, University of Michigan Press, ISBN 0-472-08149-7
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (1991), The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century, University of Michigan Press, ISBN 978-0-472-08149-3
- Curta, Florin. The Making of the Slavs: History and Archaeology of the Lower Danube Region c. 500-700. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001
- Curta, Florin and Stephenson, Paul. Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500-1250. Cambridge University Press, 2006, ISBN 0-521-81539-8
- Alexander F. Tsvirkun The history of western and southern Slavs. Kharkov., 2008
| Slavic ethnic groups | ||
|---|---|---|
| East Slavs |  | |
| West Slavs | ||
| South Slavs | ||
Categories:






