This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Hatchiko (talk | contribs) at 19:52, 6 February 2019 (Position is. The scientific school, in contrast to South Korea, possesses a huge number of archaeological sources, and this position must be in the preamble so that it would not be reconciled in favor of the opinion of one of the parties.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 19:52, 6 February 2019 by Hatchiko (talk | contribs) (Position is. The scientific school, in contrast to South Korea, possesses a huge number of archaeological sources, and this position must be in the preamble so that it would not be reconciled in favor of the opinion of one of the parties.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) This article is about the kingdom. For the sea, see Bohai Sea. Ancient kingdom in northern Korean peninsula and Manchuria (698–926)| Balhae/Bohai발해/渤海/Бохай | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 698–926 | |||||||||||||||||
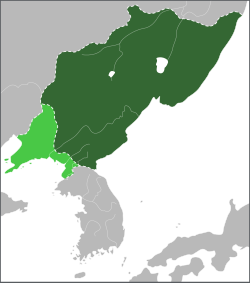 The territory of Balhae in 830, during the reign of King Seon of Balhae. The territory of Balhae in 830, during the reign of King Seon of Balhae. | |||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Dongmo Mountain (698–742) Central Capital (742–756) Upper Capital (756–785) East Capital (785–793) Upper Capital (793–926) Or Five Capital System (698-926) | ||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Bohai language and minority languages Goguryeo language, Khitan language, Even language, Old Japanese | ||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Bohai State Cult of Heaven , Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Korean shamanism, Tengrism, Evenk Shamanism, Shinto | ||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||||||||
| • 698–719 | Go (first) | ||||||||||||||||
| • 719–737 | Mu | ||||||||||||||||
| • 737–793 | Mun | ||||||||||||||||
| • 794–809 | Gang | ||||||||||||||||
| • 809–812 | Jeong | ||||||||||||||||
| • 812–817 | Hui | ||||||||||||||||
| • 818–830 | Seon | ||||||||||||||||
| • 830–857 | Dae Ijin | ||||||||||||||||
| • 906–926 | Dae Inseon (last) | ||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Ancient | ||||||||||||||||
| • Establishment | 698 | ||||||||||||||||
| • Fall of Sanggyeong | January 14 926 | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | China Russia North Korea | ||||||||||||||||
| Balhae/Bohai | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Korean name | |||||||
| Hangul | 발해 | ||||||
| Hanja | 渤海 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Alternative Korean name | |||||||
| Hangul | 진 | ||||||
| Hanja | 震 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||
| Manchu script | ᡦᡠᡥᠠᡳ | ||||||
| Romanization | Puhai | ||||||
| Russian name | |||||||
| Russian | Бохай | ||||||
| Romanization | Bohai | ||||||
| Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Manchuria |
 |
| Prehistoric period |
| Ancient to Classical period |
| Medieval to Early Modern period |
Modern period
|
Balhae or Bohai (698–926), also known from South Korean from transcriptions from korean language as Parhae or Po-hai, was a multi-ethnic kingdom in Manchuria and the Korean peninsula. Balhae according to the version of South Korea was established by refugees from Goguryeo in 698, when the first king, Dae Jo-yeong, defeated the Zhou dynasty at Tianmenling. According to another version, it was a state of predominantly Tungusic peoples with a strong influence of the Goguryeo nobility and culture. Approximately 18% of the population during the period of maximum expansion of 727-735 was the Goguryeo people who lived mostly in the South and controlled the Southern Capital.
Balhae's original capital was at Dongmo Mountain in modern Dunhua, Jilin Province. In 742 it was moved to the Central Capital in Helong, Jilin. It was moved to the Northern Capital in Ning'an, Heilongjiang in 755, to the Eastern Capital in Hunchun, Jilin in 785, and back to the Northern Capital in 794.. According to another theory, there were five Capital in the state according to the principles of Wu Xing. The monarch regularly moved from the capital to the capital. And these cities have never worn Korean names. With the exception of the southern capital in the Later Balhae period (which according to the position of Russian science is a real Parhae - korean state.)
In 926, the Khitan Liao dynasty conquered Balhae and established the autonomous kingdom of Dongdan ruled by the Liao crown prince Yelü Bei, which was soon absorbed into the Liao. Or, not absorbed by the remaining tributary state, but rather became independent and existed before its transformation into the Jin Empire, according to Russian archaeological research. And in the South, inhabited by Goguryo people, a state of Goguryo people was formed - Later Balhae. With capitals in the former Southern Capital of Bohai.
According to a Chinese source, the kingdom had 100,000 households and a population of about 500,000. Archaeological evidence suggests that the Balhae culture was an amalgamation of Chinese, Korean, and indigenous cultures.
Name
Balhae was founded in 698 under the name 震, transcribed as Jin and Zhen in Korean and Chinese romanisations. Jin is the modern Revised Romanization of Korean 진, the same as the earlier Jin state. However, the kingdom's name was written as 辰 in Chinese character, with the reconstructed Old Chinese pronunciation /*ər/ and the Middle Chinese pronunciation dzyin; King Go's state wrote its name as 震, with the Middle Chinese pronunciation tsyin. The former state's character referred to the 5th Earthly Branch of the Chinese zodiac, a division of the orbit of Jupiter identified with the dragon. This was associated with a bearing of 120° (between ESE and SE) but also with the two-hour period between 7 and 9 am, leading it to be associated with dawn and the direction east.
In 713, the Tang dynasty bestowed the ruler of Jin with the title of Head of Balhae Commandery, and in 762 the Tang recognized it as a kingdom and renamed it "Balhae".
History
Founding
There are three theories founding of the state.
One South Korean:
During the Khitan rebellion against Tang, Dae Jung-sang, a former Goguryeo official led Goguryeo refugees, allied with Geolsa Biu, a leader of the Mohe people, against the Tang in 698. After Dae Jungsang's death, his son, Dae Jo-yeong, a former Goguryeo general or chief of Somo Mohe succeeded his father, who received orders from the last King of Goguryeo to found a succeeding country. Geolsa Biu died in battle against the Tang army led by the general Li Kaigu. Dae Jo-yeong managed to escape Tang territory with the remaining Goguryeo and Mohe soldiers. He successfully defeated a pursuing army sent by Wu Zetian at the Battle of Tianmenling. which enabled him to establish the state of Jin in the former region of Yilou as King Go.
Second Chinese:
Another account of events suggests that there was no rebellion at all, and the leader of the Sumo Mohe rendered assistance to the Tang by suppressing Khitan rebels. As a reward the Tang acknowledged the leader as the local hegemon of a semi-independent state.
Third Russian and Japanese:
The state was created by the leader of the Mohe people, who subjugated the neighboring tribes both by diplomatic and military force. The people of Goguryeo were subject to diplomatic power and voluntarily recognized him as their leader. The result of this was that all the Koguryos nobility were incorporated into the state system and many became close to the first ruler. Subsequently, this was manifested in the strong cultural influence of Goguryo on some aspects of life in the state. Fortification engineering partly similar to the Goguryo in the early period, also silk manufacturing technology, pottery art and celadon manufacturing. Part of the troops were armed with armor and weapons of Goguryo. One from the most common types of women's dress was Goguryou. Among the archaeological finds are also often amulets such as Goguryeo. At the same time, the rest is very different from what it was in Goguryo and is related to the cultures of the Yilou peoples, the Khitan, and the Evenks reindeer herders, In Port An (ru:Краскинское городище) was founded in the Posyet Bay in 727. Which linked the Bohai and Japan trade relations. Which was called in Japanese verses of the 9th century - the city of peach trees. In the 8th-10th century, it was inhabited mainly by the Japanese and was strongly influenced by Japanese culture. All this speaks of the state’s pronounced multiculturalism. And that the dominant culture was Tungusic peoples, although all other nations were also perceived as equal.
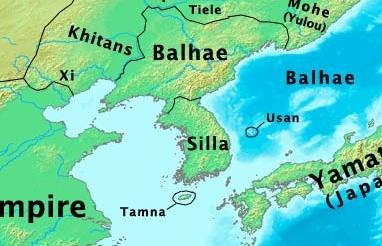
Expansion and foreign relations
In 714 Balhae conquer Protectorate General to Pacify the East, but Tang have claim to region to 761 and in 732-735 reconquest part coast region.
In 725-727 Balhae conquest Heishui (Black) Mohe territory along Black River - part of Yilou tribal confederation.
He also sent a mission to Japan in 728 to threaten Silla from the southeast. Balhae kept diplomatic and commercial contacts with Japan until the end of the kingdom. Balhae dispatched envoys to Japan 34 times, while Japan sent envoys to Balhae 13 times. Later, a compromise was forged between Tang and Balhae, which led Tang diplomatically recognize Mun of Balhae, who succeeded to his father's throne, as King of Balhae.
Fall and legacy
The Khitans were centered in Liaoning and Inner Mongolia, which overlaps Balhae's purported territories in the west. A Khitan invasion took the capital of Balhae after a 25-day siege in 926. After defeating Balhae, the Khitans established a vassal state, the Dongdan Kingdom. Some Balhae aristocrats were forced to move to Liaoyang, but Balhae's south territory remained politically independent. Goryeosa records the arrival of tens of thousands of Balhae households, led by a general escaping from the Khitans in 925, one year before the final collapse of the kingdom. The rest of the Balhae people were assimilated into the Khitan polity as well as the Jurchens who would revolt against the Khitans later in the century. Some descendants of the Balhae royalty in Goryeo changed their family name to Tae (태, 太) while Crown Prince Dae Gwang-hyeon was given the family name Wang (왕, 王), the royal family name of the Goryeo dynasty.

The Khitans themselves eventually succumbed to the Jurchen people, the descendants of the Mohe, who founded the Jin dynasty. Jurchen proclamations emphasized the common descent of the Balhae and Jurchen people from the seven Wuji(勿吉) tribes, and proclaimed "Jurchen and Balhae are from the same family". The fourth, fifth and seventh emperors of Jin were mothered by Balhae consorts. The 13th century census of Northern China by the Mongols distinguished Balhae people who belonged to khitan from other ethnic groups such as Goryeo, Khitan and Jurchen.
Aftermath
After the fall of Balhae and its last king in 926, the autonomous satellite state of Dongdan was founded by its new Khitan rulers. Restoration movements by displaced Balhae people established Later Balhae, which was later renamed to Jeongan. Though Balhae was lost, a great portion of its population including the royalty and aristocracy fled to the southern kin-state of Goryeo. There, they were given places to live along with positions in accordance to their status before the fall. The Goryeosa notes the existence of additional mass emigrations of the dispersed Balhae people before the fall of Jeongan.
Dae Gwang-hyeon, the last crown prince, and much of the ruling class of Balhae sought refuge in Goryeo, where they were granted land and the crown prince included in the royal household by Wang Geon, thus unifying the two successor nations of Goguryeo. The Goryeo scholar Choi Seungno referred these events in the Shimu 28 (Korean: 시무 28조, Chinese: 時務二十八條).
Government and culture
| Monarchs of Korea |
| Balhae |
|---|
|
Balhae's population was composed of former Goguryeo peoples and Tungusic Mohe people in Manchuria. According to Lee ki-baik, the Mohe made up the working class which served the Goguryeo ruling class. As such while the Mohe dominated common society, their influence was mainly restricted to providing labor. Nevertheless, there were instances of Mohe moving upward into the Balhae elite, however few, such as the followers of Geolsa Biu, who supported the establishment of Balhae. They were limited to the title of "Suryeong", or "chief", which is derived from Goguryeo language and played a part in the ruling elite.
After its founding, Balhae actively imported the culture and political system of the Tang dynasty and the Chinese reciprocated through an account of Balhae describing it as the "flourishing land of the East." The bureaucracy of Balhae was modeled after the Three Departments and Six Ministries and used Chinese characters to write their native language for administrative purposes. Balhae's aristocrats and nobility traveled to the Tang capital of Chang'an on a regular basis as ambassadors and students, many of whom went on to pass the Imperial examinations. Unlike Tang government, the Balhae "taenaesang" or the "great minister of the court" was superior to the other two chancelleries (the left and the right) and its system of five capitals originates from Goguryeo's administrative structure.
Balhae society was stratified into a rigid class system similar to other Korean kingdoms. Elites tended to belong to large extended aristocratic family lines designated by surnames. The commoners in comparison had no surnames at all, and upward social mobility was virtually impossible as class and status were codified into a caste system.
Balhae had five capitals, fifteen provinces, and sixty-three counties. Archaeologists studying the layout of Balhae's cities have concluded that they shared features common with cities in Goguryeo, indicating that Balhae had retained cultural similarities with Goguryeo. However the capital of Sanggyong was organized in the way of Tang's capital of Chang'an. Residential sectors were laid out on either side of the palace surrounded by a rectangular wall.
Language and script

The main language of the court of Balhae was the Tungus-Manchurian language, the ancestor of Jurchen. He using Chinese hieroglyphics, but with a different phonetic reading. The Goguryeo language was also widely used.
Politicization
Main article: Balhae controversies See also: Northeast Project of the Chinese Academy of Social SciencesThe historic position of the Balhae is controversial between Korean and Chinese historians. Due to its origins as the successor state of Goguryeo, Korean scholars consider Balhae as part of the North–South States Period of Korean history, while Chinese scholars argue Balhae is a part of Chinese history. The assessment of the borders of this state also differs between Russian and Japanese historians, and South Korean and Chinese historians. North Koreans take one or the other side of this issue.
- Different versions of borders.
-
 Map of East Asia (698 - 727)
Map of East Asia (698 - 727)
-
 The borders of the state of Balhae after 727 (period of maximum expansion of the state), according to Russian archaeological research.
The borders of the state of Balhae after 727 (period of maximum expansion of the state), according to Russian archaeological research.
-
 Administrative divisions of Balhae kingdom, with Chinese and Korean names according to Korean claim
Administrative divisions of Balhae kingdom, with Chinese and Korean names according to Korean claim
According to Russian studies in 735, the Bohai and Yamato alliance partially lost the war to the Tan and Silla alliance. The outcome of this was the rejection of claims to Silla and the transfer of two port cities on the Liaoning Peninsula to China. However, more than that, Bohai did not lose any land and continued to exist in this form until its fall in 926. . Chinese researchers dispute this and claimed about the transfer of China to the entire Liaodong Peninsula. Although in the Chinese texts, only two cities are indicated.
The confirmation of the Russian theory of the eastern border is not only the numerous attribution of archaeological finds. As well as found the border temple of the god Tenu who was called to protect the state from the East. Further this point there is no presence of Bohai not to the east, not to the north in Primorsky Krai..
Media
Balhae features in the Korean film Shadowless Sword, about the last prince of Balhae, and Korean TV drama Dae Jo Yeong, which aired from September 16, 2006 to December 23, 2007, about its founder.
See also
- Ancient Tombs at Longtou Mountain
- History of Korea
- History of Manchuria
- List of Korea-related topics
- List of Provinces of Balhae
- List of rulers of Balhae
References
- 동북아역사재단 편 (Northeast Asian History Foundation) (2007). 새롭게 본 발해사. 동북아역사재단. p. 62. ISBN 978-89-6187-003-0.
- Kradin Nikolai Nikolaevich (2018). "Динамика урбанизационных процессов в средневековых государствах Дальнего Востока" ["Dynamics of urbanization processes in the medieval states of the Far East"]. Siberian historical research. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
- Ivliev Alexander Lvovich (2014). "Эпиграфические материалы Бохая и бохайского времени из Приморья" ["The epigraphic materials of the Bohai and Bohai times from Primorye"]. Archeology, ethnography and culture. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
- Stoyakin Maxim Aleksandrovich (2012). "Культовая архитектура Бохайского времени в северной части Кореского Полуострова" ["Religious cult architecture of the Bohai time in the northern part of the Korean Peninsula"]. BUDDIST RELIGIOUS ARCHITECTURE OF PARHAE (BOHAI) LOCATED IN NORHERN PART OF KOREAN PENINSULA. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
- ^ Crossley 1997, p. 18.
- Walker, Hugh Dyson (2012), East Asia: A New History, Bloomington, IN: AuthorHouse, p. 177
- Seth, Michael J. (2016), A Concise History of Korea: From Antiquity to the Present, Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield, p. 71
- Kim, Djun Kil Kim (2014), The History of Korea, Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO, p. 54
- https://cyberleninka.ru/search?q=%D0%91%D0%BE%D1%85%D0%B0%D0%B9
- ^ Michael Dillon (1 December 2016). Encyclopedia of Chinese History. Taylor & Francis. p. 95. ISBN 978-1-317-81715-4.
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/dinamika-urbanizatsionnyh-protsessov-v-srednevekovyh-gosudarstvah-dalnego-vostoka
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/k-probleme-vydeleniya-v-primorie-pamyatnikov-gosudarstva-dundan-i-imperii-lyao
- Michael J. Seth (21 January 2016). A Concise History of Korea: From Antiquity to the Present. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. pp. 72–73. ISBN 978-1-4422-3518-2.
- ^ Baxter-Sagart.
- ^ Jinwung Kim (2012). A History of Korea: From "Land of the Morning Calm" to States in Conflict. Indiana University Press. p. 85. ISBN 978-0-253-00024-8.
- https://cyberleninka.ru/search?q=%D0%9A%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%BE+%D0%B3%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%B8%D1%89%D0%B5
- 9 Balhae and Japan Archived 2015-06-26 at the Wayback Machine Northeast Asian History Foundation
- ^ Lee Ki-baik. "The Society and Culture of Parhae." The New History of Korea, page 88-89. Harvard University Press, 1984.
- Hong Won-tak. "Liao and Jin: After Khitan and Xianbei in West Manchuria, Jurchen in Eastern Manchuria appeared" East Asian History: Distortion and Correcting, page 80-110. Seoul: Gudara, 2012.
- Kim, Jinwung (2012). A History of Korea: From "Land of the Morning Calm" to States in Conflict. Indiana University Press. pp. 87–88. ISBN 978-0253000248. Retrieved 27 August 2017.
- Lee, Ki-Baik (1984). A New History of Korea. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 103. ISBN 978-0674615762. "When Parhae perished at the hands of the Khitan around this same time, much of its ruling class, who were of Koguryŏ descent, fled to Koryŏ. Wang Kŏn warmly welcomed them and generously gave them land. Along with bestowing the name Wang Kye ("Successor of the Royal Wang") on the Parhae crown prince, Tae Kwang-hyŏn, Wang Kŏn entered his name in the royal household register, thus clearly conveying the idea that they belonged to the same lineage, and also had rituals performed in honor of his progenitor. Thus Koryŏ achieved a true national unification that embraced not only the Later Three Kingdoms but even survivors of Koguryŏ lineage from the Parhae kingdom."
- North Korea: A Country Study by Robert l. Worden
- Injae, Lee; Miller, Owen; Jinhoon, Park; Hyun-Hae, Yi (2014-12-15). Korean History in Maps. Cambridge University Press. pp. 64–65. ISBN 9781107098466. Retrieved 24 February 2017.
- ^ Crossley 1997, p. 19.
- "North Korea - Silla". Countrystudies.us. Retrieved 2012-09-15.
- Ogata, Noboru. "Shangjing Longquanfu, the Capital of the Bohai (Parhae) State". Kyoto University. January 12, 2007. Retrieved November 10, 2011.
- Ogata, Noboru. "A Study of the City Planning System of the Ancient Bohai State Using Satellite Photos (Summary)". Jinbun Chiri. Vol.52, No.2. 2000. pp.129 - 148. Retrieved November 10, 2011.
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/epigraficheskie-materialy-bohaya-i-bohayskogo-vremeni-iz-primorya
- 姜成山 2014 harvnb error: no target: CITEREF姜成山2014 (help)、p4
- 酒寄雅志 (March 2001). 渤海と古代の日本. 校倉書房. p. 16. ISBN 978-4751731703. 和書.
- 권은주. (2013). 발해의 등주공격을 통해 본 국제동맹과 외교. 역사와 세계, 44, 125p.
- http://www.rauk.ru/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=1533:2014-10-19-15-51-44&catid=126:2011-04-02%2019:33:16&lang=en&Itemid=143
- https://cyberleninka.ru/search?q=%D0%91%D0%BE%D1%85%D0%B0%D0%B9
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/k-voprosu-ob-otnosheniyah-mezhdu-silla-i-bohaem-posle-voyny-732-735-gg
- http://dostoyanieplaneti.ru/3772-gorodishche-koksharovka
Bibliography
- Mark Byington (October 7–8, 2004). "A Matter of Territorial Security: Chinese Historiographical Treatment of Koguryo in the Twentieth Century". International Conference on Nationalism and Textbooks in Asia and Europe, Seoul, The Academy of Korean Studies.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help) - 孫玉良 (1992). 渤海史料全編. 吉林文史出版社 ISBN 978-7-80528-597-9
- Crossley, Pamela Kyle (1997), The Manchus, Blackwell Publishing
- Mote, F.W. (1999), Imperial China, 900-1800, Harvard University Press, pp. 49, 61–62, ISBN 978-0-674-01212-7
- Pozzi, Alessandra; Janhunen, Juha Antero; Weiers, Michael, eds. (2006). Tumen Jalafun Jecen Aku: Manchu Studies in Honour of Giovanni Stary. Vol. Volume 20 of Tunguso Sibirica. Contributor Giovanni Stary. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. ISBN 978-3447053785. Retrieved 1 April 2013.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help)
External links
- Britannica Concise Encyclopedia
- Columbia Encyclopedia
- U.S. Library of Congress: Country Studies
- Metropolitan Museum of Art
- Stearns, Peter N. (ed.). Encyclopedia of World History (6th ed.). The Houghton Mifflin Company/Bartleby.com.
the state of Parhae (or Bohai in Chinese)
- Template:Ko icon Han's Palhae of Korea 한규철의 발해사 연구실
