This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Eyer (talk | contribs) at 14:20, 2 December 2020 (Undid revision 988892072 by GregLGII (talk)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 14:20, 2 December 2020 by Eyer (talk | contribs) (Undid revision 988892072 by GregLGII (talk))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Script used in the historic kingdoms of Israel and Judah by Israelites| Paleo-Hebrew | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Script type | Abjad |
| Time period | c. 1000 BCE – 135 CE |
| Direction | Right-to-left script |
| Languages | Biblical Hebrew |
| Related scripts | |
| Parent systems | Egyptian hieroglyphs
|
| Sister systems | |
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Phnx (115), Phoenician |
| Unicode | |
| Unicode alias | Phoenician |
| Unicode range | U+10900–U+1091F |
| This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between , / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters. | |
History of the alphabet
|
Paleo-Hebrew script (Hebrew: Template:Hebrew), also Palaeo-Hebrew, Proto-Hebrew or Old Hebrew, is the name used by modern scholars to describe the script found in Canaanite inscriptions from the region of Biblical Israel and Judah. It is considered to be the script used to record the original Ancient Hebrew language, including the texts of the Hebrew Bible in its original script. Old Hebrew, like the Phoenician alphabet, is a slight regional variant and an immediate continuation of the Proto-Canaanite script, which was used throughout Canaan in the Late Bronze Age. Hebrew is attested epigraphically from about the 10th century BCE, and no extant "Phoenician" inscription is older than 1000 BCE. The Phoenician language, Hebrew language, and all of their sister Canaanite languages were largely indistinguishable dialects before that time. The Paleo-Hebrew alphabet is an abjad of 22 consonantal letters. Use of the term "Paleo-Hebrew alphabet" is due to a 1954 suggestion by Solomon Birnbaum, who argued that "o apply the term Phoenician to the script of the Hebrews is hardly suitable".

The earliest known examples of Proto-Hebrew writing date to the 10th century BCE. By the 5th century BCE, among Jews the alphabet had been mostly replaced by the Aramaic alphabet as officially used in the Persian empire (which, like all alphabetical writing systems, was itself ultimately a descendant of the Proto-Canaanite script, though through intermediary non-Israelite stages of evolution). The "Jewish square-script" variant now known simply as the Hebrew alphabet evolved directly out of the Aramaic script by about the 3rd century BCE (although some letter shapes did not become standard until the 1st century CE). By contrast, the Samaritan alphabet, as used by Samaritans, is an immediate continuation of the Proto-Hebrew script without intermediate non-Israelite evolutionary stages. There is also some continued use of the old Hebrew script in Jewish religious contexts down to the 1st century BCE, notably in the Paleo-Leviticus text found in the Dead Sea scrolls.
History
Origins

The Paleo-Hebrew and Phoenician alphabets developed in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, out of their immediate predecessor script Proto-Canaanite (Late Proto-Sinaitic) during the 13th to 12th centuries BCE, and earlier Proto-Sinaitic scripts.

The earliest known inscription in the Paleo-Hebrew script is the Zayit Stone discovered on a wall at Tel Zayit, in the Beth Guvrin Valley in the lowlands of ancient Judea in 2005, about 50 km (31 mi) southwest of Jerusalem. The 22 letters were carved on one side of the 38 lb (17 kg) stone, which resembles a bowl on the other. The find is attributed to the mid-10th century BCE. The so-called Ophel inscription is of a similar age, but difficult to interpret, and may be classified as either Proto-Canaanite or as Paleo-Hebrew. The Gezer calendar is of uncertain date, but may also still date to the 10th century BCE.
The script on the Zayit Stone and Gezer Calendar are an earlier form than the classical Paleo-Hebrew of the 8th century and later; this early script is almost identical to the early Phoenician script on the 10th century Ahiram sarcophagus inscription. By the 8th century, a number of regional characteristics begin to separate the script into a number of national alphabets, including the Israelite (Israel and Judah), Moabite (Moab and Ammon), Edomite, Phoenician and Old Aramaic scripts.
Linguistic features of the Moabite language (rather than generic Northwest Semitic) are visible in the Mesha Stele inscription, commissioned around 840 BCE by King Mesha of Moab. Similarly, the Tel Dan Stele, dated approximately 810 BCE, is written in Old Aramaic, dating from a period when Dan had already fallen into the orbit of Damascus.

The oldest inscriptions identifiable as Biblical Hebrew have long been limited to the 8th century BCE. In 2008, however, a potsherd (ostracon) bearing an inscription was excavated at Khirbet Qeiyafa which has since been interpreted as representing a recognizably Hebrew inscription dated to as early as the 10th century BCE. The argument identifying the text as Hebrew relies on the use of vocabulary.
From the 8th century onward, Hebrew epigraphy becomes more common, showing the gradual spread of literacy among the people of the Kingdom of Israel and the Kingdom of Judah; the oldest portions of the Hebrew Bible, although transmitted via the recension of the Second Temple period, are also dated to the 8th century BCE.
Use in the Israelite kingdoms

The Paleo-Hebrew alphabet was in common use in the kingdoms of Israel and Judah throughout the 8th and 7th centuries BCE. During the 6th century BCE, the time of the Babylonian exile, the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet was gradually replaced by the use of the Imperial Aramaic alphabet. The letters of Imperial Aramaic were again given shapes characteristic for writing Hebrew during the Second Temple period, developing into the "square shape" of the Hebrew alphabet.
The Samaritans, who remained in the Land of Israel, continued to use their variant of the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, called the Samaritan script. After the fall of the Persian Empire, Jews used both scripts before settling on the Assyrian form.
The Paleo-Hebrew script evolved by developing numerous cursive features, the lapidary features of the Phoenician alphabet being ever less pronounced with the passage of time. The aversion of the lapidary script may indicate that the custom of erecting stelae by the kings and offering votive inscriptions to the deity was not widespread in Israel. Even the engraved inscriptions from the 8th century exhibit elements of the cursive style, such as the shading, which is a natural feature of pen-and-ink writing. Examples of such inscriptions include the Siloam inscription, numerous tomb inscriptions from Jerusalem, the Ketef Hinnom amulets, a fragmentary Hebrew inscription on an ivory which was taken as war spoils (probably from Samaria) to Nimrud, the hundreds of 8th to 6th-century Hebrew seals from various sites, and the Paleo-Hebrew Leviticus scroll discovered near Tel Qumran. The most developed cursive script is found on the 18 Lachish ostraca, letters sent by an officer to the governor of Lachish just before the destruction of the First Temple in 586 BCE. A slightly earlier (circa 620 BCE) but similar script is found on an ostracon excavated at Mesad Hashavyahu, containing a petition for redress of grievances (an appeal by a field worker to the fortress's governor regarding the confiscation of his cloak, which the writer considers to have been unjust).
Decline and late survival
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (June 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |


After the Babylonian capture of Judea, when most of the nobles were taken into exile, the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet continued to be used by the people who remained. One example of such writings are the 6th-century BCE jar handles from Gibeon, on which the names of winegrowers are inscribed. Beginning from the 5th century BCE onward, the Aramaic language and script became an official means of communication. Paleo-Hebrew was still used by scribes and others.
The Paleo-Hebrew script was retained for some time as an archaizing or conservative mode of writing. It is found in certain texts of the Torah among the Dead Sea Scrolls, dated to the 2nd to 1st centuries BCE: manuscripts 4Q12, 6Q1: Genesis. 4Q22: Exodus. 1Q3, 2Q5, 4Q11, 4Q45, 4Q46, 6Q2, and the Leviticus scroll (11QpaleoLev). In some Qumran documents, the tetragrammaton name of the Israelite deity, YHWH, is written in Paleo-Hebrew while the rest of the text is rendered in the adopted Aramaic square script that became today’s normative Jewish Hebrew script. The vast majority of the Hasmonean coinage, as well as the coins of the First Jewish–Roman War and Bar Kokhba's revolt, bears Paleo-Hebrew legends. The Paleo-Hebrew alphabet fell completely out of use among Jews only after 135 CE.
Legacy
Samaritan alphabet
Main article: Samaritan alphabet
The paleo-Hebrew alphabet continued to be used by the Samaritans and over time developed into the Samaritan alphabet. The Samaritans have continued to use the script for writing both Hebrew and Aramaic texts until the present day. A comparison of the earliest Samaritan inscriptions and the medieval and modern Samaritan manuscripts clearly indicates that the Samaritan script is a static script which was used mainly as a book hand.
Babylonian Talmud
The Talmudic sages did not share a uniform stance on the subject of Paleo-Hebrew. Some stated that Paleo-Hebrew was the original script used by the Israelites at the time of the Exodus, while others believed that Paleo-Hebrew merely served as a stopgap in a time when the ostensibly original script (The Assyrian Script) was lost. According to both opinions, Ezra the Scribe (c. 500 BCE) introduced, or reintroduced the Assyrian script to be used as the primary alphabet for the Hebrew language. The arguments given for both opinions are rooted in Jewish scripture and/or tradition.
A third opinion in the Talmud states that the script never changed altogether. It would seem that the sage who expressed this opinion did not believe that Paleo-Hebrew ever existed, despite the strong arguments supporting it. His stance is rooted in a scriptural verse, which makes reference to the shape of the letter vav. The sage argues further that, given the commandment to copy a Torah scroll directly from another, the script could not conceivably have been modified at any point. This third opinion was accepted by some early Jewish scholars, and rejected by others, partially because it was permitted to write the Torah in Greek.
Contemporary use

Use of Proto-Hebrew in modern Israel is negligible, but it is found occasionally in nostalgic or pseudo-archaic examples, e.g. on the ₪1 coin (𐤉𐤄𐤃 "Judea") and in the logo of the Israeli town Nahariyah (Deuteronomy 33:24 𐤁𐤓𐤅𐤊 𐤌𐤁𐤍𐤉𐤌 𐤀𐤔𐤓 "Let Asher be blessed with children").
Archaeology
In 2019, the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA) unearthed a 2,600 year-old seal impression, while conducting excavations at the City of David, containing paleo-Hebrew script, and which is thought to have belonged to a certain "Nathan-Melech," an official in King Josiah's court.
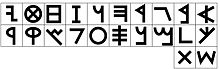
Table of letters
This article contains special characters. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols. Main article: Phoenician_alphabet § Table_of_lettersPhoenician or Paleo-Hebrew characters were never standardised and are found in numerous variant shapes. A general tendency of more cursive writing can be observed over the period of c. 800 BCE to 600 BCE. After 500 BCE, it is common to distinguish the script variants by names such as "Samaritan", "Aramaic", etc.
There is no difference in "Paleo-Hebrew" vs. "Phoenician" letter shapes. The names are applied depending on the language of the inscription, or if that cannot be determined, of the coastal (Phoenician) vs. highland (Hebrew) association (c.f. the Zayit Stone abecedary).
| Letter | Name | Meaning | Phoneme | Origin | Corresponding letter in | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image | Text | Samaritan | Hebrew | |||||||||||
| 𐤀 | ʾālep | head of cattle (אלף) | ʾ [ʔ] | 𓃾 | ࠀ | א | ||||||||
| 𐤁 | bēt | house (בית) | b [b] | 𓉐 | ࠁ | ב | ||||||||
| 𐤂 | gīml | throwing stick (?) | g [ɡ] | 𓌙 | ࠂ | ג | ||||||||
| 𐤃 | dālet | door (דלת) | d [d] | 𓇯 | ࠃ | ד | ||||||||
| 𐤄 | hē | jubilation/window | h [h] | 𓀠? | ࠄ | ה | ||||||||
| 𐤅 | wāw | hook (וו) | w [w] | 𓏲 | ࠅ | ו | ||||||||
| 𐤆 | zayin | weapon (זין) | z [z] | 𓏭 | ࠆ | ז | ||||||||
| 𐤇 | ḥēt(?) | courtyard/thread | ḥ [ħ] | 𓉗/𓈈? | ࠇ | ח | ||||||||
| 𐤈 | ṭēt | wheel (?) | ṭ [tˤ] | ? | ࠈ | ט | ||||||||
| 𐤉 | yōd | arm, hand (יד) | y [j] | 𓂝 | ࠉ | י | ||||||||
| 𐤊 | kāp | palm of a hand (כף) | k [k] | 𓂧 | ࠊ | כך | ||||||||
| 𐤋 | lāmed | goad (למד) | l [l] | 𓌅 | ࠋ | ל | ||||||||
| 𐤌 | mēm | water (מים) | m [m] | 𓈖 | ࠌ | מם | ||||||||
| 𐤍 | nūn | fish (נון) | n [n] | 𓆓 | ࠍ | נן | ||||||||
| 𐤎 | sāmek | pillar, support (סמך) | s [s] | 𓊽 | ࠎ | ס | ||||||||
| 𐤏 | ʿayin | eye (עין) | ʿ [ʕ] | 𓁹 | ࠏ | ע | ||||||||
| 𐤐 | pē | mouth (פה) | p [p] | 𓂋 | ࠐ | פף | ||||||||
| 𐤑 | ṣādē | ? | ṣ [sˤ] | ? | ࠑ | צץ | ||||||||
| 𐤒 | qōp | ? | q [q] | ? | ࠒ | ק | ||||||||
| 𐤓 | rēš | head (ריש) | r [r] | 𓁶 | ࠓ | ר | ||||||||
| 𐤔 | šīn | tooth (שין) | š [ʃ] | 𓌓 | ࠔ | ש | ||||||||
| 𐤕 | tāw | mark, sign (תו) | t [t] | 𓏴 | ࠕ | ת | ||||||||
Unicode
The Phoenician Unicode block (U+10900–U+1091F) is intended for the representation of text in Palaeo-Hebrew, Archaic Phoenician, Phoenician, Early Aramaic, Late Phoenician cursive, Phoenician papyri, Siloam Hebrew, Hebrew seals, Ammonite, Moabite, and Punic.

| Phoenician Official Unicode Consortium code chart (PDF) | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| U+1090x | 𐤀 | 𐤁 | 𐤂 | 𐤃 | 𐤄 | 𐤅 | 𐤆 | 𐤇 | 𐤈 | 𐤉 | 𐤊 | 𐤋 | 𐤌 | 𐤍 | 𐤎 | 𐤏 |
| U+1091x | 𐤐 | 𐤑 | 𐤒 | 𐤓 | 𐤔 | 𐤕 | 𐤖 | 𐤗 | 𐤘 | 𐤙 | 𐤚 | 𐤛 | 𐤟 | |||
Notes
| ||||||||||||||||
See also
- Ancient Hebrew writings
- Ancient North Arabian
- Biblical Hebrew orthography
- History of the Hebrew alphabet
- Proto-Canaanite alphabet
Notes
- Israel Finkelstein & Benjamin Sass, The West Semitic Alphabetic Inscriptions, Late Bronze II to Iron IIA: Archeological Context, Distribution and Chronology, HeBAI 2 (2013), pp. 149-220, see p. 189: "From the available evidence Hebrew appears to be the first regional variant to arise in the West Semitic alphabet – in late Iron IIA1; the scripts of the neighbouring peoples remain undifferentiated. It is only up to a century later, in early Iron IIB, that the distinct characteristics in the alphabets of Philistia, Phoenicia, Aram, Ammon and Moab develop."
- Feldman (2010)
- Shanks (2010)
- Hoffman, Joel M. (2004). In the beginning : a short history of the Hebrew language. New York, NY : New York Univ. Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-8147-3654-8. Retrieved 23 May 2017.
By 1000 B.C.E., however, we see Phoenician writings
- Naveh, Joseph (1987), "Proto-Canaanite, Archaic Greek, and the Script of the Aramaic Text on the Tell Fakhariyah Statue", in Miller; et al. (eds.), Ancient Israelite Religion.
- Reinhard G. Kratz (11 November 2015). Historical and Biblical Israel: The History, Tradition, and Archives of Israel and Judah. OUP Oxford. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-19-104448-9.
scribes wrote in Paleo-Hebrew, a local variant of the Phoenician alphabetic script
- The Hebrew scripts, Volume 2, Salomo A. Birnbaum, Palaeographia, 1954, "To apply the term Phoenician to the script of the Hebrews is hardly suitable. I have therefore coined the term Palaeo-Hebrew."
- On January 10, 2010, the University of Haifa issued a press release stating that the text "uses verbs that were characteristic of Hebrew, such as ‘śh (עשה) ("did") and ‘bd (עבד) ("worked"), which were rarely used in other regional languages. Particular words that appear in the text, such as almanah ("widow") are specific to Hebrew and are written differently in other Canaanite languages. "Most ancient Hebrew biblical inscription deciphered". University of Haifa. January 10, 2010. Archived from the original on October 5, 2011. Retrieved November 5, 2011. See also: "Qeiyafa Ostracon Chronicle". Khirbet Qeiyafa Archaeological Project. Retrieved November 5, 2011., "The keys to the kingdom". Haaretz.com. 6 May 2011. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- The Mishnah, ed. Herbert Danby, Oxford University Press: Oxford 1933, s.v. Megillah 1:8, p. 202 (note 20); Yadayim 4:5-6, p. 784 (note 6) (ISBN 0-19-815402-X)
- Angel Sáenz-Badillos (1993). A History of the Hebrew Language. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-55634-1.
- An illustration of the Siloam script is available at this link.
- An illustration of a tomb inscription said to be scratched onto an ossuary to identify the decedent is available here. An article describing the ossuaries Zvi Greenhut excavated from a burial cave in the south of Jerusalem can be found in Jerusalem Perspective (July 1, 1991), with links to other articles.
- Another tomb inscription is believed to be from the tomb of Shebna, an official of King Hezekiah. An illustration of the inscription may be viewed, but it is too large to be placed inline.
- An illustration of the Lachish script is available at this link.
- See Worker's appeal to governor.
- The conduct complained about is contrary to Exodus 22, which provides:"If you take your neighbor's garment in pledge, you must return it to him before the sun sets; it is his only clothing, the sole covering for his skin. In what else shall he sleep?"
- Dead Sea Scrolls Digital Library.
- e.g. File:Psalms Scroll.jpg
- ^ Sanhedrin 21b
- Megillah 3a, Shabbat 104a
- Sanhedrin 22a
- Exodus 27, 10
- Rabbeinu Chananel on Sanhedrin 22a
- Maimonides. "Mishne Torah Hilchos Stam 1:19".
- This is in imitation of the "Yehud coinage" minted in the Persian period. Yigal Ronen, "The Weight Standards of the Judean Coinage in the Late Persian and Early Ptolemaic Period", Near Eastern Archaeology 61, No. 2 (Jun., 1998), 122–126.
- What's in a Name... - Israel Antiquities Authority (1 April 2019)
- after Fischer, Steven R. (2001). A History of Writing. London: Reaction Books. p. 126.
- ^ The letters he and ḥēt continue three Proto-Sinaitic letters, ḥasir "courtyard", hillul "jubilation" and ḫayt "thread". The shape of ḥēt continues ḥasir "courtyard", but the name continues ḫayt "thread". The shape of he continues hillul "jubilation" but the name means "window". see: He (letter)#Origins.
- The glyph was taken to represent a wheel, but it possibly derives from the hieroglyph nefer hieroglyph 𓄤 and would originally have been called tab טוב "good".
- The root l-m-d mainly means "to teach", from an original meaning "to goad". H3925 in Strong’s Exhaustive Concordance to the Bible, 1979.
- the letter name nūn is a word for "fish", but the glyph is presumably from the depiction of a snake, which would point to an original name נחש "snake".
- H5564 in Strong's Exhaustive Concordance to the Bible, 1979.
- the letter name may be from צד "to hunt".
- "The old explanation, which has again been revived by Halévy, is that it denotes an 'ape,' the character Q being taken to represent an ape with its tail hanging down. It may also be referred to a Talmudic root which would signify an 'aperture' of some kind, as the 'eye of a needle,' Lenormant adopts the more usual explanation that the word means a 'knot'." Isaac Taylor, History of the Alphabet: Semitic Alphabets, Part 1, 2003.
References
- "Alphabet, Hebrew". Encyclopaedia Judaica (CD-ROM Edition Version 1.0). Ed. Cecil Roth. Keter Publishing House. ISBN 965-07-0665-8
- Feldman, Rachel (2010). "Most ancient Hebrew biblical inscription deciphered". Archived from the original on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 15 June 2011.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Shanks, Hershel (2010). "Oldest Hebrew Inscription Discovered in Israelite Fort on Philistine Border". Biblical Archaeology Review. 36 (2): 51–6.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
External links
- Hebrew Alphabet at the Jewish Encyclopedia
- History of the Aleph-Bet at the Jewish Virtual Library
- Aramaic/Paleo-Hebrew alphabet at Omniglot
- Unicode Modern/Paleo-Hebrew conversion tool
| The Northwest Semitic abjad | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hebrew language | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overviews | |||||||||||||
| Eras | |||||||||||||
| Reading traditions | |||||||||||||
| Orthography |
| ||||||||||||
| Phonology | |||||||||||||
| Grammar | |||||||||||||
| Academic | |||||||||||||
| Reference works | |||||||||||||