This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Fswitzer4 (talk | contribs) at 19:59, 11 January 2021 (Validated UNII). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 19:59, 11 January 2021 by Fswitzer4 (talk | contribs) (Validated UNII)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Chemical compound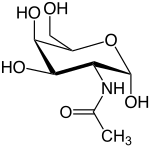 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2-(Acetylamino)-2-deoxy-D-galactose | |
| Other names GalNAc; 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galactose; N-Acetylchondrosamine; 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-galactopyranose; N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H15NO6 |
| Molar mass | 221.21 g/mol |
| Melting point | 172 to 173 °C (342 to 343 °F; 445 to 446 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related monosaccharides | N-Acetylglucosamine Galactosamine Galactose |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), is an amino sugar derivative of galactose.
Function
In humans it is the terminal carbohydrate forming the antigen of blood group A.
It is typically the first monosaccharide that connects serine or threonine in particular forms of protein O-glycosylation.
N-Acetylgalactosamine is necessary for intercellular communication, and is concentrated in sensory nerve structures of both humans and animals.
GalNAc is also used as a targeting ligand in investigational antisense oligonucleotides and siRNA therapies targeted to the liver, where it binds to the asialoglycoprotein receptors on hepatocytes.
See also
- Galactosamine
- Globoside
- (N-Acetylglucosamine) GlcNAc
References
- Donald M. Marcus; Elvin A. Kabat; Gerald Schiffman (1964). "Immunochemical Studies on Blood Groups. XXXI. Destruction of Blood Group A Activity by an Enzyme from Clostridium tertium Which Deacetylates N-Acetylgalactosamine in Intact Blood Group Substances". Biochemistry. 3 (3): 437–443. doi:10.1021/bi00891a023.
- Nair, Jayaprakash K; Willoughby, Jennifer L. S; Chan, Amy; Charisse, Klaus; Alam, Md. Rowshon; Wang, Qianfan; Hoekstra, Menno; Kandasamy, Pachamuthu; Kel'In, Alexander V; Milstein, Stuart; Taneja, Nate; o'Shea, Jonathan; Shaikh, Sarfraz; Zhang, Ligang; Van Der Sluis, Ronald J; Jung, Michael E; Akinc, Akin; Hutabarat, Renta; Kuchimanchi, Satya; Fitzgerald, Kevin; Zimmermann, Tracy; Van Berkel, Theo J. C; Maier, Martin A; Rajeev, Kallanthottathil G; Manoharan, Muthiah (2014). "Multivalent N-Acetylgalactosamine-Conjugated siRNA Localizes in Hepatocytes and Elicits Robust RNAi-Mediated Gene Silencing". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 136 (49): 16958–16961. doi:10.1021/ja505986a. PMID 25434769.
External links
- [REDACTED] Media related to N-Acetylgalactosamine at Wikimedia Commons