 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Pentan-1-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Beilstein Reference | 1730975 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.684 |
| EC Number |
|
| Gmelin Reference | 25922 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | n-Pentanol |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1105 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
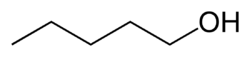
| Chemical formula | C5H12O |
| Molar mass | 88.150 g·mol |
| Density | 0.811 g cm |
| Melting point | −78 °C; −109 °F; 195 K |
| Boiling point | 137 to 139 °C; 278 to 282 °F; 410 to 412 K |
| Solubility in water | 22 g L |
| log P | 1.348 |
| Vapor pressure | 200 Pa (at 20 °C) |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -67.7·10 cm/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.409 |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Heat capacity (C) | 207.45 J K mol |
| Std molar entropy (S298) |
258.9 J K mol |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
−351.90–−351.34 kJ mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH298) |
−3331.19–−3330.63 kJ mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H315, H332, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P261 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | 49 °C (120 °F; 322 K) |
| Autoignition temperature |
300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | Hexane |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
1-Pentanol, (or n-pentanol, pentan-1-ol), is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH and is classified as a primary alcohol. It is a colourless liquid with a distinctive aroma. It is one of 8 isomeric alcohols with the formula C5H11OH. It is used as a solvent, a biological drying agent and in the synthesis of some fragrance compounds. It is also a common component of fusel alcohols (fusel oils), the undesirable byproducts of alcoholic fermentation.
Preparation
1-Pentanol is prepared from 1-butene by hydroformylation followed by hydrogenation of the resulting pentanal.
- CH3CH2CH=CH2 + CO + H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO + H2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
Pentanol can be prepared by fractional distillation of fusel oil. To reduce the use of fossil fuels, research is underway to develop cost-effective methods of producing (chemically identical) bio-pentanol with fermentation.
Uses and occurrence
The hydroxyl group (OH) is the active site of many reactions. The ester formed from 1-pentanol and butyric acid is pentyl butyrate, which has an apricot-like odor. The ester formed from 1-pentanol and acetic acid is amyl acetate (also called pentyl acetate), which has a banana-like odor.
It is a precursor to dipentyl zinc dithiophosphates, which are used in froth flotation.
In 2014, a study was conducted comparing the performance of diesel fuel blends with various proportions of pentanol as an additive. While gaseous emissions increased with higher concentrations of pentanol, particulate emissions decreased.
Pentanol is often used as a solvent.
References
- "n-pentanol - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 10 October 2011.
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 65th ed.
- ^ Lappe, Peter; Hofmann, Thomas (2011). "Pentanols". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_049.pub2. ISBN 9783527303854.
- Cann, Anthony F.; Liao, James C. (2010-01-01). "Pentanol isomer synthesis in engineered microorganisms". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 85 (4): 893–899. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2262-7. ISSN 1432-0614. PMC 2804790. PMID 19859707.
- Tseng, Hsien-Chung (2011). Production of pentanol in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli (Thesis thesis). Massachusetts Institute of Technology. hdl:1721.1/65767.
- Wei, Liangjie & Cheung, C.s & Huang, Zuohua. (2014). Effect of n-pentanol addition on the combustion, performance and emission characteristics of a direct-injection diesel engine. Energy. 70. 10.1016/j.energy.2014.03.106.
| Hypnotics/sedatives (N05C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABAA |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GABAB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| α2-Adrenergic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2A |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melatonin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orexin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| α2δ VDCC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GABAA receptor positive modulators | |
|---|---|
| Alcohols | |
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids |
|
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents | |
| Monoureides | |
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
| See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators | |